重点标识
csrf 攻击防御演示!
源码分析!
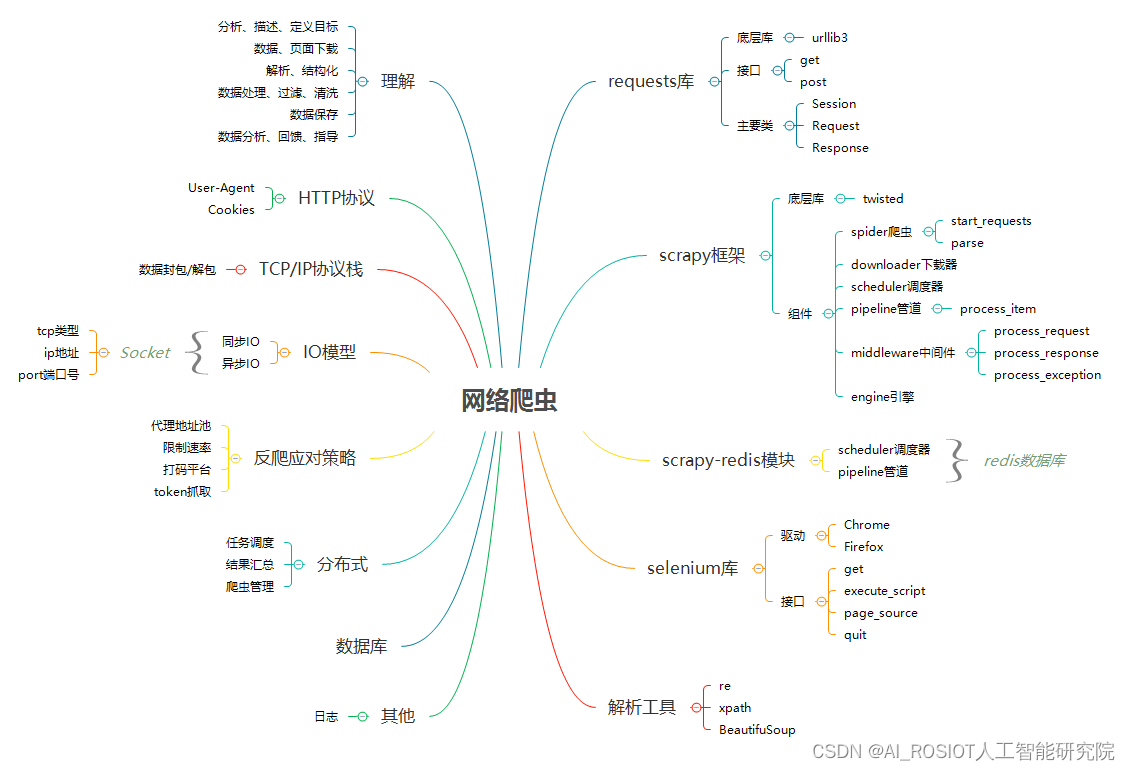
CSRF攻击与防御
CSRF是什么 ,跨站请求伪造,简单解释一下,就是用户登录某个界面,如银行界面,进行转账,完了之后并没有注销登录,而是打开一新的页面,在页面上点击了某个攻击者设下的链接,那么这个链接,就可以带着浏览器存储的cookie,发送给银行服务器,由于已经认证过了,所以银行服务器以为是用户自己的操作,就达成了攻击者的目的。
csrf攻击演示
首先,创建一个Spring Boot工程,加入web和Security依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
然后,简单配置一下,生成一个账号,以及关闭Security自带的对CSRF的防御。
@Configuration
public class Security {
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests(a->a.anyRequest().authenticated())
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults())
.csrf(c->c.disable());
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public InMemoryUserDetailsManager inMemoryUserDetailsManager() {
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(
User.withUsername("admin").password("{noop}123").roles().build()
);
}
}
再提供一个测试的接口和界面:
@RestController
public class WithDrawController {
@PostMapping("/withdraw")
public void withdraw(String from,String to,String amount) {
System.out.println("执行了一次转账操作!");
System.out.println("from:"+from);
System.out.println("to:"+to);
System.out.println("amount:"+amount);
}
}
