说明:
基本都是bfs的常见模板题型,思路都很直接,不过后面有两道题很搞心态,它们给的坐标x、y是反的,导致刚开始一直错。题目还是要看仔细,不能先入为主。
题目列表:
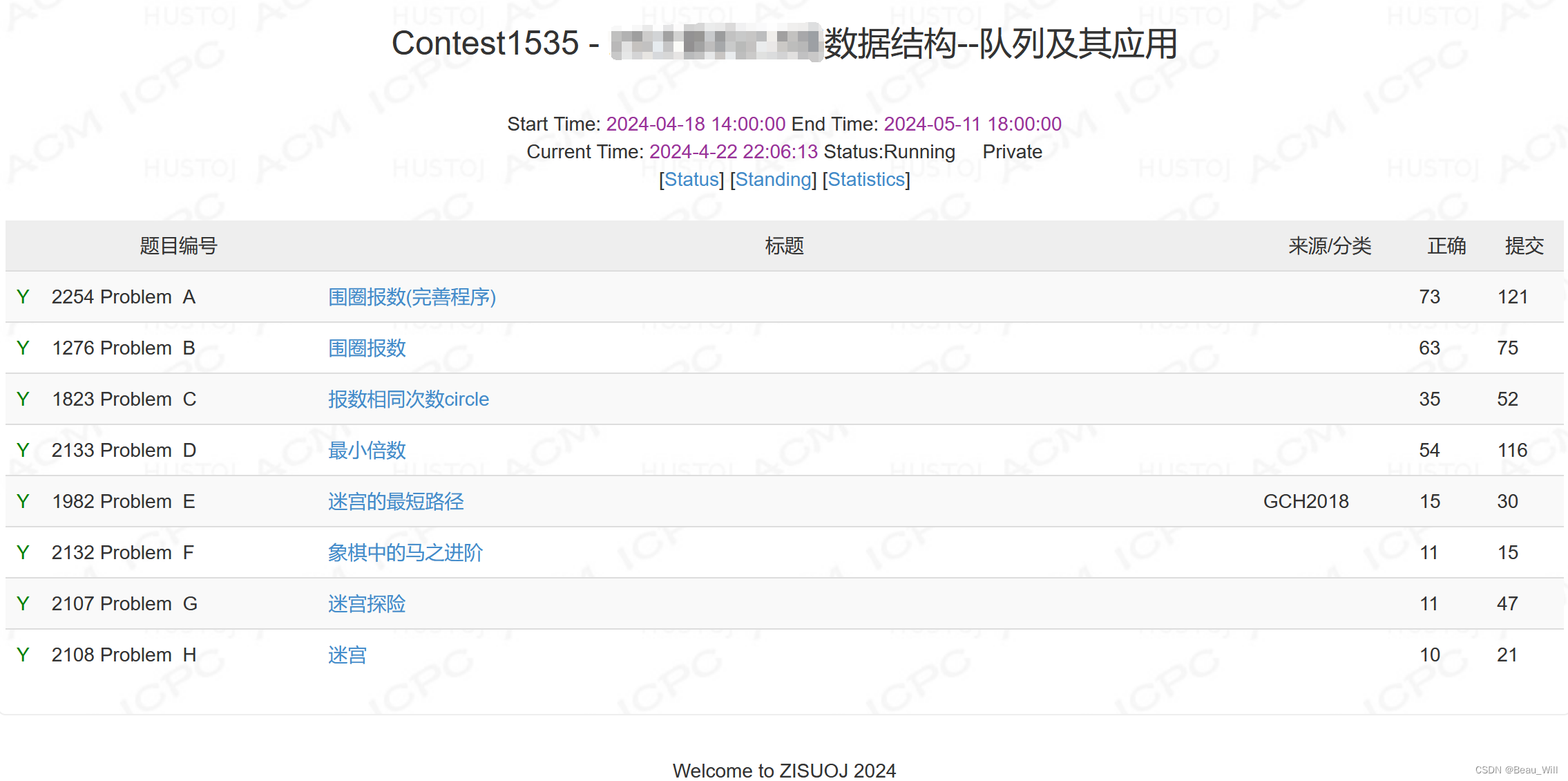
问题 A: 围圈报数(完善程序)
参考题解:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int n,m,k=1,tmp;
queue<int> arr;
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
arr.push(i);
// _____(1)____//依次进入队列
while(arr.size())
// while(_____(2)_____)//判断队列里是否还有人
{
tmp=arr.front();
if(k%m==0)
cout<<tmp<<" ";
else
arr.push(tmp);
// ______(3)______//如果不是第m个人,则重新入队
// _____(4)_____//从队列里删除
arr.pop();
k++;
}
return 0;
}问题 B: 围圈报数
参考题解:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
int main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int n,m,count = 0;cin >> n >> m;
std::queue<int> q;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) q.push(i);
while(q.size()){
auto t = q.front();
count++;
if(count%m==0) {
cout << t << ' ';
}else {
q.push(t);
}
q.pop();
}
cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}问题 C: 报数相同次数circle
