文章目录
- 需求概述
- 功能展示
- 实现搜索功能使用的技术
- 1.Android Jetpack room
- 2.Android JetPack Compose
- 代码实现
- 编写搜索界面
- 接入Room实现搜索功能的管理
- 引入依赖
- 定义包结构
- 定义操作表的Dao类
- 定义数据库的基础配置
- 定义数据库的Dao管理类
- 使用
- 数据库升级
- 源码地址
需求概述
搜索功能是很多APP都会重点维护的功能,因为搜索功能可以很好的帮助用户找到自己需要的内容,电商APP上,用户可以使用搜索功能快速找到自己想要的商品,社交App上,用户可以使用搜索功能快速找到对应的好友和内容以及使用浏览器快速搜索自己想要知道的问题答案等…。所以搜索功能的使用频率是很高的,所以搜索功能的用户体验也就相当重要,如果搜索功能只是提供搜索的话,有点美中不足,但是如果能加上搜索记录的管理就很好了。目前基本上所有的带有搜索的APP都会带有搜索记录的功能。试想下如果没有搜索记录的功能,用户搜索完自己想要的东西后,如果再次进入到搜索页还想搜索之前的内容就需要再次输入对应的关键字,关键字短还好,假如关键字很长,或者输入的是链接,那用户输入起来就太麻烦了。所以搜索记录功能的重要性不言而喻。本文就是要实现一个搜索记录的管理功能,包括显示搜索记录,删除单条搜索记录,删除全部搜索记录的功能同时实现一个搜索页面。
功能展示

如上面的gif图展示的一样,搜索界面有一个输入框,在输入框中输入我们的关键词点击搜索,这是就会产生一个搜索记录,这些搜索记录会以sqlite数据库的方式保存起来,当再次打开搜索界面后就会显示之前的搜索记录。用户可以点击搜索记录开始搜索,也可以删除不想要的搜索记录,或者是清除所有的搜索记录。搜索页面中有些细节需要关注下,刚进入搜索页面的时候会默认拉起键盘,输入框中的清除搜索内容按钮是当有输入内容的时候才展示,否则不展示,搜索小图标的颜色也是有输入内容的时候才会显示得更加清晰。这些功能会在代码实现的部分讲解
实现搜索功能使用的技术
1.Android Jetpack room
因为搜索记录需要持久化存储到手机里面,我们可以选择文件,shared perference,Sqlite数据库,这里选择Sqlite数据库无疑是最合适的,但是见过很多的小伙伴却在数据库和文件以及SP中选择了文件和SP,原因肯定是和Sqlite数据库的使用比较繁琐,甚至还涉及到数据库升级的问题。面试的时候很多小伙伴肯定都会被问到数据库升级的问题。因为数据库的升级如果处理不好,就会导致APP闪退,所以很多小伙伴选择了更为稳妥的方式。但是Android jetpack 的ROOM出现后,这一切都变得简单了,Room库在 SQLite 上提供了一个抽象层,充分利用 SQLite 的强大功能的同时,能够流畅地访问数据库。Room 提供针对 SQL 查询的编译时验证并提供方便注解,可最大限度减少重复和容易出错的样板代码并且还简化了数据库迁移升级。可以说非常的好用。搜索记录选择它持久化也非常方便,因为搜索记录会涉及到排序,删除,限制搜索记录的条数,逻辑删除等功能,使用sqlite数据库无疑是最佳选择。
2.Android JetPack Compose
Compose是Android 推出的新一代UI框架,是一种声明式的UI框架,本文涉及的搜索功能的界面全部都由Compose开发,Compose基于Kotlin的DSL语言 做界面的UI描述,UI表达能力丝毫不逊色于XML。使用Compose,我们再也不用写XML布局和findViewByID了。建议读者去了解下Compose UI。
代码实现
编写搜索界面
搜索界面主要就是包括一个输入框,返回按钮,和展示搜索记录的部分,先定义搜索界面的Composable函数,并且定义好对应的事件回调,这样做的好处是可以让我们的程序符合单向数据流的结构,我们让数据单向流向UI,而UI的更新通过事件的方式来通知数据源头更新数据,而数据源头更新数据后,由于Compose的State是一种基于观察者模式的状态,所以当State状态更新的时候,UI会自动重组更新。所以我们需要定义一个SearchHistoryState,如下所示:
@Stable
data class SearchHistoryState(
var history_id: Long = -1L,
var history_title: String = "",
var history_content: String = "",
var createTime: Long = System.currentTimeMillis(),
var isDelete: String = "0"
)
搜索界面以回调的方式向调用者提供目前搜索界面中执行的操作,这样做可以使我们的搜索界面的复用性更高,也让搜索界面的职责更加单一,不用承担数据的更新操作。
@Composable
fun SearchPage(
searchHistoryList: MutableList<SearchHistoryState>,
onBackClick: () -> Unit,
onSearchTrigger: (String) -> Unit,
onClearAllClick: () -> Unit,
onDeleteClick: (SearchHistoryState) -> Unit,
onHistoryItemClick: (SearchHistoryState) -> Unit
) {
....
