前言:
数据结构是计算机底层存储、组织数据的方式。是指数据相互之间是以什么方式排列在一起的。 通常情况下,精心选择的数据结构可以带来更高的运行或者存储效率
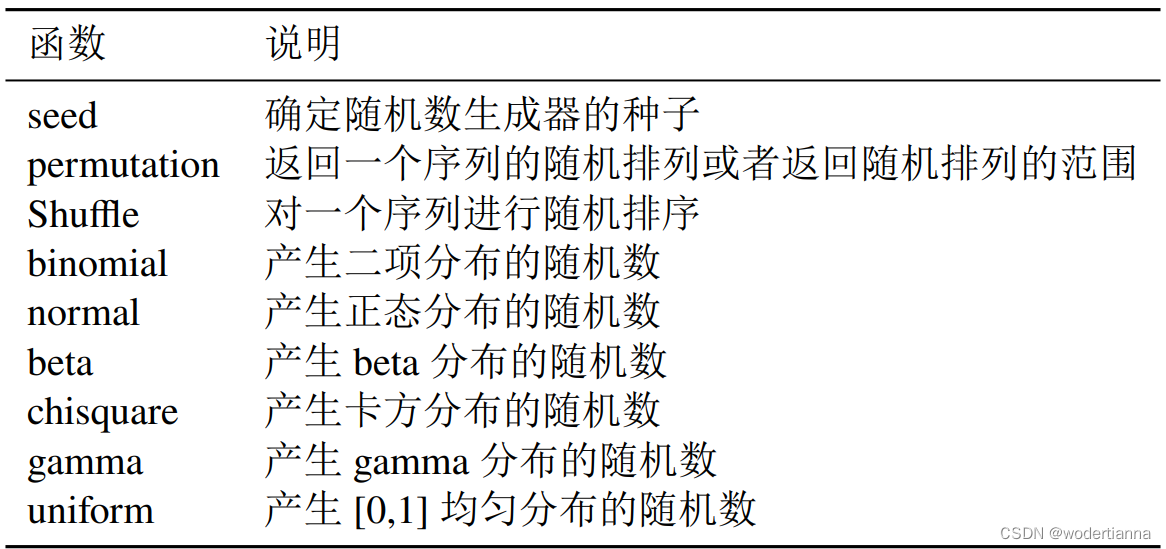
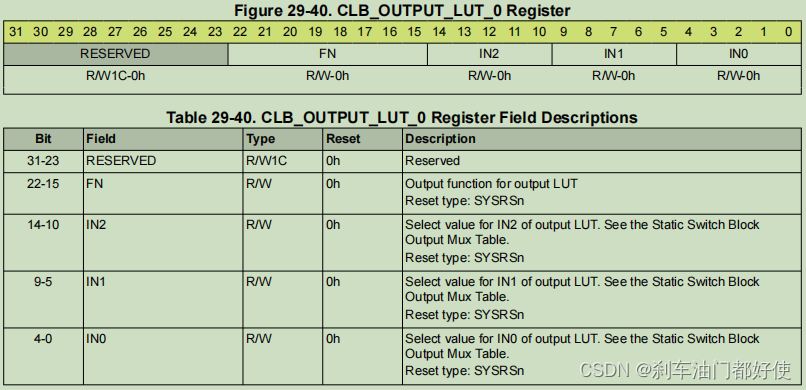
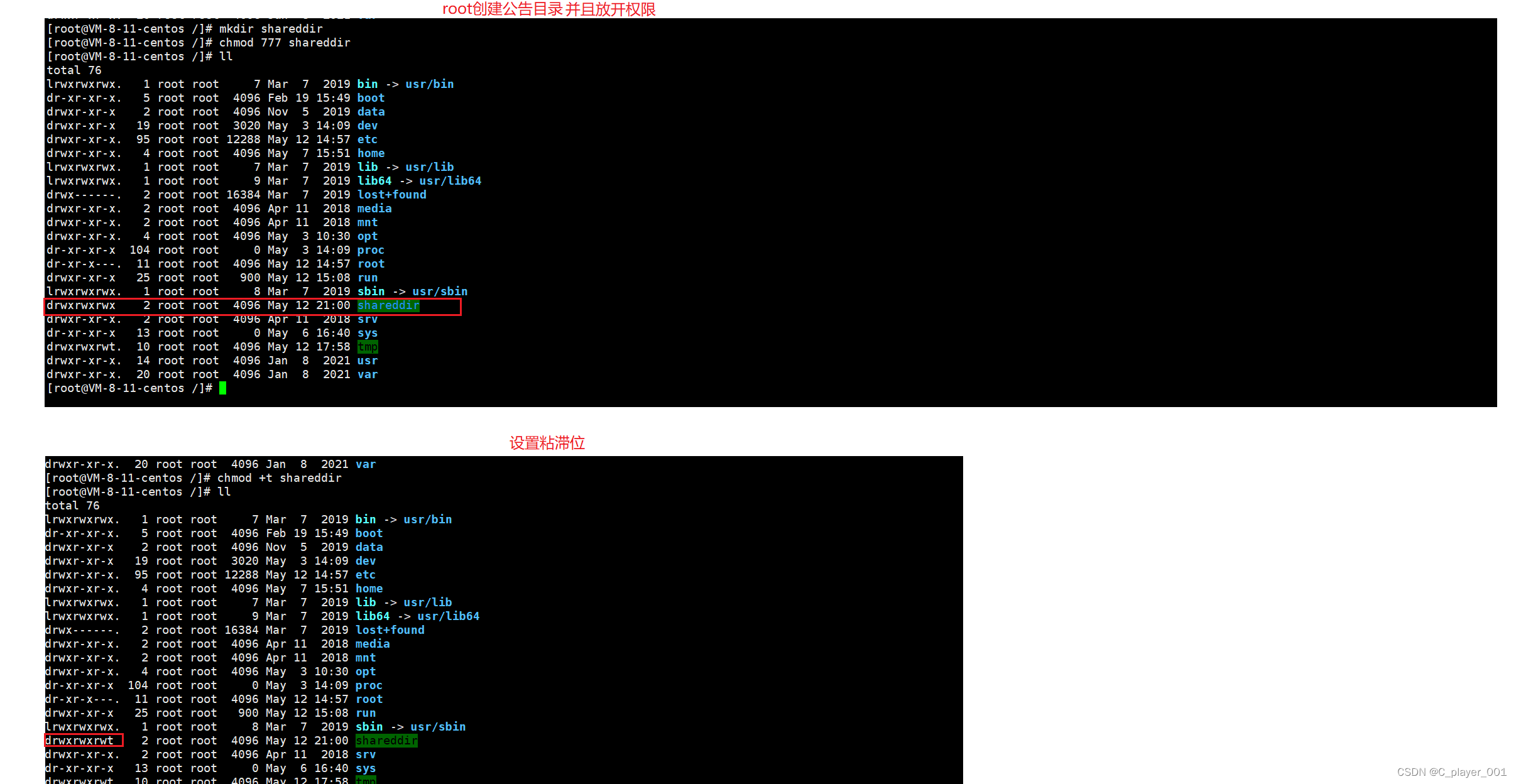
常见的八大数据结构:
栈:
思想:
栈是一种数据结构,它遵循后进先出 (LIFO) 原则。这意味着最后添加的元素(称为栈顶元素)将首先被移除。
特点:
- **简单性和效率:**栈的操作(push、pop、peek)可以在常数时间内完成。
- **后进先出:**栈的 LIFO 特性使其非常适合需要按添加顺序处理元素的应用。
- 可以理解为子弹夹一样,先进后出,后出先进
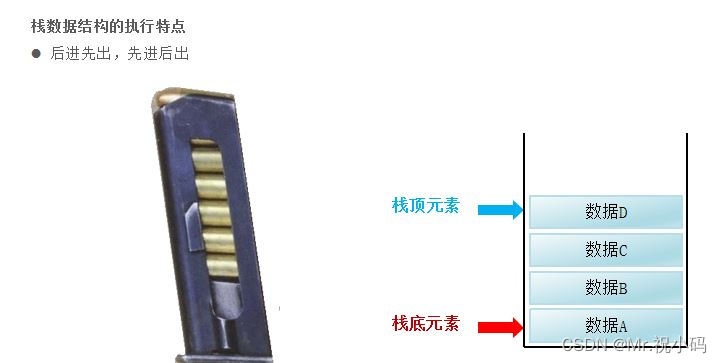
数据进入栈模型的过程称为:压/进栈
数据出栈模型的过程称为:弹/出栈
代码:
public class Stack {
private int[] arr;
private int top;
private int capacity;
public Stack(int capacity) {
this.arr = new int[capacity];
this.top = -1;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public void push(int element) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Stack overflow");
return;
}
arr[++top] = element;
}
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack underflow");
return -1;
}
return arr[top--];
}
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
return -1;
}
return arr[top];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return top == capacity - 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack(5);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
System.out.println("Top element: " + stack.peek());
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
System.out.println("Top element: " + stack.peek());
}
}
过程:
过程解释:
- 创建栈:我们创建一个容量为 5 的栈对象。栈是用数组实现的,其中
top变量跟踪栈顶元素的索引。 - 压入元素:
push方法将元素压入栈中。如果栈已满,它会打印一条错误消息。 - 弹出元素:
pop方法从栈中移除并返回栈顶元素。如果栈为空,它会打印一条错误消息。 - 查看栈顶元素:
peek方法返回栈顶元素,但不将其移除。如果栈为空,它会打印一条错误消息。 - 检查栈是否为空:
isEmpty方法检查栈是否为空。 - 检查栈是否已满:
isFull方法检查栈是否已满。 - 主方法:**在主方法中,我们创建了一个栈对象,压入一些元素,弹出一些元素,并打印栈顶元素。
最后输出:
Top element: 4
Top element: 2
