目录
1、初识Spring
1.1 Spring简介
1.2 搭建Spring框架步骤
1.3 Spring特性
1.5 bean标签详解
2、SpringIOC底层实现
2.1 BeanFactory与ApplicationContexet
2.2 图解IOC类的结构
3、Spring依赖注入数值问题【重点】
3.1 字面量数值
3.2 CDATA区
3.3 外部已声明bean及级联属性赋值
3.4 内部bean
3.5 集合
4、Spring依赖注入方式【基于XML】
4.1 set注入
4.2 构造器注入
4.3 p名称空间注入
5、Spring管理第三方bean
5.1 Spring管理druid步骤
6、Spring中FactoryBean
6.1 Spring中两种bean
6.2 FactoryBean使用步骤
1、初识Spring
1.1 Spring简介
Spring是一个为简化企业级开发而生的开源框架。
Spring是一个IOC(DI)和AOP容器框架。
IOC全称:Inversion of Control【控制反转】
将对象【万物皆对象】控制权交个Spring
DI全称:(Dependency Injection):依赖注入
AOP全称:Aspect-Oriented Programming,面向切面编程
官网:https://spring.io/
1.2 搭建Spring框架步骤
导入jar包
<!--导入spring-context-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--导入junit4.12-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>编写核心配置文件
配置文件名称:applicationContext.xml【beans.xml或spring.xml】
配置文件路径:src/main/resources
示例代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 将对象装配到IOC容器中-->
<bean id="stuZhenzhong" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="101"></property>
<property name="stuName" value="zhenzhong"></property>
</bean>
</beans>使用核心类库
@Test
public void testSpring(){
//使用Spring之前
// Student student = new Student();
//使用Spring之后
//创建容器对象
ApplicationContext iocObj =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过容器对象,获取需要对象
Student stuZhenzhong = (Student)iocObj.getBean("stuZhenzhong");
System.out.println("stuZhenzhong = " + stuZhenzhong);
}1.3 Spring特性
非侵入式:基于Spring开发的应用中的对象可以不依赖于Spring的API。
容器:Spring是一个容器,因为它包含并且管理应用对象的生命周期。
组件化:Spring实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复杂的应用。在 Spring 中可以使用XML和Java注解组合这些对象。
一站式:在IOC和AOP的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的第三方类库(实际上Spring 自身也提供了表述层的SpringMVC和持久层的JDBCTemplate)。
1.4 Spring中getBean()三种方式
getBean(String beanId):通过beanId获取对象
不足:需要强制类型转换,不灵活
getBean(Class clazz):通过Class方式获取对象
不足:容器中有多个相同类型bean的时候,会报如下错误:
expected single matching bean but found 2: stuZhenzhong,stuZhouxu
getBean(String beanId,Clazz clazz):通过beanId和Class获取对象
推荐使用
注意:框架默认都是通过无参构造器,帮助我们创建对象。
所以:如提供对象的构造器时,一定添加无参构造器
1.5 bean标签详解
属性
id:bean的唯一标识
class:定义bean的类型【class全类名】
子标签
property:为对象中属性赋值【set注入】
name属性:设置属性名称
value属性:设置属性数值
2、SpringIOC底层实现
IOC:将对象的控制器反转给Spring
2.1 BeanFactory与ApplicationContexet
BeanFactory:IOC容器的基本实现,是Spring内部的使用接口,是面向Spring本身的,不是提供给开发人员使用的。
ApplicationContext:BeanFactory的子接口,提供了更多高级特性。面向Spring的使用者,几乎所有场合都使用ApplicationContext而不是底层的BeanFactory。
2.2 图解IOC类的结构
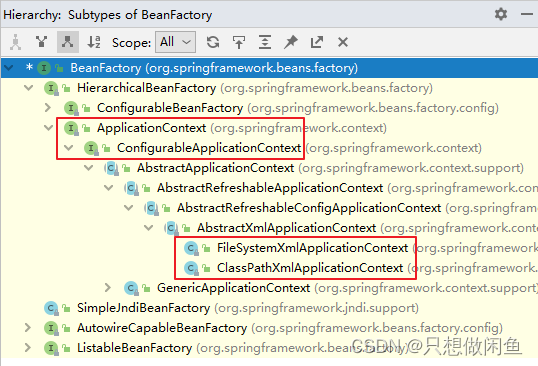
BeanFactory:Spring底层IOC实现【面向Spring框架】
ApplicationContext:面向程序员
ConfigurableApplicationContext:提供关闭或刷新容器对象方法
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:基于类路径检索xml文件
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:基于注解创建容器对象
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:基于文件系统检索xml文件
3、Spring依赖注入数值问题【重点】
3.1 字面量数值
数据类型:基本数据类型及包装类、String
语法:value属性或value标签
3.2 CDATA区
语法:\<![CDATA[]]>
作用:在xml中定义特殊字符时,使用CDATA区
3.3 外部已声明bean及级联属性赋值
语法:ref
注意:级联属性更改数值会影响外部声明bean【ref赋值的是引用】
示例代码
<bean id="dept1" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept">
<property name="deptId" value="1"></property>
<property name="deptName" value="研发部门"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="empChai" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Employee">
<property name="id" value="101"></property>