参考题解:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
int main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;cin >> n;
int a,b;cin >> a >> b;
std::queue<int> q1,q2;
for(int i = 1;i<=a;i++) q1.push(i);
for(int i = 1;i<=b;i++) q2.push(i);
int count = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
auto t1 = q1.front(),t2 = q2.front();
if(t1==t2) count++;
q1.push(t1),q2.push(t2);
q1.pop(),q2.pop();
}
cout << count << std::endl;
return 0;
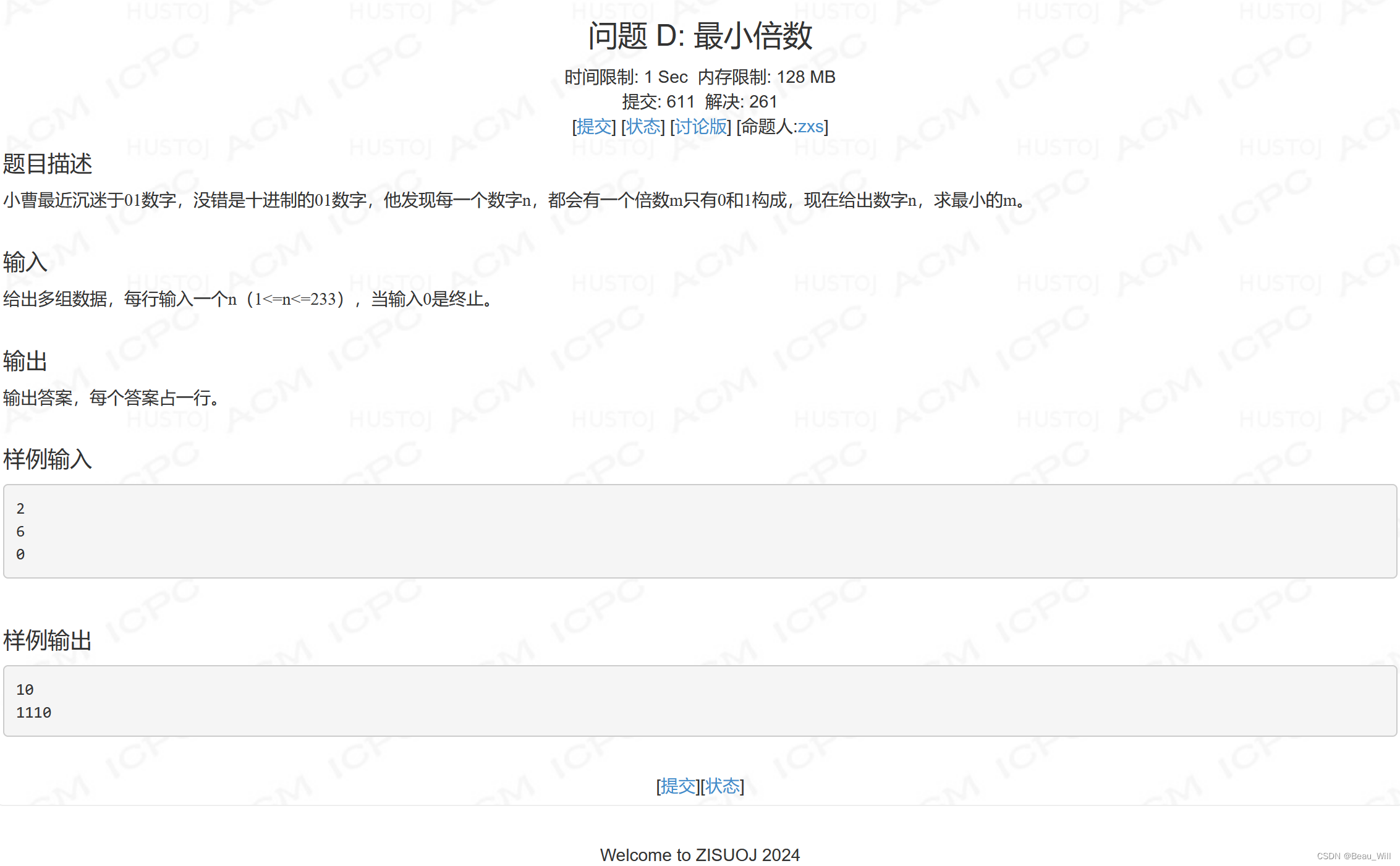
}问题 D: 最小倍数
参考题解:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using ll = long long;
ll n,x;
void bfs() {
std::queue<ll> q;
q.push(1);
while(q.size()) {
x = q.front();q.pop();
if(x%n==0&&x>=n) {
cout << x << '\n';
return;
}
q.push(x*10);
q.push(x*10+1);
}
cout << x << '\n';
}
int main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
while(cin >> n,n) {
bfs();
}
return 0;
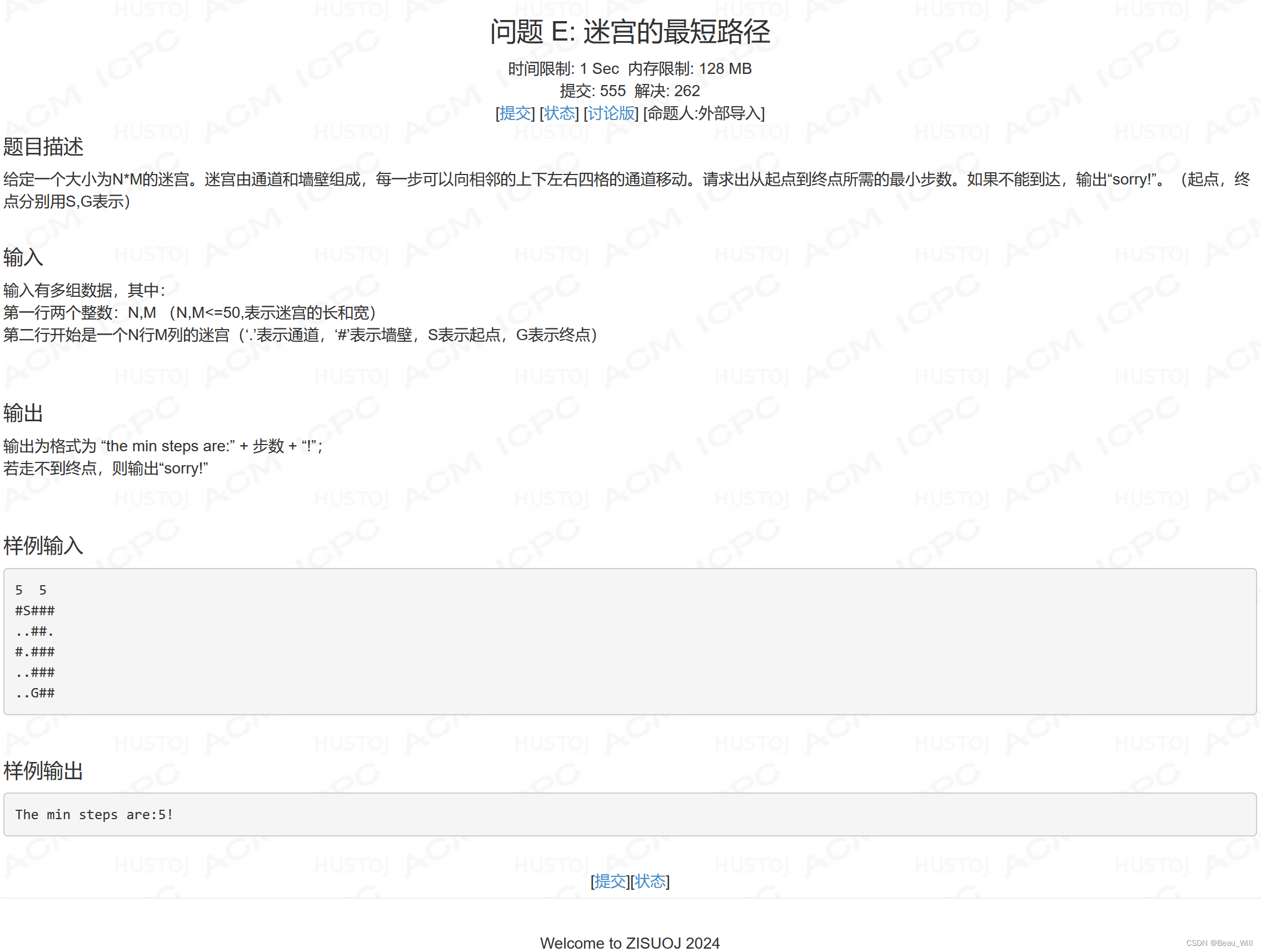
}问题 E: 迷宫的最短路径
参考题解:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
