(一)实验目的
1、掌握JAVA中文件、IO类及其构造方法;
2、重点掌握文件类型所具有的文件操作方法;
3、重点掌握IO中类所具有的IO操作方法;
4、熟悉递归调用的思想及应用;
5、掌握IO中读写常用方法。
(二)实验内容和步骤
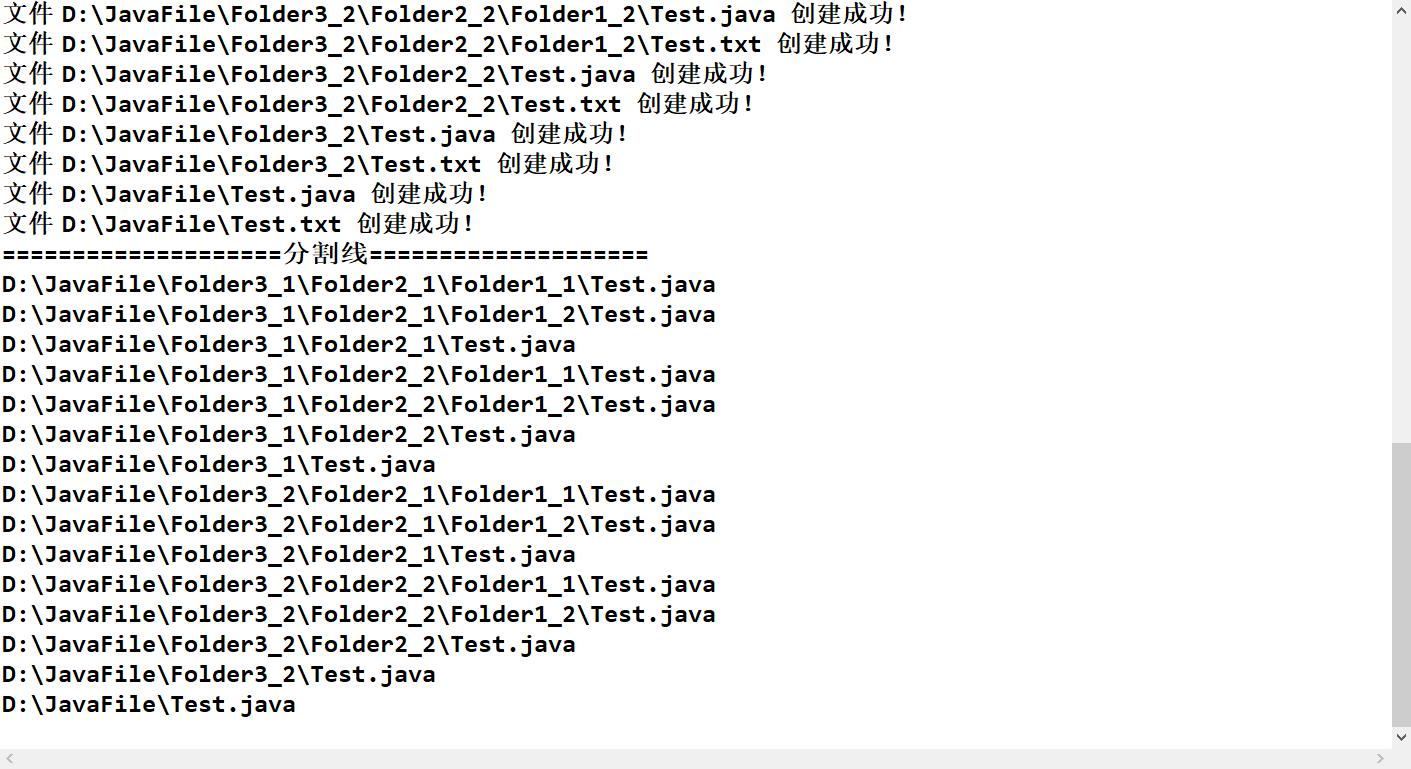
1、输出路径(以管理员的身份启动编译器)
现在在D盘中放有一个名为JavaFile的文件夹,请编写程序在控制台输出此文件夹下的所有java文件的绝对路径。
注意:要求JavaFile文件夹下至少含有三层以上的文件夹,且每层文件夹中均要求含有至少一个java文件和非java文件。
💖 IOStudy.java
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class IOStudy
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String rootFolderPath = "D:\\JavaFile";
createFolderStructure(rootFolderPath, 3); // 创建三层文件夹结构
System.out.println("====================分割线====================");
listJavaFiles(rootFolderPath);
}
/**
* 在指定路径创建几层目录和文件
*
* @param path 路径
* @param depth 层数
*/
private static void createFolderStructure(String path, int depth)
{
File folder = new File(path);
if (!folder.exists())
{
if (folder.mkdir())
{
System.out.println("文件夹 " + path + " 创建成功!");
} else
{
System.out.println("文件夹 " + path + " 创建失败!");
return;
}
}
if (depth > 0)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 2; i++)
{ // 创建两个子文件夹
String subFolderPath = path + File.separator + "Folder" + depth + "_" + i;
createFolderStructure(subFolderPath, depth - 1); // 递归创建子文件夹
}
}
// 在每个文件夹中创建一个Java文件和一个非Java文件
createFile(path, "Test.java");
createFile(path, "Test.txt");
}
/**
* 在 folderPath 目录下创建名为 filename 的文件
*
* @param folderPath 目录
* @param fileName 文件名
*/
private static void createFile(String folderPath, String fileName)
{
File file = new File(folderPath, fileName);
try
{
if (file.createNewFile())
{
System.out.println("文件 " + file.getAbsolutePath() + " 创建成功!");
}
} catch (IOException e)
{
System.out.println("文件 " + file.getAbsolutePath() + " 创建失败!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void listJavaFiles(String folderPath)
{
File folder = new File(folderPath);
if (folder.exists() && folder.isDirectory())
{
File[] files = folder.listFiles();
if (files != null)
{
for (File file : files)
{
if (file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".java"))
{
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
} else if (file.isDirectory())
{
// 递归调用listJavaFiles方法
listJavaFiles(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
} else
{
System.out.println("指定的路径不是一个文件夹。");
}
}
}
😋 输出结果
2、文件读写(以管理员的身份启动编译器)
分别使用三种以上的字节流输入输出方法(例如一次一个字节读写,一次一个字节数组读写,使用缓冲字节流进行读写),读取MultiFile文件夹下的某个java文件的内容,并写到C盘中的test.java文件中
💖 IOStudy2.java
import java.io.*;