测试界面:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/withdraw" method="post">
<tr>
<td>转出账户</td>
<td><input type="text" name="from" value="zhangsan"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>转入账户</td>
<td><input type="text" name="to" value="lisi"></td>
</tr> <tr>
<td>转入金额</td>
<td><input type="text" name="amount" value="1000"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="转账"></td>
</tr>
</form>
</body>
</html>
然后,创建第二个攻击者的项目,这次只需要加一个web依赖就行,改一下端口号:
server.port=8081
然后,提供一个具备诱惑力的界面:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/withdraw" method="post">
<tr>
<td><input type="hidden" name="from" value="zhangsan"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="hidden" name="to" value="lisi"></td>
</tr> <tr>
<td><input type="hidden" name="amount" value="1000"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="我是一张非常有诱惑力的图片"></td>
</tr>
</form>
</body>
</html>
启动项目,如此便可以测试了。
我们登录第一个项目,然后点击转账,后台会出现模拟转账的打印,然后,进入第二个项目的界面,直接点那张具备诱惑力的图片,然后,就会发现,项目一,依然打印了转账的操作日志,这个就是跨站请求伪造。
本质上,就是浏览器自动携带cookie信息,攻击者的界面携带者被攻击者已经认证过的cookie,j进行了一次伪造操作。
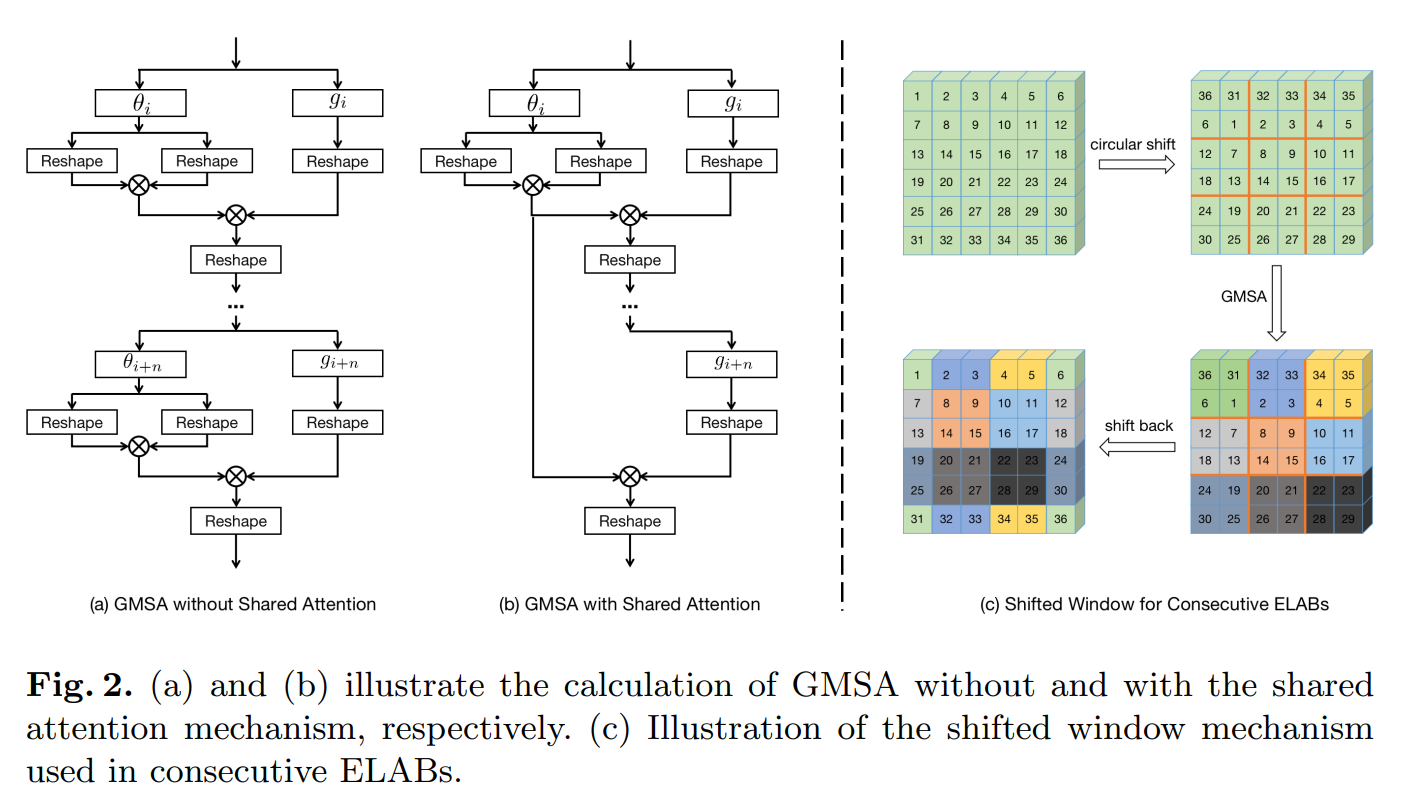
Security提供的csrf防御
如果使用Security默认的防御策略,则就是这个样子,403.
