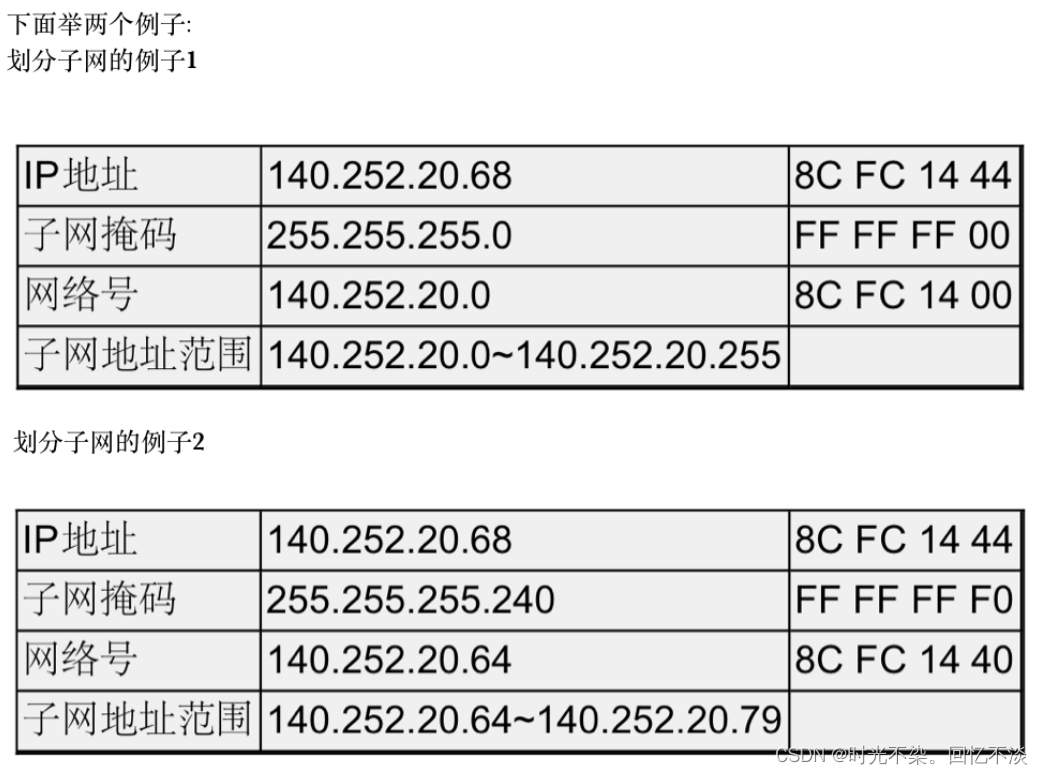
InputManagerService在systemserver进程中被启动
//frameworks\base\services\java\com\android\server\SystemServer.java
t.traceBegin("StartInputManagerService");
inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);//1
t.traceEnd();
//省略
//注册服务
ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_SERVICE, inputManager, /* allowIsolated= */ false, DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL);//2
//省略
inputManager.start();//3
注释1处创建InputManagerService对象,注释2处注册input服务。注释3处调用inputManager的start方法。先来看一下InputManagerService对象的创建过程
//frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\input\InputManagerService.java
public InputManagerService(Context context) {
//省略
mPtr = nativeInit(this, mContext, mHandler.getLooper().getQueue());
//省略
}
继续调用nativeInit方法,这是一个native方法,会通过JNI调用到com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp的nativeInit方法
//frameworks\base\services\core\jni\com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,
jobject serviceObj, jobject contextObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {
sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);
if (messageQueue == nullptr) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "MessageQueue is not initialized.");
return 0;
}
NativeInputManager* im = new NativeInputManager(contextObj, serviceObj,
messageQueue->getLooper());//1
im->incStrong(0);
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(im);
}
static const JNINativeMethod gInputManagerMethods[] = {
/* name, signature, funcPtr */
{"nativeInit",
"(Lcom/android/server/input/InputManagerService;Landroid/content/Context;Landroid/os/"
"MessageQueue;)J",
(void*)nativeInit},
//省略
注释1处,继续创建NativeInputManager对象
//frameworks\base\services\core\jni\com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
NativeInputManager::NativeInputManager(jobject contextObj,
jobject serviceObj, const sp<Looper>& looper) :
mLooper(looper), mInteractive(true) {
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
mServiceObj = env->NewGlobalRef(serviceObj);
//省略
mInteractive = true;
mInputManager = new InputManager(this, this);//1
defaultServiceManager()->addService(String16("inputflinger"),
mInputManager, false);//2
}
注释1处创建InputManager对象,注释2处,这里又在native层注册了一个inputflinger服务。
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\InputManager.cpp
InputManager::InputManager(
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy) {
mDispatcher = createInputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);//1
mClassifier = new InputClassifier(mDispatcher);//2
mReader = createInputReader(readerPolicy, mClassifier);//3
}
注释1处创建InputDispatcher对象,注释2处创建InputClassifier对象,注释3处创建InputReader对象。接下来看一下各个对象的创建过程
InputDispatcher:
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\dispatcher\InputDispatcherFactory.cpp
sp<InputDispatcherInterface> createInputDispatcher(
const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& policy) {
return new android::inputdispatcher::InputDispatcher(policy);
}
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\dispatcher\InputDispatcher.cpp
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& policy)
: mPolicy(policy),//1
mPendingEvent(nullptr),
mLastDropReason(DropReason::NOT_DROPPED),
