一,前言
上篇,主要介绍了数组依赖收集的实现
本篇,Vue 生命周期的实现
二,Vue.mixin 介绍
1,mixin 简介
Vue2 中可以通过 Vue.mixin 为 vue 进行功能扩展
开发中,经常使用 mixin 来为所有组件增加一些生命周期
2,mixin 使用
vue 初始化时,使用 beforeCreate 生命周期钩子
再通过 Vue.mixin 扩展对 beforeCreate 进行功能扩展
这样在实际执行时,多个 beforeCreate 会进行合并
3,生命周期的用法
// 使用 Vue.mixin 做全局扩展
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate(){
console.log("全局:mixin-beforeCreate")
}
})
let vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
// 用法一:
// beforeCreate(){},
// 用法二:数组写法:逻辑较多需进行分类时吗,可拆分为多个函数
beforeCreate:[
function(){
console.log("局部:new Vue-beforeCreate 1") // A 模块初始化
},
function(){
console.log("局部:new Vue-beforeCreate 2") // B 模块初始化
}
]
});
三,Vue 的 Global API
1,全局 api 和 实例 api 的使用
// 全局 api:对所有组件生效
Vue.component()
// 实例 api:仅对当前组件生效
new Vue({
component:{}
})
2,全局 api 的实现原理
new Vue 组件初始化时:
- 通过 options 使用实例 api 声明,仅对当前组件生效;
- 通过 Vue.component 全局声明的属性将被合并到每一个组件中,全局生效;
四,Vue.mixin 实现
1,添加 mixin 方法
创建 Vue 全局 api 模块:src/global-api;
新建 src/global-api/index.js,为 Vue 添加 mixi 静态方法:
//src/global-api/index.js
export function initGlobalAPI(Vue) {
Vue.mixin = function (options) {
}
}
在 src/index.js 中调用,进行 vue global api 的初始化:
// src/index.js
import { initGlobalAPI } from "./global-api";
import { initMixin } from "./init";
import { lifeCycleMixin } from "./lifecycle";
import { renderMixin } from "./render";
function Vue(options){
this._init(options);
}
initMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
lifeCycleMixin(Vue)
initGlobalAPI(Vue) // 初始化 global Api
export default Vue;
2,实现 Global API
在全局属性Vue.options中存放属性,供全局使用:
// src/global-api/index.js
export function initGlobalAPI(Vue) {
// 全局属性:Vue.options
// 功能:存放 mixin, component, filte, directive 属性
Vue.options = {};
Vue.mixin = function (options) {
}
Vue.component = function (options) {}
Vue.filte = function (options) {}
Vue.directive = function (options) {}
}
3,多个Vue.mixin的合并策略
全局 mixin 也可以被多次调用:
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate(){
console.log("全局:mixin-beforeCreate 1")
}
})
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate(){
console.log("全局:mixin-beforeCreate 2")
}
})
此时,需对全局声明进行合并:
Vue.mixin = function (options) {
// 需将多次传入的 options 与全局属性 Vue.options 进行合并
}
合并策略:
第一次合并:
parentVal:{}
childVal:{ beforeCreate:fn1 }
合并结果:{ beforeCreate:[fn1] }
第二次合并:
parentVal:{ beforeCreate:[fn1] }
childVal:{ beforeCreate:fn2 }
合并结果:{ beforeCreate:[fn1,fn2] }
所以,每次合并需要循环父亲(老值)和儿子(新值)依次进行合并
当新值存在,老值不存在时:添加到老值中
在 src/utils.js 添加工具方法 mergeOptions:
// src/utils.js
/**
* 对象合并:将childVal合并到parentVal中
* @param {*} parentVal 父值-老值
* @param {*} childVal 子值-新值
*/
export function mergeOptions(parentVal, childVal) {
let options = {};
for(let key in parentVal){
mergeFiled(key);
}
for(let key in childVal){
// 当新值存在,老值不存在时:添加到老值中
if(!parentVal.hasOwnProperty(key)){
mergeFiled(key);
}
}
function mergeFiled(key) {
// 默认合并方法:优先使用新值覆盖老值
options[key] = childVal[key] || parentVal[key]
}
return options;
}
4,生命周期的合并策略
策略模式:将不同生命周期的合并使用不同的策略做区分
// src/utils.js
let strats = {}; // 存放所有策略
let lifeCycle = [
