set、map用法详解
- 1. 关联式容器
- 2. 键值对
- 2.1 :pair
- 2.2:make_pair
- 3. 树形结构的关联式容器
- 3.1:set
- 构造函数
- find()
- erase()
- insert()
- count()
- lower_bound()
- upper_bound()
- 3.2:multiset
- 3.3:map
- 构造函数
- insert()
- operator[]
- 3.4:multimap
- 4. 在Oj中的使用
- 4.1:前K个高频单词
- 4.2:两个数组的交集I
1. 关联式容器
- 序列式容器:vector、list、deque、forward_list等这些容器统称为序列式容器,底层是线性序列的数据结构,存储的是元素本身。插入方式一般为push。
- 关联式容器:set、map、multiset、multimap等这些容器统称为关联式容器,也是用来存储数据,但存储的是<key,value>结构的键值对,数据检索的效率比序列式容器高。插入方式一般为insert。
2. 键值对
2.1 :pair
概念:用来表示具有一一对应关系的一种结构,这种结构中一般存储两个成员变量key和value,key表示键值,value表示与key对应的信息。eg:英汉词典、单词的个数。
- pair中的first为key,second为value。
2.2:make_pair


- 概念:是一种可用来构造pair类型对象的函数模板。
- 参数x用来初始化pair中第一个元素的值,参数y用来初始化pair中第二个元素的值。make_pair(x, y)返回值为pair<T1, T2>(x, y),为匿名对象。
3. 树形结构的关联式容器
- STL中总共有两种不同结构的管理式容器:树形结构和哈希结构。
- 树形结构的关联式容器主要有四种:set、multiset、map、multimap,共同特征:底层为平衡二叉树(红黑树),容器中的元素是有序序列。
3.1:set

