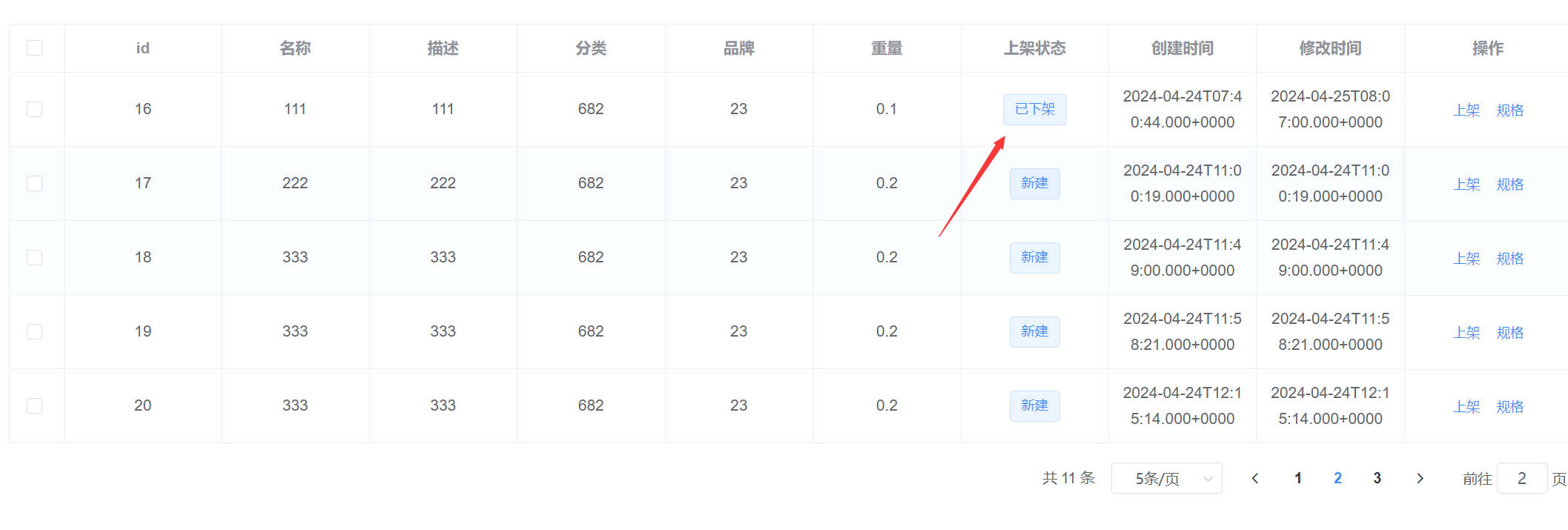
给定两个大小分别为 nxn 的方阵 A 和 B,求它们的乘法矩阵。
朴素方法:以下是两个矩阵相乘的简单方法。
def multiply(A, B, C):
for i in range(N):
for j in range( N):
C[i][j] = 0
for k in range(N):
C[i][j] += A[i][k]*B[k][j]
# this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
上述方法的时间复杂度为O(N 3 )。
分而治之 :
以下是两个方阵相乘的简单分而治之方法。
1、将矩阵 A 和 B 分为 4 个大小为 N/2 x N/2 的子矩阵,如下图所示。
2、递归计算以下值。 ae + bg、af + bh、ce + dg 和 cf + dh。

执行:
# Python program to find the resultant
# product matrix for a given pair of matrices
# using Divide and Conquer Approach
ROW_1 = 4
COL_1 = 4
ROW_2 = 4
COL_2 = 4
#Function to print the matrix
def printMat(a, r, c):
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
print(a[i][j], end = " ")
print()
print()
#Function to print the matrix
def printt(display, matrix, start_row, start_column, end_row,end_column):
print(display + " =>\n")
for i in range(start_row, end_row+1):
for j in range(start_column, end_column+1):
print(matrix[i][j], end=" ")
print()
print()
#Function to add two matrices
def add_matrix(matrix_A, matrix_B, matrix_C, split_index):
for i in range(split_index):
for j in range(split_index):
matrix_C[i][j] = matrix_A[i][j] + matrix_B[i][j]
#Function to initialize matrix with zeros
def initWithZeros(a, r, c):
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
a[i][j] = 0
#Function to multiply two matrices
def multiply_matrix(matrix_A, matrix_B):
col_1 = len(matrix_A[0])
row_1 = len(matrix_A)
col_2 = len(matrix_B[0])
row_2 = len(matrix_B)
if (col_1 != row_2):
print("\nError: The number of columns in Matrix A must be equal to the number of rows in Matrix B\n")
return 0
result_matrix_row = [0] * col_2
result_matrix = [[0 for x in range(col_2)] for y in range(row_1)]
if (col_1 == 1):
result_matrix[0][0] = matrix_A[0][0] * matrix_B[0][0]
else:
split_index = col_1 // 2
row_vector = [0] * split_index
result_matrix_00 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
result_matrix_01 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
result_matrix_10 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
result_matrix_11 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
a00 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
a01 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
a10 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
a11 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
b00 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
b01 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
b10 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
b11 = [[0 for x in range(split_index)] for y in range(split_index)]
for i in range(split_index):
for j in range(split_index):
a00[i][j] = matrix_A[i][j]
a01[i][j] = matrix_A[i][j + split_index]
a10[i][j] = matrix_A[split_index + i][j]
a11[i][j] = matrix_A[i + split_index][j + split_index]
b00[i][j] = matrix_B[i][j]
b01[i][j] = matrix_B[i][j + split_index]
b10[i][j] = matrix_B[split_index + i][j]
b11[i][j] = matrix_B[i + split_index][j + split_index]
add_matrix(multiply_matrix(a00, b00),multiply_matrix(a01, b10),result_matrix_00, split_index)
add_matrix(multiply_matrix(a00, b01),multiply_matrix(a01, b11),result_matrix_01, split_index)