mIdGenerator(IdGenerator::Source::INPUT_DISPATCHER),
mAppSwitchSawKeyDown(false),
mAppSwitchDueTime(LONG_LONG_MAX),
mNextUnblockedEvent(nullptr),
mDispatchEnabled(false),
mDispatchFrozen(false),
mInputFilterEnabled(false),
// mInTouchMode will be initialized by the WindowManager to the default device config.
// To avoid leaking stack in case that call never comes, and for tests,
// initialize it here anyways.
mInTouchMode(true),
mFocusedDisplayId(ADISPLAY_ID_DEFAULT) {
mLooper = new Looper(false);
mReporter = createInputReporter();
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry = nullptr;
policy->getDispatcherConfiguration(&mConfig);
}
注释1处将policy赋给mPolicy,这里的policy就是传进来的NativeInputManager对象。所以,InputDispatcher中的mPolicy指向的是NativeInputManager对象
InputClassifier:
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\InputClassifier.cpp
InputClassifier::InputClassifier(const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener)
: mListener(listener), mHalDeathRecipient(new HalDeathRecipient(*this)) {}
mListener指向listener,这里的listener就是我们前面创建的InputDispatcher对象,所以,InputClassifier中的mListener指向的是一个InputDispatcher对象
InputReader:
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\InputReaderFactory.cpp
sp<InputReaderInterface> createInputReader(const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy,
const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) {
return new InputReader(std::make_unique<EventHub>(), policy, listener);//1
}
注释1处先创建一个EventHub,然后创建一个InputReader对象
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\EventHub.cpp
EventHub::EventHub(void)
: mBuiltInKeyboardId(NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD),
mNextDeviceId(1),
mControllerNumbers(),
mOpeningDevices(nullptr),
mClosingDevices(nullptr),
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan(false),
mNeedToReopenDevices(false),
mNeedToScanDevices(true),
mPendingEventCount(0),
mPendingEventIndex(0),
mPendingINotify(false) {
ensureProcessCanBlockSuspend();
mEpollFd = epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC);//1
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(mEpollFd < 0, "Could not create epoll instance: %s", strerror(errno));
mINotifyFd = inotify_init();//2
mInputWd = inotify_add_watch(mINotifyFd, DEVICE_PATH, IN_DELETE | IN_CREATE);//3
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(mInputWd < 0, "Could not register INotify for %s: %s", DEVICE_PATH,
strerror(errno));
//省略
struct epoll_event eventItem = {};
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLWAKEUP;
eventItem.data.fd = mINotifyFd;
int result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mINotifyFd, &eventItem);//4
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(result != 0, "Could not add INotify to epoll instance. errno=%d", errno);
//省略
注释1处创建一个epoll,用于监听是否有数据可供读入。注释2处初始化inotify,并在注释3处将DEVICE_PATH添加到inotify的监测中,DEVICE_PATH为/dev/input。注释4处将这个inotify又添加到epoll的监测中。如果DEVICE_PATH目录下有设备节点增加或删除,inotify就可以监测到,mINotifyFd就有数据可供读入,epoll也就可以监测到了。
接着回到InputReader的创建里面
InputReader::InputReader(std::shared_ptr<EventHubInterface> eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy,
const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener)
: mContext(this),
