patch日期
收发流程的重大修改,来源于2012年的如下补丁
内核提交收发流程的patch
spi: create a message queueing infrastructure - kernel/git/stable/linux.git - Linux kernel stable tree
源代码路径及功能
| 源码 | 作用 |
| \drivers\spi\spi.c | spi 通用接口,包括发送,队列管理等。核心文件 |
| \drivers\mtd\devices\m25p80.c | 具体flash驱动,由此驱动进行SPI协议的组装,并通过spi.c的接口将数据下发 |
| drivers\spi\spidev.c | 通用spi设备驱动,即直接将用户发送的数据通过spi.c中的接口发送。具体发送的命令字构成由用户填写。 |
| \drivers\spi\spi-dw.c | 具体控制器的驱动,实现对控制器硬件的访问控制 |
kthread_queue_work
kthread_worker 和 kthread_work
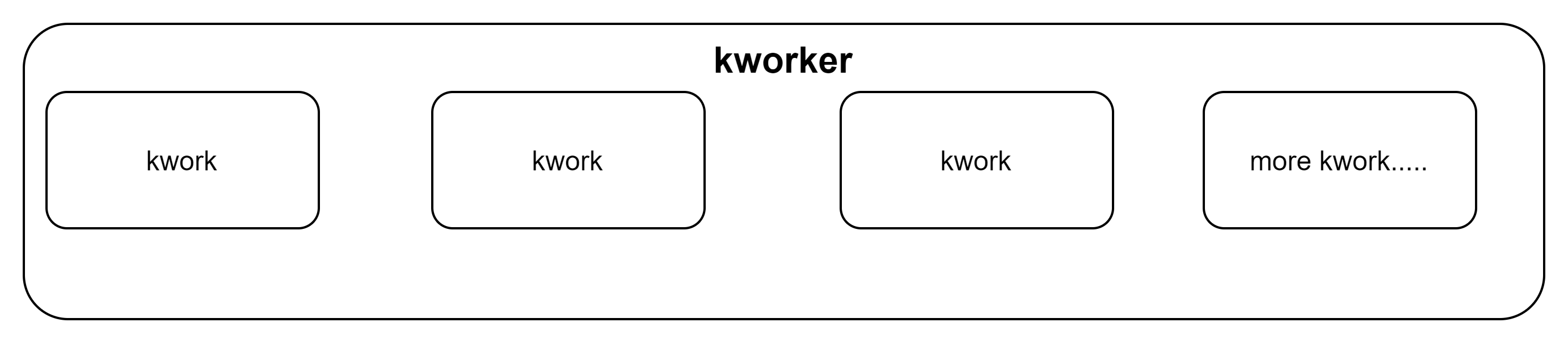
两者关系:kworker 类似任务容器;而kwork是具体的任务。
kthread_worker 的初始化
代码来源: spi_init_queue(spi.c)
kthread_init_worker(&ctlr->kworker);
ctlr->kworker_task = kthread_run(kthread_worker_fn, &ctlr->kworker,
"%s", dev_name(&ctlr->dev));可以看出worker本质上即为一个内核线程,线程采用的参数为kworker这个结构体,即容器。那就可以猜测,这个线程worker_fn的功能,就是检测kworker这个容器中是否由work,如果有,则进行处理。
问题: 这个线程的调度策略及优先级是怎么样的?
kthread_worker 的优先级
代码来源: spi_init_queue(spi.c)
struct sched_param param = { .sched_priority = MAX_RT_PRIO - 1 };
/*
* Controller config will indicate if this controller should run the
* message pump with high (realtime) priority to reduce the transfer
* latency on the bus by minimising the delay between a transfer
* request and the scheduling of the message pump thread. Without this
* setting the message pump thread will remain at default priority.