· .csrf(Customizer.withDefaults());·
他的解决思路,其实很简单,除了携带cookie之外,额外需要一个令牌,有令牌才通过,没有令牌就不通过。
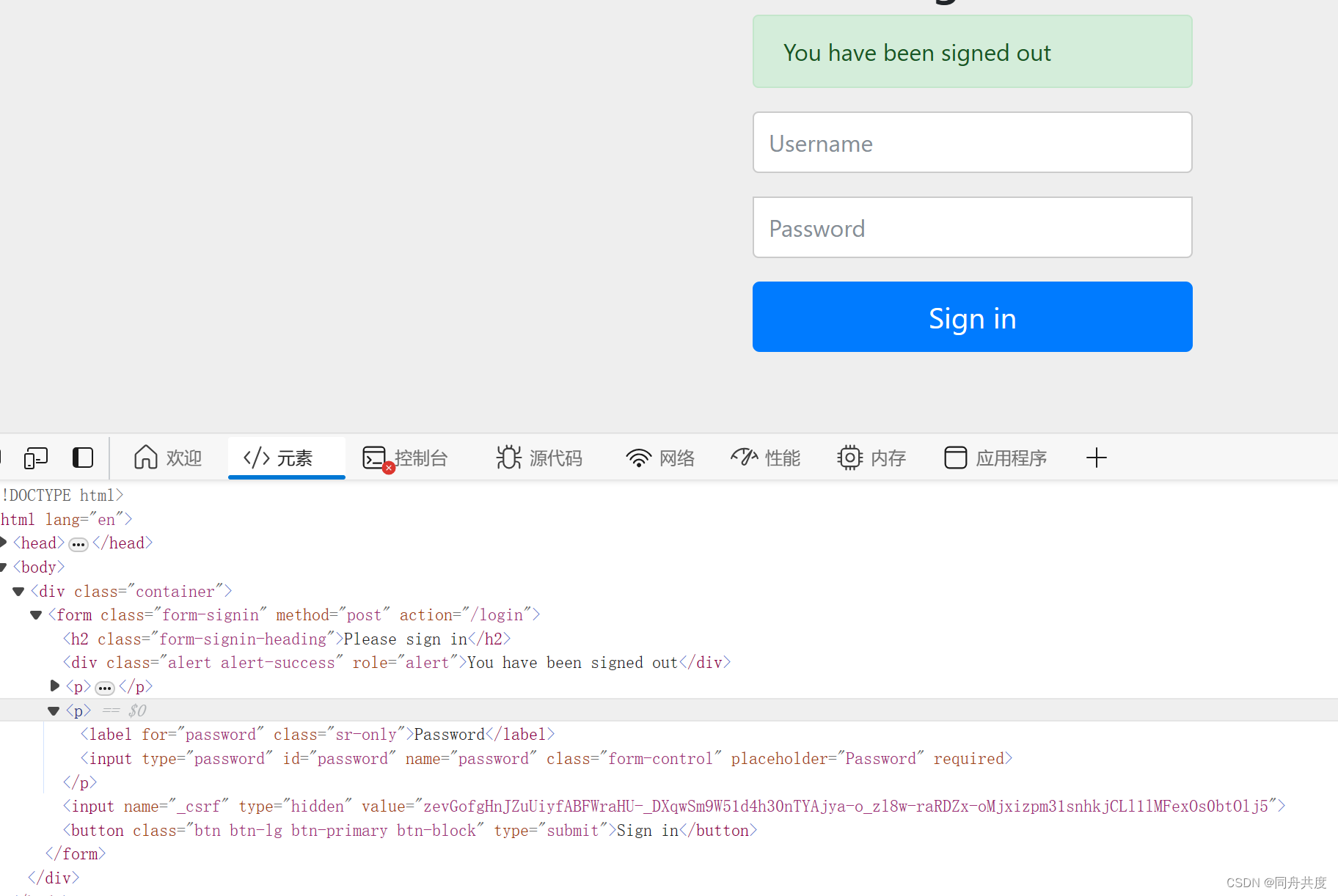
可以看到,登陆界面,多了一个隐藏的csrf令牌。
这样的话,就可以保证它的安全性了,但是这样,又产生了一个新的问题,我们自己的页面,也无法转账了,这是因为没有这个csrf的值。
有两种方案将csrf放到我们的页面中,第一种
使用thymeleaf模板
加一下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
增加一个接口
@GetMapping("/02")
public String index() {
return "02";
}
在templates下面,创建一个html和上一个相比,就多了个csrf令牌;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/withdraw" method="post">
<tr>
<td>转出账户</td>
<td><input type="text" name="from" value="zhangsan"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>转入账户</td>
<td><input type="text" name="to" value="lisi"></td>
</tr> <tr>
<td>转入金额</td>
<td><input type="text" name="amount" value="1000"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<input type="hidden" name="${_csrf.parameterName}" th:value="${_csrf.token}">
<td><input type="submit" value="转账"></td>
</tr>
</form>
</body>
</html>
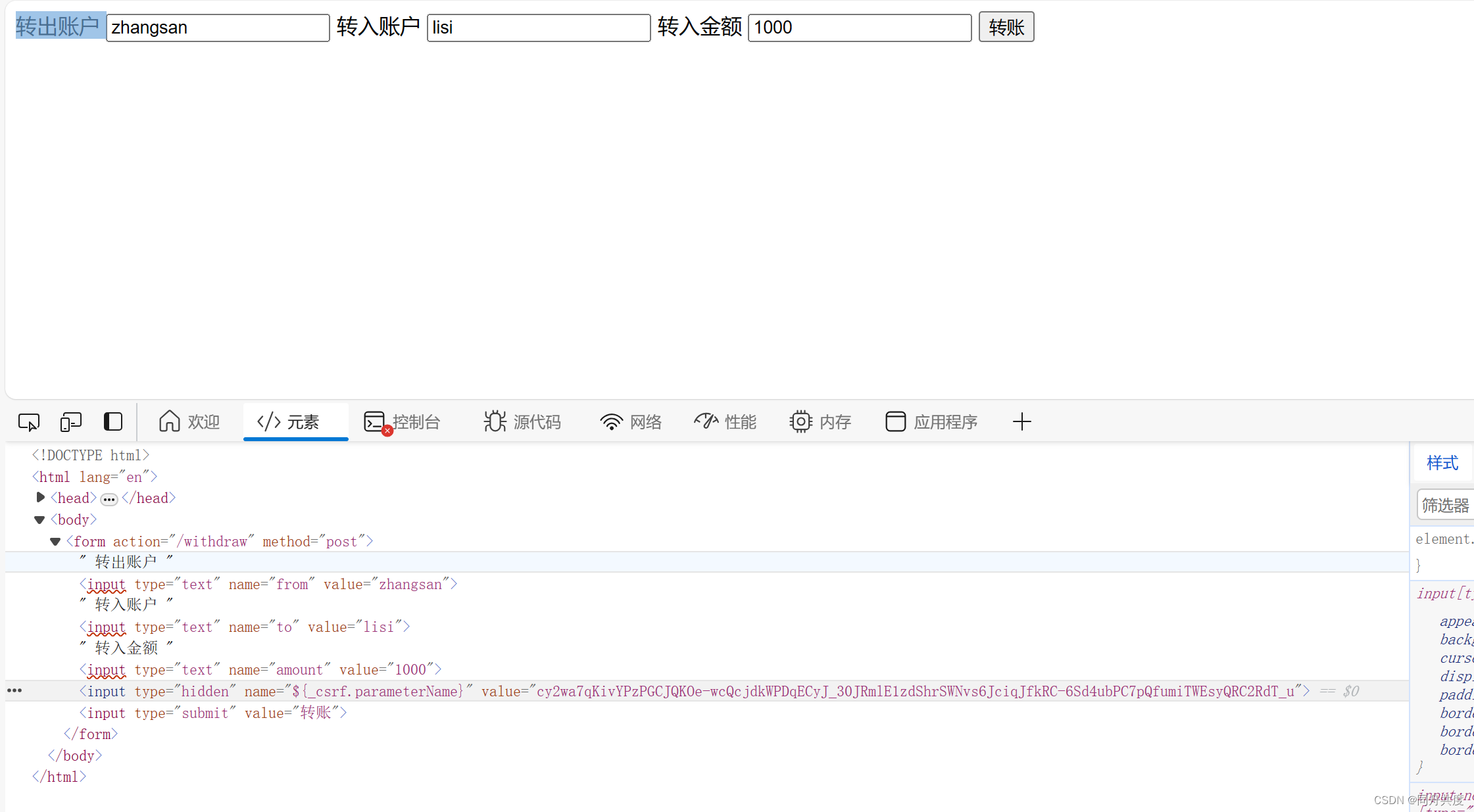
模板会自动将csrf令牌渲染上去,这样,攻击者自然就拿不到了,这是第一种方法,但是,如果不想使用thymeleaf,也可以使用第二种。
令牌存储器
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests(a->a.anyRequest().authenticated())
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults())
//设置令牌存储方式,将令牌存储在cookie中
.csrf(c-> c.csrfTokenRepository(CookieCsrfTokenRepository.withHttpOnlyFalse()));
return http.build();
}
这样存储下,后,我们在启动就可以看到在请求头中就会多出这样一个东西
XSRF-TOKEN=3fb8cd4e-69dd-4a4f-8527-91b6405ed7b8