队列:
思想:
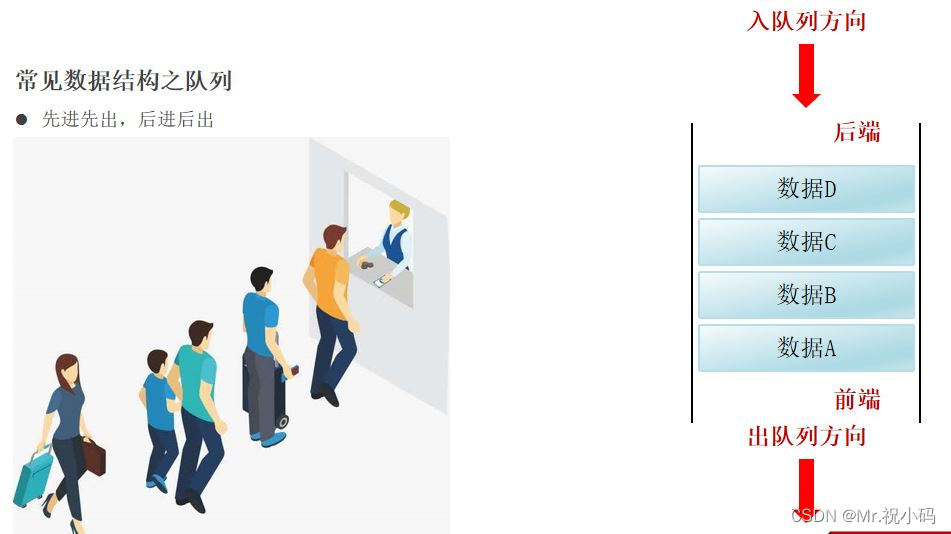
队列是一种遵循先进先出 (FIFO) 原则的数据结构。这意味着队列中的第一个添加的元素将首先被移除。与栈恰恰相反,队列两端全开,遵循先进先出,后进后出的原则
特点:
- 先进先出 (FIFO):队列遵循先进先出原则,这意味着第一个添加的元素将首先被移除。
- 线性数据结构:队列是一种线性数据结构,这意味着元素按顺序排列。
- 插入在末尾:新元素总是添加到队列的末尾(也称为尾部)。
- 删除在头部:元素从队列的头部(也称为前端)移除。
- 限制访问:队列只允许在头部和尾部进行插入和删除操作。中间元素无法直接访问。
- 队列大小:队列可以是固定大小的(使用数组实现)或动态大小的(使用链表实现)。
- 广泛的应用:队列在计算机科学中有广泛的应用,例如消息传递、任务调度、缓冲和广度优先搜索
代码:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个队列
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 向队列中添加元素
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
queue.add(4);
// 从队列中移除元素
int removedElement = queue.remove(); // 移除并返回第一个元素
// 查看队列中的第一个元素
int headElement = queue.peek(); // 返回第一个元素,但不将其移除
// 检查队列是否为空
boolean isEmpty = queue.isEmpty();
// 打印队列中的元素
System.out.println("Queue elements: " + queue);
// 打印移除的元素
System.out.println("Removed element: " + removedElement);
// 打印队列头部的元素
System.out.println("Head element: " + headElement);
// 打印队列是否为空
System.out.println("Queue is empty: " + isEmpty);
}
}
输出:
Queue elements: [2, 3, 4]
Removed element: 1
Head element: 2
Queue is empty: false
过程:
- 创建队列:我们使用 Java 的
LinkedList类创建一个队列。LinkedList 实现了 Queue 接口,它提供了队列的基本操作。 - 添加元素:
add方法将元素添加到队列的末尾。 - 移除元素:
remove方法从队列中移除并返回第一个元素。 - 查看队列头部的元素:
peek方法返回队列中的第一个元素,但不将其移除。 - 检查队列是否为空:
isEmpty方法检查队列是否为空。
数组:
思想:
数组是一种数据结构,它存储固定数量的相同类型元素的集合。数组中的元素使用索引进行访问,索引从 0 开始。
数组相对其他数据结构相对来说比较简单理解,可以理解为是一组元素,起始值下标从0开始
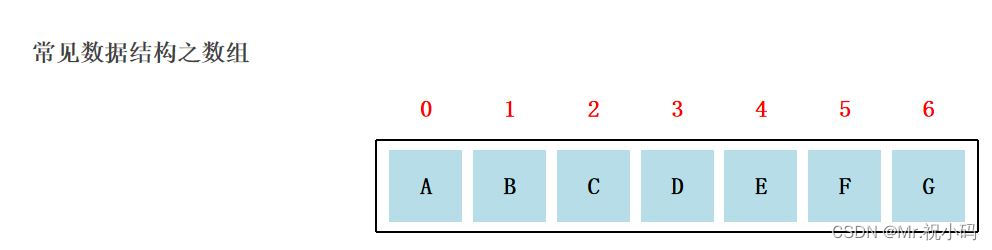
- 查询速度快:查询数据通过地址值和索引定位,查询任意数据耗时相同。
- 删除效率低:要将原始数据删除,同时后面每个数据前移。
代码:
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 声明一个长度为 7 的整型数组
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
// 遍历数组并打印每个元素