}
搜索界面也很简单页面分解如图所示:

一个纵向布局,绿色框中是一个横向布局,包括搜索框和一个返回按钮,在红色框里面就是一个纵向布局,包括显示近期浏览,全部删除按钮的头部分和展示索记录的列表部分,界面的代码就不贴了,太多了,文章结尾会给源码:
接入Room实现搜索功能的管理
引入依赖
// zoom sqlite jetpack组件
val roomVersion = "2.6.1"
implementation("androidx.room:room-runtime:$roomVersion")
implementation("androidx.room:room-ktx:$roomVersion")
implementation("androidx.room:room-paging:$roomVersion")
ksp("androidx.room:room-compiler:$roomVersion")
注意这里的KSP需要引入对应的插件
plugins {
id("com.android.application")
id("org.jetbrains.kotlin.android")
id("com.google.devtools.ksp").version("1.9.20-1.0.14") // 需要与Android的构建插件的版本相对应
}
定义包结构
如下图所示,我们先定义几个包,方便后面我们编写对应的代码,dao用来放操作数据库的方法,entitiy用于存放我们的定义的实体类,repository是我们管理dao的操作的类,调用者可以通过它获取各种dao操作接口去操作对应的表数据。
我们首先应该定义的是entity,搜索记录的entity如下所示:
@Keep //防止混淆的时候将我们的实体类混淆,导致无法找到
@Entity(tableName = "t_search_history") // 定义sqlite数据库中表的名字,后面操作搜索记录时就操作这个表
data class SearchHistory(
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)
@ColumnInfo(name = "id")
val id: Long = 0L,
@ColumnInfo(name = "title")
val title: String,
@ColumnInfo(name = "webUrl")
val webUrl: String,
@ColumnInfo(name = "create_time")
val createTime: Long = 0L,
// 是否已经删除,0表示未删除,1表示已删除
@ColumnInfo(name = "isDelete")
var isDelete: String = "0",
)
注意:我们在定义entity的类时,会映射成数据库中的表,这里就会涉及的到插入数据的记录时的id自动生成的问题,我们定义ID的时候需要将其默认值定义为0,而不是其他的
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)
@ColumnInfo(name = "id")
val id: Long = 0L,
如果定义成-1或者是其他的会导致无法插入记录,因为ID没有自增
定义操作表的Dao类
对数据进行查询,删除,更新等操作我们定义一个Dao类来实现,代码如下所示:
@Dao
interface SearchHistoryDao {
// 限制搜索记录为10条,这就是使用sqlite数据库的优势之一。可以随意变换显示的条数,并且可以通过时间排序。
@Query("select * from t_search_history where isDelete = 0 order by create_time desc limit 10")
fun getAllHistory():MutableList<SearchHistory>
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
suspend fun insertHistory(history: SearchHistory):Long
@Query("delete from t_search_history")
suspend fun clearAll()
@Transaction
@Query("select * from t_search_history where id=:id")
suspend fun findSearchHistoryById(id:Long):SearchHistory?
@Update
suspend fun update(searchHistory: SearchHistory)
}
定义数据库的基础配置
定义完entity和Dao类后,我们就可以开始定义数据库的对应配置了,之所以将这步放到entity和dao之后是因为这步需要用到entity和dao,代码如下所示:
@Database(
version = 1,//数据库的版本,这里在数据库迁移升级的时候需要改变
entities = [
SearchHistory::class,
] // 和表相互映射的实体类
)
abstract class AppSqliteDataBase:RoomDatabase(){
abstract fun searchHistoryDao():SearchHistoryDao // 定义获取Dao操作类的抽象方法。
}
// 数据库的初始化配置类,使用Room数据库时我们需要先初始化它。在我们的Application中调用AppDB.init(Context)
// 就可以初始化数据库了
class AppDB{
companion object{
fun init(context: Context):AppSqliteDataBase{
val databaseBuilder = Room.databaseBuilder(
context = context,
klass = AppSqliteDataBase::class.java,// 数据库配置类
name = "SearchDB" // 数据库的名字
).apply {
fallbackToDestructiveMigration()
}
return databaseBuilder.build()
}
}
}
定义数据库的Dao管理类
我们的项目中可能会有很多的数据库表,每个表都会有一个Dao操作接口类,所以我们需要一个类去管理这些接口,这就是我们的Repository类。如下所示:
class SearchHistoryRepository(private val db: AppSqliteDataBase) {
/**
* 获取搜索列表
*/
fun getSearchHistoryList(): MutableList<SearchHistory> {
return db.searchHistoryDao().getAllHistory()
}
/**
* 新增搜索历史记录
*/
suspend fun insertHistory(searchHistory: SearchHistory) {
val oldHistory = db
.searchHistoryDao()
.findSearchHistoryById(searchHistory.id)
if (oldHistory != null) {
db.searchHistoryDao().update(searchHistory)
} else {
db.searchHistoryDao().insertHistory(searchHistory)
}
}
/**
* 通过ID删除历史记录
*/
suspend fun deleteById(id: Long) {
val searchHistory = db.searchHistoryDao().findSearchHistoryById(id)
if (searchHistory != null) {
// 将删除的标志更新成1,表示已经删除
searchHistory.isDelete = "1"
db.searchHistoryDao().update(searchHistory)
}
}
/**
* 更新历史记录
*/
suspend fun updateHistory(searchHistory: SearchHistory) {
db.searchHistoryDao().update(searchHistory)
}
/**
* 清除历史记录
*/
suspend fun clearAllHistory() {
db.searchHistoryDao().clearAll()
}
}
使用
定义好了对应的接口后,我们就可以在ViewModel中使用了。
class SearchHistoryViewModel(db: AppSqliteDataBase) : ViewModel() {
private val TAG = "SearchHistoryViewModel"
var searchHistoryRepo: SearchHistoryRepository = SearchHistoryRepository(db = db)
var searchHistoryStateList = mutableStateListOf<SearchHistoryState>() // 使用
// compose的StateAPI,当数据更新时,界面会自动重组更新
fun loadHistoryList() {
Log.d(TAG, "loadHistoryList")
viewModelScope.launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
searchHistoryRepo.getSearchHistoryList().forEach { searchHistory: SearchHistory ->
Log.d(TAG,"loadHistoryList: $searchHistory")
val searchHistoryState = SearchHistoryState(
history_id = searchHistory.id,
history_title = searchHistory.title,
history_content = searchHistory.webUrl,
createTime = searchHistory.createTime,
