1、深入理解new和delete原理
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
new 和 delete
1、malloc和new的区别 new = 内存开辟+构造函数
2、free和 delete的区别 delete = 内存回收+析构函数
开辟失败malloc返nullptr ,new抛出bad_alloc异常
new->operator new
delete ->operator delete
*/
//先调用operator new开辟内存空间然后调对象的构造函数
//void* operator new(size_t size)
//{
// void* p = malloc(size);
// if (p == nullptr)
// throw bad_alloc();
// cout << "operator new " << p << endl;
// return p;
//}
调用delete p;调用p指向对象的析构函数,在调用operator delete释放内存空间
//
//void operator delete(void* ptr)
//{
// cout << "operator delete " << ptr << endl;
//
// free(ptr);
//}
//先调用operator new开辟内存空间然后调对象的构造函数
/*
new和delete能混用吗? 为什么区分单个元素和数组的内存分配和释放呢?
new delete
new[] delete[]
对于普通的编译器内置类型new/delete[] new[]/delete可以混用
自定义的类型有析构函数,为了正确调用,在开辟对象数组的时候会多开辟四个字节,记录对象的个数
*/
void* operator new[](size_t size)
{
void* p = malloc(size);
if (p == nullptr)
throw bad_alloc();
cout << "operator new addr[]" << p << endl;
return p;
}
//调用delete p;调用p指向对象的析构函数,在调用operator delete释放内存空间
void operator delete[](void* ptr)
{
cout << "operator delete addr[]" << ptr << endl;
free(ptr);
}
class Test
{
public:
Test(int data = 10)
{
cout << "Test()" << endl;
}
~Test()
{
cout << "~Test()" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
//try
//{
// int* p = new int;
// delete p;
// int* q = new int[10];
// delete[]q;
//}
//catch (const bad_alloc& err)
//{
// cerr << err.what() << endl;
//}
//Test* p1 = new Test();
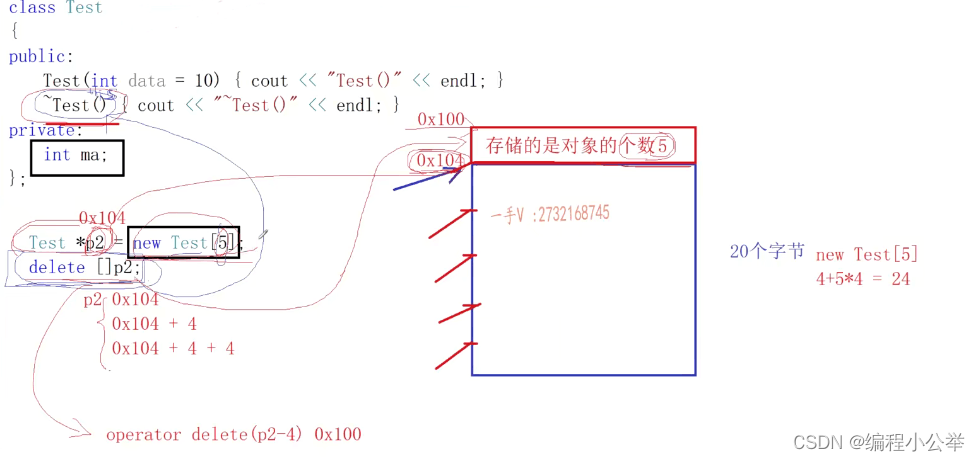
//delete[]p1; //报错
Test* p2 = new Test[5]; //delete p2;错误 Test[0]析构,直接俄free(p2)
cout << "p2: " << p2 << endl;
delete[]p2;
return 0;
}
2、new和delete重载对象池应用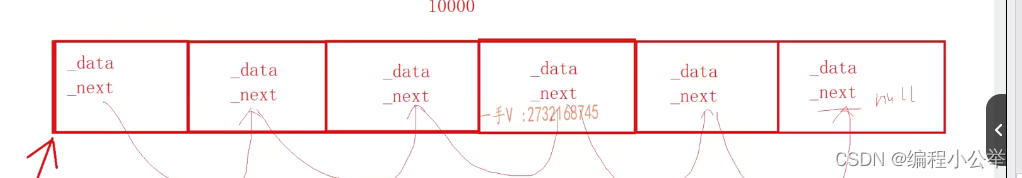
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/*运算符的重载:成员方法、全局方法
* 内存池 进程池 线程池 连接池 对象池
*/
template<typename T>
class Queue
{
public:
Queue()
{
_front = _rear = new QueueItem();
}
~Queue()
{
QueueItem* cur = _front;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
_front = _front->_next;
delete cur;
cur = _front;
}
}
void push(const T& val)
{
QueueItem* item = new QueueItem(val);
_rear->_next = item;
_rear = item;
}
void pop()
{
if (empty())
{
return;
}
QueueItem* first = _front->_next;
_front->_next = first->_next;
if (_front->_next == nullptr)
{
_rear = _front;
}
delete first;
}
T front()const
{
return _front->_next->_data;
}
bool empty() const { return _rear == _front; }
private:
struct QueueItem //产生一个QueueItem的对象池(10000个节点)
{
//给QueueItem提供自定义的内存管理
QueueItem(T data = T()) :_data(data), _next(nullptr) {}
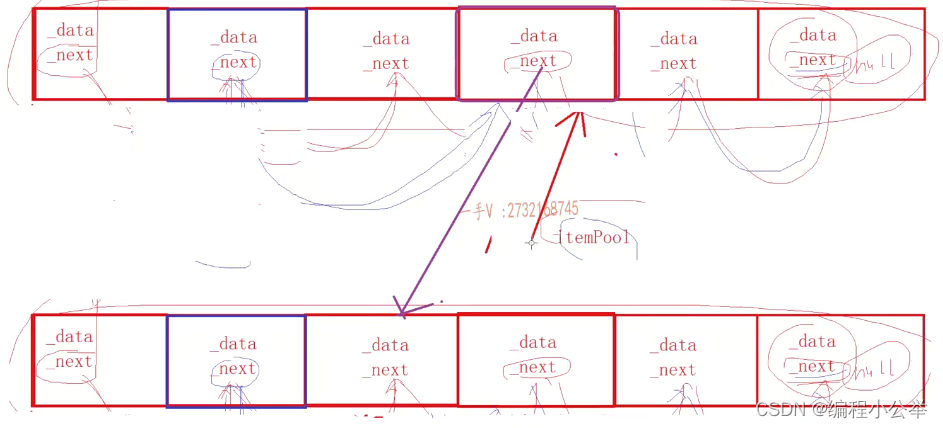
void* operator new (size_t size)
{
if (_itempool == nullptr)
{
_itempool = (QueueItem*)new char[POOL_ITEM_SIZE * sizeof(QueueItem)]; //开辟内存
QueueItem* p = _itempool;