for (int element : arr) {
System.out.println(element);
}
}
}
过程:
- 声明数组:我们声明一个长度为 7 的整型数组,并使用花括号初始化其元素。
- 遍历数组:使用增强 for 循环遍历数组并打印每个元素。
链表:
思想:
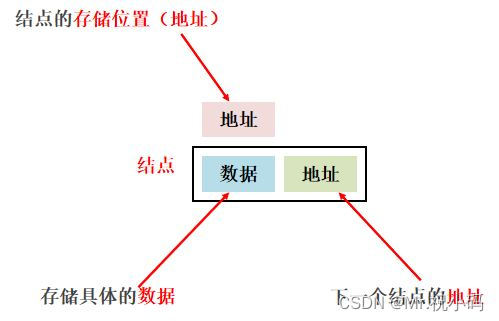
链表是一种数据结构,它由一组称为节点的对象组成。每个节点包含一个数据项和指向下一个节点的引用。
在 Java 中,链表使用以下类实现:
- LinkedList:一个双向链表,允许在列表的任何位置添加和删除元素。
- ArrayList:一个基于数组的列表,在列表末尾添加和删除元素非常高
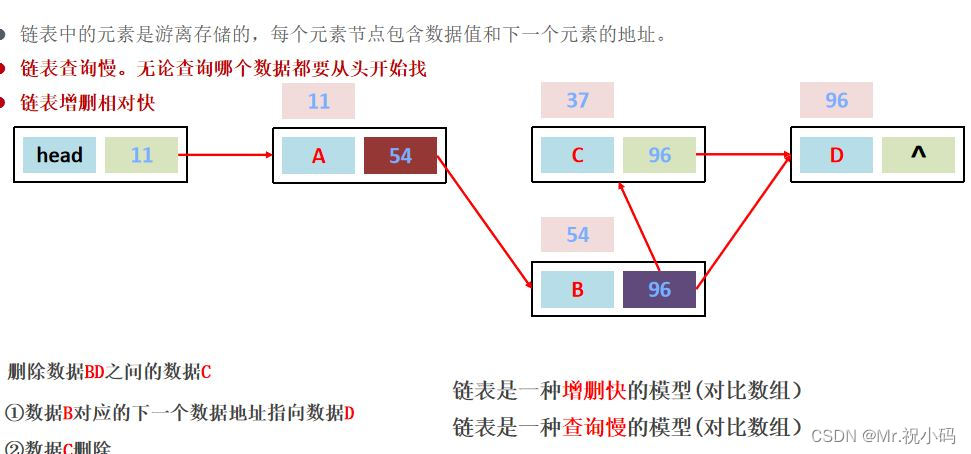
链表中的元素是游离存储的,每个元素节点包含数据值和下一个元素的地址。
链表是一种增删快、查询慢的模型(对比数组)
代码:
public class LinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个链表
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
// 向链表中添加元素
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
list.add("Orange");
// 遍历链表并打印每个元素
for (String fruit : list) {
System.out.println(fruit);
}
// 从链表中删除元素
list.remove("Banana");
// 打印修改后的链表
System.out.println("Modified list:");
for (String fruit : list) {
System.out.println(fruit);
}
}
}
输出:
Modified list:Apple Orange
Banana元素已经被链表删除
二叉树:
思想:
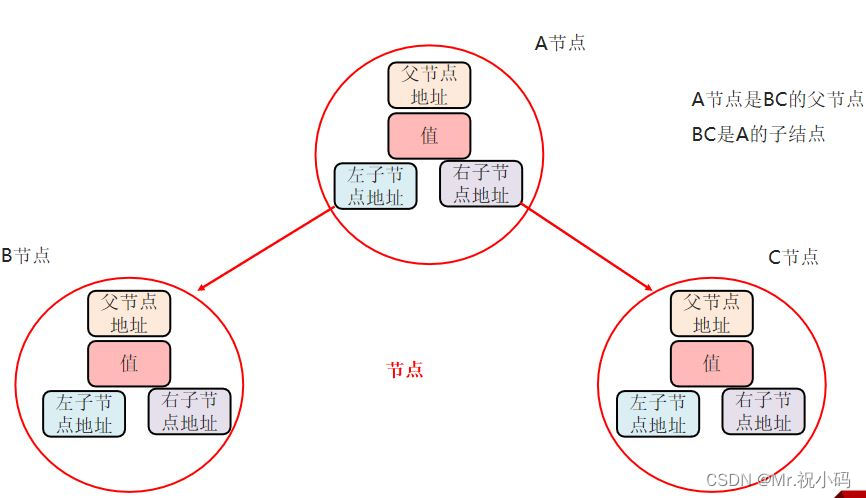
二叉树(Binary tree)是树形结构的一个重要类型。许多实际问题抽象出来的数据结构往往是二叉树形式,即使是一般的树也能简单地转换为二叉树,而且二叉树的存储结构及其算法都较为简单,因此二叉树显得特别重要。二叉树特点是每个节点最多只能有两棵子树,且有左右之分 [1]。
特点:
只能有一个根节点,每个节点最多支持2个直接子节点。
节点的度: 节点拥有的子树的个数,二叉树的度不大于2 叶子节点 度为0的节点,也称之为终端结点。
高度:叶子结点的高度为1,叶子结点的父节点高度为2,以此类推,根节点的高度最高。
层:根节点在第一层,以此类推
兄弟节点 :拥有共同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点
代码:
public class BinaryTree {
private Node root;
public void add(int data) {
root = addRecursive(root, data);
}
private Node addRecursive(Node current, int data) {
if (current == null) {
return new Node(data);
}
if (data < current.data) {
current.left = addRecursive(current.left, data);
} else if (data > current.data) {
current.right = addRecursive(current.right, data);
}