isDelete = searchHistory.isDelete
)
searchHistoryStateList.add(searchHistoryState)
}
}
}
fun deleteHistory(searchHistoryState: SearchHistoryState) {
Log.d(TAG, "deleteHistory: $searchHistoryState")
viewModelScope.launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
searchHistoryStateList.remove(searchHistoryState)
searchHistoryStateList.sortBy { it.createTime }
searchHistoryRepo.deleteById(searchHistoryState.history_id)
}
}
fun addHistory(searchHistoryState: SearchHistoryState) {
Log.d(TAG, "deleteHistory: $searchHistoryState")
if(searchHistoryStateList.size == 10){
searchHistoryStateList.removeLast()
}
viewModelScope.launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
searchHistoryStateList.add(searchHistoryState)
searchHistoryStateList.sortBy { it.createTime }
val searchHistory = SearchHistory(
title = searchHistoryState.history_title,
webUrl = searchHistoryState.history_content,
createTime = searchHistoryState.createTime
)
searchHistoryRepo.insertHistory(searchHistory)
}
}
fun clearAllHistory() {
Log.d(TAG, "clearAllHistory")
searchHistoryStateList.clear()
viewModelScope.launch {
searchHistoryRepo.clearAllHistory()
}
}
fun updateHistory(searchHistoryState: SearchHistoryState){
viewModelScope.launch {
val searchHistory = SearchHistory(
title = searchHistoryState.history_title,
webUrl = searchHistoryState.history_content,
createTime = searchHistoryState.createTime
)
searchHistoryRepo.updateHistory(searchHistory)
}
}
}
在Activity中,初始化ViewModel根据搜索页面中触发的事件去做对应的搜索记录操作。
SearchPage(searchHistoryViewModel.searchHistoryStateList,
onBackClick = { finish() },
onSearchTrigger = { url ->
if (url.isNotEmpty()) {
val searchHistoryState = SearchHistoryState(
history_title = url,
history_content = url,
createTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
)
searchHistoryViewModel.addHistory(searchHistoryState)
}
},
onClearAllClick = {
searchHistoryViewModel.clearAllHistory()
},
onDeleteClick = { searchHistoryState ->
Log.d(TAG, "onDeleteClick=>searchHistoryState: $searchHistoryState")
searchHistoryViewModel.deleteHistory(searchHistoryState)
},
onHistoryItemClick = { searchHistoryState ->
Log.d(TAG, "onHistoryItemClick=>searchHistoryState: $searchHistoryState")
val content = searchHistoryState.history_content
val searchHistory = SearchHistoryState(
history_title = content,
history_content = content,
createTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
)
searchHistoryViewModel.updateHistory(searchHistory)
}
)
数据库升级
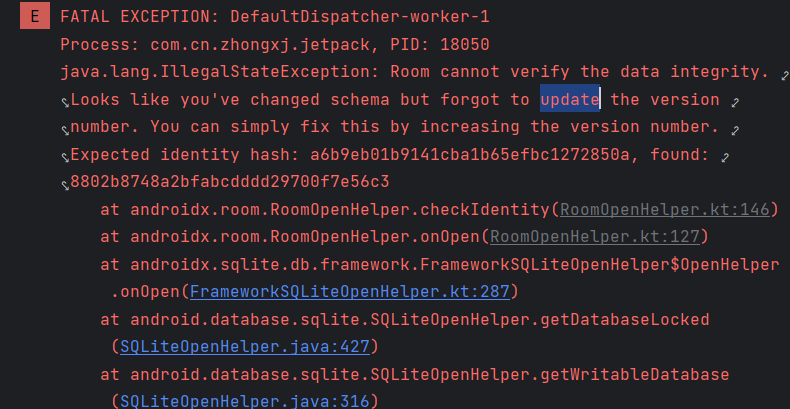
