题目描述
给定一个链表的头节点
head,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回null。如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪
next指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数pos来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果pos是-1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。不允许修改 链表。
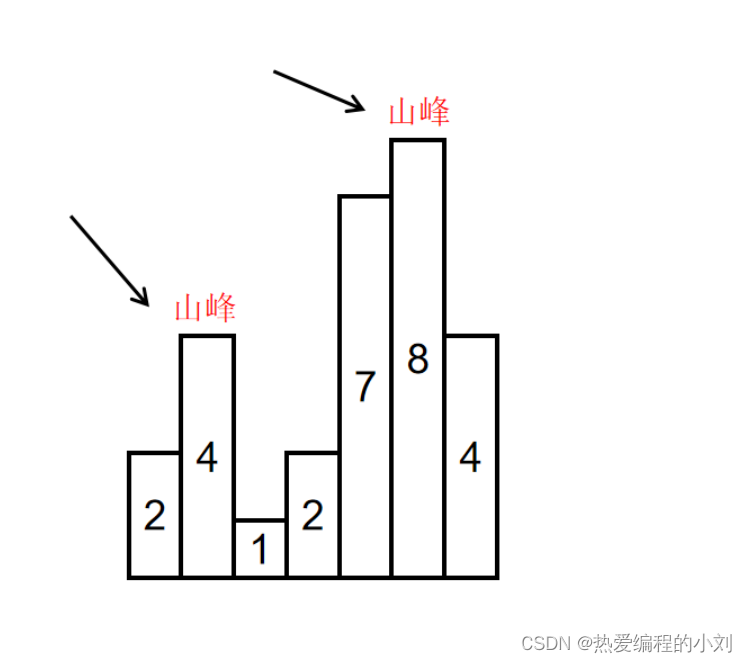
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:返回 null 解释:链表中没有环。提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围在范围
[0, 104]内-105 <= Node.val <= 105pos的值为-1或者链表中的一个有效索引进阶:你是否可以使用
O(1)空间解决此题?
方法一
思路:
和环形链表Ⅰ一样,哈希表,遍历判断有无出现过,没出现过就添加进set,出现过就返回。
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
Map<ListNode,Integer> map=new HashMap<ListNode,Integer>();
while(head!=null){
if(map.containsKey(head)){
return head;
}
map.put(head,head.val);
head=head.next;
}
return null;
}
}方法二
思路:
快慢指针,快慢指针相等了说明有环。之后的就是要证明快指针比慢指针多走了多少。这里看看就好,我自己肯定是想不出来。假设从链表头到环入口距离为a,快慢指针相遇处距入口距离为b,那么慢指针走了a+b,而快指针走了2a+2b,记相遇处绕回到入口处距离为c,那么快指针多走了一圈,即c+b,即a=c,此时让一个指针从链表头开始走c步,一个指针同时在相遇处走c步,那么他们会在入口相遇
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) return null;
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null){
slow=slow.next;
if(fast.next!=null) fast=fast.next.next;
else return null;
if(fast==slow) {
ListNode ptr=head;
while(ptr!=slow){
ptr=ptr.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return ptr;
}
}
return null;
}
}参考链接:142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
【LeetCode热题100】【链表】环形链表 II-CSDN博客



![[华为OD]C卷 精准核算检测 100](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/def0a2e0a8094829a341daf82da47c82.png)