文章目录
系列:链表专练
语言:java & go
题目来源:Leetcode
常考点: 单链表 & 双链表 &双指针
思路和参考答案
- 文章目录
- 链表专题总结
- 链表专练
链表专题总结

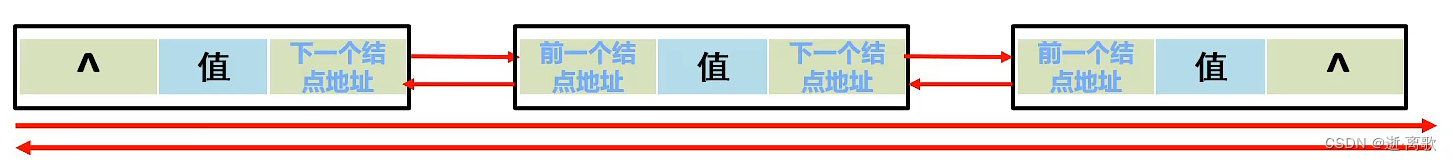
- 链表是一种通过指针串联在一起的线性结构,每一个节点由两部分组成,一个是数据域,一个是指针域(存放指向下一个节点的指针),最后一个节点的指针域指向NULL(空指针)。
- 链表有三种,单链表,双链表,循环链表,存储方式不象数组那样子连续分布,而是通过指针域的指针来连接内存中各个节点的。分布是不连续的,是散乱分布在内存中的某地址上。
- 链表的长度是不固定的,可以动态增删,适合数量不固定,频闪增删,较少查询的场景。
- 常用虚拟头节点的添加来便捷链表之后的操作。
链表专练
- leetcode203. 移除链表元素 难度:简单
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
分析:如果需要删除第三个节点,那我们应该知道前一个节点才能完成相关操作。那么如果只有一个节点head时,如何进行操作呢,那就要进行相关判断,所以我们可以建一个虚拟头节点来使对每个符合条件的节点进行相同的删除操作,就是通过前一个节点来进行删除操作
java参考代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1,head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!= null){
if(cur.val == val){
pre.next = cur.next;
}else{
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
//这里为什么要返回dummy.next 而不是head呢?
//因为新的头节点使dummy.next,而不是原来的head了
return dummy.next;
}
}
go参考代码:
func removeElements(head *ListNode, val int) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{}
dummy.Next = head
cur := dummy
for cur != nil && cur.Next != nil {
if cur.Next.Val == val {
cur.Next = cur.Next.Next
} else {
cur = cur.Next
}
}
return dummy.Next
}
- Leetcode707. 设计链表 难度:中等
设计链表的实现。您可以选择使用单链表或双链表。单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点都是 0-index 的。
在链表类中实现这些功能:
get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。
addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。
addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。
addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点。
deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
这道题非常适合用来练习链表相关操作,可以多加练习熟悉链表的操作,这里使用的依然是添加虚拟头节点的前提,不懂的可以跟着先敲,多敲几遍就理解其中的含义了,我至少跟着敲了十遍,才渐渐明白链表的相关操作以及含义,好事多磨!
java解法:分为单链表实现和双链表实现
//单链表解法
class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(){};
ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
int size;
ListNode head;
ListNode dummy;
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);
dummy = new ListNode(-1);
head = dummy.next;
}
public int get(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index >=size){
return -1;
}
ListNode cur = dummy;
for(int i =0;i<index;i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.next.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0,val);
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size,val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index >size){
return;
}
if(index < 0){
index = 0;
}
size++;
ListNode perd = dummy;
for(int i =0;i<index;i++){
perd = perd.next;
}
ListNode toAdd = new ListNode(val);
toAdd.next = perd.next;
perd.next = toAdd;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if(index<0 || index >= size){
return;
}
size--;
ListNode perd = dummy;
for(int i =0;i<index;i++){
perd = perd.next;
}
perd.next = perd.next.next;
}
}
//双链表写法
//双链表
class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next,prev;
ListNode() {};
ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
//记录链表中元素的数量
int size;
//记录链表的虚拟头结点和尾结点
ListNode head,tail;
public MyLinkedList() {
//初始化操作
this.size = 0;
this.head = new ListNode(0);
this.tail = new ListNode(0);
//这一步非常关键,否则在加入头结点的操作中会出现null.next的错误!!!
