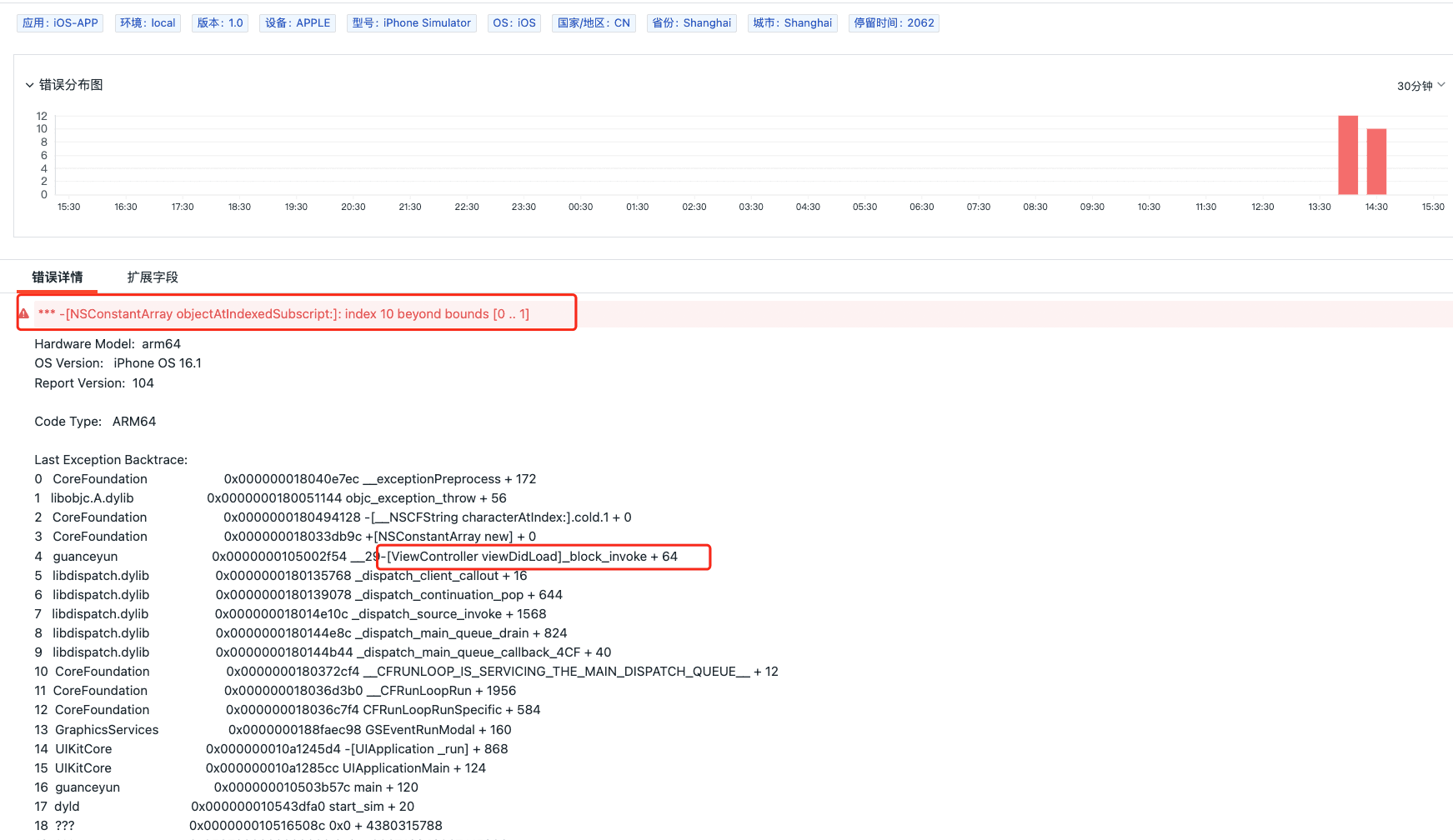
顺序表的应用-通讯录
- 1.操作
- 2.功能要求
- 2.1.功能要求
- 2.2.思路小结
- 2.3.文件梳理
- 2.4.代码实现
- "SeqList.h"
- "Contact.h"
- "SeqList.c"
- "Contact.c"
- "test.c"
1.操作
链接: 顺序表专题
这篇文章介绍了顺序表的概念与基本操作。
本文将在此基础上进行一定的拓展,完成应用通讯表。
2.功能要求
2.1.功能要求
1)至少能够存储100个⼈的通讯信息
2)能够保存用户信息:名字、性别、年龄、电话、地址等
3)增加联系人信息
4)删除指定联系人
5)查找制定联系人
6)修改指定联系人
7)显示联系人信息
2.2.思路小结
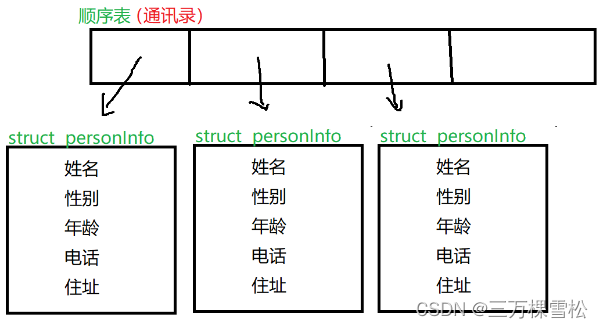
简单来说,通讯录与之前的最典型顺序表的区别在于数组存储的类型.
最典型顺序表存储的就是整数类型,是一个个数字.
而通讯录则是在数组中存储相关结构体,包含功能要求的信息.
除此之外,基本操作思路与代码都如出一辙.
- 定义通讯录信息存储结构体类型
#define NAME_MAX 20
#define GENDER_MAX 10
#define TEL_MAX 20
#define ADDR_MAX 100
//定义联系人数据 结构
//姓名 性别 年龄 电话 地址
typedef struct personInfo
{
char name[NAME_MAX];
char gender[GENDER_MAX];
int age;
char tel[TEL_MAX];
char addr[ADDR_MAX];
}peoInfo;
- 定义动态顺序表基本结构
typedef peoInfo SLDataType;
//动态顺序表
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* arr;
int size; //有效数据个数
int capacity; //空间大小
}SL;
- 各种操作
//通讯录的初始化
void ContactInit(Contact* con);
//通讯录的销毁
void ContactDesTroy(Contact* con);
//通讯录添加数据
void ContactAdd(Contact* con);
//通讯录删除数据
void ContactDel(Contact* con);
//通讯录的修改
void ContactModify(Contact* con);
//通讯录查找
void ContactFind(Contact* con);
//展示通讯录数据
void ContactShow(Contact* con);
- 菜单显示
int main()
{
int op = -1;
Contact con;
ContactInit(&con);
do {
menu();
printf("请选择您的操作:\n");
scanf("%d", &op);
//要根据对应的op执行不同的操作
switch (op)
{
case 1:
ContactAdd(&con);
break;
case 2:
ContactDel(&con);
break;
case 3:
ContactModify(&con);
break;
case 4:
ContactFind(&con);
break;
case 5:
ContactShow(&con);
break;
case 0:
printf("退出通讯录....\n");
break;
default:
printf("输入错误,请重新选择您的操作!\n");
break;
}
} while (op != 0);
ContactDesTroy(&con);
return 0;
}
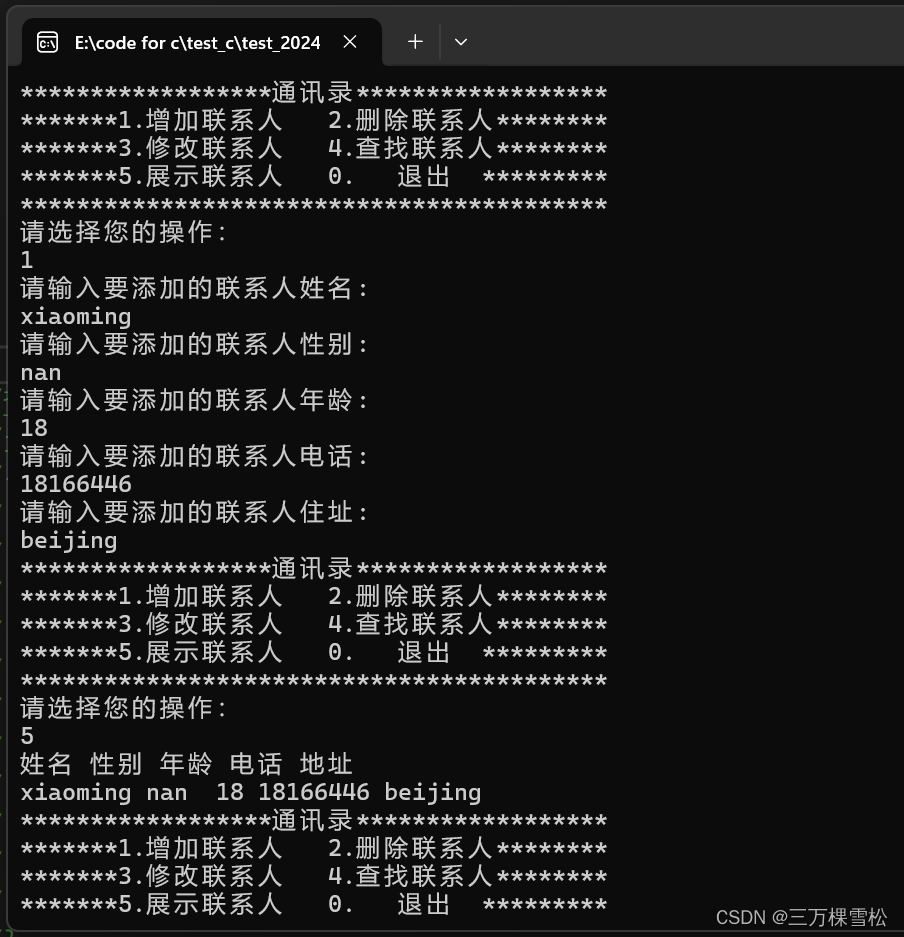
2.3.文件梳理
主要有5个文件,
2个.h头文件:
“SeqList.h”主要是基本顺序表操作的罗列
“Contact.h”
主要是通讯录操作的罗列
“Contact.h"是在"SeqList.h"的基础上发展而来的.
部分通用的代码按照"SeqList.h”
需要调整的代码主要写于"Contact.h"
3个.c源文件.
“SeqList.c”顺序表操作的具体代码实现
“Contact.c”
通讯录操作的具体代码实现
“test.c”
调试测试
2.4.代码实现
“SeqList.h”
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include"Contact.h"