for (; p < _itempool + POOL_ITEM_SIZE - 1; ++p)
{
p->_next = p + 1;
}
p->_next = nullptr;
}
QueueItem* p = _itempool;
_itempool = _itempool->_next;
return p;
}
void operator delete(void* ptr)
{
QueueItem* p = (QueueItem*)ptr;
p->_next = _itempool;
_itempool = p;
}
T _data;
QueueItem* _next;
static const int POOL_ITEM_SIZE = 1000000;
static QueueItem* _itempool; //指向头节点的指针
};
QueueItem* _front; //指向头节点
QueueItem* _rear; //指向队尾
};
template<typename T>
typename Queue<T>::QueueItem* Queue<T>::QueueItem::_itempool = nullptr;
int main()
{
Queue<int> que;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
que.push(i);
que.pop();
}
cout << que.empty() << endl;
return 0;
}
3、运算符重载 复数类
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
* C++运算符重载:使得对象的运算表现得和内置类型一样
*/
//复数类
class CComplex
{
public:
CComplex(int r = 0, int i = 0)
:mreal(r), mimage(i) {}
//指导编译器如何做加法操作
CComplex& operator+(const CComplex& comp)
{
this->mimage += comp.mimage;
this->mreal += comp.mreal;
return *this;
}
CComplex& operator+(const int& b)
{
this->mreal += b;
return *this;
}
CComplex& operator++()
{
mreal += 1;
mimage += 1;
return *this;
}
CComplex& operator++(int)
{
CComplex tmp = *this;
this->mimage++;
this->mreal++;
return tmp;
}
friend CComplex& operator+(const int& a, CComplex& comp);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const CComplex& comp);
void show() { cout << "real: " << mreal << " image: " << mimage << endl; }
private:
int mreal;
int mimage;
};
CComplex& operator+(const int& a, CComplex& comp)
{
comp.mreal += a;
return comp;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const CComplex& comp)
{
os << "real: " << comp.mreal << " image: " << comp.mimage << endl;
return os;
}
int main()
{
CComplex comp1(10, 10);
CComplex comp2(20, 20);
//CComplex comp3 = comp1 + comp2;
CComplex comp3 = comp1.operator+(comp2);
comp3.show();
comp3.operator+(10);
comp3.show();
comp3 = 15 + comp3;
comp3.show();
CComplex comp4 = comp3++; //operator++()前置++ operator++(int)后置++
comp4.show();
++comp4;
comp4.show();
cout << comp4 << endl;
return 0;
}
4、string类的实现
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//自己实现string类
class String
{
public:
String(const char* p = nullptr)
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
_str = new char[strlen(p) + 1];
strcpy_s(_str, strlen(p) + 1, p);
}
else
{
_str = new char[1];
*_str = '\0';
}
}
~String()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
String(const String& str)
{
_str = new char[strlen(str._str) + 1];
strcpy_s(_str, strlen(str._str) + 1, str._str);
}
String& operator=(const String& src)
{
if (this == &src)
{
return *this;
}
delete[]_str;
_str = new char[strlen(src._str) + 1];
strcpy_s(_str, strlen(src._str) + 1, src._str);