head.next=tail;
tail.prev=head;
}
public int get(int index) {
//判断index是否有效
if(index<0 || index>=size){
return -1;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
//判断是哪一边遍历时间更短
if(index >= size / 2){
//tail开始
cur = tail;
for(int i=0; i< size-index; i++){
cur = cur.prev;
}
}else{
for(int i=0; i<= index; i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return cur.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
//等价于在第0个元素前添加
addAtIndex(0,val);
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
//等价于在最后一个元素(null)前添加
addAtIndex(size,val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
//index大于链表长度
if(index>size){
return;
}
//index小于0
if(index<0){
index = 0;
}
size++;
//找到前驱
ListNode pre = this.head;
for(int i=0; i<index; i++){
pre = pre.next;
}
//新建结点
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
newNode.next = pre.next;
pre.next.prev = newNode;
newNode.prev = pre;
pre.next = newNode;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
//判断索引是否有效
if(index<0 || index>=size){
return;
}
//删除操作
size--;
ListNode pre = this.head;
for(int i=0; i<index; i++){
pre = pre.next;
}
pre.next.next.prev = pre;
pre.next = pre.next.next;
}
}
go参考代码: 分为单链表和双链表实现
//单链表实现
// 节点结构体
type Node struct {
Val int
Next *Node
}
// MylinkedList是一个对象,需要去实现LinkedList接口的所有方法
type MyLinkedList struct {
DummyHead *Node //虚拟头节点
Size int //链表长度
}
//创建一个链表
func Constructor() MyLinkedList { //成功
// 创建一个虚拟头节点,非真正的头节点(真正的头节点是数组第一个节点)
dummyHead := &Node{
Val : -1,
Next : nil,
}
return MyLinkedList{DummyHead: dummyHead,Size: 0}
}
// 获取index位置的元素Val
// 获取到第index个节点数值,如果index是非法数值直接返回-1, 注意index是从0开始的,第0个节点就是头结点
func (this *MyLinkedList) Get(index int) int {
// 判断index是否非法
if (index < 0) || (index > (this.Size - 1)) {
return -1
}
// 查找
var cur *Node = this.DummyHead// dummy节点的index = -1
for i := 0;i < index;i++ {//找到index为 index的节点
cur = cur.Next //0,1,2,3,4....index
}
return cur.Next.Val
}
// 在头节点前面再次添加一个节点
func (this *MyLinkedList) AddAtHead(val int) { //成功
// 在dummy节点后面直接添加一个节点
var newNode *Node = &Node{Val:val, Next:nil,} //所有变量都要显示的初始化
newNode.Next = this.DummyHead.Next
this.DummyHead.Next = newNode
this.Size++
}
// 在尾结点添加节点
func (this *MyLinkedList) AddAtTail(val int) {
var newNode *Node = &Node{val, nil}
cur := this.DummyHead
for cur.Next != nil { //找到末尾节点
cur = cur.Next
}
cur.Next = newNode //新元素添加到末尾节点后面
this.Size++
}
// 在index节点前面添加一个节点
func (this *MyLinkedList) AddAtIndex(index int, val int) {
if index > this.Size {
return
}else if index == this.Size { //直接添加到末尾
this.AddAtTail(val)
return
}else if index < 0 {
index = 0
}
var newNode *Node = &Node{val, nil}
cur := this.DummyHead
for i:=0; i<index; i++ { //找到index为 index-1的节点,如果index=0,则不会进入循环,直接插入到dummy后面
cur = cur.Next
}
newNode.Next = cur.Next
cur.Next = newNode
this.Size++
}
// 删除index节点
func (this *MyLinkedList) DeleteAtIndex(index int) {
// 判断是否有效
if index > this.Size-1 || index < 0 {
return
}
cur := this.DummyHead
for i := 0; i < index; i++ {
cur = cur.Next
}
cur.Next = cur.Next.Next
this.Size--
}
// func main(){
// obj := Constructor()
// obj.AddAtHead(1)
// obj.AddAtTail(2)
// obj.AddAtIndex(0,0)
// obj.DeleteAtIndex(0)
// fmt.Println(obj.Get(0),obj.Get(1),obj.Get(2))
// }
//双链表写法
//双链表解法
// 节点结构体
type Node struct {
Val int
Next *Node
Pre *Node
}
// 链表对象
type MyLinkedList struct {
DummyHead *Node
DummyTail *Node
Size int
}
// 创建一个有虚拟首位节点的链表
func Constructor() MyLinkedList {
dummyHead := &Node{-1, nil, nil}
dummyTail := &Node{-1, nil, dummyHead}
