24. 两两交换链表中的节点
这道题的关键在于:
1、在置换两个节点的时候,当前节点需要在这俩节点之前一个节点。并且要提前保存cur.next以及cur.next.next。
2、每次置换完一组节点,cur = cur.next.next
3、判断结束的标志:奇数个节点:cur.next.next != null 偶数个节点:cur.next != null 为了保证cur.next.next不会产生空指针,需要先判断next != null
4、最终返回的是虚拟节点的下一个节点,因为最初的head节点已经不在链表最前面了
具体步骤如下:
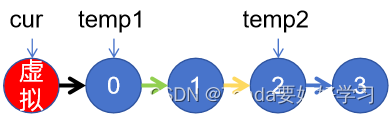
dummyNode.next = head;//对于0、1节点,需要创建一个虚拟节点.
ListNode temp1 = cur.next;
ListNode temp2 = cur.next.next.next;//并保存temp1和temp2.
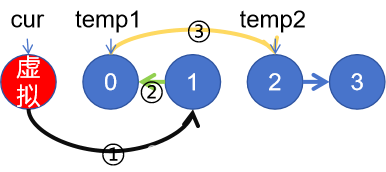
①②③步骤按序进行
①cur.next = cur.next.next;
②cur.next.next = temp1;
③ temp1.next = temp2;

cur = cur.next.next;
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode();
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummyNode;
while(cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null){
ListNode temp1 = cur.next;
ListNode temp2 = cur.next.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
cur.next.next = temp1;
temp1.next = temp2;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
法一:遍历链表得出链表长度length,用length - n定位要删除的节点,缺点是需要第二次遍历链表
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
int length = 0;
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode();
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummyNode;
while(cur.next != null){
length++;
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode cur2 = dummyNode;
for(int i = 0;i < length - n;i++){
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur2.next = cur2.next.next;
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
法二:让快指针先走n步,然后快慢指针同时走。
这个思想很巧妙也很好理解,关键是临界值的设定很容易出错,可以用只有一个节点的链表删除倒数第一个节点的特殊情况去写临界值。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode();
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode fast = dummyNode;
ListNode slow = dummyNode;
for(int i = 0;i < n-1;i++){
fast = fast.next;
}//假设只有一个节点的链表要删除倒数第一个节点,n=1,此时快慢节点不需要中间有差值,slow和fast都指向dummyNode
while(fast.next.next != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//因为fast.next.next == null,fast和slow都不需要往下移动
slow.next = slow.next.next;//删除第一个节点
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
或者这样也可以:
这俩区别在于如果在
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
fast = fast.next;
}中i移动的条件为这个,fast为向下移动一位。那么响应的下面