public class IOStudy2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 定义目录路径
String directoryPath = "D:\\MultiFile";
// 定义文件路径
String filePath = directoryPath + "\\Hello.java";
// 检查MultiFile目录是否存在,如果不存在则创建
File directory = new File(directoryPath);
if (!directory.exists())
{
if (directory.mkdirs())
{
System.out.println("MultiFile目录创建成功!");
} else
{
System.out.println("MultiFile目录创建失败!");
return; // 如果目录创建失败,退出程序
}
}
// 使用try-with-resources语句自动关闭资源
try (FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(filePath))
{
// 写入简单的Hello, World!程序
writer.write("public class Hello {\n");
writer.write(" public static void main(String[] args) {\n");
writer.write(" System.out.println(\"Hello, World!\");\n");
writer.write(" }\n");
writer.write("}\n");
System.out.println("Hello.java 文件创建成功!");
} catch (IOException e)
{
System.out.println("文件创建失败!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
String destinationPath = "C:\\test.java";
// 方法一:一次一个字节读写
copyFileWithByteByByte(filePath, destinationPath);
// 方法二:一次一个字节数组读写
copyFileWithByteArray(filePath, destinationPath);
// 方法三:使用缓冲字节流进行读写
copyFileWithBufferedStream(filePath, destinationPath);
}
private static void copyFileWithByteByByte(String sourcePath, String destinationPath)
{
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(sourcePath); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(destinationPath))
{
int b;
while ((b = in.read()) != -1)
{
out.write(b);
}
} catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void copyFileWithByteArray(String sourcePath, String destinationPath)
{
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(sourcePath); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(destinationPath))
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length;
while ((length = in.read(buffer)) != -1)
{
out.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
} catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void copyFileWithBufferedStream(String sourcePath, String destinationPath)
{
try (BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(sourcePath));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destinationPath)))
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length;
while ((length = bis.read(buffer)) != -1)
{
bos.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
} catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
😋 输出结果