一 、关于vector
在STL中有一个称为vector的数据结构,可以用来代替数组。
定义Book特性
private:
vector<string> shelf_books;
Notic : 类中不能使用类似的定义:vector<sttring> shelf_boos( 10 );
定义Book方法
public:
void setName(string name)
{
shelf_books.push_back(name);
}
string getName(unsigned short idx)
{
if (idx < shelf_books.size())
return shelf_books[idx];
else
return "NULL";
}
unsigned short getSize(void)
{
return shelf_books.size();
}
vector<string>& getVector()
{
return shelf_books;
}
void display_all(void)
{
unsigned short idx = 0U;
cout << "There are " << shelf_books.size() << " books:" << endl;
for(string name : shelf_books)
{
cout << name << endl;
}
}
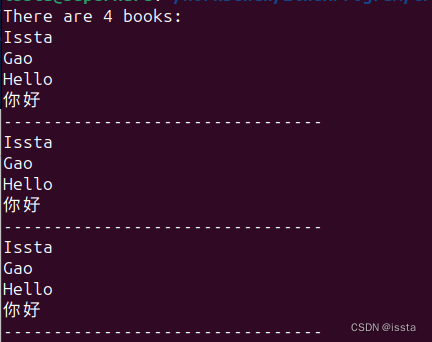
测试:
Book book;
book.setName("Issta");
book.setName("Gao");
book.setName("Hello");
book.setName("你好");
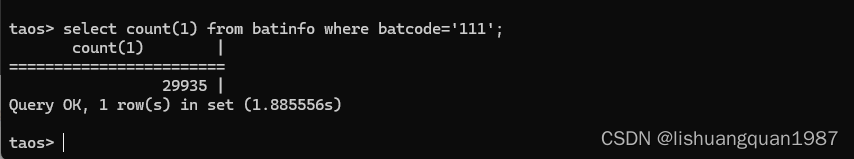
book.display_all();
cout << "--------------------------------" << endl;
vector<string>& b_v = book.getVector();
for(string _name : b_v)
{
cout << _name << endl;
}
cout << "--------------------------------" << endl;
for(unsigned short idx = 0; idx < book.getSize(); idx++)
{
cout << book.getName(idx) << endl;
}
cout << "--------------------------------" << endl;
输出:
二、静态vector与iterator
int key = itr->first; // 从迭代器中获得键
int value = itr->second; // 从迭代器中获得值
代码
vector<string> wap(5);
wap[0] = "激光大炮";
wap[1] = "巡航导弹";
wap[2] = "喀秋莎";
wap[3] = "导弹";
wap[4] = "东风快递使命必达";
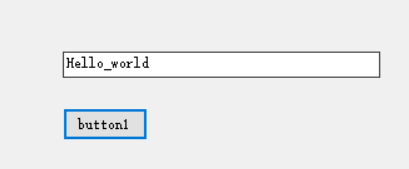
for(int i = 0; i < wap.size(); i++)
{
cout << wap[i] << endl;
}
cout << "Next using iterator..." << endl;
vector<string>::iterator wap_itr = wap.begin();
vector<string>::iterator wap_itr_end = wap.end();
for(; wap_itr != wap_itr_end; ++wap_itr)
{
cout << *wap_itr << endl;
}
cout << "--------------------------------" << endl;
测试结果

三、map与iterator
特征
private:
map<string, string> name_to_email;
属性
void add_context(string name, string email)
{
name_to_email["issta"] = "issta0309@163.com";
name_to_email[name] = email;
}
void show_email(void)
{
if(!name_to_email.empty())
{
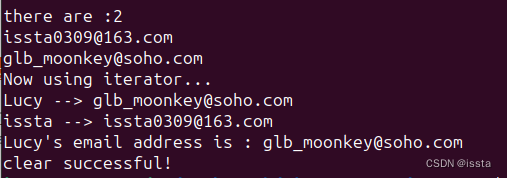
cout << "there are :" << name_to_email.size() << endl;
cout << name_to_email["issta"] << endl;
cout << name_to_email["Lucy"] << endl;
}
cout << "Now using iterator..." << endl;
map<string, string>::iterator map_itr = name_to_email.begin();
map<string, string>::iterator map_itr_end = name_to_email.end();
for(; map_itr != map_itr_end; ++map_itr)
{
cout << map_itr->first << " --> " << map_itr->second << endl;
}
map<string, string>::iterator find_itr = name_to_email.find("Lucy");
if(find_itr != map_itr_end)
{
cout << "Lucy's email address is : " << find_itr->second << endl;
}
name_to_email.clear();
if(name_to_email.empty())
{
cout << "clear successful!" << endl;
}
测试代码
book.add_context("Lucy", "glb_moonkey@soho.com");
book.show_email();
运行结果