dummyHead.Next = dummyTail
return MyLinkedList{dummyHead, dummyTail, 0}
}
// 获取index节点
func (this *MyLinkedList) Get(index int) int {
if index >= this.Size || index < 0 {
return -1
} else {
p := this.DummyHead
for i := 0; i < index; i++ {
p = p.Next
}
return p.Next.Val
}
}
// 在头结点前面添加一个节点称为新的头节点
func (this *MyLinkedList) AddAtHead(val int) {
var newNode *Node = &Node{val, nil, nil}
//后插法添加节点
newNode.Next = this.DummyHead.Next
newNode.Pre = this.DummyHead
this.DummyHead.Next.Pre = newNode
this.DummyHead.Next = newNode
this.Size++
}
// 在尾结点后面添加一个节点
func (this *MyLinkedList) AddAtTail(val int) {
//在dummytail前面添加一个节点
var newNode *Node = &Node{val, nil, nil}
//前插法添加节点
newNode.Next = this.DummyTail
newNode.Pre = this.DummyTail.Pre
this.DummyTail.Pre.Next = newNode
this.DummyTail.Pre = newNode
this.Size++
}
// 在指定位置插入一个节点
func (this *MyLinkedList) AddAtIndex(index int, val int) {
if index > this.Size {
return
} else if index < 0 {
this.AddAtHead(val)
} else {
p := this.DummyHead
for i := 0; i < index; i++ {
p = p.Next
}
var newNode *Node = &Node{val, p.Next, p}
p.Next.Pre = newNode
p.Next = newNode
this.Size++
}
}
// 删除指定index的节点
func (this *MyLinkedList) DeleteAtIndex(index int) {
if index >= this.Size || index < 0 {
return
} else {
p := this.DummyHead
for i := 0; i < index; i++ {
p = p.Next
}
p.Next.Next.Pre = p
p.Next = p.Next.Next
this.Size--
}
}
- leetcode206. 反转链表 难度:简单
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
思路:通过快慢指针,来改变链表的指向,将链表的指向反过来,如果本来指针指向是1->2->3,我们将链表指向改为1<-2<-3,通过移动两个指针来实现,最后打印输出指针即可
java参考代码:双指针和递归
//双指针
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre=null ;
ListNode temp =null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur= temp;
}
return pre;
}
}
//递归
class Solution{
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){
return reverse(null,head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode pre,ListNode cur){
if(cur == null){
return pre;
}
ListNode temp = null;
temp = cur.next; //先保存下一个节点
cur.next = pre; //反转
//更新pre cur位置
return reverse(cur,temp);
}
}
go参考代码: 双指针和递归
//双指针
func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
var pre *ListNode
cur := head
for cur != nil {
next := cur.Next
cur.Next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next
}
return pre
}
//递归
func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
return help(nil, head)
}
func help(pre, head *ListNode)*ListNode{
if head == nil {
return pre
}
next := head.Next
head.Next = pre
return help(head, next)
}
- leetcode24. 两两交换链表中的节点 难度:中等
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
思路:有一点你需要明白,链表不同于其他类型,如果要交换两个节点的位置,需要改变的是指针的指向,比如dummy(虚拟头结点)->1->2->3->4,我们交换完后是dummy(虚拟头结点)->2->1->4->3,怎样实现:将头结点的next指向2,而不是指向1,将2的next指向1,1的next指向4,4的next指向3,这样的话就实现了交换两个节点。
java实现:
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1,head);
ListNode cur = dummy;
ListNode temp;
ListNode firstNode;
ListNode secondNode;
while(cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null){
temp = cur.next.next.next;
firstNode = cur.next;
secondNode = cur.next.next;
cur.next = secondNode;
secondNode.next = firstNode;
firstNode.next = temp;
cur = firstNode; //cur移动,准备下一轮交换
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
go实现:
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{
Next: head,
}
pre := dummy
for head != nil && head.Next != nil{
pre.Next = head.Next
next := head.Next.Next
head.Next.Next = head
head.Next = next
pre = head
head = next
}
return dummy.Next
}