return *this;
}
bool operator>(const String& str)const
{
return strcmp(_str, str._str) > 0;
}
bool operator<(const String& str)const
{
return strcmp(_str, str._str) < 0;
}
bool operator==(const String& str)const
{
return strcmp(_str, str._str) == 0;
}
char& operator[](int index)
{
return _str[index];
}
char& operator[](int index)const
{
return _str[index];
}
int length()const { return strlen(_str); }
const char* c_str() const { return _str; }
friend String operator+(const String& lhs, const String& rhs);
public:
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os)
{
os << _str;
return os;
}
private:
char* _str;
};
// 重载加法运算符
String operator+(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
{
String tmp;
delete[] tmp._str;
tmp._str = new char[strlen(lhs._str) + strlen(rhs._str) + 1];
strcpy_s(tmp._str, strlen(lhs._str) + 1, lhs._str);
strcat_s(tmp._str, strlen(lhs._str) + strlen(rhs._str) + 1, rhs._str);
return tmp;
}
int main()
{
String a("aaa");
String b("ccc");
a.operator<<(cout) << endl;
(a + b).operator<<(cout) << endl;
//string str1;
//string str2 = "aaa";
//string str3 = "bbbb";
//string str4 = str2 + str3;
//cout << str4 << endl;
return 0;
}
5、迭代器

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//自己实现string类 以及迭代器
class String
{
public:
String(const char* p = nullptr)
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
_str = new char[strlen(p) + 1];
strcpy_s(_str, strlen(p) + 1, p);
}
else
{
_str = new char[1];
*_str = '\0';
}
}
~String()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
String(const String& str)
{
_str = new char[strlen(str._str) + 1];
strcpy_s(_str, strlen(str._str) + 1, str._str);
}
String& operator=(const String& src)
{
if (this == &src)
{
return *this;
}
delete[]_str;
_str = new char[strlen(src._str) + 1];
strcpy_s(_str, strlen(src._str) + 1, src._str);
return *this;
}
bool operator>(const String& str)const
{
return strcmp(_str, str._str) > 0;
}
bool operator<(const String& str)const
{
return strcmp(_str, str._str) < 0;
}
bool operator==(const String& str)const
{
return strcmp(_str, str._str) == 0;
}
char& operator[](int index)
{
return _str[index];
}
char& operator[](int index)const
{
return _str[index];
}
int length()const { return strlen(_str); }
const char* c_str() const { return _str; }
friend String operator+(const String& lhs, const String& rhs);
//提供迭代器
class iterator
{
public:
iterator(char* p = nullptr) :_p(p) {}
bool operator!=(const iterator& it)
{
return _p != it._p;
}
void operator++()
{
++_p;
}
char& operator*() { return *_p; }
private:
char* _p;
};
iterator begin() { return iterator(_str); }
iterator end() { return iterator(_str + length()); }
public:
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os)
