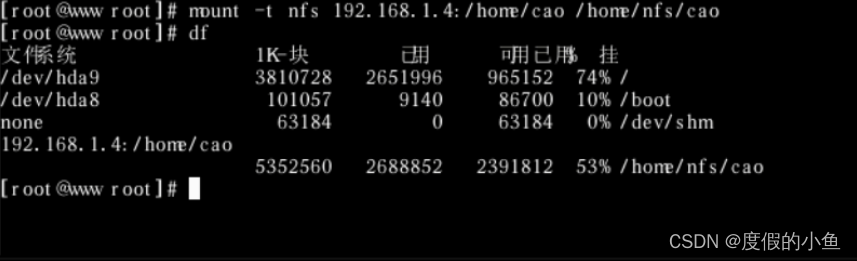
题目
简单
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6] 输出:5
提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在
[0, 105]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
面试中遇到过这道题?
1/5
是
否
通过次数
685.3K
提交次数
1.3M
通过率
54.0%
方法一:广度优先搜索
根节点的深度为1,从根节点开始搜索,每次搜索一层深度+1,若是搜索某一层时,发现了叶子节点,说明该叶子是层数最低的叶子,就返回该叶子的深度。
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> pq;
int depth=0;
pq.push(root);
while(!pq.empty())
{
depth++;
int n=pq.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
TreeNode *p=pq.front();
pq.pop();
if(!p->left&&!p->right) return depth;
if(p->left) pq.push(p->left);
if(p->right) pq.push(p->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};方法二:广度优先搜索
树的最小深度=min(左子树的最小深度,右子树的最小深度)+1。
叶子结点的深度为1,空节点的深度为0。
这种方法我没写,下面是官解。
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
return 1;
}
int min_depth = INT_MAX;
if (root->left != nullptr) {
min_depth = min(minDepth(root->left), min_depth);
}
if (root->right != nullptr) {
min_depth = min(minDepth(root->right), min_depth);
}
return min_depth + 1;
}
};