return current;
}
public boolean contains(int data) {
return containsRecursive(root, data);
}
private boolean containsRecursive(Node current, int data) {
if (current == null) {
return false;
}
if (data == current.data) {
return true;
} else if (data < current.data) {
return containsRecursive(current.left, data);
} else {
return containsRecursive(current.right, data);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.add(10);
tree.add(5);
tree.add(15);
System.out.println("Contains 5: " + tree.contains(5));
System.out.println("Contains 12: " + tree.contains(12));
}
}
class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
过程:
- 添加元素:
add()方法使用递归将元素添加到二叉树中。它将新元素与当前节点进行比较,并将其添加到左子树或右子树中,具体取决于元素的值。 - 查找元素:
contains()方法使用递归在二叉树中查找元素。它将查找值与当前节点进行比较,并根据需要递归地遍历左子树或右子树。 - 主方法:
main()方法创建二叉树并向其中添加元素。然后,它调用contains()方法来查找树中是否存在特定值。 - 输出:Contains 5: true Contains 12: false
二叉查找树:
思想:
二叉搜索树又被称为排序树,它或者是一颗空树,或者是一棵具有以下性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
特点:
1,每一个节点上最多有两个子节点
2,左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
3,右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
目的:提高检索数据的性能。
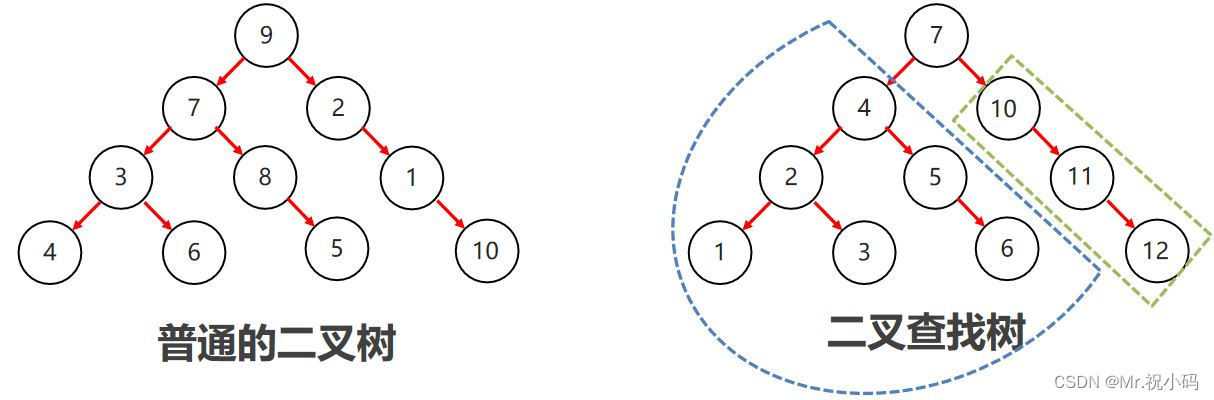
不同点:
二叉树
- 每个节点最多有两个子节点(左子节点和右子节点)。
- 没有排序规则。
- 可以用于表示各种数据结构,例如堆和哈夫曼树。
二叉搜索树(BST)
- 一个特殊的二叉树,其中每个节点的值都比其左子树的所有值大,并且比其右子树的所有值小。
- 具有以下性质:
- 左子树中的所有值都小于根节点的值。
- 右子树中的所有值都大于根节点的值。
- 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树。
区别
二叉搜索树和二叉树之间的主要区别在于排序规则:
- 二叉树没有排序规则,而二叉搜索树中的节点根据其值进行排序。
代码:
public class BinarySearchTree {
private Node root;
public void add(int data) {
root = addRecursive(root, data);
}
private Node addRecursive(Node current, int data) {
if (current == null) {
return new Node(data);
}