这个cookie就是为了防御csrf攻击生成的令牌,请求参数中要携带着它,才能正常访问。我们知道,csrf说白了,就是利用浏览器不区分cookie的特点,全部一股脑地,发送给服务器,开启了令牌存储,httponly只读设置为false,则就能从cookie中获取到令牌的信息的加以处理了。
至于令牌的信息会不会被盗用,这又是另一个漏洞。
源码分析
看一下CsrfFilter过滤器,在它的doFilterInternal中执行了具体的逻辑。
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//返回的数据加上csrf
DeferredCsrfToken deferredCsrfToken = this.tokenRepository.loadDeferredToken(request, response);
request.setAttribute(DeferredCsrfToken.class.getName(), deferredCsrfToken);
this.requestHandler.handle(request, response, deferredCsrfToken::get);
//查看当前请求是否满足csrf保护,我们知道GET请求是不涉及CSRF的 登录请求直接从这里就走了
if (!this.requireCsrfProtectionMatcher.matches(request)) {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Did not protect against CSRF since request did not match "
+ this.requireCsrfProtectionMatcher);
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
//拿到令牌,进行验证!
CsrfToken csrfToken = deferredCsrfToken.get();
String actualToken = this.requestHandler.resolveCsrfTokenValue(request, csrfToken);
if (!equalsConstantTime(csrfToken.getToken(), actualToken)) {
boolean missingToken = deferredCsrfToken.isGenerated();
this.logger
.debug(LogMessage.of(() -> "Invalid CSRF token found for " + UrlUtils.buildFullRequestUrl(request)));
AccessDeniedException exception = (!missingToken) ? new InvalidCsrfTokenException(csrfToken, actualToken)
: new MissingCsrfTokenException(actualToken);
this.accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response, exception);
return;
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