int main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
constexpr int N = 1e2+5;
int sx = 1,sy = 1,ex = 1,ey = 1;
struct node {
int x,y,s;
}t,t1;
char g[N][N];
bool vis[N][N];
memset(vis,false,sizeof vis);
int dx[] = {0,0,-1,1};
int dy[] = {-1,1,0,0};
std::queue<node> q;
int n,m;cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
for(int j = 1;j<=m;j++) {
cin >> g[i][j];
if(g[i][j]=='S') {
sx=i,sy=j;
}else if(g[i][j]=='G') {
ex=i,ey=j;
}
}
}
auto bfs = [&]()->void{
t.x = sx,t.y = sy,t.s = 0;
q.push(t);
vis[sx][sy] = true;
while(!q.empty()) {
t = q.front();q.pop();
if(t.x==ex&&t.y==ey) {
cout << "The min steps are:" << t.s << "!\n";
return;
}
for(int i = 0;i<4;i++) {
int u = t.x+dx[i],v = t.y+dy[i];
if(u<1||u>n||v<1||v>m||vis[u][v]||g[u][v]=='#') continue;
vis[u][v] = true;
t1.x = u,t1.y = v,t1.s = t.s+1;
q.push(t1);
}
}
cout << "sorry!\n";
};
bfs();
return 0;
}问题 F: 象棋中的马之进阶

参考题解:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