mEventHub(eventHub),//1
mPolicy(policy),//2
mGlobalMetaState(0),
mGeneration(1),
mNextInputDeviceId(END_RESERVED_ID),
mDisableVirtualKeysTimeout(LLONG_MIN),
mNextTimeout(LLONG_MAX),
mConfigurationChangesToRefresh(0) {
mQueuedListener = new QueuedInputListener(listener);//3
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
refreshConfigurationLocked(0);
updateGlobalMetaStateLocked();
} // release lock
}
注释1处将mEventHub指向上面创建的EventHub对象。注释2处将mPolicy指向传进来的policy,而传进来的policy为NativeInputManager对象,所以,InputReader中的mPolicy也是指向NativeInputManager对象,注释3处根据传进来的InputClassifier对象构造QueuedInputListener
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\InputListener.cpp
QueuedInputListener::QueuedInputListener(const sp<InputListenerInterface>& innerListener) :
mInnerListener(innerListener) {
}
所以QueuedInputListener对象中的mInnerListener指向的是一个InputClassifier对象
至此,各个对象的创建都已完毕,来看一下各对象简易的类图

接着回到systemserver中,InputManagerService对象创建后,就会调用该对象的start方法
//frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\input\InputManagerService.java
public void start() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting input manager");
nativeStart(mPtr);
//省略
继续调用nativeStart,这也是一个Native方法,调用com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp的nativeStart方法
//frameworks\base\services\core\jni\com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static void nativeStart(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */, jlong ptr) {
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
status_t result = im->getInputManager()->start();//2
if (result) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "Input manager could not be started.");
}
}
static const JNINativeMethod gInputManagerMethods[] = {
/* name, signature, funcPtr */
//省略
{"nativeStart", "(J)V", (void*)nativeStart},
//省略
注释1处getInputManager返回的是上面创建的InputManager对象,调用InputManager的start方法
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\InputManager.cpp
status_t InputManager::start() {
status_t result = mDispatcher->start();//1
if (result) {
ALOGE("Could not start InputDispatcher thread due to error %d.", result);
return result;
}
result = mReader->start();//2
if (result) {
ALOGE("Could not start InputReader due to error %d.", result);
mDispatcher->stop();
return result;
}
return OK;
}
注释1处调用InputDispatcher的start方法,注释2处调用InputReader的start方法
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\dispatcher\InputDispatcher.cpp
status_t InputDispatcher::start() {
if (mThread) {
return ALREADY_EXISTS;
}
mThread = std::make_unique<InputThread>(
"InputDispatcher", [this]() { dispatchOnce(); }, [this]() { mLooper->wake(); });
return OK;
}
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\InputReader.cpp
status_t InputReader::start() {
if (mThread) {
return ALREADY_EXISTS;
}
mThread = std::make_unique<InputThread>(
"InputReader", [this]() { loopOnce(); }, [this]() { mEventHub->wake(); });
return OK;
}
可以看出,分别启动了InputDispatcher和InputReader线程。InputReader线程启动调用loopOnce读取事件,InputDispatcher线程启动调用dispatchOnce分发事件
总结
在InputManagerService启动过程中,会启动两个线程,InputReader和InputDispatcher线程,用于读取数据和分发数据。其中在InputReader对象的创建过程中,会创建EventHub对象,初始化Epoll和inotify用于监测/dev/input目录
InputDispatcher和InputReader对象的创建流程

InputDispatcher和InputReader线程的启动流程: