REST(Representational State Transfer),表现形式状态转换,它是一种软件架构风格。
当我们想要表示一个网络资源时,传统方式通常是用一个请求url表示一个操作。这样既不方便,也不安全,因为操作对于用户是透明的,可以通过地址得知要实现的是什么操作。
为了解决这样的问题,可以使用REST风格表示网络资源。

这样请求地址变的简单了,并且光看请求URL并不是很能猜出来该URL的具体功能。
但是我们的需求不只有保存,我们目标实现增删改查,而url只有一个,怎么办呢?
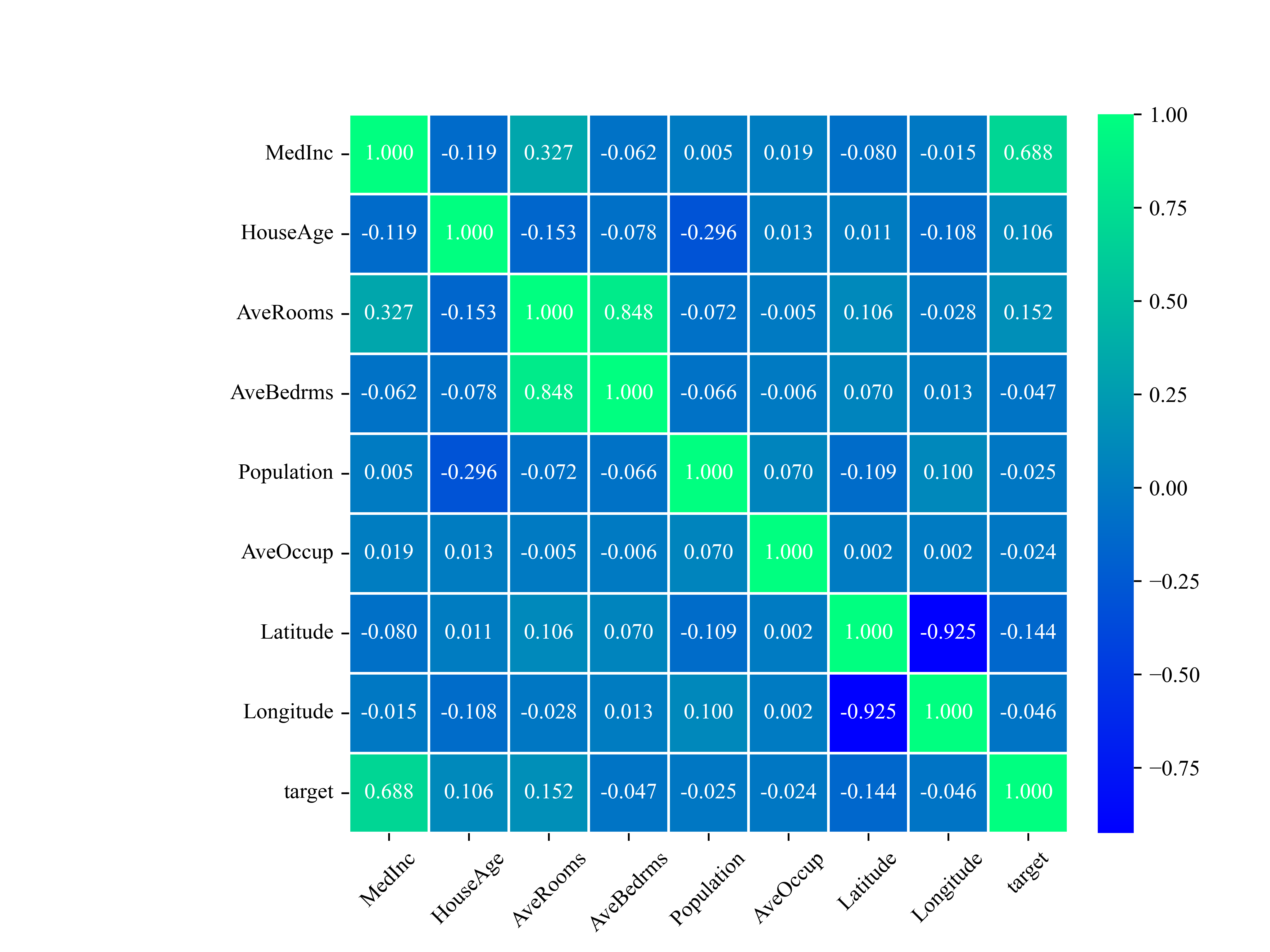
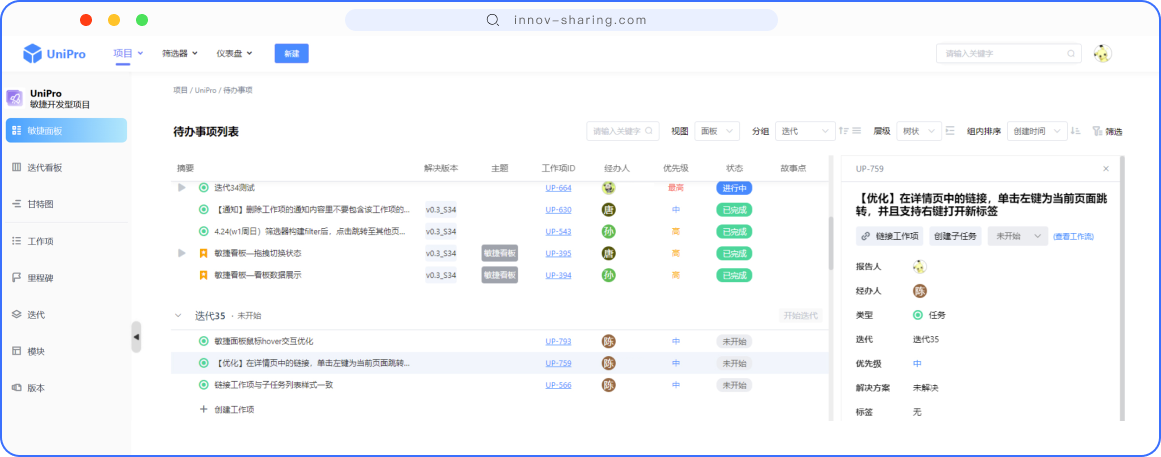
所以,REST风格访问资源时使用行为动作区分对资源进行了何种操作:
http://localhost/users查询全部用户信息 GET(查询)http://localhost/users/1查询指定用户信息 GET(查询)http://localhost/users添加用户信息 POST(新增/保存)http://localhost/users修改用户信息 PUT(修改/更新)http://localhost/users/1删除用户信息 DELETE(删除)
上述行为是约定方式,约定不是规范,可以打破,所以称REST风格,而不是REST规范。
描述模块的名称通常使用复数,也就是加s的格式描述,表示此类资源,而非单个资源,例
如:users、books、accounts…
添加示例
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为POST,表示REST风格中的添加操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String save() {
System.out.println("user save...");
return "{'module':'user save'}";
}
}
删除示例
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为DELETE,表示REST风格中的删除操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(Integer id) {
System.out.println("user delete..." + id);
return "{'module':'user delete'}";
}
}
修改示例
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为PUT,表示REST风格中的修改操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseBody
public String update(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("user update..." + user);