int main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
constexpr int N = 15;
struct node {
int x,y,s;
}t,t1;
int dx[] = {-1,1,2,2,1,-1,-2,-2};
int dy[] = {2,2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1,1};
int sx,sy,ex,ey;
bool vis[N][N];
memset(vis,false,sizeof vis);
cin >> sy >> sx >> ey >> ex;
std::queue<node> q;
auto bfs = [&]() ->void {
t.x = sx,t.y = sy,t.s = 0;
vis[sx][sy] = true;
q.push(t);
while(!q.empty()) {
t = q.front();q.pop();
if(t.x==ex&&t.y==ey) {
cout << t.s << std::endl;
return;
}
for(int i = 0;i<8;i++) {
int u = t.x+dx[i],v = t.y+dy[i];
if(u<1||u>10||v<1||v>9||vis[u][v]) continue;
vis[u][v] = true;
t1.x = u,t1.y = v,t1.s = t.s+1;
q.push(t1);
}
}
cout << 0 << std::endl;
};
bfs();
return 0;
}
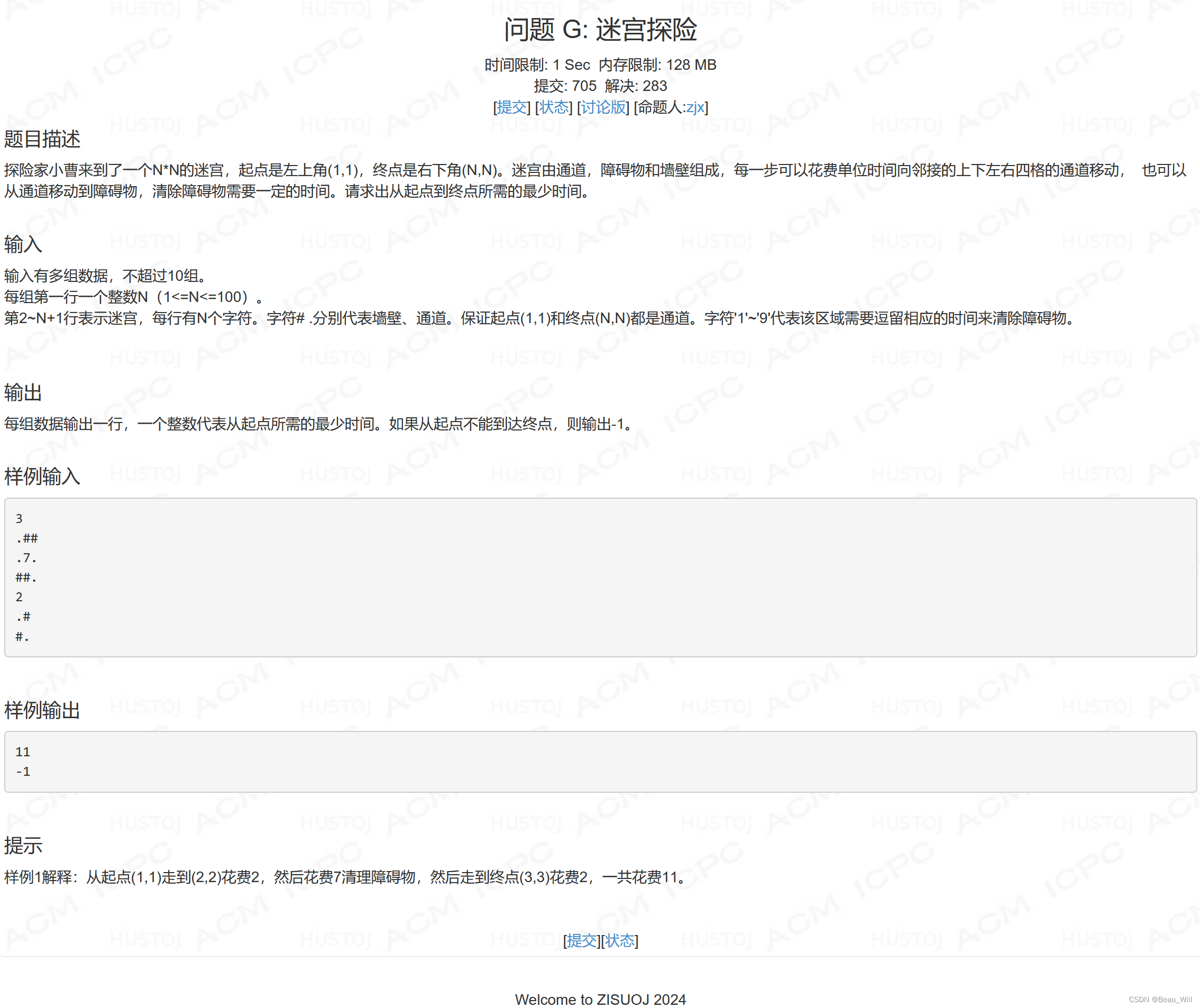
问题 G: 迷宫探险
参考题解:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
int main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
constexpr int N = 1e2+5;
struct node {
int x,y,s;