看下这个handle方法,很简单csrfRequestAttributeName 是不是空的,不是就用自定义的,没有自定义,则使用默认的,也就是this.csrfRequestAttributeName
private String csrfRequestAttributeName = "_csrf";
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Supplier<CsrfToken> deferredCsrfToken) {
Assert.notNull(request, "request cannot be null");
Assert.notNull(response, "response cannot be null");
Assert.notNull(deferredCsrfToken, "deferredCsrfToken cannot be null");
request.setAttribute(HttpServletResponse.class.getName(), response);
CsrfToken csrfToken = new SupplierCsrfToken(deferredCsrfToken);
request.setAttribute(CsrfToken.class.getName(), csrfToken);
String csrfAttrName = (this.csrfRequestAttributeName != null) ? this.csrfRequestAttributeName
: csrfToken.getParameterName();
request.setAttribute(csrfAttrName, csrfToken);
}
key为_csrf,value则为CsrfToken对象
public interface CsrfToken extends Serializable {
/**
* Gets the HTTP header that the CSRF is populated on the response and can be placed
* on requests instead of the parameter. Cannot be null.
* @return the HTTP header that the CSRF is populated on the response and can be
* placed on requests instead of the parameter
*/
String getHeaderName();
/**
* Gets the HTTP parameter name that should contain the token. Cannot be null.
* @return the HTTP parameter name that should contain the token.
*/
String getParameterName();
/**
* Gets the token value. Cannot be null.
* @return the token value
*/
String getToken();
}
就是在这里渲染了csrf。