文章目录
- 一、数据处理
- 二、环境
- 三、训练
一、数据处理
import traceback
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
import shutil
import random
import cv2
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
def convert_annotation_to_list(xml_filepath, size_width, size_height, classes):
in_file = open(xml_filepath, encoding='UTF-8')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
# size = root.find('size')
# size_width = int(size.find('width').text)
# size_height = int(size.find('height').text)
yolo_annotations = []
# if size_width == 0 or size_height == 0:
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = [float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text)]
# 标注越界修正
if b[1] > size_width:
b[1] = size_width
if b[3] > size_height:
b[3] = size_height
txt_data = [((b[0] + b[1]) / 2.0) / size_width, ((b[2] + b[3]) / 2.0) / size_height,
(b[1] - b[0]) / size_width, (b[3] - b[2]) / size_height]
# 标注越界修正
if txt_data[0] > 1:
txt_data[0] = 1
if txt_data[1] > 1:
txt_data[1] = 1
if txt_data[2] > 1:
txt_data[2] = 1
if txt_data[3] > 1:
txt_data[3] = 1
yolo_annotations.append(f"{cls_id} {' '.join([str(round(a, 6)) for a in txt_data])}")
in_file.close()
return yolo_annotations
def main():
classes = ["red", "green", "yellow", "off"]
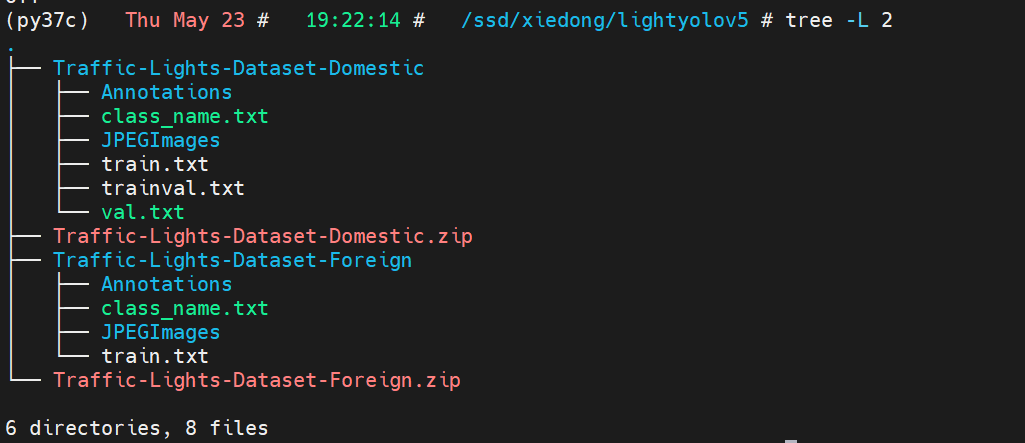
root = r"/ssd/xiedong/lightyolov5"
img_path_1 = os.path.join(root, "Traffic-Lights-Dataset-Domestic/JPEGImages")
xml_path_1 = os.path.join(root, "Traffic-Lights-Dataset-Domestic/Annotations")