bool operator > (const node &W) const {
return s > W.s;
}
}t,t1;
char g[N][N];
bool vis[N][N];
int dx[] = {0,0,-1,1};
int dy[] = {-1,1,0,0};
int n,sx = 1,sy = 1,ex = 1,ey = 1;
std::priority_queue<node,std::vector<node>,std::greater<node>> pq;
auto bfs = [&]() ->void {
while(!pq.empty()) pq.pop();
memset(vis,false,sizeof vis);
t.x = sx,t.y = sy,t.s = 0;
vis[sx][sy] = true;
pq.push(t);
while(!pq.empty()) {
t = pq.top();pq.pop();
if(t.x==ex&&t.y==ey) {
cout << t.s << '\n';
return;
}
for(int i = 0;i<4;i++) {
int u = t.x+dx[i],v = t.y+dy[i];
if(u<1||u>n||v<1||v>n||vis[u][v]||g[u][v]=='#') continue;
vis[u][v] = true;
int ds = 1;
if(g[u][v]!='.') ds += int(g[u][v]^48);
t1.x = u,t1.y = v,t1.s = t.s+ds;
pq.push(t1);
}
}
cout << -1 << '\n';
};
while(cin >> n) {
ex = n,ey = n;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
for(int j = 1;j<=n;j++) {
cin >> g[i][j];
}
}
bfs();
}
return 0;
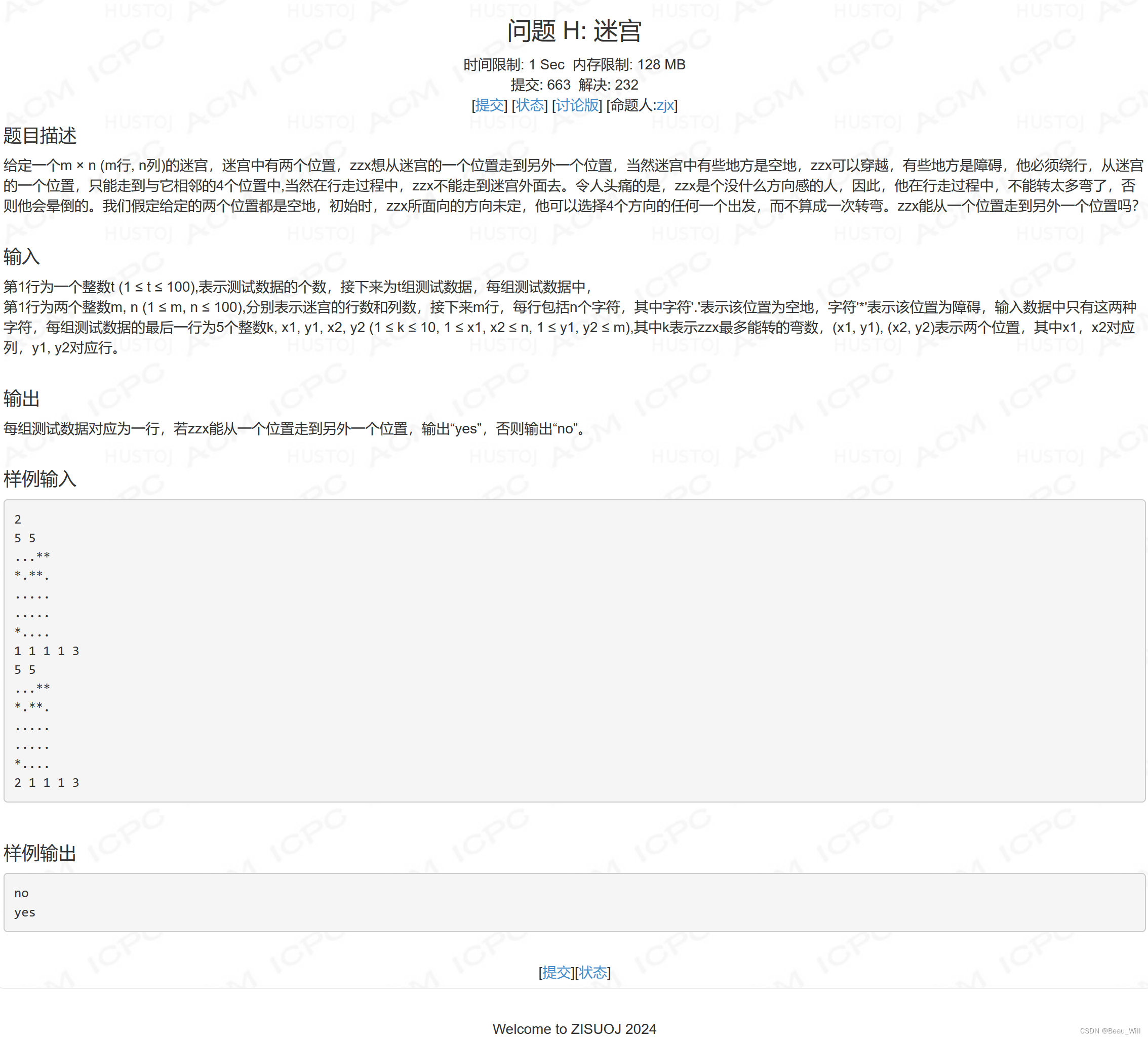
}问题 H: 迷宫