//定义顺序表的结构
//#define N 100
//
静态顺序表
//struct SeqList
//{
// int arr[N];
// int size;//有效数据个数
//};
//typedef int SLDataType;//方便后续类型的替换
typedef peoInfo SLDataType;
//动态顺序表
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* arr;
int size; //有效数据个数
int capacity; //空间大小
}SL;
//typedef struct SeqList SL;
//顺序表初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps);
//顺序表的销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);
void SLPrint(SL s);
//头部插入删除 / 尾部插入删除
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);
//指定位置之前插入/删除数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);
//查找指定位置
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
“Contact.h”
#pragma once
#define NAME_MAX 20
#define GENDER_MAX 10
#define TEL_MAX 20
#define ADDR_MAX 100
//定义联系人数据 结构
//姓名 性别 年龄 电话 地址
typedef struct personInfo
{
char name[NAME_MAX];
char gender[GENDER_MAX];
int age;
char tel[TEL_MAX];
char addr[ADDR_MAX];
}peoInfo;
//要用到顺序表相关的方法,对通讯录的操作实际就是对顺序表进行操作
//给顺序表改个名字,叫做通讯录
typedef struct SeqList Contact; //前置声明+改名字成Contact
//不能直接用SL 原因是SL是struct SeqList定义之后取得新名字,如果是用当前顺序表这个结构,必须用struct SeqList
// 或者说,写SL不能直接找到顺序表这个结构体
//通讯录相关的方法
//通讯录的初始化
void ContactInit(Contact* con);
//通讯录的销毁
void ContactDesTroy(Contact* con);
//通讯录添加数据
void ContactAdd(Contact* con);
//通讯录删除数据
void ContactDel(Contact* con);
//通讯录的修改
void ContactModify(Contact* con);
//通讯录查找
void ContactFind(Contact* con);
//展示通讯录数据
void ContactShow(Contact* con);
“SeqList.c”
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"SeqList.h"
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//顺序表的销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->arr) //等价于 if(ps->arr != NULL)
{
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
//插入数据之前先看空间够不够
if (ps->capacity == ps->size)
{
//申请空间
//malloc calloc realloc int arr[100] --->增容realloc
//三目表达式
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));//要申请多大的空间
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail!");
exit(1);//直接退出程序,不再继续执行
}
//空间申请成功
