实验一 Hadoop伪分布式实验环境搭建与WordCount程序
一、实验目的
1、学习搭建Hadoop伪分布式实验环境
2、在伪分布式实验环境下运行WordCount程序
二、实验内容
1、搭建Hadoop伪分布式实验环境,并安装Eclipse。
2、在Eclipse环境下,编写并执行WordCount程序。
三、实验步骤
1.创建hadoop用户
sudo useradd -m hadoop -s /bin/bash
sudo passwd hadoop
sudo adduser hadoop sudo
2.更新ubuntu软件包
sudo apt-get update
3.安装vim
sudo apt install vim
安装软件时若需要确认,在提示处输入 y 即可
vim的常用模式有分为命令模式,插入模式,可视模式,正常模式。本教程中,只需要用到正常模式和插入模式。二者间的切换即可以帮助你完成本指南的学习。
(1)正常模式
正常模式主要用来浏览文本内容。一开始打开vim都是正常模式。在任何模式下按下Esc键就可以返回正常模式
(2)插入编辑模式
插入编辑模式则用来向文本中添加内容的。在正常模式下,输入i键即可进入插入编辑模式
(3)退出vim
如果有利用vim修改任何的文本,一定要记得保存。Esc键退回到正常模式中,然后输入:wq即可保存文本并退出vim
4.安装SSH、配置SSH无密码登陆
sudo apt-get install openssh-server
ssh localhost
首先退出刚才的 ssh,就回到了我们原先的终端窗口,然后利用 ssh-keygen 生成密钥,并将密钥加入到授权中:
exit # 退出刚才的 ssh localhost
cd ~/.ssh/ # 若没有该目录,请先执行一次ssh localhost
ssh-keygen -t rsa # 会有提示,都按回车就可以
cat ./id_rsa.pub >> ./authorized_keys # 加入授权
5.安装Java环境
cd /usr/lib
sudo mkdir jvm #创建/usr/lib/jvm目录用来存放JDK文件
cd ~ #进入hadoop用户的主目录
cd Downloads #注意区分大小写字母,刚才已经通过FTP软件把JDK安装包jdk-8u371-linux-x64.tar.gz上传到该目录下
sudo tar -zxvf ./jdk-8u371-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /usr/lib/jvm #把JDK文件解压到/usr/lib/jvm目录下
JDK文件解压缩以后,可以执行如下命令到/usr/lib/jvm目录查看一下:
cd /usr/lib/jvm
ls
可以看到,在/usr/lib/jvm目录下有个jdk1.8.0_371目录。
下面继续执行如下命令,设置环境变量:
cd ~
vim ~/.bashrc
打开了hadoop这个用户的环境变量配置文件,请在这个文件的开头位置,添加如下几行内容:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.8.0_371
export JRE_HOME=${JAVA_HOME}/jre
export CLASSPATH=.:${JAVA_HOME}/lib:${JRE_HOME}/lib
export PATH=${JAVA_HOME}/bin:$PATH
保存.bashrc文件并退出vim编辑器。然后,继续执行如下命令让.bashrc文件的配置立即生效:
source ~/.bashrc
查看是否安装成功
java -version
6.安装 Hadoop3.3.5
将 Hadoop 安装至 /usr/local/ 中:
sudo tar -zxvf ~/下载/hadoop-3.3.5.tar.gz -C /usr/local
# 解压到/usr/local中
cd /usr/local/
sudo mv ./hadoop-3.3.5/ ./hadoop # 将文件夹名改为hadoop
sudo chown -R hadoop ./hadoop # 修改文件权限
Hadoop 解压后即可使用。输入如下命令来检查 Hadoop 是否可用,成功则会显示 Hadoop 版本信息:
cd /usr/local/hadoop
./bin/hadoop version
7.Hadoop伪分布式配置
修改配置文件 core-site.xml (通过 gedit 编辑会比较方便: gedit ./etc/hadoop/core-site.xml)
<configuration>
<property>
<name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name>
<value>file:/usr/local/hadoop/tmp</value>
<description>Abase for other temporary directories.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://localhost:9000</value>
</property>
</configuration>
修改配置文件 hdfs-site.xml:
<configuration>
<property>
<name>dfs.replication</name>
<value>1</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.name.dir</name>
<value>file:/usr/local/hadoop/tmp/dfs/name</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name>
<value>file:/usr/local/hadoop/tmp/dfs/data</value>
</property>
</configuration>
配置完成后,执行 NameNode 的格式化:
cd /usr/local/hadoop
./bin/hdfs namenode -format
接着开启 NameNode 和 DataNode 守护进程:
cd /usr/local/hadoop
./sbin/start-dfs.sh
四、实验结果
cd /usr/local/hadoop
./sbin/start-dfs.sh
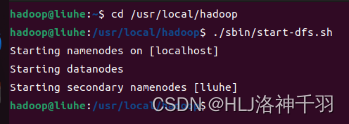
jps