while(fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}中while的判定条件由fast.next.next!= null变为fast.next != null
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode();
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode fast = dummyNode;
ListNode slow = dummyNode;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
fast = fast.next;
}
while(fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
142.环形链表II
这道题老是犯一个错误,就是控制fast和slow相遇的循环条件写成fast != slow,slow和fast就移动,但是要注意一点,slow和fast在初始的时候就应该分别向下移动一位和两位,以防止while进入死循环。
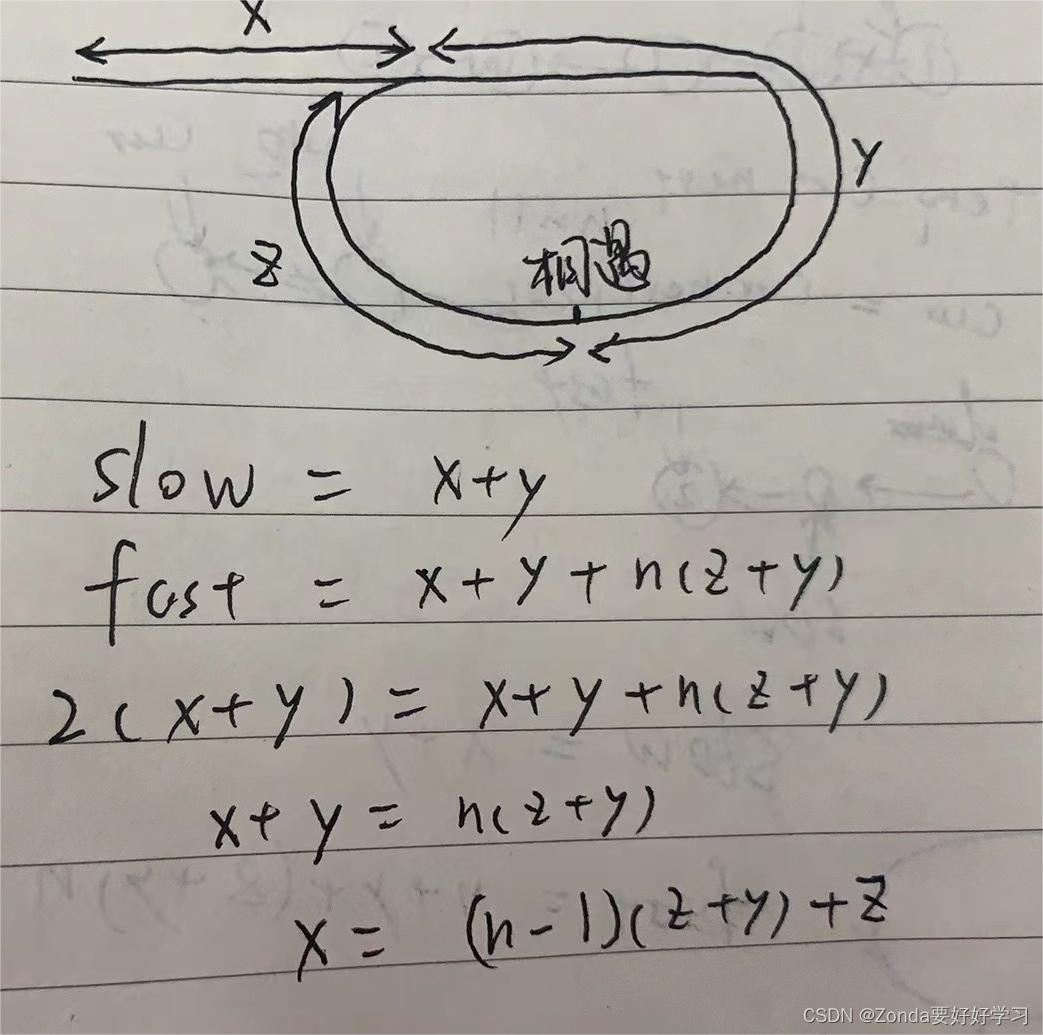
定义slow和fast两个快慢指针,slow每次移动一位,fast每次移动两位,直到相遇。slow和fast走过的路程分别为
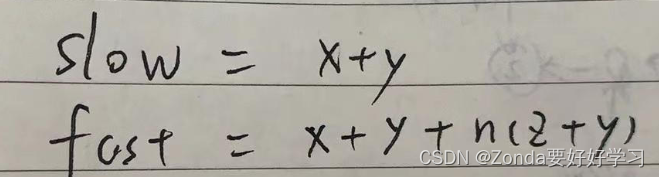
fast是slow的两倍,可以得到等式,最终得到x和z、y的关系式
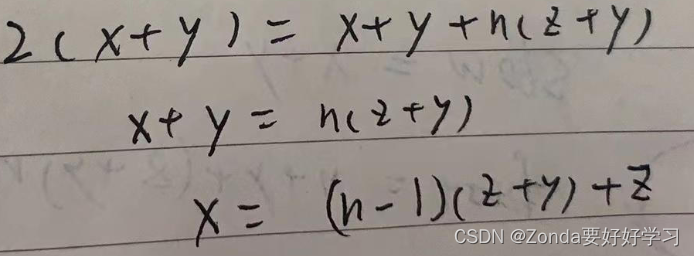
这个时候slow和fast在同一位置,再定义一个res节点指针指向head,res和slow指针同时一位一位向下移动,当两个指针相遇的时候,这个节点就是环形的入口。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null) return null;
ListNode fast = head.next.next;
ListNode slow = head.next;
while(fast != slow){
if(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
}else{
return null;
}
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode res = head;
while(slow != res){
slow = slow.next;
res = res.next;
}
return res;
}
}
这里寻找fast和slow相遇节点的while循环可以优化一下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null) return null;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(true){
if(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) fast = fast.next.next;
else return null;
slow = slow.next;
if(slow == fast) break;
}
ListNode res = head;
while(slow != res){
slow = slow.next;
res = res.next;
}
return res;
}
}
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
思路:
先计算出两条链表的长度,再将短的那一条链表的指针先移动链表长度差值个,然后再一起向下遍历直到相遇,如果没有相遇,最终都会到达null,返回停下之后的那个节点即可。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
int lengthA = 0;
int lengthB = 0;
while(curA != null){
curA = curA.next;
lengthA++;
}
while(curB != null){
curB = curB.next;
lengthB++;
}
if(lengthA > lengthB){
for(int i = 0;i < lengthA-lengthB;i++){
headA = headA.next;
}
}else{
for(int i = 0;i < lengthB-lengthA;i++){
headB = headB.next;
}
}
while(headA != null && headA != headB){
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
return headA;
}
}