*/
if (ctlr->rt) {
dev_info(&ctlr->dev,
"will run message pump with realtime priority\n");
sched_setscheduler(ctlr->kworker_task, SCHED_FIFO, ¶m);
}
这里设置的调度策略为FIFO。
kthread_work的初始化
代码来源: spi_init_queue(spi.c)
kthread_init_work(&ctlr->pump_messages, spi_pump_messages);
struct kthread_worker kworker;
struct task_struct *kworker_task;
struct kthread_work pump_messages;即将 work的功能函数设置为 spi_pump_messages.
kthread_work的执行
kthread_queue_work(&ctlr->kworker, &ctlr->pump_messages);if (!worker->current_work && likely(worker->task))
wake_up_process(worker->task)将work加入到 worker中,并唤醒worker这个线程。当worker为空,即没有work要处理时,则worker休眠。
总体上讲,从字面意思,worker是干活的人,work是活,有活就唤醒干活的人,没活干活的人就休息。
消息队列
发送流程
数据的传输载体
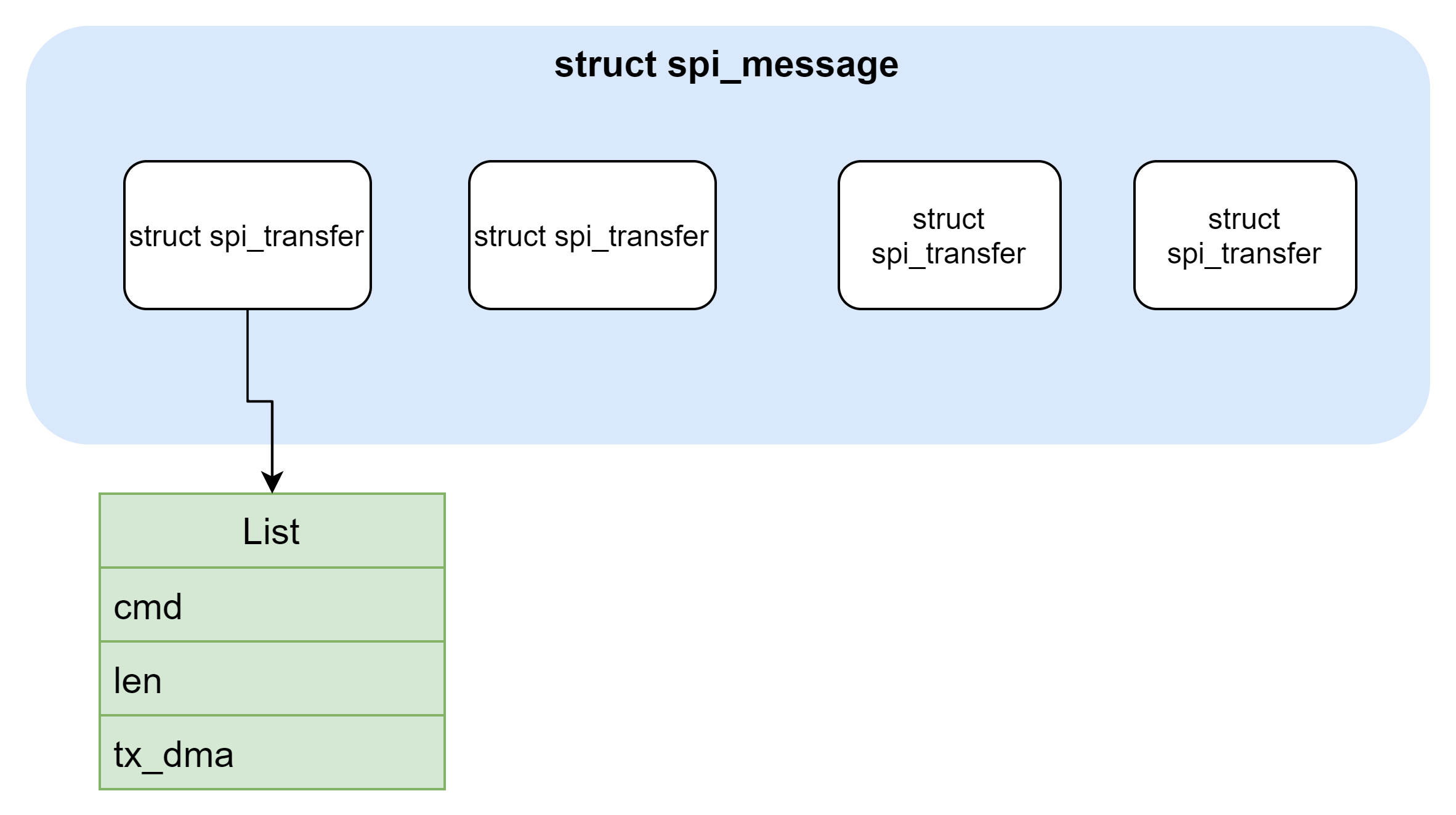
struct spi_message 与 struct spi_transfer
fmsh\include\linux\spi\spi.h
核心数据结构,用于表示一次数据的传输
/**
* struct spi_message - one multi-segment SPI transaction
* @transfers: list of transfer segments in this transaction
* @spi: SPI device to which the transaction is queued
* @is_dma_mapped: if true, the caller provided both dma and cpu virtual
* addresses for each transfer buffer
* @complete: called to report transaction completions
* @context: the argument to complete() when it's called
* @frame_length: the total number of bytes in the message
* @actual_length: the total number of bytes that were transferred in all
* successful segments
* @status: zero for success, else negative errno
* @queue: for use by whichever driver currently owns the message
* @state: for use by whichever driver currently owns the message
* @resources: for resource management when the spi message is processed
*
* A @spi_message is used to execute an atomic sequence of data transfers,
* each represented by a struct spi_transfer. The sequence is "atomic"
* in the sense that no other spi_message may use that SPI bus until that
* sequence completes. On some systems, many such sequences can execute as
* as single programmed DMA transfer. On all systems, these messages are
* queued, and might complete after transactions to other devices. Messages
* sent to a given spi_device are always executed in FIFO order.