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
温柔的解决方式
//if (ps == NULL)
//{
// return;
//}
assert(ps); //等价与assert(ps != NULL)
//ps->arr[ps->size] = x;
//++ps->size;
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->arr[ps->size++] = x;
}
//头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//先让顺序表中已有的数据整体往后挪动一位
for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];//arr[1] = arr[0]
}
ps->arr[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//void SLPrint(SL s)
//{
// for (int i = 0; i < s.size; i++)
// {
// printf("%d ", s.arr[i]);
// }
// printf("\n");
//}
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
//顺序表不为空
//ps->arr[ps->size - 1] = -1;
--ps->size;
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
//数据整体往前挪动一位
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1]; //arr[size-2] = arr[size-1]
}
ps->size--;
}
//在指定位置之前插入数据
// 1 2 size = 2
//pos 0 -1 100000
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
//插入数据:空间够不够
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//让pos及之后的数据整体往后挪动一位
for (int i = ps->size; i > pos; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];//arr[pos+1] = arr[pos]
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//删除指定位置的数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
//查找
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->arr[i] == x)
{
//找到啦
return i;
}
}
//没有找到
return -1;
}
“Contact.c”
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"Contact.h"
#include"SeqList.h"
//通讯录的初始化
void ContactInit(Contact* con)//sl
{
//实际上要进行的是顺序表的初始化
//顺序表的初始化已经实现好了
SLInit(con);
}
//通讯录的销毁
void ContactDesTroy(Contact* con)
{
SLDestroy(con);
}
//通讯录添加数据
void ContactAdd(Contact* con)
{
//获取用户输入的内容:姓名+性别+年龄+电话+地址
peoInfo info;
printf("请输入要添加的联系人姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", info.name);
printf("请输入要添加的联系人性别:\n");
scanf("%s", info.gender);
printf("请输入要添加的联系人年龄:\n");
scanf("%d", &info.age);
printf("请输入要添加的联系人电话:\n");
scanf("%s", info.tel);
printf("请输入要添加的联系人住址:\n");
scanf("%s", info.addr);
