参考:
- metagpt环境配置参考
- 模型智能体开发之metagpt-单智能体实践
需求分析
- 之前有过单智能体的测试case,但是现实生活场景是很复杂的,所以单智能体远远不能满足我们的诉求,所以仍然还需要了解多智能体的实现。通过多个role对动作的关联、组合来构建一个工作流程,从而使智能体能够完成更加复杂的任务
- 基于单智能体测试case的扩展,我们的诉求在简单的输出code的基础上新增一条就是生成code并且立刻运行code。那么这个时候我们就需要两个action,一个负责生成code,一个负责执行code
实现
-
定义一个负责生成code的action,参照单智能体的测试case
模型智能体开发之metagpt-单智能体实践 -
定义一个负责运行code的action
class SimpleRunCode(Action): name: str = "SimpleRunCode" async def run(self, code_text: str): result = subprocess.run(["python3", "-c", code_text], capture_output=True, text=True) code_result = result.stdout logger.info(f"{code_result=}") return code_result- 运行code不需要调用llm,所以不涉及到prompt模版的设计
- 这里通过python的标准库 subprocess来fork一个子进程,运行一个外部程序
- subprocess:包内定义了多个可以创建子进程的函数,这些函数分别以不同的方法来创建子进程,所以按需使用即可
- 在本次的case里面通过subprocess.run在fork一个子进程执行传入的代码,那么在fork之后,存在两个进程,一个是python程序本身的进程,另一个就是subprocess.run创建的子进程,两个进程是互不干预的
- 在父进程中通过result.stdout来获取子进程的执行结果
-
定义 RunnableCoder 角色
-
完整的代码
class RunnableCoder(Role): name: str = "Alice" profile: str = "RunnableCoder" def __init__(self, **kwargs): super().__init__(**kwargs) self.set_actions([SimpleWriteCode, SimpleRunCode]) self._set_react_mode(react_mode=RoleReactMode.BY_ORDER.value) async def _act(self) -> Message: logger.info(f"{self._setting}: to do {self.rc.todo}({self.rc.todo.name})") # By choosing the Action by order under the hood # todo will be first SimpleWriteCode() then SimpleRunCode() todo = self.rc.todo msg = self.get_memories(k=1)[0] # find the most k recent messages result = await todo.run(msg.content) msg = Message(content=result, role=self.profile, cause_by=type(todo)) self.rc.memory.add(msg) return msg -
可以看到在重写init方法的时候,这里关联了两个actionSimpleWriteCode, SimpleRunCode
- 将
react_mode设置为 “by_order”,这意味着Role将按照self._init_actions中指定的顺序执行其能够执行的Action。在这种情况下,当Role执行_act时,self._rc.todo将首先是SimpleWriteCode,然后是SimpleRunCode。
def __init__(self, **kwargs): super().__init__(**kwargs) self.set_actions([SimpleWriteCode, SimpleRunCode]) self._set_react_mode(react_mode=RoleReactMode.BY_ORDER.value) - 将
-
重写act方法
- 覆盖
_act函数。Role从上一轮的人类输入或动作输出中检索消息,用适当的Message内容提供当前的Action(self._rc.todo),最后返回由当前Action输出组成的Message
async def _act(self) -> Message: logger.info(f"{self._setting}: to do {self.rc.todo}({self.rc.todo.name})") # By choosing the Action by order under the hood # todo will be first SimpleWriteCode() then SimpleRunCode() todo = self.rc.todo msg = self.get_memories(k=1)[0] # find the most k recent messages result = await todo.run(msg.content) msg = Message(content=result, role=self.profile, cause_by=type(todo)) self.rc.memory.add(msg) return msg - 覆盖
-
测试
-
代码
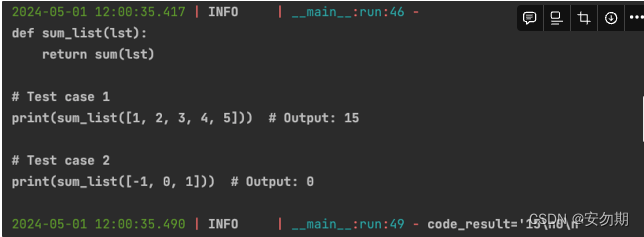
async def main(): msg = "write a function that calculates the sum of a list" role = RunnableCoder() logger.info(msg) result = await role.run(msg) logger.info(result) asyncio.run(main()) -
运行
-
-
-
demo如果想正常运行的话,需要调用llm的key,环境配置可以参照 metagpt环境配置参考