if (data < current.data) {
current.left = addRecursive(current.left, data);
} else if (data > current.data) {
current.right = addRecursive(current.right, data);
}
return current;
}
public boolean contains(int data) {
return containsRecursive(root, data);
}
private boolean containsRecursive(Node current, int data) {
if (current == null) {
return false;
}
if (data == current.data) {
return true;
} else if (data < current.data) {
return containsRecursive(current.left, data);
} else {
return containsRecursive(current.right, data);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
tree.add(10);
tree.add(5);
tree.add(15);
System.out.println("Contains 5: " + tree.contains(5));
System.out.println("Contains 12: " + tree.contains(12));
}
}
class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
过程:
- 添加元素:
add()方法使用递归将元素添加到二叉查找树中。它将新元素与当前节点进行比较,并将其添加到左子树或右子树中,具体取决于元素的值。 - 查找元素:
contains()方法使用递归在二叉查找树中查找元素。它将查找值与当前节点进行比较,并根据需要递归地遍历左子树或右子树。 - 主方法:
main()方法创建二叉查找树并向其中添加元素。然后,它调用contains()方法来查找树中是否存在特定值
输出:
Contains 5: true
Contains 12: false
平衡二叉树:
思想:
平衡二叉树是一种特殊的二叉搜索树,其中每个节点的左子树和右子树的高度差至多为 1。这确保了树在很大程度上保持平衡,并且查找、插入和删除操作的时间复杂度为 O(log n),其中 n 是树中的节点数。
平衡二叉树可以通过使用称为旋转的操作来实现。旋转是重新排列树中节点以维护平衡的一种方法。AVL 树和红黑树使用不同的旋转规则来保持平衡。
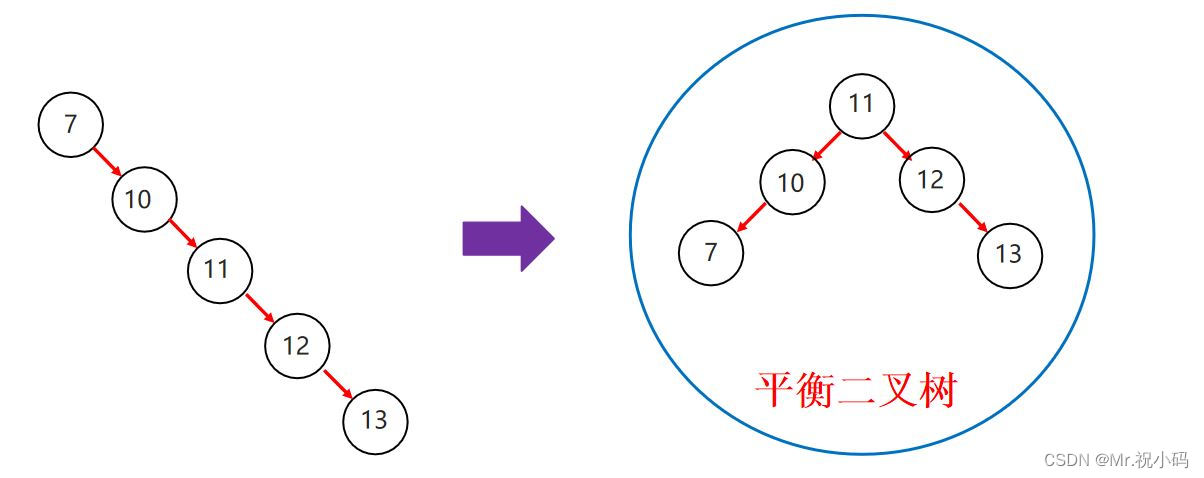
平衡二叉树是在满足查找二叉树的大小规则下,让树尽可能矮小,以此提高查数据的性能。
代码:
public class AVLTree {
private Node root;
public void add(int data) {
root = addRecursive(root, data);
}
private Node addRecursive(Node current, int data) {
if (current == null) {
return new Node(data);
}
if (data < current.data) {
current.left = addRecursive(current.left, data);
} else if (data > current.data) {
current.right = addRecursive(current.right, data);