<property name="lastName" value="chai"></property>
<property name="email" value="chai@163.com"></property>
<property name="salary" value="50.5"></property>
<property name="dept" ref="dept1"></property>
<property name="dept.deptName" value="财务部门"></property>
</bean>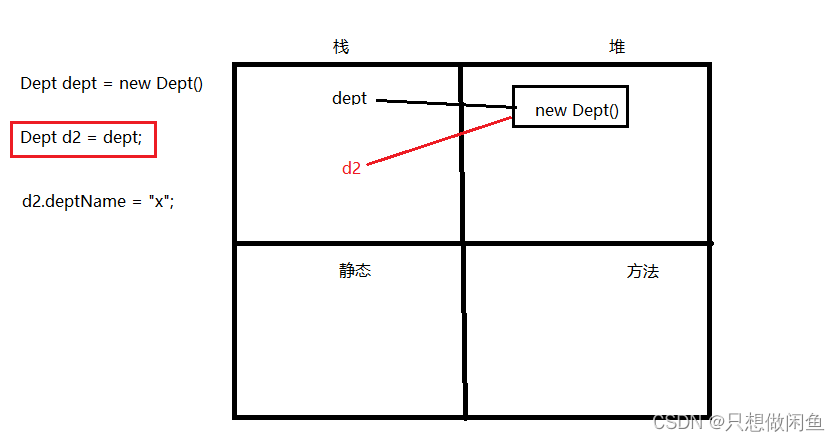
3.4 内部bean
概述
内部类:在一个类中完整定义另一个类,当前类称之为内部类
内部bean:在一个bean中完整定义另一个bean,当前bean称之为内部bean
注意:内部bean不会直接装配到IOC容器中
示例代码
<!-- 测试内部bean-->
<bean id="empXin" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Employee">
<property name="id" value="102"></property>
<property name="lastName" value="xx"></property>
<property name="email" value="xx@163.com"></property>
<property name="salary" value="51.5"></property>
<property name="dept">
<bean class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept">
<property name="deptId" value="2"></property>
<property name="deptName" value="人事部门"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
3.5 集合
List
<!-- 测试集合-->
<bean id="dept3" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept">
<property name="deptId" value="3"></property>
<property name="deptName" value="程序员鼓励师"></property>
<property name="empList">
<list>
<ref bean="empChai"></ref>
<ref bean="empXin"></ref>
<!-- <bean></bean>-->
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 测试提取List-->
<util:list id="empList">
<ref bean="empChai"></ref>
<ref bean="empXin"></ref>
</util:list>
<bean id="dept4" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept">
<property name="deptId" value="4"></property>
<property name="deptName" value="运营部门"></property>
<property name="empList" ref="empList"></property>
</bean>Map
<!-- 测试Map-->
<bean id="dept5" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept">
<property name="deptId" value="5"></property>
<property name="deptName" value="采购部门"></property>
<property name="empMap">
<map>
<entry key="101" value-ref="empChai"></entry>
<entry>
<key><value>103</value></key>
<ref bean="empChai"></ref>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>102</value></key>
<ref bean="empXin"></ref>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
<util:map id="empMap">
<entry key="101" value-ref="empChai"></entry>
<entry>
<key><value>103</value></key>
<ref bean="empChai"></ref>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>102</value></key>
<ref bean="empXin"></ref>
</entry>
</util:map>
<bean id="dept6" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept">
<property name="deptId" value="106"></property>
<property name="deptName" value="后勤部门"></property>
<property name="empMap" ref="empMap"></property>
</bean>
4、Spring依赖注入方式【基于XML】
为属性赋值方式:
-
通过xxxset()方法:这是一种常见的方式,在类中提供了一系列的set方法,用于设置类的属性值。例如,如果有一个属性名为
name,那么可能会有一个名为setName()的方法用于设置name属性的值。 -
通过构造器:另一种常见的方式是通过类的构造器来传递属性值。在构造对象时,通过构造器的参数列表将属性值传递给对象。这种方式可以在对象被创建时一次性地设置属性值,使得对象的状态在创建后就被确定下来。
-
反射:反射是一种高级的Java特性,允许在运行时检查类、获取类的信息以及动态调用类的方法和操作类的属性。通过反射,可以通过类的
Field对象来设置对象的属性值,无论这些属性的可见性如何。
4.1 set注入
通过在XML配置文件中使用<property>标签来进行属性注入。在这种方式中,你可以指定属性的名称,并通过value属性或ref属性为属性赋值。如果是基本数据类型或字符串等简单类型,可以使用value属性直接赋值;如果是引用其他bean,可以使用ref属性指定引用的bean的id。
语法:\<property>
4.2 构造器注入
通过在XML配置文件中使用<constructor-arg>标签来进行构造器注入。与set注入类似,你可以在构造对象时指定构造器的参数,并通过value属性或ref属性为构造器参数赋值。这种方式适用于在创建对象时将属性值通过构造器传递给对象。
语法:\<constructor-arg>
4.3 p名称空间注入
导入名称空间:xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
