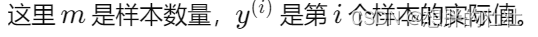从0实现一个基于SpringBoot的个人博客系统
- 项目介绍
- 准备工作
- 数据准备
- 创建项目
- 准备前端页面
- 编写配置文件
- 项目公共模块
- 实体类
- 公共层
- 业务代码
- 持久层
- 实现博客列表
- 实现博客列表
- 约定前后端交互接口
- 实现博客详情
- 约定前后端交互接口
- 实现服务器代码
- 实现登录
- JWT令牌
- JWT令牌生成和校验
- 实现用户登录
- 约定前后端交互接⼝
- 实现服务器代码
- 实现强制要求登录
- 添加拦截器
- 实现显示用户信息
- 约定前后端交互接口
- 实现服务器代码
- 实现发布博客
- 实现服务器代码
- 实现删除/编辑博客
- 约定前后端交互接口
- 实现服务器代码
- 加密/加盐
- 写加密/解密工具类
项目介绍
使⽤SSM框架实现⼀个简单的博客系统
共5个⻚⾯
- ⽤⼾登录
- 博客发表⻚
- 博客编辑⻚
- 博客列表⻚
- 博客详情⻚
功能描述:
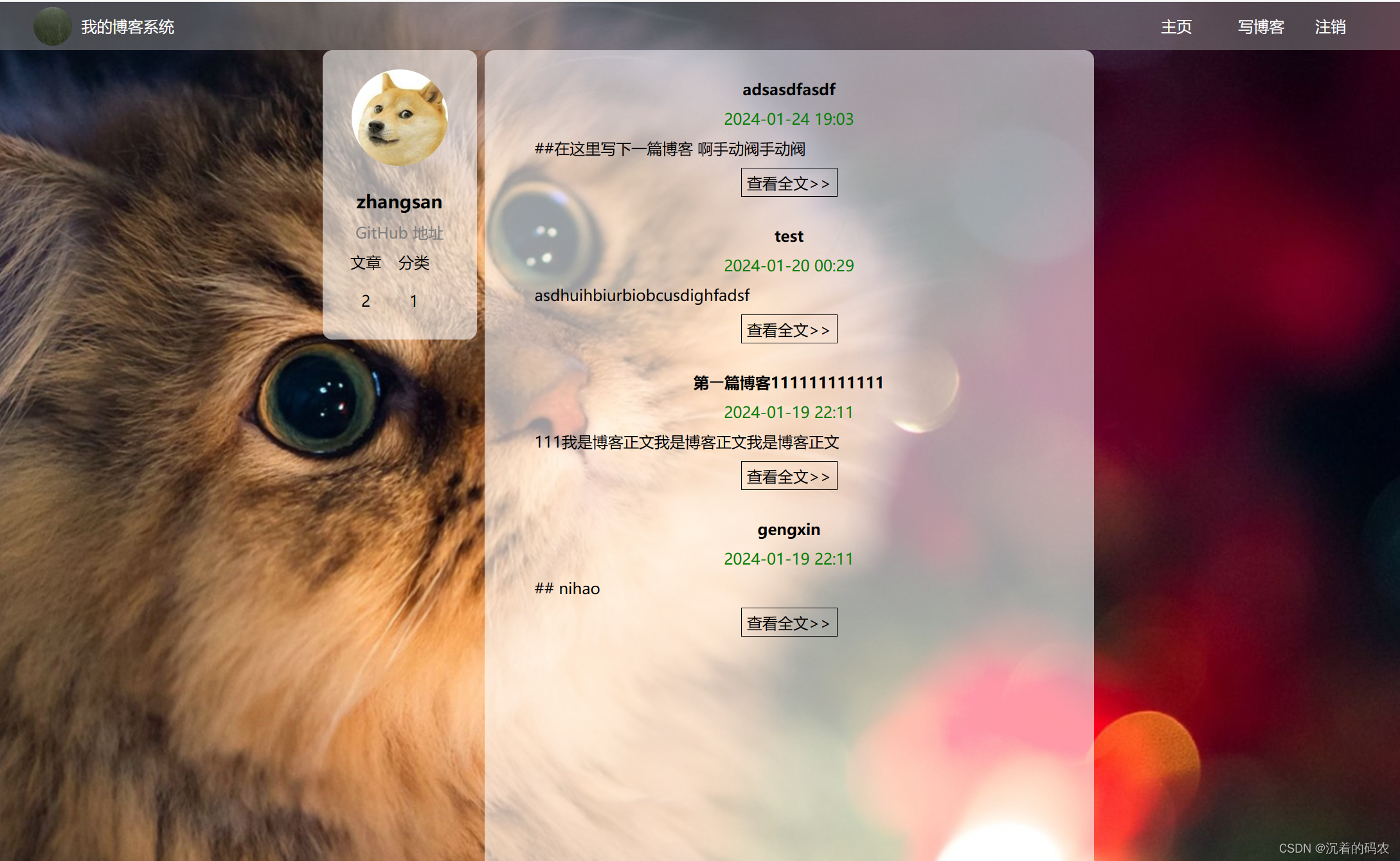
⽤⼾登录成功后, 可以查看所有⼈的博客. 点击 <<查看全⽂>> 可以查看该博客的正⽂内容. 如果该博客作者为当前登录⽤⼾, 可以完成博客的修改和删除操作, 以及发表新博客
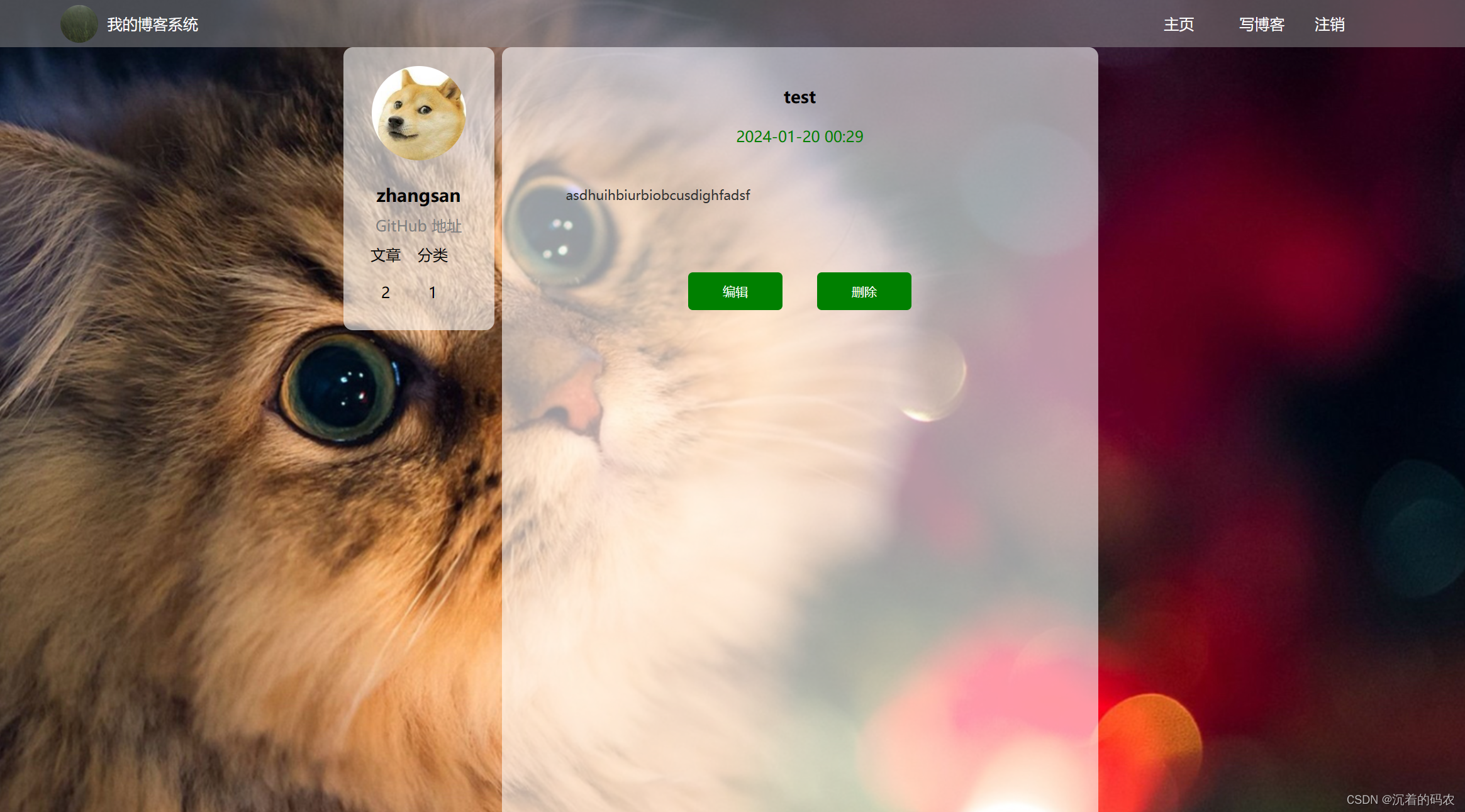
页面预览
用户登录
博客详情
博客列表
博客发布
准备工作
数据准备
建表sql
-- 建表SQL
create database if not exists java_blog_spring charset utf8mb4;