*
* The code that submits an spi_message (and its spi_transfers)
* to the lower layers is responsible for managing its memory.
* Zero-initialize every field you don't set up explicitly, to
* insulate against future API updates. After you submit a message
* and its transfers, ignore them until its completion callback.
*/
struct spi_message {
struct list_head transfers;
struct spi_device *spi;
unsigned is_dma_mapped:1;
/* REVISIT: we might want a flag affecting the behavior of the
* last transfer ... allowing things like "read 16 bit length L"
* immediately followed by "read L bytes". Basically imposing
* a specific message scheduling algorithm.
*
* Some controller drivers (message-at-a-time queue processing)
* could provide that as their default scheduling algorithm. But
* others (with multi-message pipelines) could need a flag to
* tell them about such special cases.
*/
/* completion is reported through a callback */
void (*complete)(void *context);
void *context;
unsigned frame_length;
unsigned actual_length;
int status;
/* for optional use by whatever driver currently owns the
* spi_message ... between calls to spi_async and then later
* complete(), that's the spi_controller controller driver.
*/
struct list_head queue;
void *state;
/* list of spi_res reources when the spi message is processed */
struct list_head resources;
};
一个transfer即一次硬件的命令字及数据的传输过程;
一个message则包含多个transfer
将数据发送到控制器的队列--spi_sync
当flash驱动准备好数据,完成message 数据部分的初始化后,就调用此接口将数据传递给控制器的队列。
__spi_sync
static int __spi_sync(struct spi_device *spi, struct spi_message *message)
{
DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done);
int status;
struct spi_controller *ctlr = spi->controller;
unsigned long flags;
status = __spi_validate(spi, message);
if (status != 0)
return status;
message->complete = spi_complete;
message->context = &done;
message->spi = spi;
SPI_STATISTICS_INCREMENT_FIELD(&ctlr->statistics, spi_sync);
SPI_STATISTICS_INCREMENT_FIELD(&spi->statistics, spi_sync);
/* If we're not using the legacy transfer method then we will
* try to transfer in the calling context so special case.