}
updateHeight(current);
return balance(current);
}
private Node balance(Node current) {
int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(current);
if (balanceFactor > 1) {
if (getBalanceFactor(current.left) < 0) {
current.left = leftRotate(current.left);
}
return rightRotate(current);
} else if (balanceFactor < -1) {
if (getBalanceFactor(current.right) > 0) {
current.right = rightRotate(current.right);
}
return leftRotate(current);
}
return current;
}
private int getBalanceFactor(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
return height(node.left) - height(node.right);
}
private int height(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
return node.height;
}
private void updateHeight(Node node) {
node.height = 1 + Math.max(height(node.left), height(node.right));
}
private Node leftRotate(Node node) {
Node newRoot = node.right;
node.right = newRoot.left;
newRoot.left = node;
updateHeight(node);
updateHeight(newRoot);
return newRoot;
}
private Node rightRotate(Node node) {
Node newRoot = node.left;
node.left = newRoot.right;
newRoot.right = node;
updateHeight(node);
updateHeight(newRoot);
return newRoot;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree();
tree.add(10);
tree.add(5);
tree.add(15);
System.out.println("Inorder traversal of the AVL tree:");
inorderTraversal(tree.root);
}
private static void inorderTraversal(Node node) {
if (node != null) {
inorderTraversal(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inorderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
}
class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
int height;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.height = 1;