-- ⽤⼾表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS java_blog_spring.user;
CREATE TABLE java_blog_spring.user(
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_name` VARCHAR ( 128 ) NOT NULL,
`password` VARCHAR ( 128 ) NOT NULL,
`github_url` VARCHAR ( 128 ) NULL,
`delete_flag` TINYINT ( 4 ) NULL DEFAULT 0,
`create_time` DATETIME DEFAULT now(),
`update_time` DATETIME DEFAULT now(),
PRIMARY KEY ( id ),
UNIQUE INDEX user_name_UNIQUE ( user_name ASC )) ENGINE = INNODB DEFAULT CHARACT SET = utf8mb4 COMMENT = '⽤⼾表';
-- 博客表
drop table if exists java_blog_spring.blog;
CREATE TABLE java_blog_spring.blog (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`title` VARCHAR(200) NULL,
`content` TEXT NULL,
`user_id` INT(11) NULL,
`delete_flag` TINYINT(4) NULL DEFAULT 0,
`create_time` DATETIME DEFAULT now(),
`update_time` DATETIME DEFAULT now(),
PRIMARY KEY (id))
ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4 COMMENT = '博客表';
创建项目
创建SpringBoot项⽬, 添加Spring MVC 和MyBatis对应依赖
准备前端页面
编写配置文件
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java_blog_spring?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 111111
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true #驼峰自动转换
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl #打印sql语句
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/**Mapper.xml
# 设置⽇志⽂件的⽂件名
logging:
file:
name: spring-blog.log
项目公共模块
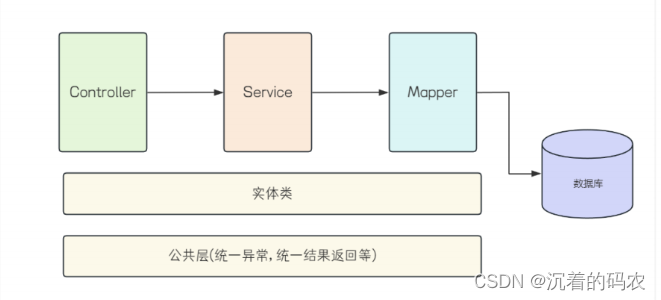
项⽬分为控制层(Controller), 服务层(Service), 持久层(Mapper).
实体类
实体类主要有Blog和User
@Data
public class BlogInfo {
private Integer id;
private String title;
private String content;
private Integer userId;
private Integer deleteFlag;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
private boolean isLoginUser;
public String getCreateTime() {
return DateUtils.formatDate(createTime);
}
}
@Data
public class UserInfo {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String githubUrl;
private Integer deleteFlag;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}
公共层
- 统一返回结果实体类
业务状态码:200 业务处理成功 -1业务处理失败 -2用户未登录
msg:业务处理失败时,返回的错误信息
data:业务返回数据
@Data
public class Result<T> {
private int code;
private String errorMsg;
private T data;
public static <T> Result<T> success(T data){
Result result = new Result();
result.setCode(Constants.RESULT_SUCCESS);
result.setData(data);
result.setErrorMsg("");
return result;
}
public static <T> Result<T> fail(String errorMsg){
Result result = new Result();
result.setCode(Constants.RESULT_FAIL);
result.setErrorMsg(errorMsg);
return result;
}
public static <T> Result<T> fail(String errorMsg, T data){
Result result = new Result();
result.setCode(Constants.RESULT_FAIL);
result.setErrorMsg(errorMsg);
result.setData(data);
return result;
}
}
- 统一返回结果
/**
* 统一返回结果
*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class ResponseAdvice implements ResponseBodyAdvice {
@Override
public boolean supports(MethodParameter returnType, Class converterType) {
return true;
}
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public Object beforeBodyWrite(Object body, MethodParameter returnType, MediaType selectedContentType, Class selectedConverterType, ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {
if(body instanceof Result){
return body;
}
if(body instanceof String){
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
return objectMapper.writeValueAsString(Result.success(body));
}
return Result.success(body);
}
}
- 统一异常处理
@ResponseBody
@ControllerAdvice
public class ErrorAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler
public Result errorHandler(Exception e){
Result result = new Result<>();
result.setErrorMsg("内部错误,请联系管理员");
result.setCode(Constants.RESULT_FAIL);
return result;
}
}
业务代码
持久层
根据需求, 先⼤致计算有哪些DB相关操作, 完成持久层初步代码, 后续再根据业务需求进⾏完善
- ⽤⼾登录⻚
a. 根据⽤⼾名查询⽤⼾信息
- 博客列表⻚
a. 根据id查询user信息 b. 获取所有博客列表
- 博客详情⻚
a. 根据博客ID查询博客信息 b. 根据博客ID删除博客(修改delete_flag=1)
- 博客修改⻚
a. 根据博客ID修改博客信息
- 发表博客
a. 插⼊新的博客数据
实现博客列表
@Mapper
public interface BlogInfoMapper {
/**
* 获取博客列表
*/
@Select("select * from blog where delete_flag = 0 order by create_time desc")
List<BlogInfo> queryBlogList();
/**
*根据博客id 获取博客详情
*/
@Select("select * from blog where id = #{id} and delete_flag = 0")
BlogInfo queryById(Integer id);
/**
* 编辑博客
*/
@Update("update blog set title = #{title}, content = #{content} where id = #{id}")
Integer update(BlogInfo blogInfo);
/**
* 删除博客
*/
@Update("update blog set delete_flag = 1 where id = #{id}")
Integer deleteBlog(Integer id);
/**
* 添加博客
*/
@Insert("insert into blog(title,content,user_id) values(#{title}, #{content}, #{userId})")
Integer insertBlog(BlogInfo blogInfo);
}
@Mapper
public interface UserInfoMapper {
/**
* 根据用户名 查询用户信息
*/
@Select("select * from user where user_name = #{userName} and delete_flag = 0")
UserInfo queryByName(String userName);
/**
* 根据用户ID 查询用户信息
*/
@Select("select * from user where id = #{id} and delete_flag = 0")
UserInfo queryById(Integer id);
}
实现博客列表
约定前后端交互接口
[请求] /blog/getlist
[响应]
{
“code”: 200,
“msg”: “”,
“data”: [{
“id”: 1,
“title”: “第⼀篇博客”,
“content”: “111我是博客正⽂我是博客正⽂我是博客正⽂”,
“userId”: 1,
“deleteFlag”: 0,
“createTime”: “2023-10-21 16:56:57”,
“updateTime”: “2023-10-21T08:56:57.000+00:00”
},
…
]
}
客户端给服务器发送一个/blog/getList的HTTP请求 服务器给客户端返回一个JSON格式的数据
@RequestMapping("/getList")
public List<BlogInfo> getBlogList() {
return blogService.getBlogList();
}
public List<BlogInfo> getBlogList(){
return blogInfoMapper.queryBlogList();
}
实现博客详情
⽬前点击博客列表⻚的 “查看全⽂” , 能进⼊博客详情⻚, 但是这个博客详情⻚是写死的内容. 我们期望能够根据当前的 博客 id 从服务器动态获取博客内容.
约定前后端交互接口
[请求] /blog/getBlogDetail?blogId=1
[响应] {
“code”: 200,
“msg”: “”,
“data”: {
“id”: 1,
“title”: “第⼀篇博客”,
“content”: “111我是博客正⽂我是博客正⽂我是博客正⽂”,
“userId”: 1,
“deleteFlag”: 0,
“createTime”: “2023-10-21 16:56:57”,
“updateTime”: “2023-10-21T08:56:57.000+00:00”
}
}
实现服务器代码
@RequestMapping("/getBlogDetail")
public Blog getBlogDeatail(Integer blogId){
return blogService.getBlogDeatil(blogId);
}
public BlogInfo getBlogDetail(Integer blogId) {
return blogInfoMapper.queryById(blogId);
}
实现登录
分析
传统思路:
• 登陆⻚⾯把⽤⼾名密码提交给服务器.
• 服务器端验证⽤⼾名密码是否正确, 并返回校验结果给后端
• 如果密码正确, 则在服务器端创建 Session . 通过 Cookie 把 sessionId 返回给浏览器.
问题
集群环境下⽆法直接使⽤Session.
解决方案
使用令牌
令牌其实就是⼀个⽤⼾⾝份的标识, 名称起的很⾼⼤上, 其实本质就是⼀个字符串.
服务器具备⽣成令牌和验证令牌的能⼒我们使⽤令牌技术, 继续思考上述场景:
- ⽤⼾登录 ⽤⼾登录请求, 经过负载均衡, 把请求转给了第⼀台服务器, 第⼀台服务器进⾏账号密码验证, 验证成功后, ⽣成⼀个令牌, 并返回给客⼾端.
- 客⼾端收到令牌之后, 把令牌存储起来. 可以存储在Cookie中, 也可以存储在其他的存储空间(⽐如localStorage)
- 查询操作 ⽤⼾登录成功之后, 携带令牌继续执⾏查询操作, ⽐如查询博客列表. 此时请求转发到了第⼆台机器, 第⼆台机器会先进⾏权限验证操作. 服务器验证令牌是否有效, 如果有效, 就说明⽤⼾已经执⾏了登录操作, 如果令牌是⽆效的, 就说明⽤⼾之前未执⾏登录操作.
JWT令牌
令牌本质就是⼀个字符串, 他的实现⽅式有很多, 我们采⽤⼀个JWT令牌来实现
介绍
JWT全称: JSON Web Token
官⽹: https://jwt.io/
JSON Web Token(JWT)是⼀个开放的⾏业标准(RFC 7519), ⽤于客⼾端和服务器之间传递安全可靠的信息.
其本质是⼀个token, 是⼀种紧凑的URL安全⽅法.
jwt组成
Header(头部) 头部包括令牌的类型(即JWT)及使⽤的哈希算法(如HMAC SHA256或RSA)
Payload(负载) 负载部分是存放有效信息的地⽅, ⾥⾯是⼀些⾃定义内容. ⽐如:{“userId”:“123”,“userName”:“zhangsan”} , 也可以存在jwt提供的现场字段, ⽐如exp(过期时间戳)等.
Signature(签名) 此部分⽤于防⽌jwt内容被篡改, 确保安全性防⽌被篡改, ⽽不是防⽌被解析.JWT之所以安全, 就是因为最后的签名. jwt当中任何⼀个字符被篡改, 整个令牌都会校验失败.就好⽐我们的⾝份证, 之所以能标识⼀个⼈的⾝份, 是因为他不能被篡改, ⽽不是因为内容加密.(任何⼈都可以看到⾝份证的信息, jwt 也是)
JWT令牌生成和校验
- 引⼊JWT令牌的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-api</artifactId>
<version>0.11.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.jsonwebtoken/jjwt-impl -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-impl</artifactId>
<version>0.11.5</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-jackson</artifactId> <!-- or jjwt-gson if Gson is
preferred -->
<version>0.11.5</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
- 使⽤Jar包中提供的API来完成JWT令牌的⽣成和校验
@Slf4j
public class JwtUtils {
//三十分钟过期时间
public static final long expiration = 30 * 60 * 1000;
public static final String secretString = "dVnsmy+SIX6pNptQdeclDSJ26EMSPEIhvZYKBTTug4k=";
public static final Key key = Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(Decoders.BASE64.decode(secretString));
public static String genToken(Map<String,Object> claim){
String token = Jwts.builder()
.setClaims(claim)//设置载荷信息
.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + expiration))//设置过期时间
.signWith(key)//设置密钥
.compact();
return token;
}
public static Claims parseToken(String token){
if(token == null){
return null;
}
//构建解析器
JwtParser build = Jwts.parserBuilder().setSigningKey(key).build();
Claims claims = null;
try {
claims = build.parseClaimsJws(token).getBody();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("解析token失败 token:{}",token);
}
return claims;
}
public static Integer getUserIdFromToken(String token){
Claims claims = parseToken(token);
if(claims == null){
return null;
}
return (Integer) claims.get("id");
}
}
实现用户登录
学习令牌的使⽤之后, 接下来我们通过令牌来完成⽤⼾的登录
- 登陆⻚⾯把⽤⼾名密码提交给服务器.
- 服务器端验证⽤⼾名密码是否正确, 如果正确, 服务器⽣成令牌, 下发给客⼾端.
- 客⼾端把令牌存储起来(⽐如Cookie, local storage等), 后续请求时, 把token发给服务器
- 服务器对令牌进⾏校验, 如果令牌正确, 进⾏下⼀步操作
约定前后端交互接⼝
[请求]/user/login username=test&password=123
[响应]{
“code”: 200,
“msg”: “”,
“data”: "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJpZCI6MSwidXNlcm5hbWUiOiJ6aGFuZ3NhbiIsImlhdC
}
//验证成功, 返回token, 验证失败返回 “”
实现服务器代码
创建UserController
@RequestMapping("/login")
public Result login(String userName, String password){
/**
* 参数校验
* 密码校验
* 生成token 并返回
*/
if(!StringUtils.hasLength(userName) || !StringUtils.hasLength(password)){
return Result.fail("用户名或密码为空");
}
//获取数据库中的密码
UserInfo userInfo = userService.queryByName(userName);
if(userInfo == null || userInfo.getId() < 0){
return Result.fail("用户不存在");
}
// if(!password.equals(userInfo.getPassword())){
// return Result.fail("密码错误!");
// }
boolean isOk = SecurityUtils.verify(password,userInfo.getPassword());
if(!isOk){
return Result.fail("密码错误!");
}
//生成token
Map<String,Object> claim = new HashMap<>();
claim.put("id",userInfo.getId());
claim.put("name",userInfo.getUserName());
String token = JwtUtils.genToken(claim);
return Result.success(token);
}
实现强制要求登录
当⽤⼾访问 博客列表⻚ 和 博客详情⻚ 时, 如果⽤⼾当前尚未登陆, 就⾃动跳转到登陆⻚⾯.我们可以采⽤拦截器来完成, token通常由前端放在header中, 我们从header中获取token, 并校验token是否合法
添加拦截器
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//此处进行用户强制登陆校验
//1.从header中获取token
//验证token(约定前端发送请求时 header之中有key为user_token 值为token的键值对)
String token = request.getHeader("user_token");
log.info("从header中获取token,token:{}",token);
Claims claims = JwtUtils.parseToken(token);
if(claims == null){
//token是不合法的
response.setStatus(401);
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
public static final List<String> excludepath = Arrays.asList(
"/user/login",
"/**/*.html",
"/pic/**",
"/js/**",
"/css/**",
"/blog-editormd/**"
);
@Autowired
private LoginInterceptor loginInterceptor;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(loginInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**")
.excludePathPatterns(excludepath);
}
}
实现显示用户信息
约定前后端交互接口
在博客列表页 获取当前文章作者的用户信息
请求]
/user/getUserInfo
[响应]
{
userId: 1,
username: test
…
}
在博客详情页 获取当前文章作者的用户信息
[请求]
/user/getAuthorInfo?blogId=1
[响应]
{
userId: 1,
username: test
}
实现服务器代码
在UserController添加代码
//获取登录用户的信息
@RequestMapping("/getUserInfo")
public UserInfo userInfo(HttpServletRequest request){
//1.从token 中获取用户Id
//2.根据用户Id 获取用户信息
String token = request.getHeader("user_token");
Integer userId = JwtUtils.getUserIdFromToken(token);
if(userId == null){
return null;
}
return userService.queryById(userId);
}
//获取当前作者的信息
@RequestMapping("/getAuthorInfo")
public UserInfo getAuthorInfo(Integer blogId){
if(blogId == null && blogId < 0){
return null;
}
return userService.getAuthorInfo(blogId);
}
UserService
public UserInfo getAuthorInfo(Integer blogId) {
//根据blogId获取userId
//根据userId获取userInfo
BlogInfo blogInfo = blogInfoMapper.queryById(blogId);
if(blogInfo == null){
return null;
}
return userInfoMapper.queryById(blogInfo.getUserId());
}
实现发布博客
约定前后端交互接口
[请求]
/blog/add
title=标题&content=正⽂…
[响应]
{
“code”: 200,
“msg”: “”,
“data”: true
}
//true 成功
//false 失败
实现服务器代码
修改BlogController代码
@RequestMapping("/add")
public Result publishBlog(String title, String content, HttpServletRequest request) {
//从token中获取userId
String token = request.getHeader("user_token");
Integer userId = JwtUtils.getUserIdFromToken(token);
if (userId == null || userId < 0) {
return Result.fail("用户未登录", false);
}
//插入博客
BlogInfo blogInfo = new BlogInfo();
blogInfo.setUserId(userId);
blogInfo.setTitle(title);
blogInfo.setContent(content);
blogService.insertBlog(blogInfo);
return Result.success(true);
}
实现删除/编辑博客
进⼊⽤⼾详情⻚时, 如果当前登陆⽤⼾正是⽂章作者, 则在导航栏中显⽰ [编辑] [删除] 按钮, ⽤⼾点击时则进⾏相应处理.