- set是按特定顺序存储唯一元素的容器。使用迭代器遍历set中的元素,进行中序遍历,可以得到一个有序序列。
- set具有排序+去重的功能。set中元素必须不能重复,可以用set进行去重。set中元素类型为const T,所以set中的元素不能被修改,但可以在容器中插入或者删除他们。
- set中元素value就是key,所以set在插入元素时,只需要插入value即可,不需要构造键值对。与map、multimap不同,map、multimap中存储的是<key,value>键值对,set中只存储value,但在底层中实际存放的是由<value, value>构成的键值对。
- 在默认情况下,set中仿函数为less,元素是按照小于来比较,元素呈升序进行排序。set在底层使用平衡二叉搜索树(红黑树)来实现,所以set查找某个元素时,时间复杂度为O(logn)。
- set容器通过key访问单个元素的速度通常比unordered_set容器慢,允许根据顺序直接对子集进行迭代,即:因为set的有序性,当你迭代一个set时,会按照元素被添加到集合中的顺序看到它们。
构造函数
💡set s1;
- 功能:无参构造。构造空的set。
💡set s2( InputIterator first, InputIterator last ) ;
- 功能:迭代器区间构造。构造与[first, last)范围一样多元素的对象。
💡set s3(const set& s2) ;
- 功能:拷贝构造函数。
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
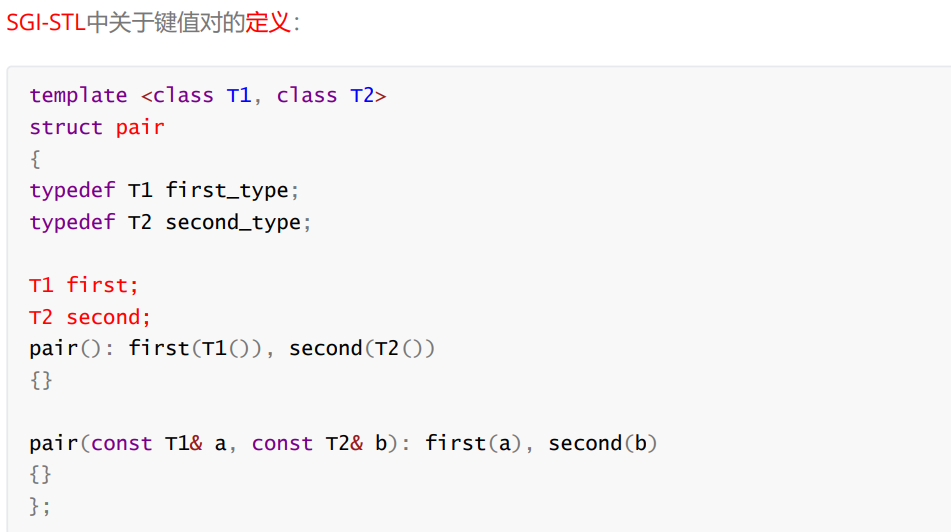
set<int> s1; //无参构造
//注意set:排序 + 去重
int a[] = { 6, 3, 4, 2, 1, 6, 4, 5, 2};
set<int> s2(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int)); //迭代器区间构造
set<int> s3(s2); //拷贝构造
auto it = s2.begin();
while (it != s2.end()) //用迭代器进行遍历,中序遍历,升序序列
{
cout << *it << ' '; //迭代器指向空间的值不能被修改,因为key为const T
it++;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto& e : s3) //支持迭代器就支持范围for
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
- 迭代器指向空间的值不能被修改,因为set中key类型为const T。
find()
💡iterator find(const T& val)const ;
- 功能:在set中查找是否存在值为val的元素,若查找到了,则返回该元素的迭代器,若查找不到了,则返回set: :end( )迭代器。
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
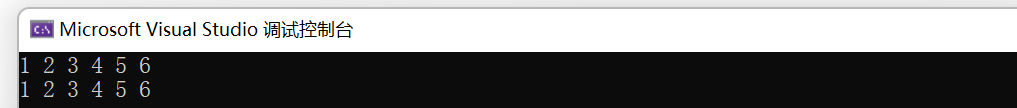
int a[] = { 6, 3, 4, 2, 1, 6, 4, 5, 2};
set<int, greater<int>> s1(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int)); //仿函数为greater,按大于进行比较
auto it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end()) //用迭代器进行遍历,中序遍历,仿函数为greater, 降序序列
{
cout << *it1 << ' '; //迭代器指向的空间值不能被修改,因为key为const T
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
set<int>::iterator it2 = s1.find(10); //查找
if (it2 != s1.end())
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
return 0;
}

erase()
💡void erase(iterator pos) ;
- 功能:删除指定位置pos(迭代器)处的值。
- 注意:删除某个值时,这个值必须存在,找到该值的有效位置,才能进行删除。若这个值不在,删除的是无效位置,则编译器会崩溃。
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = { 6, 3, 4, 2, 1, 6, 4, 5, 2};
set<int, greater<int>> s1(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
auto it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
set<int>::iterator pos = s1.find(10);
//s1.erase(pos); 错误,删除的值不存在,为无效位置,编译器会崩溃
return 0;
}
💡size_t erase(const T& val) ;
- 功能:删除值为val的元素,并返回删除元素的个数。
- 注意:若val在,就进行删除,不在编译器不做任何处理。
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = { 6, 3, 4, 2, 1, 6, 4, 5, 2};
set<int> s1(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
auto it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
s1.erase(10); //10不在,编译器不做任何处理
s1.erase(6);
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

💡void erase ( iterator first, iterator last ) ;
- 功能:删除[first , last)区间内的元素,剩余的元素仍有序。
insert()
💡pair<iterator,bool> insert(const T& val) ;

- insert返回值为pair<iterator, bool>,若val在set中已经存在,因为set中不能出现重复元素,所以pair::first指向在set中与val值相等的迭代器,pair::second为false。若val在set中不存在,pair::first指向在set中新插入元素的迭代器,pair::second为true。insert相当于查找。set容器元素仍为有序序列。
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = { 6, 3, 4, 2, 1, 6, 4, 5, 2};
set<int> s1(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
auto it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> ret1 = s1.insert(10);
cout << ret1.second << endl;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> ret2 = s1.insert(6);
cout << ret2.second << endl;
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