img_path_2 = os.path.join(root, "Traffic-Lights-Dataset-Foreign/JPEGImages")
xml_path_2 = os.path.join(root, "Traffic-Lights-Dataset-Foreign/Annotations")
dst_yolo_root = os.path.join(root, "Traffic-Lights-Dataset-YOLO")
dst_yolo_root_img = os.path.join(dst_yolo_root, "images")
os.makedirs(dst_yolo_root_img, exist_ok=True)
dst_yolo_root_txt = os.path.join(dst_yolo_root, "labels")
os.makedirs(dst_yolo_root_txt, exist_ok=True)
index = 0
img_path_1_files = os.listdir(img_path_1)
xml_path_1_files = os.listdir(xml_path_1)
for img_id in tqdm(img_path_1_files):
# 右边的.之前的部分
xml_id = img_id.split(".")[0] + ".xml"
if xml_id in xml_path_1_files:
try:
new_name = f"{index:06d}.jpg"
img = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(os.path.join(img_path_1, img_id), dtype=np.uint8), 1) # img是矩阵
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(dst_yolo_root_img, new_name), img)
new_txt_name = f"{index:06d}.txt"
yolo_annotations = convert_annotation_to_list(os.path.join(xml_path_1, img_id[:-4] + ".xml"),
img.shape[1],
img.shape[0],
classes)
with open(os.path.join(dst_yolo_root_txt, new_txt_name), 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(yolo_annotations))
index += 1
except:
traceback.print_exc()
img_path_1_files = os.listdir(img_path_2)
xml_path_1_files = os.listdir(xml_path_2)
for img_id in tqdm(img_path_1_files):
# 右边的.之前的部分
xml_id = img_id.split(".")[0] + ".xml"
if xml_id in xml_path_1_files:
try:
new_name = f"{index:06d}.jpg"
img = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(os.path.join(img_path_2, img_id), dtype=np.uint8), 1) # img是矩阵
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(dst_yolo_root_img, new_name), img)
new_txt_name = f"{index:06d}.txt"
yolo_annotations = convert_annotation_to_list(os.path.join(xml_path_2, img_id[:-4] + ".xml"),
img.shape[1],
img.shape[0],
classes)
with open(os.path.join(dst_yolo_root_txt, new_txt_name), 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(yolo_annotations))
index += 1
except:
traceback.print_exc()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
二、环境
conda create -n py310_yolo8 python=3.10 -y
conda activate py310_yolo8
conda install pytorch==2.1.2 torchvision==0.16.2 torchaudio==2.1.2 pytorch-cuda=11.8 -c pytorch -c nvidia
pip install ultralytics
data.yaml
path: /ssd/xiedong/lightyolov5/Traffic-Lights-Dataset-YOLO/
train: images
val: images
test: # test images (optional)
# Classes
names:
0: 'red'
1: 'green'
2: 'yellow'
3: 'off'
三、训练
教程:
https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/train/#comet
新建训练代码文件train.py:
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO("yolov8s.pt") # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
# Train the model with 2 GPUs
results = model.train(data="data.yaml", epochs=100, imgsz=640, device=[0, 1, 2, 3], batch=128)
开启训练:
python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 4 train.py
结果会存在这里:
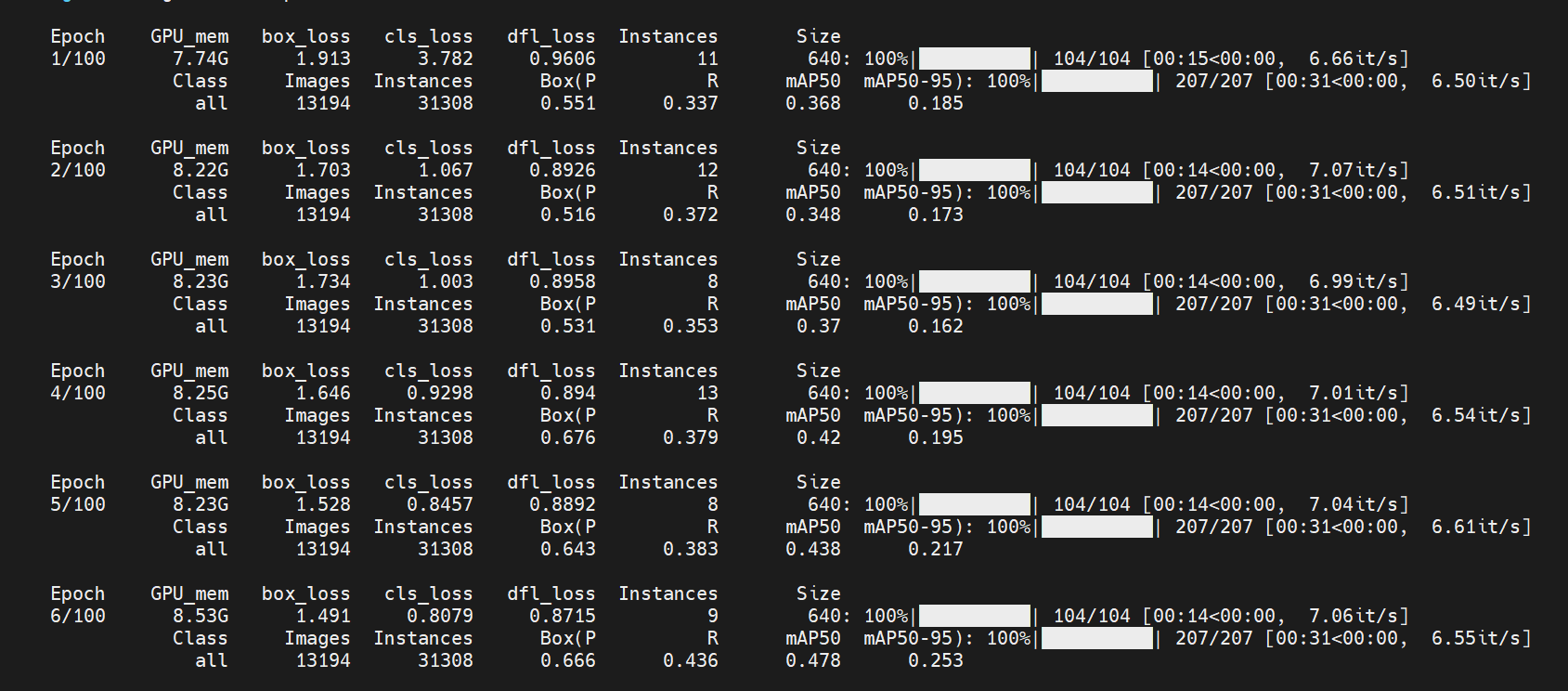
训练截图:
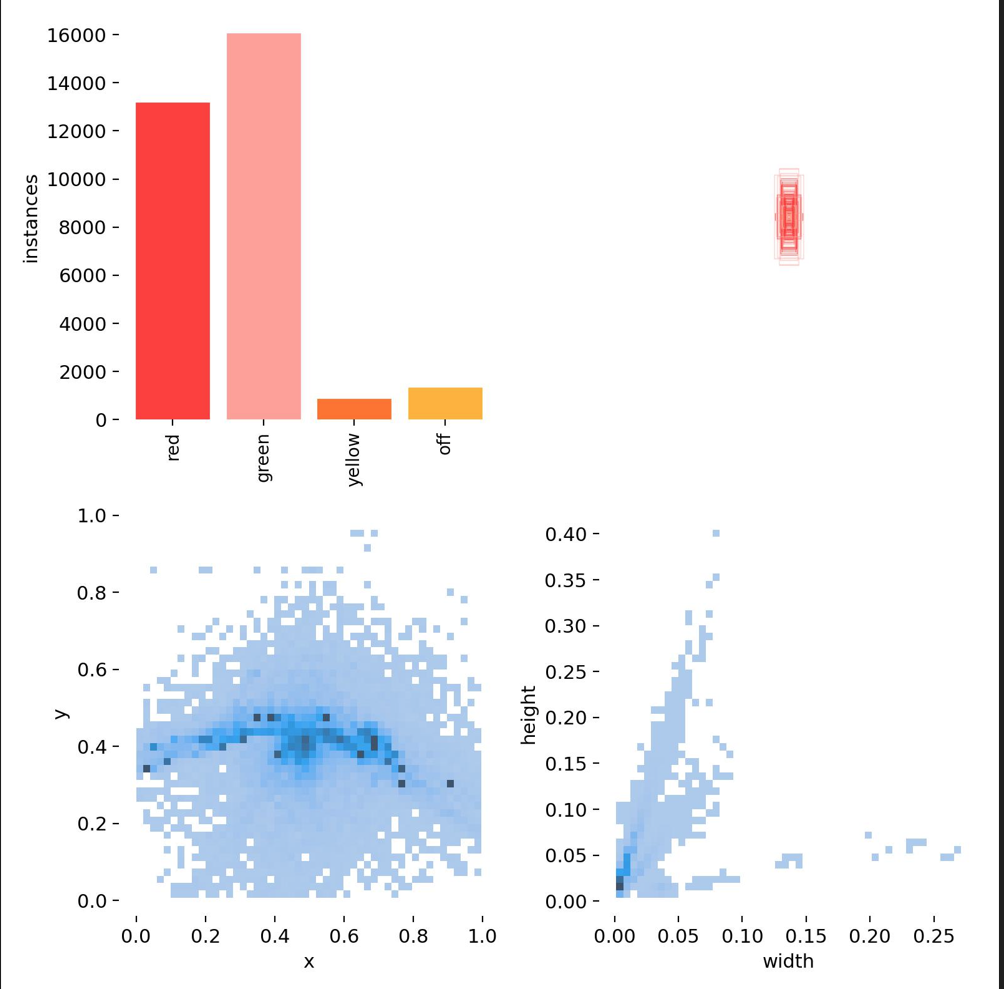
数据分布: