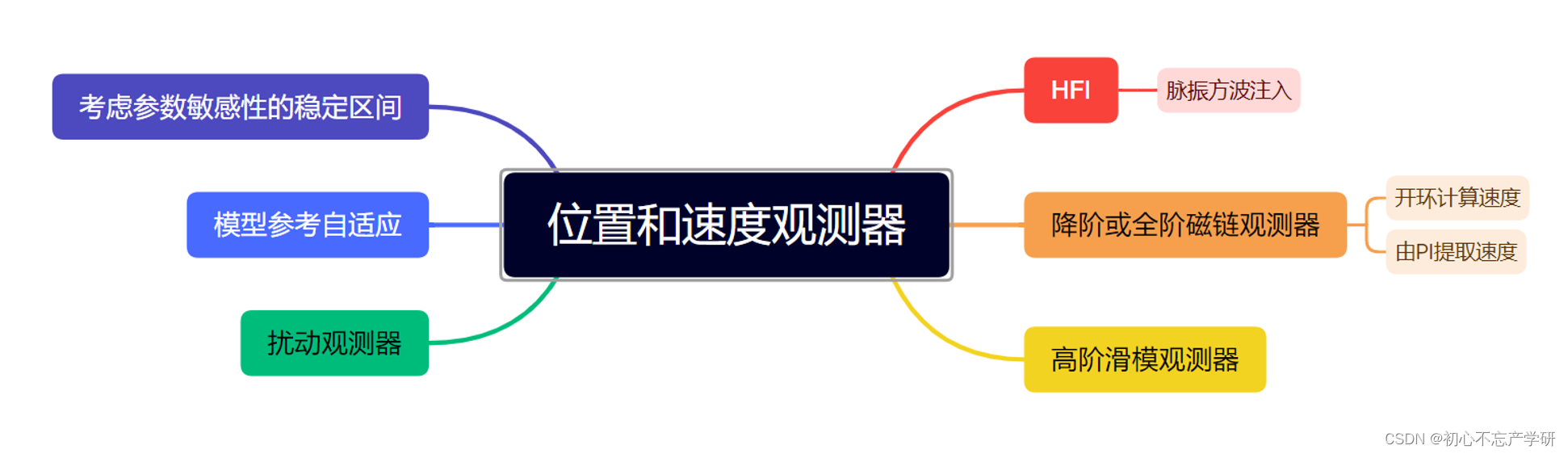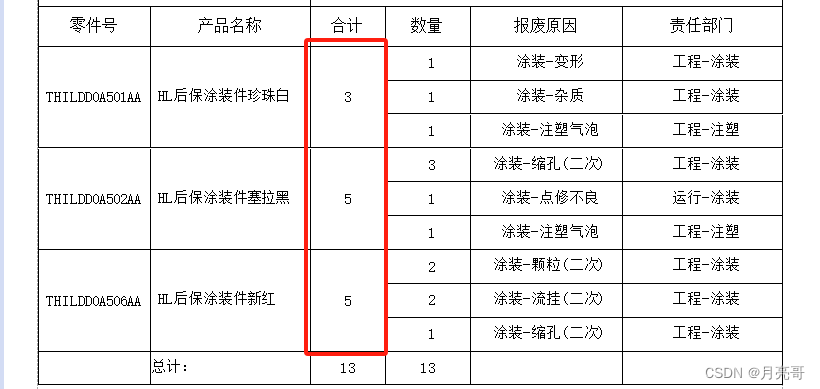
二分搜索是竞争性编程或任何算法竞赛的重要组成部分,了解速记函数可以减少编写代码的时间。二分查找是最有效的查找算法。
二分搜索是一种在排序数组中使用的搜索算法,通过重复将搜索间隔一分为二。二分查找的思想是利用数组已排序的信息,将时间复杂度降低到O(Log N)。
使用二分搜索执行的一般操作:
1、寻找一个元素
2、下界
3、上限
1. 二进制搜索:
binary_search(start_ptr, end_ptr, num):如果元素存在于容器中,则该函数返回 true,否则返回 false。start_ptr变量保存二分查找的起点,end_ptr保存二分查找空间的结束位置,num是要查找的值。
binary_search函数的编码实现:
// C++ code to demonstrate the working of binary_search()
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Driver's code
int main()
{
// initializing vector of integers
vector<int> arr = { 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 };
// using binary_search to check if 15 exists
if (binary_search(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 15))
cout << "15 exists in vector";
else
cout << "15 does not exist";
cout << endl;
// using binary_search to check if 23 exists
if (binary_search(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 23))
cout << "23 exists in vector";
else
cout << "23 does not exist";
cout << endl;
}
输出
15 存在于向量中
23 不存在
时间复杂度: O(log N) – 其中 N 是数组中的元素数量。
辅助空间: O(1)
2.下界:
lower_bound(start_ptr, end_ptr, num):如果容器仅包含一次num,则返回指向 num 位置的指针。如果容器包含多次出现的 num,则返回指向 num 的第一个位置的指针。如果容器不包含num ,则返回指向刚好高于 num 的数字位置的指针,num是插入到已排序数组并再次排序时的数字位置。从指针中减去第一个位置,即 vect.begin(),返回实际索引。start_ptr变量保存二分查找的起点,end_ptr保存二分查找空间的结束位置,num是要查找的值。
lower_bound函数的编码实现:
// C++ code to demonstrate the working of lower_bound()
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Driver's code
int main()
{
// initializing vector of integers
// for single occurrence
vector<int> arr1 = { 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 };
// initializing vector of integers
// for multiple occurrences
vector<int> arr2 = { 10, 15, 20, 20, 25, 30, 35 };
// initializing vector of integers
// for no occurrence
vector<int> arr3 = { 10, 15, 25, 30, 35 };
// using lower_bound() to check if 20 exists
// single occurrence
// prints 2
cout << "The position of 20 using lower_bound "
" (in single occurrence case) : ";
cout << lower_bound(arr1.begin(), arr1.end(), 20)
- arr1.begin();
cout << endl;
// using lower_bound() to check if 20 exists
// multiple occurrence
// prints 2
cout << "The position of 20 using lower_bound "
"(in multiple occurrence case) : ";
cout << lower_bound(arr2.begin(), arr2.end(), 20)
- arr2.begin();
cout << endl;
// using lower_bound() to check if 20 exists
// no occurrence
// prints 2 ( index of next higher)
cout << "The position of 20 using lower_bound "
"(in no occurrence case) : ";
cout << lower_bound(arr3.begin(), arr3.end(), 20)
- arr3.begin();
cout << endl;
}
输出
使用 lower_bound 的 20 的位置(在单次出现的情况下):2
使用 lower_bound 的 20 的位置(在多次出现的情况下):2
使用 lower_bound 的 20 的位置(在没有出现的情况下):2
时间复杂度: O(log N) – 其中 N 是数组中的元素数量。
辅助空间: O(1)
3.上限:
upper_bound(start_ptr, end_ptr, num):如果容器包含一次num,则返回指向下一个比 num 大的数字的位置的指针。如果容器包含多次出现的 num,则返回指向比最后一次出现的 num 更大的下一个数字的第一个位置的指针。如果容器不包含num,则返回指向下一个比 num 大的数字的位置的指针。从指针中减去第一个位置,即 vect.begin(),返回实际索引。start_ptr变量保存二分查找的起点,end_ptr保存二分查找空间的结束位置,num是要查找的值。
upper_bound函数的编码实现:
// C++ code to demonstrate the working of upper_bound()
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Driver's code
int main()
{
// initializing vector of integers
// for single occurrence
vector<int> arr1 = { 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 };
// initializing vector of integers
// for multiple occurrences
vector<int> arr2 = { 10, 15, 20, 20, 25, 30, 35 };
// initializing vector of integers
// for no occurrence
vector<int> arr3 = { 10, 15, 25, 30, 35 };
// using upper_bound() to check if 20 exists
// single occurrence
// prints 3
cout << "The position of 20 using upper_bound"
" (in single occurrence case) : ";
cout << upper_bound(arr1.begin(), arr1.end(), 20)
- arr1.begin();
cout << endl;
// using upper_bound() to check if 20 exists
// multiple occurrence
// prints 4
cout << "The position of 20 using upper_bound "
"(in multiple occurrence case) : ";
cout << upper_bound(arr2.begin(), arr2.end(), 20)
- arr2.begin();
cout << endl;
// using upper_bound() to check if 20 exists
// no occurrence
// prints 2 ( index of next higher)
cout << "The position of 20 using upper_bound"
" (in no occurrence case) : ";
cout << upper_bound(arr3.begin(), arr3.end(), 20)
- arr3.begin();
cout << endl;
}
输出
使用 upper_bound 的 20 的位置(在单次出现的情况下):3
使用 upper_bound 的 20 的位置(在多次出现的情况下):4
使用 upper_bound 的 20 的位置(在没有出现的情况下):2
时间复杂度: O(log N) – 其中 N 是数组中的元素数量。
辅助空间: O(1)