💡iterator insert(iterator pos , const T& val) ;
- 功能:插入val。
- insert返回值为iterator,因为set不允许出现重复元素,若val值不存在,则指向在set中新插入元素的迭代器,否则,返回在set中值与val相等元素的迭代器。
- 此处不一定是在pos位置前插入val,因为set容器中的元素为有序序列且唯一,为了保证有序性和唯一性。
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = { 6, 3, 4, 2, 1, 6, 4, 5, 2};
set<int> s1(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
auto it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
auto pos = s1.find(3);
auto it2 = s1.insert(pos, 20);
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

💡void insert(iterator first , iterator last) ;
- 功能:将区间[first, last)中的元素插入到set中。元素仍为唯一且有序。
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a1[] = { 6, 3, 4, 2, 1, 6, 4, 5, 2};
set<int> s1(a1, a1 + sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
auto it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
int a2[] = { 10, 11, 10, 8, 6 };
s1.insert(a2, a2 + sizeof(a2) / sizeof(int));
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

count()
💡size_t count( const T& val)const ;
- 功能:返回值为val的元素个数。
- 因为set中元素唯一,所以count的返回值不是0就是1,可以用来检查key是否在set中。
lower_bound()
💡iterator lower_bound(const T& val)cosnt;
- 功能:返回>=val元素的迭代器。
upper_bound()
💡iterator upper_bound(const T& val)cosnt;
- 功能:返回>val元素的迭代器。
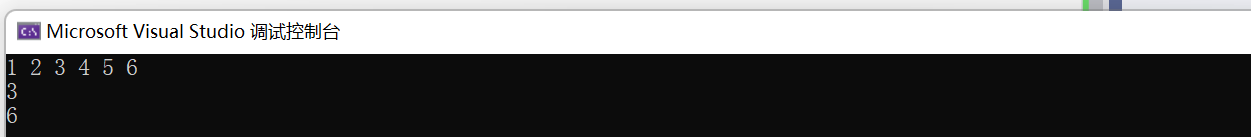
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a1[] = { 6, 3, 4, 2, 1, 6, 4, 5, 2};
set<int> s1(a1, a1 + sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
auto it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
auto it2 = s1.lower_bound(3); // >=3
cout << *it2 << endl;
auto it3 = s1.upper_bound(5); // >5
cout << *it3 << endl;
return 0;
}
3.2:multiset

- multiset只具有 排序 功能。使用时与set包含的头文件相同#include。
- multiset容器与set容器所提供的成员函数接口以及规定基本相同,两者唯一的区别是:set中key是唯一的,multiset中的key可以重复。
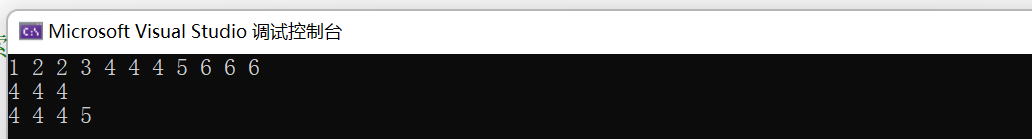
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a1[] = { 6, 3, 4, 2, 1, 6, 6, 4, 4, 5, 2};
multiset<int> s1(a1, a1 + sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int)); //只具有 排序 功能
auto it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
auto start1 = s1.find(4); //find返回二叉搜索树中序的第一个值为4元素的迭代器
while (start1 != s1.end() && *start1 == 4)
{
cout << *start1 << ' ';
start1++;
}
cout << endl;
auto start2 = s1.lower_bound(4); //lower_bound返回二叉搜索树中序>=4第一个元素的迭代器
auto end2 = s1.upper_bound(5); //upper_bound返回二叉搜索树中序>5第一个元素的迭代器
while (start2 != end2)
{
cout << *start2 << ' ';
start2++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
3.3:map