* This code would be less tricky if we could remove the
* support for driver implemented message queues.
*/
if (ctlr->transfer == spi_queued_transfer) {
spin_lock_irqsave(&ctlr->bus_lock_spinlock, flags);
trace_spi_message_submit(message);
status = __spi_queued_transfer(spi, message, false);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ctlr->bus_lock_spinlock, flags);
} else {
status = spi_async_locked(spi, message);
}
if (status == 0) {
/* Push out the messages in the calling context if we
* can.
*/
if (ctlr->transfer == spi_queued_transfer) {
SPI_STATISTICS_INCREMENT_FIELD(&ctlr->statistics,
spi_sync_immediate);
SPI_STATISTICS_INCREMENT_FIELD(&spi->statistics,
spi_sync_immediate);
__spi_pump_messages(ctlr, false);
}
wait_for_completion(&done);
status = message->status;
}
message->context = NULL;
return status;
}
这里主要注意3点:
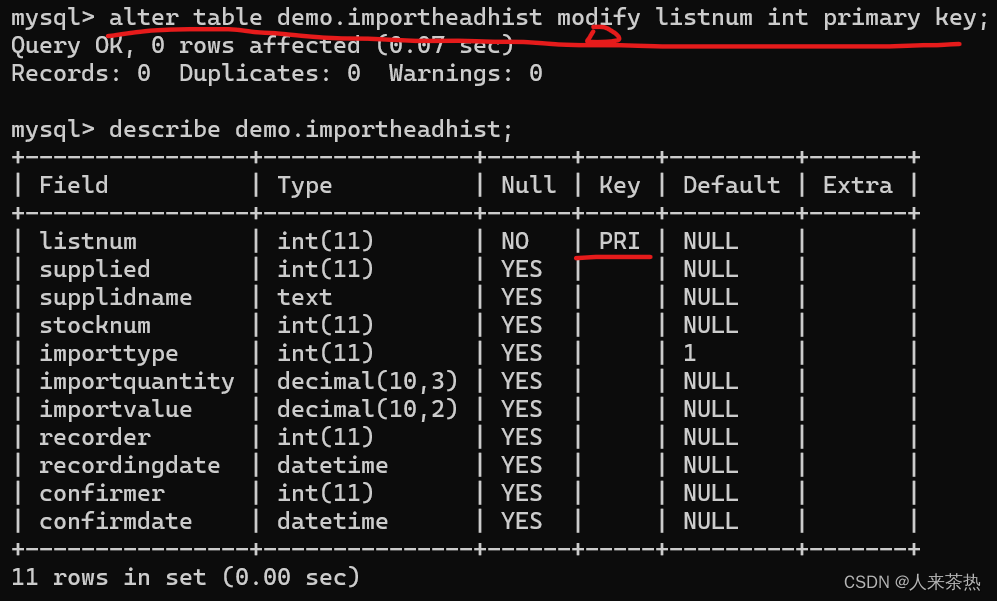
1) status = __spi_queued_transfer(spi, message, false);时,第二个参数为flase,也就是说,此处仅仅是将message 放入到ctrl的queue中,并不会唤醒 kthead worker开始正式的下发数据。此接口在用户进程上下文中。最终变成如下图,一个ctrl queue里面有了多个message,处于待发送状态。
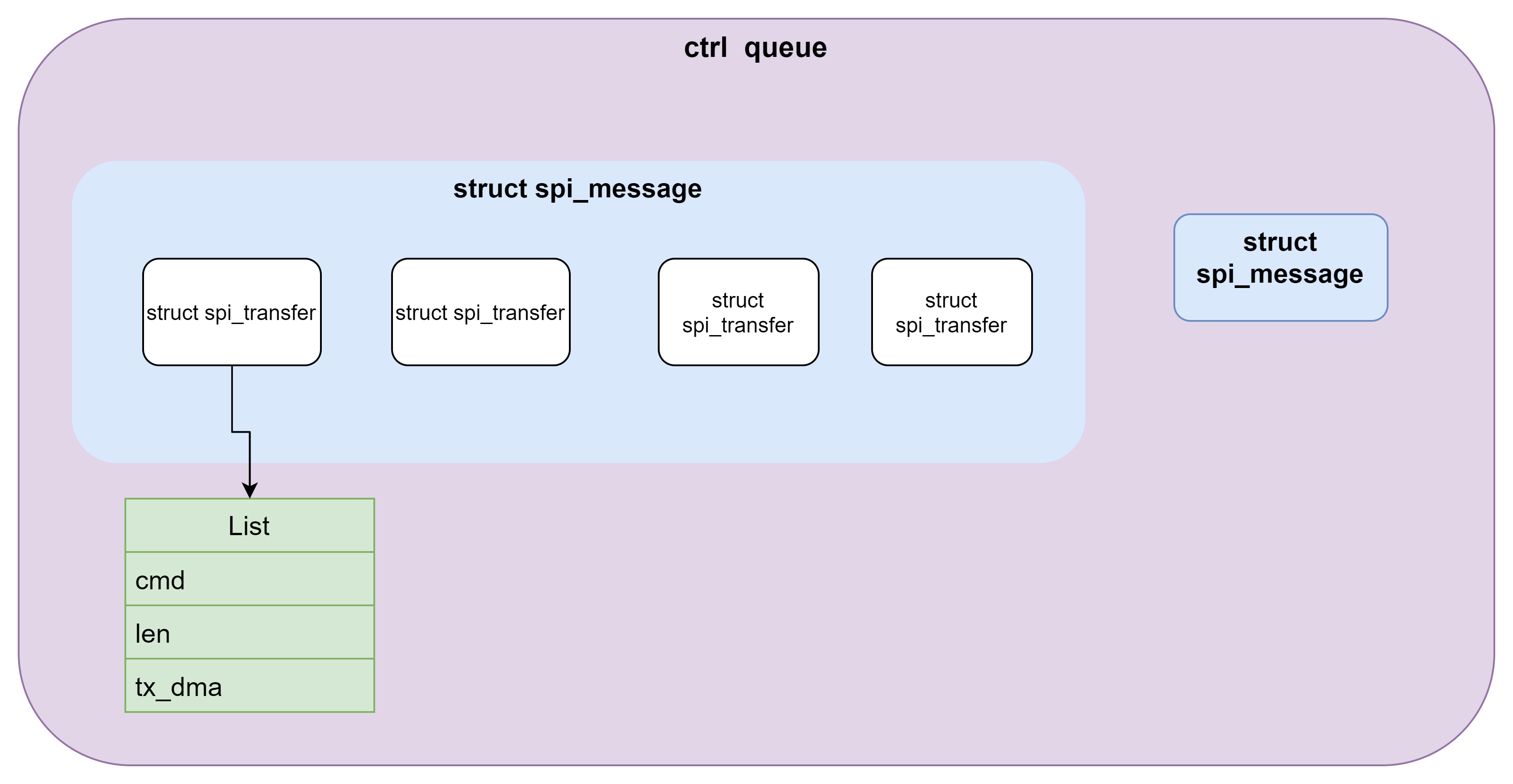
2) __spi_pump_messages(ctlr, false); ,第二个参数也为false,在此时才会唤醒kthread worker干活。
3) 将message放入队列后,接口调用并没有立即返回,而是调用如下接口,等待完成。
wait_for_completion(&done);往硬件发送数据__spi_pump_messages
此函数的调用处有两个:
1) 上一节描述的调用进程的上下文。
2) work的工作函数。
/**
* __spi_pump_messages - function which processes spi message queue
* @ctlr: controller to process queue for
* @in_kthread: true if we are in the context of the message pump thread
*
* This function checks if there is any spi message in the queue that
* needs processing and if so call out to the driver to initialize hardware
* and transfer each message.