参考题解:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
int main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
constexpr int N = 1e2+5;
struct node {
int x,y,s;
}t,t1;
char g[N][N];
bool vis[N][N];
int dx[] = {0,0,-1,1};
int dy[] = {-1,1,0,0};
int sx,sy,ex,ey,k,n,m;
std::queue<node> q;
auto bfs = [&]()->void {
memset(vis,false,sizeof vis);
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
t.x = sx,t.y = sy,t.s = -1;
vis[sx][sy] = true;
q.push(t);
while(!q.empty()) {
t = q.front();q.pop();
if(t.x==ex&&t.y==ey&&t.s<=k) {
cout << "yes\n";
return;
}
for(int i = 0;i<4;i++) {
t1.x = t.x+dx[i],t1.y = t.y+dy[i];
int &u = t1.x,&v = t1.y;
while(u>=1&&u<=n&&v>=1&&v<=m&&g[u][v]=='.') {
if(!vis[u][v]) {
t1.s=t.s+1;
vis[u][v] = true;
q.push(t1);
}
u+=dx[i],v+=dy[i];
}
}
}
cout << "no\n";
};
int T = 1;cin >> T;
while(T--) {
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
for(int j = 1;j<=m;j++) {
cin >> g[i][j];
}
}
cin >> k >> sy >> sx >> ey >> ex;
bfs();
}
return 0;
}