需要实现两件事:
• 判定当前博客详情⻚中是否要显⽰[编辑] [删除] 按钮
• 实现编辑/删除逻辑.
删除采⽤逻辑删除, 所以和编辑其实为同⼀个接⼝.
约定前后端交互接口
- 判定是否要显⽰[编辑] [删除] 按钮
修改之前的 获取博客 信息的接⼝, 在响应中加上⼀个字段.
获取博客详情
请求]
/blog/getBlogDetail?blogId=1
[响应]
{
“code”: 200,
“msg”: “”,
“data”: {
“id”: 1,
“title”: “第⼀篇博客”,
“content”: “111我是博客正⽂我是博客正⽂我是博客正⽂”,
“userId”: 1,
“loginUser”: 1
“deleteFlag”: 0,
“createTime”: “2023-10-21 16:56:57”,
“updateTime”: “2023-10-21T08:56:57.000+00:00”
}
}
修改博客
[请求]
/blog/update
[参数]
Content-Type: application/json
{
“title”: “测试修改⽂章”,
“content”: “在这⾥写下⼀篇博客”,
“blogId”: “4”
}
[响应]
{
“code”: 200,
“msg”: “”,
“data”: true
}
删除博客
[请求]
/blog/delete?blogId=1
[响应]
{
“code”: 200,
“msg”: “”,
“data”: true
}
实现服务器代码
给blog类新增一个字段
@Data
public class BlogInfo {
private Integer id;
private String title;
private String content;
private Integer userId;
private Integer deleteFlag;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
private boolean isLoginUser;
public String getCreateTime() {
return DateUtils.formatDate(createTime);
}
}
修改BlogControl
//获取博客详情
@RequestMapping("/getBlogDetail")
public BlogInfo getBlogDetail(Integer blogId, HttpServletRequest request) {
BlogInfo blogInfo = blogService.getBlogDetail(blogId);
//判断作者是否是登录用户
String token = request.getHeader("user_token");
Integer userId = JwtUtils.getUserIdFromToken(token);
if (userId != null && userId == blogInfo.getUserId()) {
blogInfo.setLoginUser(true);
}
return blogInfo;
}
添加update/delete方法
/**
* 编辑博客
*/
@RequestMapping("/update")
public boolean updateBlog(Integer id, String title, String content){
BlogInfo blogInfo = new BlogInfo();
blogInfo.setTitle(title);
blogInfo.setContent(content);
//根据博客ID去更新数据
blogInfo.setId(id);
blogService.updateBlog(blogInfo);
return true;
}
/**
* 删除博客
*/
@RequestMapping("/delete")
public boolean deleteBlog(Integer blogId){
blogService.delete(blogId);
return true;
}
加密/加盐
加密介绍
在MySQL数据库中, 我们常常需要对密码, ⾝份证号, ⼿机号等敏感信息进⾏加密, 以保证数据的安全性.如果使⽤明⽂存储, 当⿊客⼊侵了数据库时, 就可以轻松获取到⽤⼾的相关信息, 从⽽对⽤⼾或者企业造成信息泄漏或者财产损失.⽬前我们⽤⼾的密码还是明⽂设置的, 为了保护⽤⼾的密码信息, 我们需要对密码进⾏加密
密码算法分类
密码算法主要分为三类: 对称密码算法, ⾮对称密码算法, 摘要算法
- 对称密码算法 是指加密秘钥和解密秘钥相同的密码算法. 常⻅的对称密码算法有: AES, DES, 3DES, RC4, RC5, RC6 等.
- ⾮对称密码算法 是指加密秘钥和解密秘钥不同的密码算法. 该算法使⽤⼀个秘钥进⾏加密, ⽤另外⼀ 个秘钥进⾏解密. ◦ 加密秘钥可以公开,⼜称为 公钥 ◦ 解密秘钥必须保密,⼜称为 私钥 常⻅的⾮对称密码算法有:RSA,DSA,ECDSA, ECC 等
- 摘要算法 是指把任意⻓度的输⼊消息数据转化为固定⻓度的输出数据的⼀种密码算法. 摘要算法是 不可逆的, 也就是⽆法解密. 通常⽤来检验数据的完整性的重要技术, 即对数据进⾏哈希计算然后⽐ 较摘要值, 判断是否⼀致. 常⻅的摘要算法有: MD5,SHA系列(SHA1, SHA2等), CRC(CRC8, CRC16, CRC32)
我们在博客系统中使用摘要算法中的MD5算法来加密
问题: 虽然经过MD5加密后的密⽂⽆法解密, 但由于相同的密码经过MD5哈希之后的密⽂是相同的, 当存储⽤⼾密码的数据库泄露后, 攻击者会很容易便能找到相同密码的⽤⼾, 从⽽降低了破解密码的难度. 因此, 在对⽤⼾密码进⾏加密时,需要考虑对密码进⾏包装, 即使是相同的密码, 也保存为不同的密⽂. 即使⽤⼾输⼊的是弱密码, 也考虑进⾏增强, 从⽽增加密码被攻破的难度.
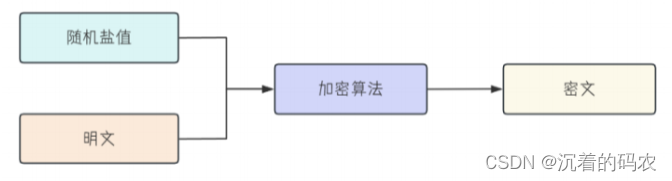
解决⽅案: 采⽤为⼀个密码拼接⼀个随机字符来进⾏加密, 这个随机字符我们称之为"盐". 假如有⼀个加盐后的加密串,⿊客通过⼀定⼿段这个加密串, 他拿到的明⽂并不是我们加密前的字符串, ⽽是加密前的字符串和盐组合的字符串, 这样相对来说⼜增加了字符串的安全性.
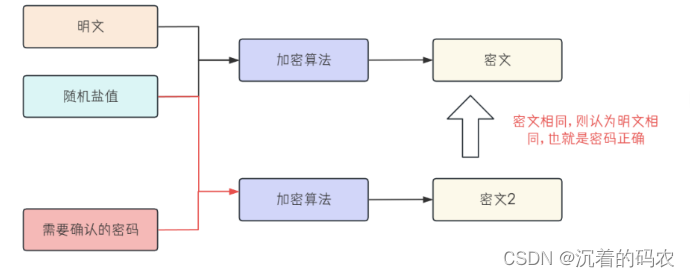
解密流程: MD5是不可逆的, 通常采⽤"判断哈希值是否⼀致"来判断密码是否正确.如果⽤⼾输⼊的密码, 和盐值⼀起拼接后的字符串经过加密算法, 得到的密⽂相同, 我们就认为密码正确(密⽂相同, 盐值相同, 推测明⽂相同)
写加密/解密工具类
@Slf4j
public class SecurityUtils {
/**
* 加密
* @param password 明文密码
* @return 盐值+密文
*/
public static String encry(String password){
//生成随机盐值
String salt = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-","");
System.out.println(salt);
//加密 盐值+明文
String securityPassword = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex((salt + password).getBytes());
//数据库中存储 盐值+明文
return salt+securityPassword;
}
/**
* 校验
* @param inputPassword 输入的密码
* @param sqlPassword 数据库中取到的密码
* @return 密码是否正确
*/
public static boolean verify(String inputPassword, String sqlPassword){
//取出盐值
if(sqlPassword == null || sqlPassword.length() != 64){
return false;
}
String salt = sqlPassword.substring(0,32);
//得到密文
String securityPassword = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex((salt+inputPassword).getBytes());
log.info(salt + securityPassword);
return (salt + securityPassword).equals(sqlPassword);
}
}