*
* Note that it is called both from the kthread itself and also from
* inside spi_sync(); the queue extraction handling at the top of the
* function should deal with this safely.
*/
static void __spi_pump_messages(struct spi_controller *ctlr, bool in_kthread)
{
unsigned long flags;
bool was_busy = false;
int ret;
/* Lock queue */
spin_lock_irqsave(&ctlr->queue_lock, flags);
/* Make sure we are not already running a message */
if (ctlr->cur_msg) {
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ctlr->queue_lock, flags);
return;
}
/* If another context is idling the device then defer */
if (ctlr->idling) {
kthread_queue_work(&ctlr->kworker, &ctlr->pump_messages);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ctlr->queue_lock, flags);
return;
}
/* Check if the queue is idle */
if (list_empty(&ctlr->queue) || !ctlr->running) {
if (!ctlr->busy) {
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ctlr->queue_lock, flags);
return;
}
/* Only do teardown in the thread */
if (!in_kthread) {
kthread_queue_work(&ctlr->kworker,
&ctlr->pump_messages);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ctlr->queue_lock, flags);
return;
}
ctlr->busy = false;
ctlr->idling = true;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ctlr->queue_lock, flags);
kfree(ctlr->dummy_rx);
ctlr->dummy_rx = NULL;
kfree(ctlr->dummy_tx);
ctlr->dummy_tx = NULL;
if (ctlr->unprepare_transfer_hardware &&
ctlr->unprepare_transfer_hardware(ctlr))
dev_err(&ctlr->dev,
"failed to unprepare transfer hardware\n");
if (ctlr->auto_runtime_pm) {
pm_runtime_mark_last_busy(ctlr->dev.parent);
pm_runtime_put_autosuspend(ctlr->dev.parent);
}
trace_spi_controller_idle(ctlr);
spin_lock_irqsave(&ctlr->queue_lock, flags);
ctlr->idling = false;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ctlr->queue_lock, flags);
return;
}
/* Extract head of queue */
ctlr->cur_msg =
list_first_entry(&ctlr->queue, struct spi_message, queue);
list_del_init(&ctlr->cur_msg->queue);
if (ctlr->busy)
was_busy = true;
else
ctlr->busy = true;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ctlr->queue_lock, flags);
mutex_lock(&ctlr->io_mutex);
if (!was_busy && ctlr->auto_runtime_pm) {
ret = pm_runtime_get_sync(ctlr->dev.parent);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&ctlr->dev, "Failed to power device: %d\n",
ret);
mutex_unlock(&ctlr->io_mutex);
return;
}
}
if (!was_busy)
trace_spi_controller_busy(ctlr);
if (!was_busy && ctlr->prepare_transfer_hardware) {
ret = ctlr->prepare_transfer_hardware(ctlr);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&ctlr->dev,
"failed to prepare transfer hardware\n");
if (ctlr->auto_runtime_pm)
pm_runtime_put(ctlr->dev.parent);
mutex_unlock(&ctlr->io_mutex);
return;
}
}
trace_spi_message_start(ctlr->cur_msg);
if (ctlr->prepare_message) {
ret = ctlr->prepare_message(ctlr, ctlr->cur_msg);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&ctlr->dev, "failed to prepare message: %d\n",
ret);
ctlr->cur_msg->status = ret;
spi_finalize_current_message(ctlr);
goto out;
}
ctlr->cur_msg_prepared = true;
}
ret = spi_map_msg(ctlr, ctlr->cur_msg);
if (ret) {
ctlr->cur_msg->status = ret;
spi_finalize_current_message(ctlr);
goto out;
}
ret = ctlr->transfer_one_message(ctlr, ctlr->cur_msg);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&ctlr->dev,
"failed to transfer one message from queue\n");
goto out;
}
out:
mutex_unlock(&ctlr->io_mutex);
/* Prod the scheduler in case transfer_one() was busy waiting */
if (!ret)
cond_resched();
}
发送messages
spi_transfer_one_message
\drivers\spi\spi.c
1) 设置片选
spi_set_cs(msg->spi, true);2) 遍历message每个transfer,调用具体控制器接口发送数据
3) 等待transfer的传输完成。
if (ret > 0) {
ret = 0;
ms = 8LL * 1000LL * xfer->len;
do_div(ms, xfer->speed_hz);
ms += ms + 200; /* some tolerance */
if (ms > UINT_MAX)
ms = UINT_MAX;
ms = wait_for_completion_timeout(&ctlr->xfer_completion,
msecs_to_jiffies(ms));
}4)整个message的传输完成
if (mesg->complete)