//往通讯录中添加联系人数据
SLPushBack(con, info);
}
int FindByName(Contact* con, char name[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < con->size; i++)
{
if (0 == strcmp(con->arr[i].name, name))
{
//找到了
return i;
}
}
//没有找到
return -1;
}
//通讯录删除数据
void ContactDel(Contact* con)
{
//要删除的数据必须要存在,才能执行删除操作
//查找
char name[NAME_MAX];
printf("请输入要删除的联系人姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", name);
int find = FindByName(con, name);
if (find < 0)
{
printf("要删除的联系人数据不存在!\n");
return;
}
//要删除的联系人数据存在--->知道了要删除的联系人数据对应的下标
SLErase(con, find);
printf("删除成功!\n");
}
//展示通讯录数据
void ContactShow(Contact* con)
{
//表头:姓名 性别 年龄 电话 地址
printf("%s %s %s %s %s\n", "姓名", "性别", "年龄", "电话", "地址");
//遍历通讯录,按照格式打印每个联系人数据
for (int i = 0; i < con->size; i++)
{
printf("%3s %3s %3d %3s %3s\n", //手动调整一下格式
con->arr[i].name,
con->arr[i].gender,
con->arr[i].age,
con->arr[i].tel,
con->arr[i].addr
);
}
}
//通讯录的修改
void ContactModify(Contact* con)
{
//要修改的联系人数据存在
char name[NAME_MAX];
printf("请输入要修改的用户姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", name);
int find = FindByName(con, name);
if (find < 0)
{
printf("要修改的联系人数据不存在!\n");
return;
}
//直接修改
printf("请输入新的姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", con->arr[find].name);
printf("请输入新的性别:\n");
scanf("%s", con->arr[find].gender);
printf("请输入新的年龄:\n");
scanf("%d", &con->arr[find].age);
printf("请输入新的电话:\n");
scanf("%s", con->arr[find].tel);
printf("请输入新的住址:\n");
scanf("%s", con->arr[find].addr);
printf("修改成功!\n");
}
//通讯录查找
void ContactFind(Contact* con)
{
//11
char name[NAME_MAX];
printf("请输入要查找的联系人姓名\n");
scanf("%s", name);
int find = FindByName(con, name);
if (find < 0)
{
printf("要查找的联系人数据不存在!\n");
return;
}
// 姓名 性别 年龄 电话 地址
// 11 11 11 11 11
printf("%s %s %s %s %s\n", "姓名", "性别", "年龄", "电话", "地址");
printf("%3s %3s %3d %3s %3s\n", //手动调整一下格式
con->arr[find].name,
con->arr[find].gender,
con->arr[find].age,
con->arr[find].tel,
con->arr[find].addr
);
}
“test.c”
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"SeqList.h"
//void SLTest01()
//{
// SL sl;
// SLInit(&sl);
// //增删查改操作
// //测试尾插
// SLPushBack(&sl, 1);
// SLPushBack(&sl, 2);
// SLPushBack(&sl, 3);
// SLPushBack(&sl, 4);
// SLPrint(sl);//1 2 3 4
//
// //SLPushFront(&sl, 5);
// //SLPushFront(&sl, 6);
//
// //测试尾删
// SLPopBack(&sl);
// SLPrint(sl);//1 2 3
// SLPopBack(&sl);
// SLPrint(sl);
// SLPopBack(&sl);
// SLPrint(sl);
// SLPopBack(&sl);
// SLPrint(sl);
// SLPopFront(&sl);
// SLPrint(sl);
// //...........
// SLDestroy(&sl);
//}
//void SLTest02()
//{
// SL sl;
// SLInit(&sl);
// SLPushBack(&sl, 1);
// SLPushBack(&sl, 2);
// SLPushBack(&sl, 3);
// SLPushBack(&sl, 4);
// SLPrint(sl);//1 2 3 4
// //测试指定位置之前插入数据
// //SLInsert(&sl, 1, 99);
// //SLInsert(&sl, sl.size, 88);
//
// //测试删除指定位置的数据
// //SLErase(&sl, 1);
// //SLPrint(sl);//1 3 4
//
// //测试顺序表的查找
// int find = SLFind(&sl, 40);
// if (find < 0)
// {
// printf("没有找到!\n");
// }
// else {
// printf("找到了!下标为%d\n",find);
// }
// SLDestroy(&sl);
//}
通讯录的测试方法
//void ContactTest01()
//{
// Contact con;//创建的通讯录对象 实际上就是 顺序表对象,等价于SL sl
// ContactInit(&con);
// ContactAdd(&con);
// ContactAdd(&con);
// ContactShow(&con);
//
// //ContactDel(&con);
// ContactModify(&con);
// ContactShow(&con);
// ContactFind(&con);
//
// ContactDesTroy(&con);
//}
//int main()
//{
// //SLTest01();
// //SLTest02();
// ContactTest01();
// return 0;
//}
void menu()
{
printf("******************通讯录******************\n");
printf("*******1.增加联系人 2.删除联系人********\n");
printf("*******3.修改联系人 4.查找联系人********\n");
printf("*******5.展示联系人 0. 退出 *********\n");
printf("******************************************\n");
}
int main()
{
int op = -1;
Contact con;
ContactInit(&con);
do {
menu();
printf("请选择您的操作:\n");
scanf("%d", &op);
//要根据对应的op执行不同的操作
switch (op)
{
case 1:
ContactAdd(&con);
break;
case 2:
ContactDel(&con);
break;
case 3:
ContactModify(&con);
break;
case 4:
ContactFind(&con);
break;
case 5:
ContactShow(&con);
break;
case 0:
printf("退出通讯录....\n");
break;
default:
printf("输入错误,请重新选择您的操作!\n");
break;
}
} while (op != 0);
ContactDesTroy(&con);
return 0;
}