Is It A Tree?
问题
考试时应该做不出来,果断放弃
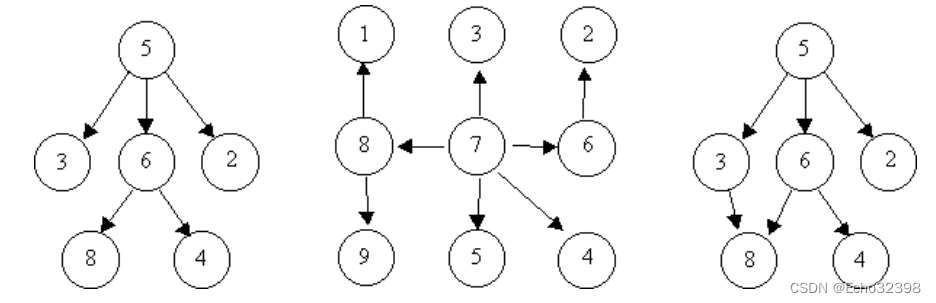
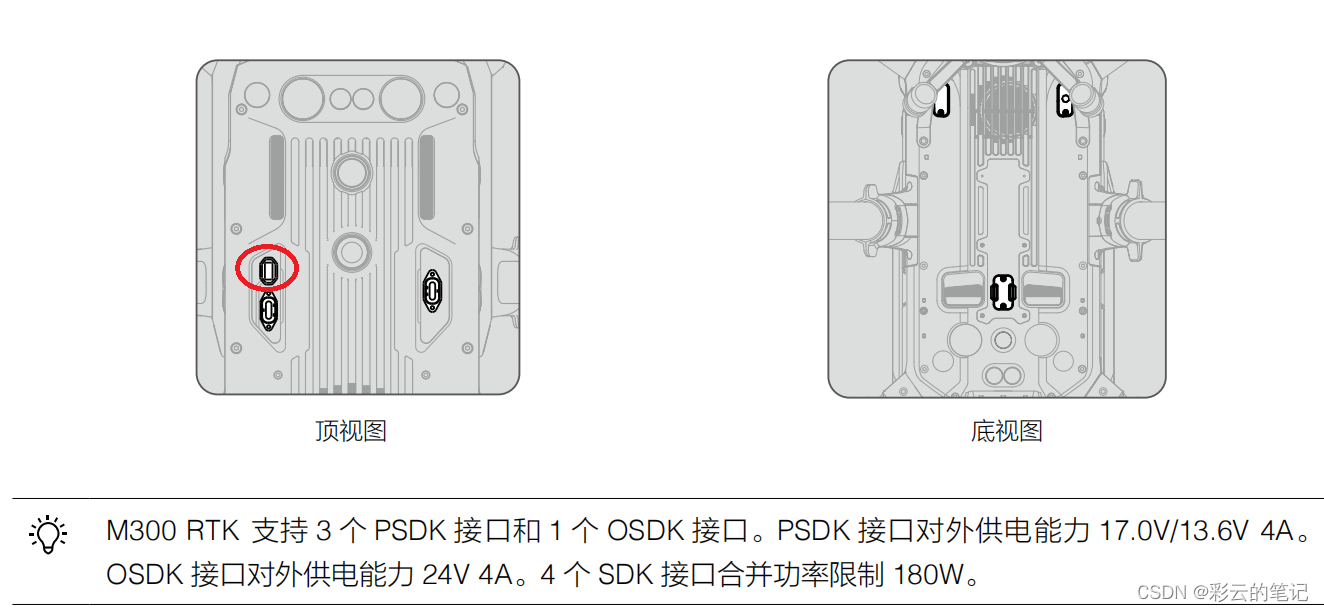
树是一种众所周知的数据结构,它要么是空的(null, void, nothing),要么是一个或的集合满足以下属性的节点之间有向边连接的节点较多。
•只有一个节点,称为根节点,它没有有向边指向。
•除了根节点外,每个节点都有一条边指向它。
•从根到每个节点有一个唯一的有向边序列。
例如,考虑下面的插图,其中节点由圆圈和边表示用带箭头的线表示。前两个是树,最后一个不是。
在这个问题中,你会得到一些有向连接的节点集合的描述边缘。对于其中的每一个,您都要确定集合是否满足树的定义。
输入
输入将由一系列描述(测试用例)和一对负整数组成。每个测试用例将由边缘描述序列组成,每个边缘后面跟着一对零描述将由一对整数组成;第一个整数标识该边从哪个节点出发开始,第二个整数标识该边所指向的节点。节点号将总是大于0。
输出
对于每个测试用例,显示“case k是一个树”这行。’或者‘Case k不是树’这条线。”,即K对应于测试用例编号(它们从1开始顺序编号)。
思路
①先判断是不是空树,如果是空树(直接输入两个0),就直接判断是树;
②然后找这棵树的根节点,如果有一个节点它的入度为0而出度不为0,那它就是根节点,如果没有找到这样的结点就判断它不是树;
③在找到一个根节点之后,用广度优先遍历的方法,通过根节点遍历一遍这棵树,如果两次遍历到同一个结点,那就说明这个结点的入度不是1,这就不是树;
④广度优先遍历结束之后,如果所有的结点都被访问过了,那就说明这是树,否则就不是树(不是连通的)。
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <climits>
#include <memory>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10000;
int first[maxn];
int second[maxn];
int counter;
bool visited[maxn];
queue<int> q;
bool isRoot(int index, int counter)
{
bool retVal = false;
for(int i = 0; i < counter; i++)
{
if(second[i] == index) return false;
if(first[i] == index) retVal = true;
}
return retVal;
}
int main()
{
int number = 0;
int first_in, second_in;
while(cin>>first_in>>second_in)
{
if(first_in == -1 || second_in == -1) break;
if(first_in == 0 && second_in == 0)
{
printf("Case %d is a tree.\n", ++number);
continue;
}
counter = 0;
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
do
{
if(first_in == 0 && second_in == 0) break;
first[counter] = first_in;
second[counter] = second_in;
++counter;
}
while(cin>>first_in>>second_in);
// find a root node
int index;
for(index = 0; index < maxn; index++)
{
if(isRoot(index, counter)) break;
}
if(index == maxn)
{
printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n", ++number);
continue;
}
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
q.push(index);
bool isTree = true;
int treesize = counter;
while(!q.empty())
{
int root = q.front();
q.pop();
if(visited[root])
{
isTree = false;
break;
}
visited[root] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < counter; i++)
{
if(first[i] == root)
{