}
}
过程:
- 添加元素:
add()方法使用递归将元素添加到 AVL 树中。它将新元素与当前节点进行比较,并将其添加到左子树或右子树中,具体取决于元素的值。添加后,它更新节点的高度并平衡树以保持 AVL 性质。 - 平衡树:
balance()方法检查节点的平衡因子并执行必要的旋转以平衡树。 - 获取平衡因子:
getBalanceFactor()方法计算节点的平衡因子,它等于左子树的高度减去右子树的高度。 - 获取高度:
height()方法计算节点的高度,它等于其子树中最大高度加 1。 - 更新高度:
updateHeight()方法更新节点的高度,它等于其子树中最大高度加 1。 - 左旋转:
leftRotate()方法执行左旋转操作,它将当前节点的右子树作为新根,并将当前节点作为新根的左子树。 - 右旋转:
rightRotate()方法执行右旋转操作,它将当前节点的左子树作为新根,并将当前节点作为新根的右子树。 - 主方法:
main()方法创建 AVL 树并向其中添加元素。然后,它打印树的中序遍历以显示树的顺序。
结果:
Inorder traversal of the AVL tree:
5 10 15
红黑树:
规则:
每一个节点或是红色的,或者是黑色的,根节点必须是黑色。
如果某一个节点是红色,那么它的子节点必须是黑色(不能出现两个红色节点相连的情况)。
对每一个节点,从该节点到其所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色节点。
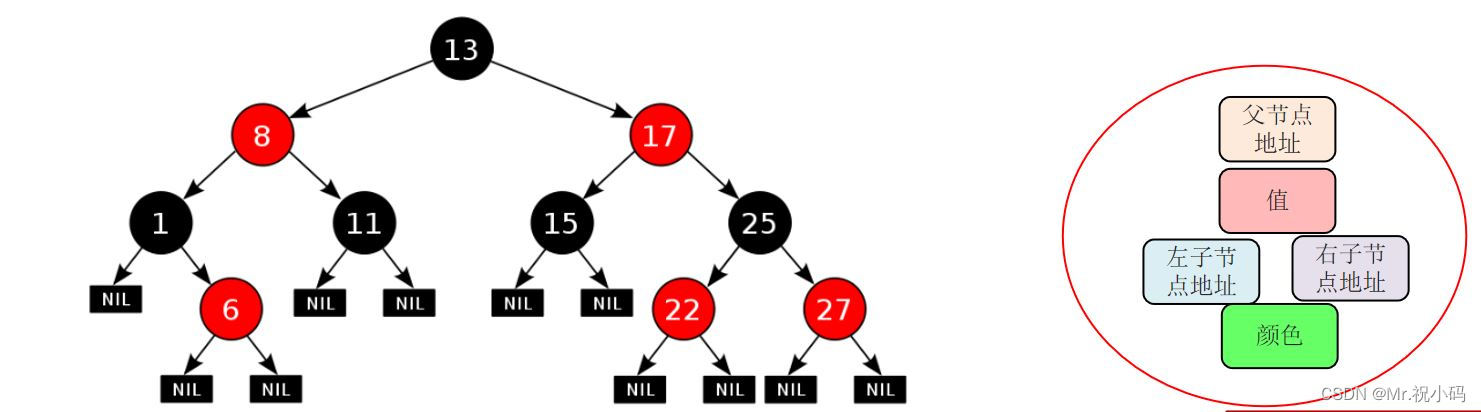
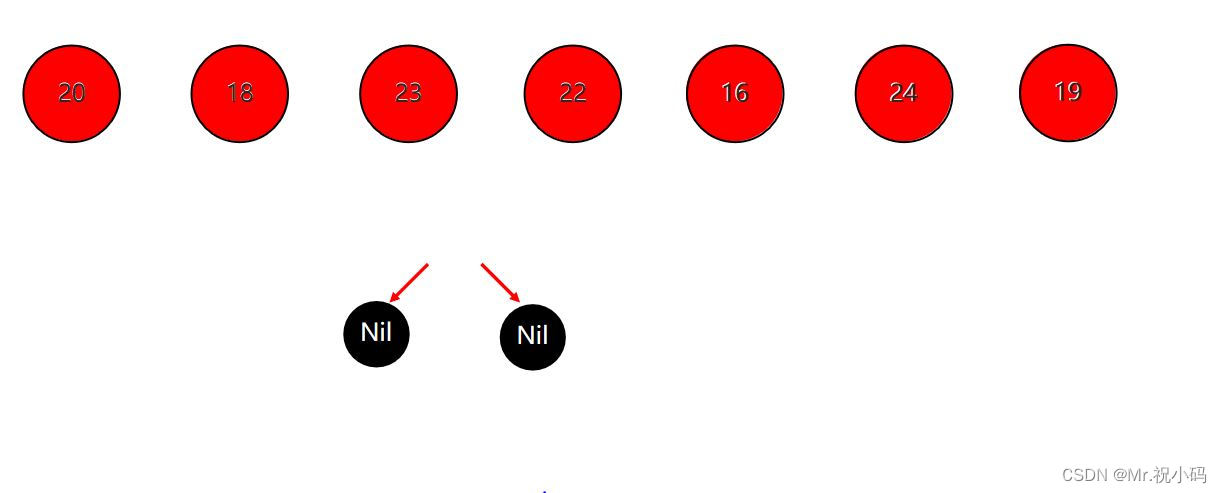
当添加的节点为根节点时,直接变成黑色就可以了
代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class RedBlackTree {
private Node root;
public void add(int data) {
root = addRecursive(root, data);
root.color = Color.BLACK;
}
private Node addRecursive(Node current, int data) {
if (current == null) {
return new Node(data);
}
if (data < current.data) {
current.left = addRecursive(current.left, data);
} else if (data > current.data) {
current.right = addRecursive(current.right, data);
}
if (isRed(current.left) && isRed(current.right)) {
flipColors(current);
}
if (isRed(current.left) && isRed(current.left.left)) {
current = rightRotate(current);
}
if (isRed(current.right) && isRed(current.right.right)) {
current = leftRotate(current);
}
return current;
}
private void flipColors(Node node) {
node.color = Color.RED;
node.left.color = Color.BLACK;
node.right.color = Color.BLACK;
}
private Node rightRotate(Node node) {