访问web页面
localhost:9870

详细可参考
厦门大学林子雨教授安装教程
https://dblab.xmu.edu.cn/blog/2441/
词频统计
https://dblab.xmu.edu.cn/blog/4289/
实验二 Hadoop二次排序程序
一、实验目的
1、掌握大数据排序程序的原理
2、掌握大数据二次排序程序的设计方法
二、实验内容
1、设计一个关于温度的二次排序程序。
2、设计一个关于时间序列数据的二次排序程序(选作)。
三、实验步骤
1、启动HDFS文件系统,并将输入数据上传到HDFS文件系统中。
2、利用eclipse建立一个Hadoop工程,编写程序代码,设计一个关于温度的二次排序程序。
3、实验参考数据
输入数据:
2000,12,04,10
2000,11,01,20
2000,12,02,-20
2000,11,07,30
2000,11,24,-40
2012,12,21,30
2012,12,22,-20
2012,12,23,60
2012,12,24,70
2012,12,25,10
2013,01,23,90
2013,01,24,70
2013,01,20,-10
输出数据
201301 90, 70, -10
201212 70, 60, 30, 10, -20
200012 10, -20
200011 30, 20, -40
四、实验代码
DateTemperatureGroupingComparator类
package twosort;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
//分组比较器
// 根据DateTemperaturePair对象的YearMonth字段进行比较,
// 确保具有相同YearMonth的键值对被分到同一个Reducer进行处理,
// 以便在Reducer阶段对具有相同日期的数据进行分组聚合
public class DateTemperatureGroupingComparator extends WritableComparator {
public DateTemperatureGroupingComparator() {
super(DateTemperaturePair.class, true);
}
// 重写的compare方法中,首先将参数wc1和wc2强制转换为DateTemperaturePair对象,
// 然后通过比较这两个对象的YearMonth字段来确定它们的顺序。
// 最终返回比较结果,用于确定键值对在Reducer阶段的分组。
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable wc1, WritableComparable wc2) {
DateTemperaturePair pair = (DateTemperaturePair) wc1;
DateTemperaturePair pair2 = (DateTemperaturePair) wc2;
return pair.getYearMonth().compareTo(pair2.getYearMonth());
}
}
/*
分区器会根据映射器的输出键来决定哪个映射器的输出发送到哪个规约器。
为此我们需要定义两个插件类
首先需要一个定制分区器控制哪个规约器处理哪些键,
另外还要定义一个定制比较器对规约器值排序。
这个定制比较器对规约器值排序,
它会控制哪些键要分组到一个Reducer.reduce()函数调用
*/
DateTemperaturePair类
package twosort;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
//DateTemperaturePair是自定义的数据类型,用于存储日期和温度信息。
//在Map阶段,将输入数据解析为DateTemperaturePair对象
//在Reduce阶段,作为中间结果的键值对进行传递
//组合键数据结构
public class DateTemperaturePair implements Writable, WritableComparable<DateTemperaturePair> {
//年月
private final Text yearMonth = new Text();
//日
private final Text day = new Text();
//温度
private final IntWritable temperature = new IntWritable();
public DateTemperaturePair() {
}
public DateTemperaturePair(String yearMonth, String day, int temperature) {
this.yearMonth.set(yearMonth);
this.day.set(day);
this.temperature.set(temperature);
}
// 用于从输入流中读取数据并返回DateTemperaturePair对象
public static DateTemperaturePair read(DataInput in) throws IOException {
DateTemperaturePair pair = new DateTemperaturePair();
pair.readFields(in);
return pair;
}
// 将对象的数据写入输出流
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
yearMonth.write(out);
day.write(out);
temperature.write(out);
}
// 从输入流中读取数据并设置对象的属性
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
yearMonth.readFields(in);
day.readFields(in);
temperature.readFields(in);
}
// 比较两个DateTemperaturePair对象的年月和温度信息,用于排序
// 根据年月和温度进行比较,实现二次排序
@Override
public int compareTo(DateTemperaturePair pair) {
int compareValue = this.yearMonth.compareTo(pair.getYearMonth());
if (compareValue == 0) {//如果年月相等,再比较温度
compareValue = temperature.compareTo(pair.getTemperature());
}
return -1 * compareValue;
}
public Text getYearMonthDay() {
return new Text(yearMonth.toString() + day.toString());
}
public Text getYearMonth() {
return yearMonth;
}
public Text getDay() {
return day;
}
public IntWritable getTemperature() {
return temperature;
}
public void setYearMonth(String yearMonthAsString) {
yearMonth.set(yearMonthAsString);
}
public void setDay(String dayAsString) {
day.set(dayAsString);
}
public void setTemperature(int temp) {
temperature.set(temp);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
DateTemperaturePair that = (DateTemperaturePair) o;
if (temperature != null ? !temperature.equals(that.temperature) : that.temperature != null) {
return false;
}
if (yearMonth != null ? !yearMonth.equals(that.yearMonth) : that.yearMonth != null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = yearMonth != null ? yearMonth.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + (temperature != null ? temperature.hashCode() : 0);
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("DateTemperaturePair{yearMonth=");
builder.append(yearMonth);
builder.append(", day=");
builder.append(day);
builder.append(", temperature=");
builder.append(temperature);
builder.append("}");
return builder.toString();
}
}
DateTemperaturePartitioner类
package twosort;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
// 分区器类
// 根据DateTemperaturePair的YearMonth字段的哈希值来选择分区,
// 以确保相同YearMonth的键值对被分配到相同的分区。
// 这有助于在Reducer阶段对相同日期的数据进行聚合处理。
public class DateTemperaturePartitioner extends Partitioner<DateTemperaturePair, Text> {
//首先,通过pair.getYearMonth().hashCode()获取YearMonth的哈希值,然后取绝对值以确保分区数是非负的。
//接着,通过取哈希值与分区数取模的方式,将键值对映射到具体的分区。
//最后,返回计算得到的分区号作为结果。
@Override
public int getPartition(DateTemperaturePair pair, Text text, int numberOfPartitions) {
return Math.abs(pair.getYearMonth().hashCode() % numberOfPartitions);
}
}
/*
* 定制分区器
* 分区器会根据映射器的输出键来决定哪个映射器的输出发送到哪个规约器。为此我们需要定义两个插件类
* 首先需要一个定制分区器控制哪个规约器处理哪些键,另外还要定义一个定制比较器对规约器值排序。
* 这个定制分区器可以确保具有相同键(自然键,而不是包含温度值的组合键)的所有数据都发送给同一个规约器。
* 定制比较器会完成排序,保证一旦数据到达规约器,就会按自然键对数据分组。
*/SecondarySortDriver类
package twosort;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
//SecondarySortDriver是驱动程序,用于配置和运行MapReduce任务。
//在Driver中设置Mapper、Reducer、Partitioner、GroupingComparator等组件。
//配置作业的输入输出路径,以及其他相关参数。
//最终启动整个MapReduce作业的运行。
public class SecondarySortDriver extends Configured implements Tool {
private static final String INPATH = "input/twosort.txt";// 输入文件路径
private static final String OUTPATH = "output/sample_output";// 输出文件路径
private static Logger theLogger = Logger.getLogger(SecondarySortDriver.class);
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = getConf();
Job job = new Job(conf);
job.setJarByClass(SecondarySortDriver.class);
job.setJobName("SecondarySortDriver");
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.setOutputKeyClass(DateTemperaturePair.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setMapperClass(SecondarySortMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(SecondarySortReducer.class);
job.setPartitionerClass(DateTemperaturePartitioner.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(DateTemperatureGroupingComparator.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));// 为map-reduce任务设置OutputFormat实现类
// 设置输出路径
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
Path outPath = new Path(OUTPATH);
if (fs.exists(outPath)) {
fs.delete(outPath, true);
}
boolean status = job.waitForCompletion(true);
theLogger.info("run(): status=" + status);
return status ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
args = new String[2];
args[0] = INPATH;
args[1] = OUTPATH;
// Make sure there are exactly 2 parameters
if (args.length != 2) {
theLogger.warn("SecondarySortDriver <input-dir> <output-dir>");
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"SecondarySortDriver <input-dir> <output-dir>");
}
int returnStatus = submitJob(args);
theLogger.info("returnStatus=" + returnStatus);
System.exit(returnStatus);
}
public static int submitJob(String[] args) throws Exception {
int returnStatus = ToolRunner.run(new SecondarySortDriver(), args);
return returnStatus;
}
}
SecondarySortMapper类
package twosort;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
// 该Mapper类将输入的数据解析成年月日和温度信息,
// 然后创建一个DateTemperaturePair对象来存储这些信息,并将温度信息存储在Text对象中。
// 最后,将DateTemperaturePair对象作为键,温度信息作为值输出到Reducer阶段进行进一步处理。
public class SecondarySortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, DateTemperaturePair, Text> {
private final Text theTemperature = new Text();
private final DateTemperaturePair pair = new DateTemperaturePair();
// 重写了Mapper类的map方法,实现了具体的映射逻辑。
// 在该方法中,首先将输入的Text类型的数据转换为字符串,并进行处理。
// 然后根据逗号分割字符串得到年、月、日和温度信息,分别设置到pair对象中。
// 接着将温度信息设置到theTemperature对象中,并通过context.write方法输出键值对。
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString().trim();
String[] tokens = line.split(",");
// YYYY = tokens[0]
// MM = tokens[1]
// DD = tokens[2]
// temperature = tokens[3]
String yearMonth = tokens[0] + tokens[1];
String day = tokens[2];
int temperature = Integer.parseInt(tokens[3]);
pair.setYearMonth(yearMonth);
pair.setDay(day);
pair.setTemperature(temperature);
theTemperature.set(tokens[3]);
context.write(pair, theTemperature);
}
}
SecondarySortReducer类
package twosort;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
//具有相同年月的温度值连接成一个字符串,并以年月作为键,连接后的字符串作为值输出
public class SecondarySortReducer extends Reducer<DateTemperaturePair, Text, Text, Text> {
@Override
protected void reduce(DateTemperaturePair key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (Text value : values) {
builder.append(value.toString());
builder.append(",");
}
context.write(key.getYearMonth(), new Text(builder.toString()));
}
}
/*
规约器
对于已经按年-月分区,分区内按温度排好序的键和值集合,
进行规约,即按顺序写成一行
*/pom文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>TwoSortDemo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>3.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.30</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>包结构
五、操作步骤
1.首先启动Hadoop