add_matrix(multiply_matrix(a10, b00),multiply_matrix(a11, b10),result_matrix_10, split_index)
add_matrix(multiply_matrix(a10, b01),multiply_matrix(a11, b11),result_matrix_11, split_index)
for i in range(split_index):
for j in range(split_index):
result_matrix[i][j] = result_matrix_00[i][j]
result_matrix[i][j + split_index] = result_matrix_01[i][j]
result_matrix[split_index + i][j] = result_matrix_10[i][j]
result_matrix[i + split_index][j + split_index] = result_matrix_11[i][j]
return result_matrix
# Driver Code
matrix_A = [ [1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3, 3],
[2, 2, 2, 2] ]
print("Array A =>")
printMat(matrix_A,4,4)
matrix_B = [ [1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3, 3],
[2, 2, 2, 2] ]
print("Array B =>")
printMat(matrix_B,4,4)
result_matrix = multiply_matrix(matrix_A, matrix_B)
print("Result Array =>")
printMat(result_matrix,4,4)
输出
数组A =>
1 1 1 1
2 2 2 2
3 3 3 3
2 2 2 2
数组 B =>
1 1 1 1
2 2 2 2
3 3 3 3
2 2 2 2
结果数组=>
8 8 8 8
16 16 16 16
24 24 24 24
16 16 16 16
在上述方法中,我们对大小为 N/2 x N/2 的矩阵进行 8 次乘法和 4 次加法。两个矩阵相加需要 O(N 2 ) 时间。所以时间复杂度可以写成
T(N) = 8T(N/2) + O(N 2 )
根据马斯特定理,上述方法的时间复杂度为 O(N 3 )
不幸的是,这与上面的简单方法相同。
简单的分而治之也导致O(N 3 ),有更好的方法吗?
在上面的分而治之的方法中,高时间复杂度的主要成分是8次递归调用。Strassen 方法的思想是将递归调用次数减少到 7 次。Strassen 方法与上述简单的分而治之方法类似,该方法也将矩阵划分为大小为 N/2 x N/2 的子矩阵:如上图所示,但在Strassen方法中,结果的四个子矩阵是使用以下公式计算的。
Strassen 方法的时间复杂度
两个矩阵的加法和减法需要 O(N 2 ) 时间。所以时间复杂度可以写成
T(N) = 7T(N/2) + O(N 2 )
根据马斯特定理,上述方法的时间复杂度为
O(N Log7 ) 大约为 O(N 2.8074 )
一般来说,由于以下原因,施特拉森方法在实际应用中并不优选。
1、Strassen 方法中使用的常数很高,对于典型应用,Naive 方法效果更好。
2、对于稀疏矩阵,有专门为其设计的更好的方法。
3、递归中的子矩阵占用额外的空间。
4、由于计算机对非整数值的运算精度有限,Strassen 算法中累积的误差比 Naive 方法中更大。
执行:
# Version 3.6
import numpy as np
def split(matrix):
"""
Splits a given matrix into quarters.
Input: nxn matrix
Output: tuple containing 4 n/2 x n/2 matrices corresponding to a, b, c, d
"""
row, col = matrix.shape
row2, col2 = row//2, col//2
return matrix[:row2, :col2], matrix[:row2, col2:], matrix[row2:, :col2], matrix[row2:, col2:]
def strassen(x, y):
"""
Computes matrix product by divide and conquer approach, recursively.
Input: nxn matrices x and y
Output: nxn matrix, product of x and y
"""
# Base case when size of matrices is 1x1
if len(x) == 1:
return x * y
# Splitting the matrices into quadrants. This will be done recursively
# until the base case is reached.
a, b, c, d = split(x)
e, f, g, h = split(y)
# Computing the 7 products, recursively (p1, p2...p7)
p1 = strassen(a, f - h)
p2 = strassen(a + b, h)
p3 = strassen(c + d, e)
p4 = strassen(d, g - e)
p5 = strassen(a + d, e + h)
p6 = strassen(b - d, g + h)
p7 = strassen(a - c, e + f)
# Computing the values of the 4 quadrants of the final matrix c
c11 = p5 + p4 - p2 + p6
c12 = p1 + p2
c21 = p3 + p4
c22 = p1 + p5 - p3 - p7
# Combining the 4 quadrants into a single matrix by stacking horizontally and vertically.
c = np.vstack((np.hstack((c11, c12)), np.hstack((c21, c22))))
return c
输出
数组A =>
1 1 1 1
2 2 2 2
3 3 3 3
2 2 2 2
数组 B =>
1 1 1 1
2 2 2 2
3 3 3 3
2 2 2 2
结果数组=>
8 8 8 8
16 16 16 16
24 24 24 24
16 16 16 16








![[Linux]服务管理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/6a1ba0dcd424476ebba46e736f38509c.png)