'beforeCreate',
'created',
'beforeMount',
'mounted'
];
lifeCycle.forEach(hook => {
// 创建生命周期的合并策略
strats[hook] = function (parentVal, childVal) {
if(childVal){ // 儿子有值,需要进行合并
if(parentVal){
// 父亲儿子都有值:父亲一定是数组,将儿子合入父亲
return parentVal.concat(childVal);
}else{
// 儿子有值,父亲没有值:儿子放入新数组中
// 注意:如果传入的生命周期函数是数组,已经是数组无需再包成数组
if(Array.isArray(childVal)){
return childVal;
}else{
return [childVal];
}
}
}else{ // 儿子没有值,无需合并,直接返回父亲即可
return parentVal;
}
}
})
// src/global-api/index.js
export function initGlobalAPI(Vue) {
// 全局属性:Vue.options
// 功能:存放 mixin, component, filte, directive 属性
Vue.options = {};
Vue.mixin = function (options) {
this.options = mergeOptions(this.options, options);
console.log("打印mixin合并后的options", this.options);
return this; // 返回this,提供链式调用
}
Vue.component = function (options) {}
Vue.filte = function (options) {}
Vue.directive = function (options) {}
}
5,测试
测试 Vue.mixin 中的生命周期合并结果:

五,全局与实例的生命周期合并
全局生命周期合并完成后,还要在和 new Vuechu 初始化中的局部声明再进行合并
new Vue 初始化时,会进入 _init 原型方法:
// src/init.js#initMixin
Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {
const vm = this;
// 此时需使用 options 与 mixin 合并后的全局 options 再进行一次合并
vm.$options = mergeOptions(vm.constructor.options, options);
...
}
打印 vm.$options 查看合并后的结果:
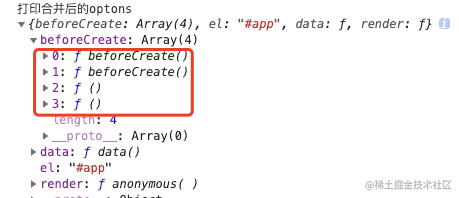
问题:vm.constructor.options 和 Vue.options的区别?
此处的 vm 有可能是 vm 的子类:
Vue 的子类对 Vue 可能做了增强;子组件可能会继承 Vue;
Vue.options 就是指 Vue;而 vm.constructor 指子类(子组件)的构造函数;
六,生命周期的实现
1,创建生命周期执行函数
在src/lifecycle.js生命周期模块中,创建执行生命周期钩子函数 callHook:
// src/lifecycle.js
/**
* 执行生命周期钩子
* 从$options取对应的生命周期函数数组并执行
* @param {*} vm vue实例
* @param {*} hook 生命周期
*/
export function callHook(vm, hook){
// 获取生命周期对应函数数组
let handlers = vm.$options[hook];
if(handlers){
handlers.forEach(fn => {
fn.call(vm); // 生命周期中的 this 指向 vm 实例
})
}
}
2,添加生命周期钩子
- 当视图渲染前,调用钩子: beforeCreate
- 视图更新后,调用钩子: created
- 当视图挂载完成,调用钩子: mounted
// src/lifecycle.js
export function mountComponent(vm) {
// vm._render():调用 render 方法
// vm._update:将虚拟节点更新到页面上
// 初始化流程
// vm._update(vm._render());
// 改造
let updateComponent = ()=>{
vm._update(vm._render());
}
// 当视图渲染前,调用钩子: beforeCreate
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate');
// 渲染 watcher :每个组件都有一个 watcher
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, ()=>{
console.log('Watcher-update')
// 视图更新后,调用钩子: created
callHook(vm, 'created');
},true)
// 当视图挂载完成,调用钩子: mounted
callHook(vm, 'mounted');
}
- watcher做视图更新前,调用钩子: beforeUpdate
- 视图更新完成后,调用钩子: updated
// src/scheduler.js
/**
* 刷新队列:执行所有 watcher.run 并将队列清空;
*/
function flushschedulerQueue() {
// 更新前,执行生命周期:beforeUpdate
queue.forEach(watcher => watcher.run()) // 依次触发视图更新
queue = []; // reset
has = {}; // reset
pending = false; // reset
// 更新完成,执行生命周期:updated
}
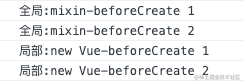
3,测试生命周期执行流程
Vue.mixin 中的 2 个 beforeCreate 钩子;
new Vue 中的 2 个 beforeCreate 钩子;
按照合并后的顺序依次执行完成;
七,结尾
本篇,Vue 生命周期的实现,主要涉及以下几点:
- Vue.mixin 介绍
- Vue 的 Global API
- Vue.mixin 实现
下篇,diff 算法的流程分析
维护日志:
- 20210708:修复“四-4,生命周期的合并策略”,当生命周期函数为数组时,无需二次包装
- 20210806:修复排版问题