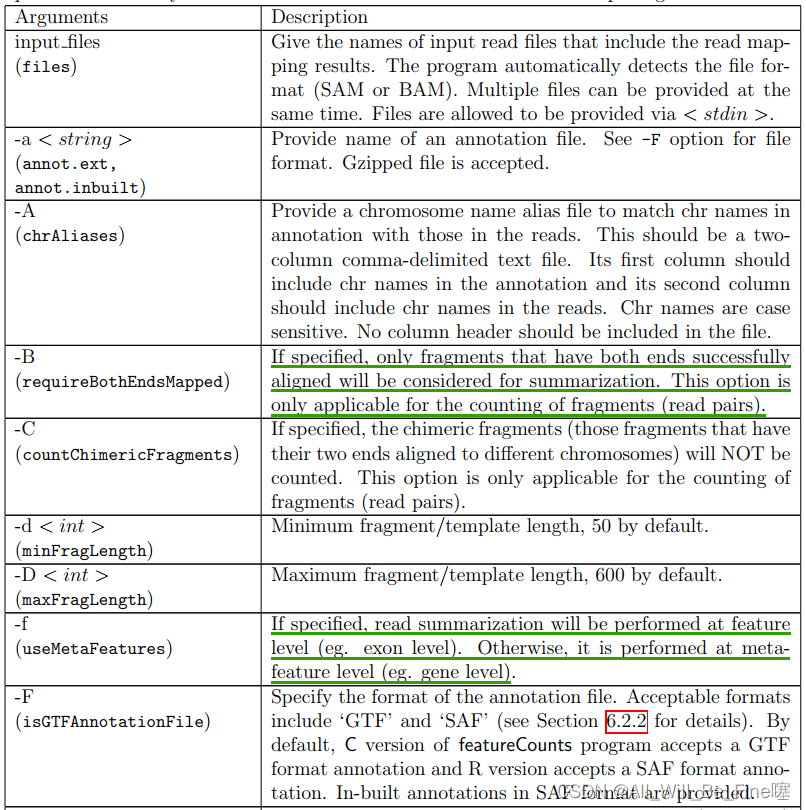
Input
- one or more files of aligned reads (short or long reads) in either SAM or BAM format
- a list of genomic features in either Gene Transfer Format (GTF) or General Feature Format (GFF) or Simplified Annotation Format (SAF)
- 比对后产生的bam或者sam文件,而且没要求samtools sort或者samtools index处理
- 基因组注释文件,需要和比对时用的基因组注释文件一致
If the input contains location-sorted paired-end reads, featureCounts will automatically re-order the reads to place next to each other the reads from the same pair before counting them. Sometimes name-sorted paired-end input reads are not compatible with featureCounts (due to for example reporting of multi-mapping results) and in this case featureCounts will also automatically re-order them
If paired reads are used, then each pair of reads defines a DNA or RNA fragment bookended by the two reads. In this case, featureCounts can be instructed to count fragments rather than reads. featureCounts automatically sorts reads by name if paired reads are not in consecutive positions in the SAM or BAM file, with minimal cost. Users do not need to sort their paired reads before providing them to featureCounts
A feature is an interval (range of positions) on one of the reference sequences. A meta-feature is a set of features that represents a biological construct of interest. For example, features often correspond to exons and meta-features to genes. Features sharing the same feature identifier in the GTF or SAF annotation are taken to belong to the same meta-feature
Users may use ‘{minOverlap (minOverlap in R)’ and ‘{fracOverlap (fracOverlap in R)’ options to specify the minimum number of overlapping bases and minimum fraction of overlapping bases requried for assigning a read to a feature, respectively. The ‘{fracOverlap’ option might be particularly useful for counting reads with variable lengths
When counting reads at meta-feature level, a hit is called for a meta-feature if the read overlaps any component feature of the meta-feature. Note that if a read hits a meta-feature, it is always counted once no matter how many features in the meta-feature this read overalps with. For instance, an exon-spanning read overlapping with more than one exon within the same gene only contributes 1 count to the gene
When assigning reads to genes or exons, most reads can be successfully assigned without ambiguity. However if reads are to be assigned to transcripts, due to the high overlap between transcripts from the same gene, many reads will be found to overlap more than one transcript and therefore cannot be uniquely assigned. Specialized transcript-level quantification tools are recommended for counting reads to transcripts. Such tools use model-based approaches to deconvolve reads overlapping with multiple transcripts.