语法:<bean p:xxx>
示例代码
<bean id="stuZhouxu" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="102"></property>
<property name="stuName">
<value><![CDATA[<<zhouxu>>]]></value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="stuZhiFeng" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student">
<constructor-arg name="stuId" value="103"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="stuName" value="zhifeng"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="stuXiaoxi"
class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student"
p:stuId="104"
p:stuName="xiaoxi"></bean>5、Spring管理第三方bean
5.1 Spring管理druid步骤
导入jar包
<!--导入druid的jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--导入mysql的jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.37</version>
<!-- <version>8.0.26</version>-->
</dependency>编写db.properties配置文件
properties
#key=value
db.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db220106
db.username=root
db.password=root编写applicationContext.xml相关代码
<!-- 加载外部属性文件db.properties-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!-- 装配数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${db.driverClassName}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${db.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${db.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${db.password}"></property>
</bean>测试
@Test
public void testDruidDataSource() throws Exception{
//获取容器对象
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_druid.xml");
DruidDataSource dataSource = ioc.getBean("dataSource", DruidDataSource.class);
System.out.println("dataSource = " + dataSource);
DruidPooledConnection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println("connection = " + connection);
}
6、Spring中FactoryBean
6.1 Spring中两种bean
一种是普通bean:
普通bean是指在Spring容器中以普通的方式配置和管理的bean。这些bean通常是通过在XML配置文件或Java配置类中定义并注册的,它们的创建和初始化由Spring容器负责。
另一种是工厂bean【FactoryBean】:
工厂bean是一种特殊的bean,它实现了org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean接口。与普通bean不同,工厂bean负责创建其他bean实例,允许程序员在bean的创建过程中进行参数化或自定义。使用工厂bean可以更灵活地控制bean的创建逻辑和初始化过程。
作用:如需我们程序员参数到bean的创建时,使用FactoryBean
6.2 FactoryBean使用步骤
实现FactoryBean接口:创建一个类并实现FactoryBean接口,该接口要求实现getObject()方法来返回所创建的bean实例,并可选择实现getObjectType()方法来指定工厂bean所创建的对象类型。
重写方法【三个】:在实现FactoryBean接口的类中,需要重写getObject()方法来指定如何创建所需的bean实例。可选地,也可以重写getObjectType()方法来提供所创建的bean的类型。
装配工厂bean:将实现了FactoryBean接口的类配置到Spring容器中,可以通过XML配置文件或Java配置类进行装配。
测试
示例代码:
示例代码:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
// 实现FactoryBean接口
public class MyBeanFactory implements FactoryBean<MyBean> {
// 重写getObject()方法,指定创建bean的逻辑
@Override
public MyBean getObject() throws Exception {
// 这里可以根据需要进行一些自定义的逻辑,然后创建并返回所需的bean实例
return new MyBean();
}
// 可选地重写getObjectType()方法,指定所创建的bean的类型
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return MyBean.class;
}
}
在Spring配置文件中装配工厂bean:
<bean id="myBeanFactory" class="com.example.MyBeanFactory"/>
在测试代码中获取并使用工厂bean:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 加载Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 获取工厂bean实例
MyBean myBean = context.getBean("myBeanFactory", MyBean.class);
// 使用工厂创建的bean实例
myBean.doSomething();
}
}



![[开发|安卓] Android Studio 开发环境配置](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8567451675dd400bba1f881c182619d2.png)