Node newRoot = node.left;
node.left = newRoot.right;
newRoot.right = node;
newRoot.color = node.color;
node.color = Color.RED;
return newRoot;
}
private Node leftRotate(Node node) {
Node newRoot = node.right;
node.right = newRoot.left;
newRoot.left = node;
newRoot.color = node.color;
node.color = Color.RED;
return newRoot;
}
private boolean isRed(Node node) {
return node != null && node.color == Color.RED;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RedBlackTree tree = new RedBlackTree();
int[] data = {20, 18, 23, 20, 16, 24, 19};
for (int value : data) {
tree.add(value);
}
List<Node> redNodes = new ArrayList<>();
inorderTraversal(tree.root, redNodes);
System.out.println("Red nodes in the Red-Black tree:");
for (Node node : redNodes) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
private static void inorderTraversal(Node node, List<Node> redNodes) {
if (node != null) {
inorderTraversal(node.left, redNodes);
if (node.color == Color.RED) {
redNodes.add(node);
}
inorderTraversal(node.right, redNodes);
}
}
private enum Color {
RED,
BLACK
}
private static class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
Color color;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.color = Color.RED;
}
}
}
步骤:
20(B)
/ \
18(R) 23(R)
/ / \
16(B) 20(R) 24(B)
/
19(R)
红色节点R表示,黑节点B表示
总结:
红黑树不是高度平衡的,它的平衡是通过"红黑规则"进行实现的
每一个节点或是红色的,或者是黑色的,根节点必须是黑色
如果一个节点没有子节点或者父节点,则该节点相应的指针属性值为Nil,这些Nil视为叶节点,每个叶节点(Nil)是黑色的;
如果某一个节点是红色,那么它的子节点必须是黑色(不能出现两个红色节点相连的情况) 对每一个节点,从该节点到其所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色节点。



![[hpssupfast@mailfence.com].Elbie勒索病毒如何恢复数据和预防](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/e4452962d8964533ae6aae74b711ff6f.jpeg)