return "{'module':'user update'}";
}
}
根据ID查询示例
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为GET,表示REST风格中的查询操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}" ,method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("user getById..."+id);
return "{'module':'user getById'}";
}
}
查询全部示例
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为GET,表示REST风格中的查询操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users" ,method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getAll() {
System.out.println("user getAll...");
return "{'module':'user getAll'}";
}
}
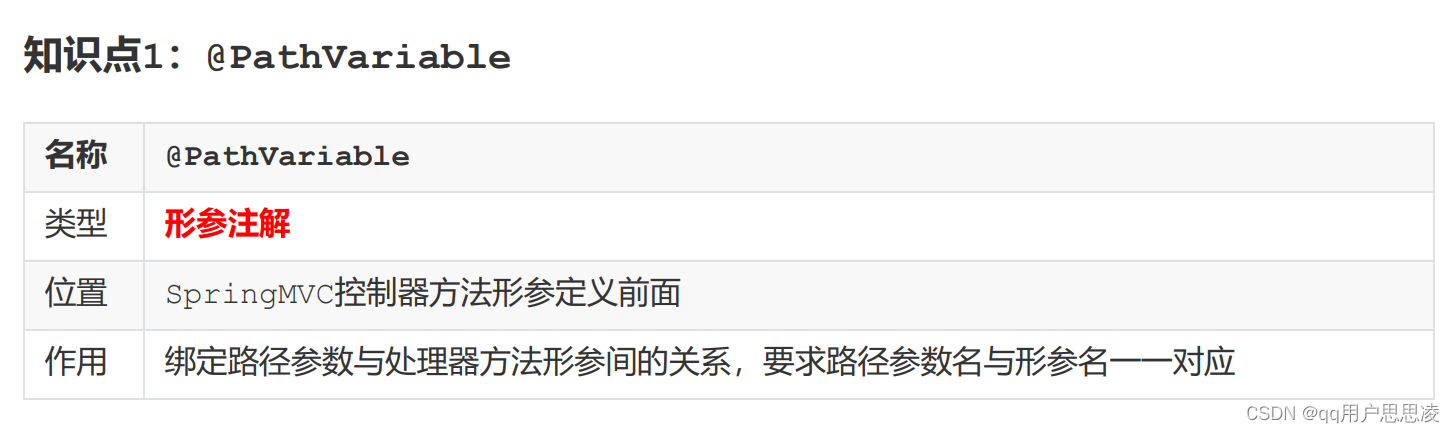
如果value中的变量名和控制类需要的变量名不一样,或者打算传递多个参数时,可以使用@PathVariable注解
例如:

@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为DELETE,表示REST风格中的删除操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}/{name}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id,@PathVariable String name)
{
System.out.println("user delete..." + id+","+name);
return "{'module':'user delete'}";
}
}
总结:
设定Http请求动作(动词):
@RequestMapping(value="",method = RequestMethod.POST|GET|PUT|DELETE)
设定请求参数(路径变量):
@RequestMapping(value="/users/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ReponseBody
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id){
}