{
os << _str;
return os;
}
private:
char* _str;
};
// 重载加法运算符
String operator+(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
{
String tmp;
delete[] tmp._str;
tmp._str = new char[strlen(lhs._str) + strlen(rhs._str) + 1];
strcpy_s(tmp._str, strlen(lhs._str) + 1, lhs._str);
strcat_s(tmp._str, strlen(lhs._str) + strlen(rhs._str) + 1, rhs._str);
return tmp;
}
int main()
{
String s("hello world!");
for (String::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
//c++11
cout << endl;
for (char ch : s)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
return 0;
}
6、Vector迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
template <class _Ty,
class _Alloc = allocator<_Ty>>
class Vector
容器的空间配置器allocator做四件事情 内存开辟 内存释放 对象构造 对象析构
*/
//定义容器的空间配置器,和c++标准库的allocator实现一样
template<typename T>
class Allocator
{
public:
T* allocate(size_t size) //负责内存开辟
{
return (T*)malloc(sizeof(T) * size);
}
void deallocate(void* p) //负责内存释放
{
free(p);
}
void construct(T* p, const T& val) //负责对象构造
{
new (p) T(val);//定位new
}
void destroy(T* p)//负责对象析构
{
p->~T();//代表了T类型的析构函数
}
};
template<typename T, typename Alloc = Allocator<T>>
class Vector
{
public:
Vector(int size = 10)
{
//需要把内存开辟和对象构造分开处理
//_first = new T[size];
_first = _allocator.allocate(size);
_last = _first;
_end = _first + size;
}
~Vector()
{
//delete[]_first;
//析构有效的元素,然后释放_first指针指向的堆内存
for (T* p = _first; p != _last; p++)
{
_allocator.destroy(p); //把first指针指向的数组的有效元素进行析构操作
}
_allocator.deallocate(_first);//释放堆上的数组内存
_first = _last = _end = nullptr;
}
Vector(const Vector<T>& rhs)
{
int size = rhs._end - rhs._first;
//_first = new T[size]; //空间大小
_first = _allocator.allocate(size);
int len = rhs._last - rhs._first;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
//_first[i] = rhs._first[i];
_allocator.construct(_first + i, rhs._first[i]);
}
_last = _first + len;
_end = _first + size;
}
Vector<T>& operator=(const Vector<T>& rhs) //拷贝构造
{
if (this == &rhs)return *this;
//delete[] _first;
for (T* p = _first; p != _last; p++)
{
_allocator.destroy(p); //把first指针指向的数组的有效元素进行析构操作
}
_allocator.deallocate(_first);//释放堆上的数组内存
int size = rhs._end - rhs._first;
int len = rhs._last - rhs._first;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
//_first[i] = rhs._first[i];
_allocator.construct(_first + i, rhs._first[i]);
}
_last = _first + len;
_end = _first + size;
return *this;
}
void push_back(const T& val)
{
if (full())
{
expand();
}
//*_last = val;
_allocator.construct(_last, val);
_last++;
}
void pop_back()
{
if (empty())
{
return;
}
//--_last;
--_last;
_allocator.destroy(_last);
}
T back()const //返回容器末尾的元素值
{
return *(_last - 1);
}
bool full()const { return _last == _end; }
bool empty()const { return _first == _last; }