mesg->complete(mesg->context);设备驱动的发送接口
.55-fmsh\drivers\spi\spi-dw.c
static int dw_spi_transfer_one(struct spi_master *master,
struct spi_device *spi, struct spi_transfer *transfer)总体流程
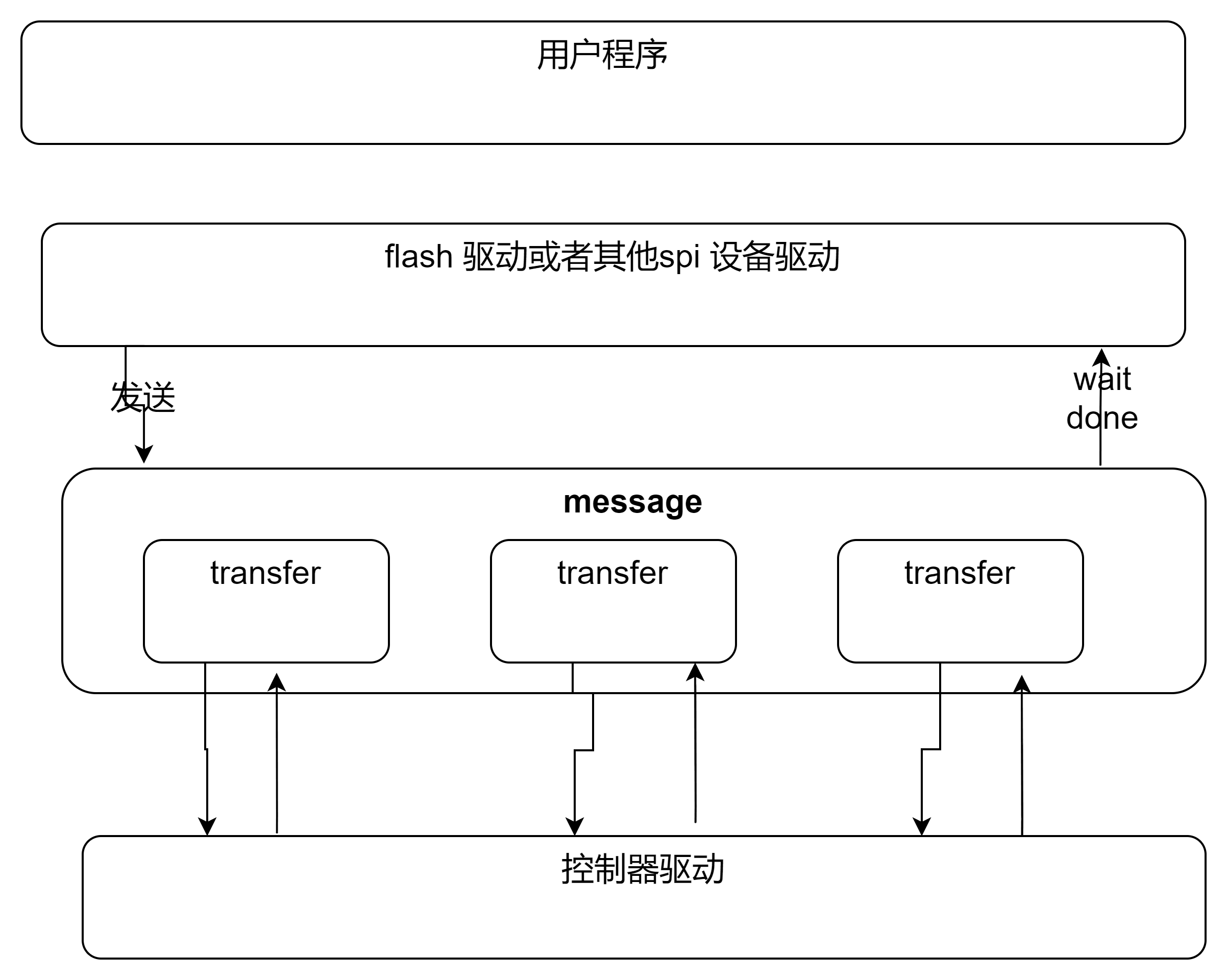
注意这里有几个上下文:
1) 用户发送上下文,将message 传递个控制器后,就在此上下文中等待message的处理结果。
2)发送线程上下文。
3)设备驱动发送数据时的中断上下文。
实现细节
锁的使用
1. ctlr->queue_lock
用户进程和实际发送线程之间对queue 链表的互斥。
spinlock_t queue_lock;
使用处:
将message 放入ctrl 队列时
spin_lock_irqsave(&ctlr->queue_lock, flags);以及内核线程将message 从队列取出,下发到硬件时
__spi_pump_messages
2. bus_lock_spinlock
/* If we're not using the legacy transfer method then we will
* try to transfer in the calling context so special case.
* This code would be less tricky if we could remove the
* support for driver implemented message queues.
*/
if (ctlr->transfer == spi_queued_transfer) {
spin_lock_irqsave(&ctlr->bus_lock_spinlock, flags);
trace_spi_message_submit(message);
status = __spi_queued_transfer(spi, message, false);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ctlr->bus_lock_spinlock, flags);
}3. bus_lock_mutex
mutex_lock(&spi->controller->bus_lock_mutex);
ret = __spi_sync(spi, message);
mutex_unlock(&spi->controller->bus_lock_mutex);
多个用户或者flash、spi外设驱动之间互斥。
也就是说,一个SPI发送过程,需要先获取 mutex,然后bus_spinlock ,然后 queue spinlock。
这里有了bus mutex,为什么还有一个bus spin lock?
总结
为什么针对SPI的驱动,单独设置了FIFO的调度?而实时进程则是采用SCHED_FIFO或SCHED_RR。
参考资料
Kthread worker
linux kthread_worker-CSDN博客
内核 kthread_worker 和 kthread_work 机制_kthread_queue_work-CSDN博客
查看进程调度策略
Linux系统动态查看每个CPU上任务的调度情况_linux cpu 调度 记录-CSDN博客
linux进程的查看和调度 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
Linux的进程线程调度策略_如何查看线程的policy-CSDN博客
linux内核调度的机制 tasklet/workqueue/kthread_worker/kthreadx详解及示例【转】 - Sky&Zhang - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
混乱的Linux内核实时线程优先级 - 知乎 (zhihu.com) 5: linux内核调度的机制 tasklet/workqueue/kthread_worker/kthreadx详解及示例_kthread_worker和workqueue-CSDN博客
【驱动】SPI驱动分析(四)-关键API解析 - 学习,积累,成长 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)