数据库升级就是我们发布了app的第一个版本,这个版本上只有搜索记录的数据库表t_searchhistory,然后我们打算发布app的第二个版本,在第二个版本上我们新增了数据库的表t_test,或者是修改了t_searchhistory的字段,这时如果用户更新我们的app第二个版本时,由于数据库中没有我们新增的第二张表,这就会导致出现下面的异常导致APP直接闪退。
所以需要我们做数据库的升级迁移,当用户安装我们第二个app版本时,我们将更新的表更新到用户的本地数据库中,我们在项目中新建一个TestEntity演示数据库的迁移升级,定义的过程和我们的搜索记录的定义过程一样,不同的点在于。我们需要新建一个Migration类去管理我们的升级版本,如下所示:
val MIGRATION_1_2 = object : Migration(1,2){
override fun migrate(db: SupportSQLiteDatabase) {
db.execSQL("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `t_test` (`id` INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT
NULL, `name` TEXT NOT NULL)")
}
}
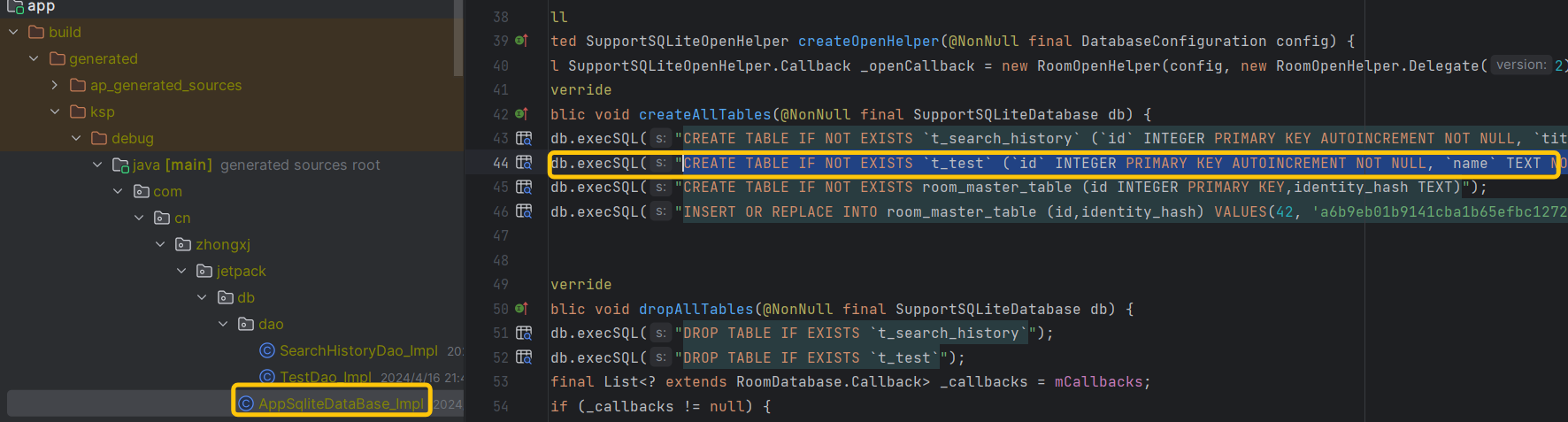
比如我们新增了一张表,就像上面的写法一样。有读者可能会决定Sqlite语句的写法有难度,还容易错,这里有个很好的办法,因为Room是使用注解去生成代码的,所以我们定义好我们的功能后,构建下项目,然后去到生成的代码中复制对应的Sqlite代码就可以了。比如本例中生成的代码如下:
 然后就是配置AppSqliteDataBase,配置对应的升级策略和版本号,如下所示:
然后就是配置AppSqliteDataBase,配置对应的升级策略和版本号,如下所示:
@Database(
version = 2,//数据库的版本升级到2
entities = [
SearchHistory::class,
TestEntity::class
] // 和表相互映射的实体类
)
abstract class AppSqliteDataBase:RoomDatabase(){
abstract fun searchHistoryDao():SearchHistoryDao
abstract fun testEntityDao():TestDao
}
class AppDB{
companion object{
fun init(context: Context):AppSqliteDataBase{
val databaseBuilder = Room.databaseBuilder(
context = context,
klass = AppSqliteDataBase::class.java,
name = "SearchDB"
).apply {
fallbackToDestructiveMigration()
addMigrations( // 数据库升级迁移
MIGRATION_1_2 // 将我们的新版APP的新增的数据库操作配置到这里就可以了
)
}
return databaseBuilder.build()
}
}
}
为了验证我们的数据库是否升级成功,我们在SearchHistoryViewModel的loadHistoryList中加入如下的测试代码:
fun loadHistoryList() {
Log.d(TAG, "loadHistoryList")
viewModelScope.launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
searchHistoryRepo.getSearchHistoryList().forEach { searchHistory: SearchHistory ->
Log.d(TAG,"loadHistoryList: $searchHistory")
val searchHistoryState = SearchHistoryState(
history_id = searchHistory.id,
history_title = searchHistory.title,
history_content = searchHistory.webUrl,
createTime = searchHistory.createTime,
isDelete = searchHistory.isDelete
)
searchHistoryStateList.add(searchHistoryState)
}
searchHistoryRepo.insertTest(TestEntity(name = "walt"))
searchHistoryRepo.insertTest(TestEntity(name = "zhong"))
searchHistoryRepo.insertTest(TestEntity(name = "007"))
searchHistoryRepo.getTestList().forEach {
Log.d(TAG,"result: $it")
}
}
}
运行结果如下表示我们数据库升级成功了。完整的例子请参考源码。
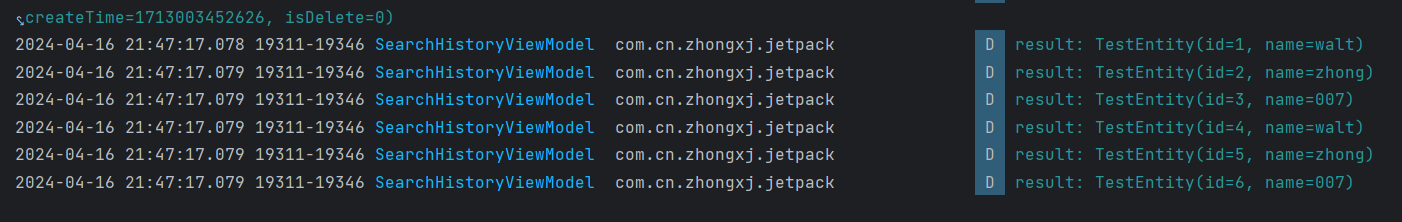
源码地址
为了方便读者熟悉Room的使用,在此贴上源码,建议读者下载源码自己动手实现一遍,后面遇到相关的需求时就可以快速搞定了。这个仓库我以后涉及到jetpack的使用时都会更新,欢迎读者克隆更新,相互参考学习。有问题欢迎评论区交流。
搜索记录功能的源码



![[阅读笔记16][Orca-2]Teaching Small Language Models How to Reason](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3162f310f55a47a08334d07cac3f2f8a.png)