int size()const { return _last - _first; }
T& operator[](int index)
{
if (index < 0 || index >= size())
{
throw "outofrangeException";
}
return _first[index];
}
//迭代器一般是现成容器的嵌套类型
class iterator
{
public:
iterator(T* _ptr = nullptr)
:_ptr(_ptr) {}
bool operator!= (const iterator& it)const
{
return _ptr != it._ptr;
}
void operator++()
{
_ptr++;
}
T& operator*() { return *_ptr; } //解引用读取与赋值
const T& operator*() const { return *_ptr; } //解引用读取与赋值
private:
T* _ptr;
};
//需要给容提供begin和end的方法
iterator begin() { return iterator(_first); }
iterator end() { return iterator(_last); }
private:
void expand()
{
int _size = _end - _first;
//T* tmp = new T[_size * 2];
T* tmp = _allocator.allocate(2 * _size);
for (int i = 0; i < _size; i++)
{
//tmp[i] = _first[i];
_allocator.construct(tmp + i, _first[i]);
}
//delete[]_first;
for (T* p = _first; p != _last; p++)
{
_allocator.destroy(p);
}
_allocator.deallocate(_first);
_first = tmp;
_last = _first + _size;
_end = _first + 2 * _size;
}
T* _first; //指向数组的起始的位置
T* _last; //指向数组有效元素的后继位置
T* _end; //指向数组空间的后继位置
Alloc _allocator;//定义i容器中的空间配置项
};
//容器空间分配器
class Test
{
public:
Test() { cout << "test()" << endl; }
~Test() { cout << "~test()" << endl; }
Test(const Test&) { cout << "Test(const Test&)" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
Vector<int>vec;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
vec.push_back(rand() % 100 + 1);
}
Vector<int>::iterator it = vec.begin();
for (; it != vec.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

7、迭代器失效:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
/*
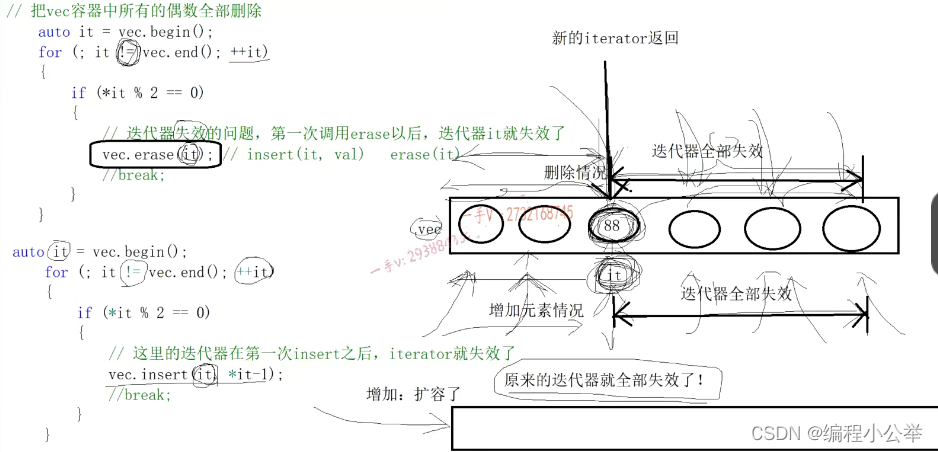
迭代器的失效问题?
1、迭代器为什么会失效?
a、容器调用erase方法后,当前位置到容器末尾元素的所有迭代器全部失效了
b、容器调用insert后,当前位置到容器末尾元素的所有迭代器全部失效了
迭代器依然有效 迭代器全部失效
*/
int main()
{
vector<int> vec;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
vec.push_back(rand() % 100 + 1);
}
for (int v : vec)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
auto it = vec.begin();
for (; it != vec.end(); it++)
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
{
it = vec.insert(it, *it - 1);
++it;
}
}
for (int v : vec)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//给vec容器中所有的偶数前面添加一个小于偶数值1的数字
//auto it = vec.begin();
//for (; it != vec.end(); it++)
//{
// if (*it % 2 == 0)
// {
// //这里的迭代器在第一次insert之后就失效了
// vec.insert(it, *it - 1);
// //it += 2;
// //break;
// }
//}
#if 0
auto it = vec.begin();
for (; it != vec.end(); it++)
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
{
vec.erase(it); //迭代器失效的问题 第一次调用erase以后迭代器就失效了
//break;
}
}
#endif
return 0;
}
下次学习vector迭代器失效的实现过程。
![[Kubernetes] Istio on Kubernetes 实践](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/76459f32b4454c2f912b313cd0bd0cde.png)