q.push(second[i]);
--treesize;
}
}
}
if(!isTree || treesize != 0)
printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n", ++number);
else
printf("Case %d is a tree.\n", ++number);
}
}Global Raining at Bididibus
问题
好难呀


思路
(⊙o⊙)…这道题网络上居然没有找到解题方法
代码
在CSDN上看到唯一提到这道题的点进去发现居然是我自己![]()
【碎碎念】
我终于知道为什么往届同学做这套题的很少,原来是因为太难了QAQ
这套题第一道题和第三道题可以尝试去做,第二套争取会做
Tokitsukaze and All Zero Sequence
代码
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
for(int i=0;i<t;i++){
int flag=0;//注意初始化
int ch;
int n;
int a[101]={0};
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&ch);
a[ch]++;
if(a[ch]>1)//注意是大于1
flag=1;
}
if(a[0]>0)
printf("%d\n",n-a[0]);
else {
if(flag==1)
printf("%d\n",n);//输出0和1时不要弄混
if(flag==0)
printf("%d\n",n+1);
}
}
return 0;
}Aggressive cows
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int n,c;
int a[100005];
bool fun(int m){
int cnt=1,cur=0,next=1;
while(next<n){
next++;
if(a[next]-a[cur]>=m){
cnt++;
cur=next;
}
}
if(cnt>=c) return true;
else return false;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d",&n,&c);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
int l=a[0],r=a[n-1];
int ans=0;
sort(a,a+n);
while(l<=r){
int mid=(l+r)/2;
if(fun(mid)){
ans=mid;
l+mid+1;
}else{
r=mid-1;
}
}
printf("%d",ans);
return 0;
}Brainman
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int n=200000;
int a[n];//一个N个数的序列
int main(){
int m;
scanf("%d",&m);//场景的数量
for(int k=1;k<=m;k++) {
int p;
sccanf("%d",&p);//长度
for(int i=1;i<=p;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]) ;//元素
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=p;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<=p;j++){
if(a[i]>a[j])//交换位置
cnt++;
}
}
printf("Scenario #%d:\n%d\n\n",k,cnt);
}
return 0;
}Tokitsukaze and Good 01-String (hard version)
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n;
string s;
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
cin >> n >> s;
int x = 0, y = 0;
char last = ' ';
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i += 2)
{
if (s[i] != s[i+1])
x++;
else
{
if (last != s[i])
y++;
last = s[i];
}
}
printf("%d %d\n", x, (y > 1) ? y : 1);
}
return 0;
}学习规划