- map是按特定顺序存储唯一元素的容器,元素是pair<const key, value>键值对,map中的key是唯一的,且不能被修改。使用迭代器遍历map中的元素,进行中序遍历,可以得到一个按照key排序的有序序列。
- 在默认情况下,map中仿函数为less,元素是按照键值key进行小于方式的比较,元素中key呈升序进行排序。map在底层使用平衡搜索树(红黑树)来实现,所以map按照key值查找某个元素时,时间复杂度为O(logn)。
- 模板参数中的Compare,缺省情况下按照小于进行比较,一般情况下,T为内置类型,该参数不需要传递,若T为自定义类型,需要用户自己手动传递比较规则,一般情况下是按照仿函数或者函数指针来传递。
- map支持下标访问,在[ ]中放key,就可以找到与key相对应得value。operator[ ]操作符,具有插入、查找、修改、查找+修改功能。
- map中通过键值key访问单个元素的速度比unordered_map容器慢,但map允许根据顺序直接对元素直接进行迭代,即:对map中的元素进行迭代时,可以得到一个有序序列。
- map和set,一个是KV模型,一个是K模型,KV模型相比于K模型,只是在插入时多插入了value值,删除、查找都是对key进行操作,操作中的比较也是按key的值进行比较的。K模型类似于单身,KV模型类似于结婚。
构造函数
💡map<T1, T2> s1;
- 功能:无参构造。构造空的map。
💡map<T1, T2> s2( InputIterator first, InputIterator last ) ;
- 功能:迭代器区间构造。构造与[first, last)范围一样多元素的对象。
💡map<T1, T2> s3(const map<T1, T2>& s2) ;
- 功能:拷贝构造函数。
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, string> m1; //无参构造
pair<string, string> a[] = { {"sort", "排序"},{"left", "左"}, {"remove", "去除"}, {"right", "右"} };
map<string, string> m2(a, a + sizeof(a)/sizeof(pair<string, string>)); //迭代器区间构造
map<string, string> m3(m2); //拷贝构造
auto it1 = m2.begin();
while (it1 != m2.end()) //用迭代器进行遍历,中序遍历,key呈升序序列
{
cout << (*it1).first << ":" << (*it1).second << endl; //pair中的key不能被修改
cout << it1->first << ":" << it1->second << endl;
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto& e : m3) //支持迭代器就支持范围for
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
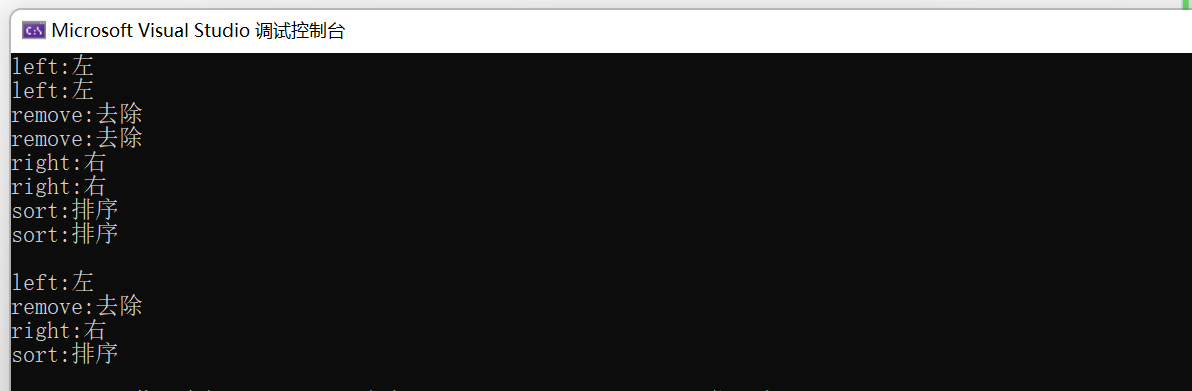
insert()
💡pair<iterator,bool> insert(const value_type& val) ;
- 功能:在map中插入一个键值对。