- leetcode19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 难度:中等
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
思路:双指针思路,:通过将slow和fast两个指针之间间隔为n,即fast比slow多走n步,然后根据判断fast的下一个节点是否是空,然后此时slow指向的刚好是目标节点的前一个节点,所以可以完成删除
//双指针解法:通过将slow和fast两个指针之间间隔为n,即fast比slow多走n步
//
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1,head);
ListNode fastNode = dummy;
ListNode slowNode = dummy;
for(int i =0;i<n;i++){
fastNode = fastNode.next;
}
while(fastNode.next != null){
fastNode = fastNode.next;
slowNode = slowNode.next;
}
slowNode.next = slowNode.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
go语言版本同样的道理:通过一快一慢指针,先将fast指针比slow指针快移动n步,然后再开始移动slow指针,类比上面java的思路 一样的
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{}
dummy.Next = head
cur := head
pre := dummy
i:=1
for cur!= nil{
cur= cur.Next
if i>n{
pre = pre.Next
}
i++
}
pre.Next = pre.Next.Next
return dummy.Next
}
- leetcode面试题 02.07. 链表相交
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
思路:首先要想比较两个链表的相同点,比较的不是开头,长的链表需要向后移动两个链表长度差,然后才能开始比较,这个是前提,所以我们同时也需要分别统计出链表a和链表b的长度;然后对齐后开始比较,有相同交点直接返回
java方法:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
int lenA = 0,lenB = 0;
while(curA != null){ //求链表A的长度
lenA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curB != null){ //求链表B的长度
lenB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
if(lenB>lenA){
int tmplen = lenA;
lenA = lenB;
lenB = tmplen;
ListNode tmpNode =curA;
curA = curB;
curB = tmpNode;
}
//求长度差
int gap = lenA-lenB;
//让curA和curB在同一起点上(末尾位置对齐)
while(gap-->0){
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curA != null){
if(curA == curB){
return curA;
}
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
go方法:
func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode {
curA := headA
curB := headB
lenA, lenB := 0, 0
// 求A,B的长度
for curA != nil {
curA = curA.Next
lenA++
}
for curB != nil {
curB = curB.Next
lenB++
}
var step int
var fast, slow *ListNode
// 请求长度差,并且让更长的链表先走相差的长度
if lenA > lenB {
step = lenA - lenB
fast, slow = headA, headB
} else {
step = lenB - lenA
fast, slow = headB, headA
}
for i:=0; i < step; i++ {
fast = fast.Next
}
// 遍历两个链表遇到相同则跳出遍历
for fast != slow {
fast = fast.Next
slow = slow.Next
}
return fast
}
- leetcode142. 环形链表 II 难度:中等
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
思路:首先判断是否有环,通过双指针进行判断,一快一慢,fast快指针比slow慢指针每次多走一步,如果有环的话,快慢指针会相遇的,否则无环;如果找到环的出口,因为每次fast快指针走的路程是慢指针走的路程的两倍,所以根据数学公式。
假设从头结点到环形入口节点 的节点数为x。 环形入口节点到 fast指针与slow指针相遇节点 节点数为y。 从相遇节点 再到环形入口节点节点数为 z。
那么相遇时: slow指针走过的节点数为: x + y, fast指针走过的节点数:x + y + n (y + z),n为fast指针在环内走了n圈才遇到slow指针, (y+z)为 一圈内节点的个数A。
因为fast指针是一步走两个节点,slow指针一步走一个节点, 所以 fast指针走过的节点数 = slow指针走过的节点数 * 2:
(x + y) * 2 = x + y + n (y + z)
两边消掉一个(x+y): x + y = n (y + z)
因为要找环形的入口,那么要求的是x,因为x表示 头结点到 环形入口节点的的距离。
所以要求x ,将x单独放在左面:x = n (y + z) - y ,
再从n(y+z)中提出一个 (y+z)来,整理公式之后为如下公式:x = (n - 1) (y + z) + z 注意这里n一定是大于等于1的,因为 fast指针至少要多走一圈才能相遇slow指针。
先拿n为1的情况来举例,意味着fast指针在环形里转了一圈之后,就遇到了 slow指针了。
当 n为1的时候,公式就化解为 x = z
java解法:
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(slow == fast){//有环
ListNode index1 = fast;
ListNode index2 = head;
while(index1 != index2){
index1 = index1.next;
index2 = index2.next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return null;
}
}
go解法:
func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
slow, fast := head, head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
if slow == fast {
for slow != head {
slow = slow.Next
head = head.Next
}
return head
}
}
return nil
}
希望对您的算法学习能有所帮助,您的支持是我前进的最大动力,感谢您的关注和认可!!!