2.查看自己/user/hadoop/目录下有没有input、output文件夹,有的话删除。

3.重新创建input文件夹
![]()
4.查看input文件夹是否创建出来

5.编辑测试用例的文件twosort.txt

twosort.txt内容为:
2000,12,04,10
2000,11,01,20
2000,12,02,-20
2000,11,07,30
2000,11,24,-40
2012,12,21,30
2012,12,22,-20
2012,12,23,60
2012,12,24,70
2012,12,25,10
2013,01,23,90
2013,01,24,70
2013,01,20,-10
6.将文件上传到input文件夹

7.利用idea将代码打成jar包,将jar包放在/usr/local/hadoop/myapp目录下

8.运行jar包

9.查看结果

实验三 Hadoop TopN程序
一、实验目的
1、掌握大数据多个MapReduce任务程序的设计方法
2、掌握大数据TopN程序的设计方法
二、实验内容
1、设计一个关于TopN的程序。
三、实验步骤
1、启动HDFS文件系统,并将输入数据上传到HDFS文件系统中。
2、利用eclipse建立一个Hadoop工程,编写程序代码,设计一个关于TopN的程序。
3、实验参考数据
输入数据:
A,1
B,24
C,33
D,24
E,13
G,25
Z,100
输出数据:
100 Z
73 A
37 C
29 G
27 B
四、实验代码
package topn;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class TopN {
public static class TopNMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, IntWritable, Text> {
private TreeMap<Integer, String> topNMap = new TreeMap<>();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] tokens = value.toString().split(",");
String word = tokens[0];
int count = Integer.parseInt(tokens[1]);
topNMap.put(count, word);
}
public void cleanup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Integer key : topNMap.descendingKeySet()) {
context.write(new IntWritable(key), new Text(topNMap.get(key)));
}
}
}
public static class TopNReducer extends Reducer<IntWritable, Text, IntWritable, Text> {
private TreeMap<Integer, String> topNMap = new TreeMap<>();
public void reduce(IntWritable key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String word = "";
int count = key.get();
for (Text value : values) {
word = value.toString();
}
topNMap.put(count, word);
if (topNMap.size() > 5) {
topNMap.remove(topNMap.firstKey());
}
}
public void cleanup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Integer key : topNMap.descendingKeySet()) {
context.write(new IntWritable(key), new Text(topNMap.get(key)));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "TopN");
job.setJarByClass(TopN.class);
job.setMapperClass(TopNMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(TopNReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("input/topn.txt"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("output"));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
pom文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>TopN</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>3.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.30</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>五、操作步骤
1.首先启动Hadoop

2.查看自己/user/hadoop/目录下有没有input、output文件夹,有的话删除。
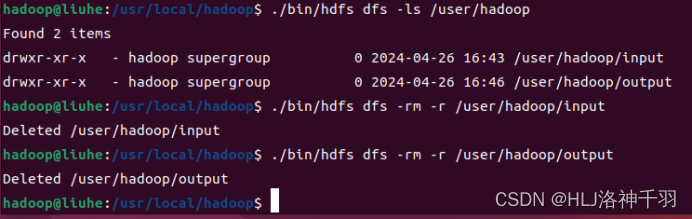
3.重新创建input文件夹
![]() 4.查看input文件夹是否创建出来
4.查看input文件夹是否创建出来

5.编辑测试用例的文件topn.txt

topn.txt内容为:
A,1
B,24
C,33
D,24
E,13
G,25
Z,100
6.将文件上传到input文件夹
 7.利用idea将代码打成jar包,将jar包放在/usr/local/hadoop/myapp目录下
7.利用idea将代码打成jar包,将jar包放在/usr/local/hadoop/myapp目录下

8.运行jar包
 9.查看结果
9.查看结果