- insert返回值为pair<iterator, bool>,若key在map中存在,因为map中不能出现重复的键值key,所以pair::first指向在map中与key值相等的迭代器,pair::second为false。若key在map中不存在,pair::first指向在map中新插入元素的迭代器,pair::second为true。insert相当于查找。map容器元素中键值key仍有序且唯一。
- value_type为pair<const key, value>。需要先构造出pair类型对象,有以下三种方式,有名对象,匿名对象,多参数构造函数隐式类型转换(c++11支持)、make_pair(c++98支持)。
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, string> m;
//多参数构造函数支持隐式类型转换,中间会产生临时对象,临时对象具有常属性
pair<string, string> p = { "appeal", "吸引" };
m.insert(p); //有名对象
m.insert(pair<string, string>("give", "给予")); //匿名对象
//c++11
m.insert({ "big", "大的" });
//c++98
m.insert(make_pair("thing", "事情")); //make_pair构造pair类型对象
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}

operator[]
💡T2& operatot[ ](const T1& key) ;
- 功能:访问与key相对应的value值。即可读又可写。
- 原理:operator[ ]底层是通过调用insert( )将键值队插入到map中。如果key存在,插入失败,insert返回与map中key值相同元素的迭代器。如果key不存在,插入成功,insert返回在map中新插入元素的迭代器。operator最后返回与key值相对应的value值的引用。
- operator[ ] 具有插入、查找、插入+修改、查找+修改功能。

#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, string> m;
m.insert(make_pair("thing", "事情"));
m.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
m["right"] = "右"; //插入+修改
m["sort"] = "xxx"; //查找+修改
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
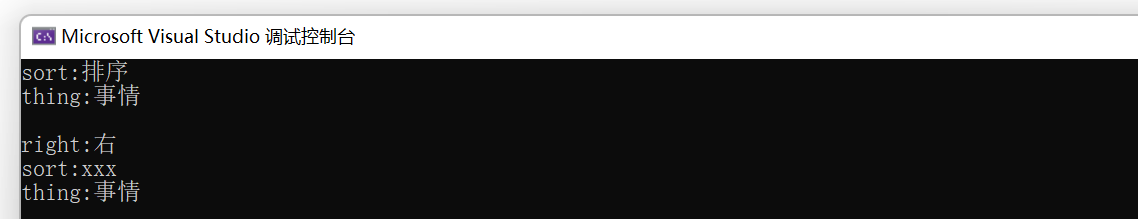
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//统计水果的个数
map<string, int> m1;
string a[] = { "苹果", "香蕉", "梨子", "苹果", "苹果", "香蕉", "草莓" };
for (auto& e : a)
{
auto it = m1.find(e); //方法1
if (it != m1.end())
it->second++;
else
m1.insert({ e, 1 });
}
for (auto& e : m1)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
map<string, int> m2;
for (auto& e : a)
{
m2[e]++; //方法2
}
for (auto& e : m2)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}

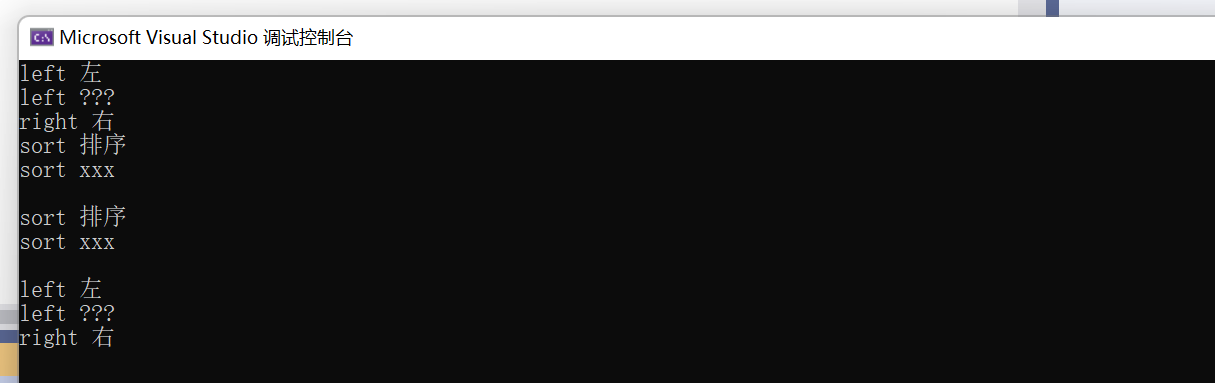
3.4:multimap
- multimap容器与map容器所提供的成员函数接口以及规定基本相同,两者的区别是:map中key是唯一的,multimap中的key可以重复。map支持下标访问,multimap不支持下标访问,因为[ ]中存储的是key,而multimap中同一key,可能有多个value。
- 在使用时与map包含的头文件相同#include
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
pair<string, string> a1[] = { {"sort", "排序"}, {"left", "左"}, {"right", "右"},{"sort", "xxx"} ,{"left", "???"} };
multimap<string, string> m1(a1, a1 + sizeof(a1) / sizeof(pair<string, string>));
auto it1 = m1.begin();
while (it1 != m1.end())
{
cout << it1->first << ' ' << it1->second << endl;
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
auto start1 = m1.find("sort"); //find返回二叉搜索树中序的第一个key为sort元素的迭代器
while (start1 != m1.end())
{
cout << start1->first << ' ' << start1->second << endl;
start1++;
}
cout << endl;
auto start2 = m1.lower_bound("left"); //lower_bound返回二叉搜索树中序>key为left第一个元素的迭代器
auto end2 = m1.upper_bound("right"); //upper_bound返回二叉搜索树中序>key为right第一个元素的迭代器
while (start2 != end2)
{
cout << start2->first << ' ' << start2->second << endl;
start2++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
4. 在Oj中的使用
4.1:前K个高频单词
https://leetcode.cn/problems/top-k-frequent-words/description/
class Solution {
public:
template<class T>
class KvCompare{
public:
bool operator()(const T& p1, const T& p2)
{
return p1.second > p2.second || (p1.second == p2.second && p1.first < p2.first);
}
};
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
map<string, int> m;
for(auto& e : words)
m[e]++; //使用map来统计单词的个数
priority_queue<pair<string, int>, KvCompare<pair<string, int>>> pq(m.begin(), m.end());
vector<string> ret;
while(k--)
{
ret.push_back(pq.top());
pq.pop();
}
return ret;
}
};
4.2:两个数组的交集I
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/description/
/*方法1:nums1、nums2都用set进行排序+去重,在遍历s2, 判断是否s1.count(e)==1;
方法2:sort+unique+erase,nums2[5]={1,1,2,2,3}->nums2{1,2,3,1,2},unique返回值为nums2+3;
方法3:set+数据同步、备份算法,前提都是有序+去重,同时从头开始往后走,值小的++,值相同,同时++,
直到有一个走到了尾就停止*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
set<int> s1(nums1.begin(), nums1.end());
set<int> s2(nums2.begin(), nums2.end());
vector<int> ret;
auto it1 = s1.begin(); //数据同步、备份算法
auto it2 = s2.begin();
while(it1 != s1.end() && it2 != s2.end())
{
if(*it1 < *it2) //小的往后走
it1++;
else if(*it1 > *it2)
it2++;
else //相等,同时往后走
{
ret.push_back(*it1);
it1++;
it2++;
}
}
return ret;
}
};











![[算法][数组][leetcode]2391. 收集垃圾的最少总时间](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9846c5262cd14897bd4965c6efb73d64.gif#pic_center)