Output
Number and percentage of successfully assigned alignments are also shown in featureCounts screen output.
- Unassigned Unmapped: unmapped reads cannot be assigned.
- Unassigned Read Type: reads that have an unexpected read type (eg. being a single end read included in a paired end dataset) and also cannot be counted with confidence (eg. due to stranded counting). Such reads are typically generated from a read trimming program.
- Unassigned Singleton: read pairs that have only one end mapped.
- Unassigned MappingQuality: alignments with a mapping quality score lower than the threshold
- Unassigned Chimera: two ends in a paired end alignment are located on different chromosomes or have unexpected orientation
- Unassigned FragementLength: fragment length inferred from paired end alignment does not meet the length criteria
- Unassigned Duplicate: alignments marked as duplicate (indicated in the FLAG field)
- Unassigned MultiMapping: alignments reported for multi-mapping reads (indicated by ‘NH’ tag)
- Unassigned Secondary: alignments reported as secondary alignments (indicated in the FLAG field)
- Unassigned Split (or Unassigned NonSplit): alignments that contain junctions (or do not contain junctions)
- Unassigned NoFeatures: alignments that do not overlap any feature
- Unassigned Overlapping Length: alignments that do not overlap any feature (or metafeature) with the minimum required overlap length
- Unassigned Ambiguity: alignments that overlap two or more features (feature-level summarization) or meta-features (meta-feature-level summarization)
Notes
A multi-mapping read is a read that maps to more than one location in the reference genome. There are multiple options for counting such reads. Users can specify the ‘-M’ option (set countMultiMappingReads to TRUE in R) to fully count every alignment reported for a multimapping read (each alignment carries 1 count),or do not count such reads at all (this is the default behavior)
A multi-overlapping read is a read that overlaps more than one meta-feature when counting reads at meta-feature level or overlaps more than one feature when counting reads at feature level.
By default, featureCounts does not count multi-overlapping reads
featureCounts implements a variety of read filters to facilitate flexible read counting, which should satisfy the requirement of most downstream analyses. The order of these filters being applied is as following (from first to last): unmapped > read type > singleton > mapping quality > chimeric fragment > fragment length > duplicate > multi-mapping > secondary alignment > split reads (or nonsplit reads) > no overlapping features > overlapping length > assignment ambiguity
The ‘read type’ filter removes those reads that have an unexpected read type and also cannot be counted with confidence. For example, if there are single end reads included in a paired end read dataset (such data can be produced from a read trimming program for instance) and reads are required to be counted in a strand-specific manner, then all the single end reads will be excluded from counting because their strandness cannot be determined
Column ‘Length’ always contains one single value which is the total number of non-overlapping bases included in a meta-feature (or a feature)
- 对于我来说,比较迷惑性的是 -f参数和 -t 参数;-f 指的是在哪个level上描述统计的reads数,比如在gene level上统计了多少reads,在exon level 上统计了多少reads;-t 指的是在那个feature上统计reads,feature可以是exon,utr,gene等,比如-t exon 参数reads map到exon上会被统计,reads map 到utr上就不会被统计。
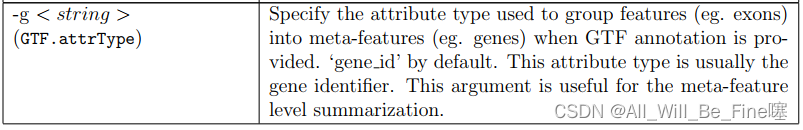
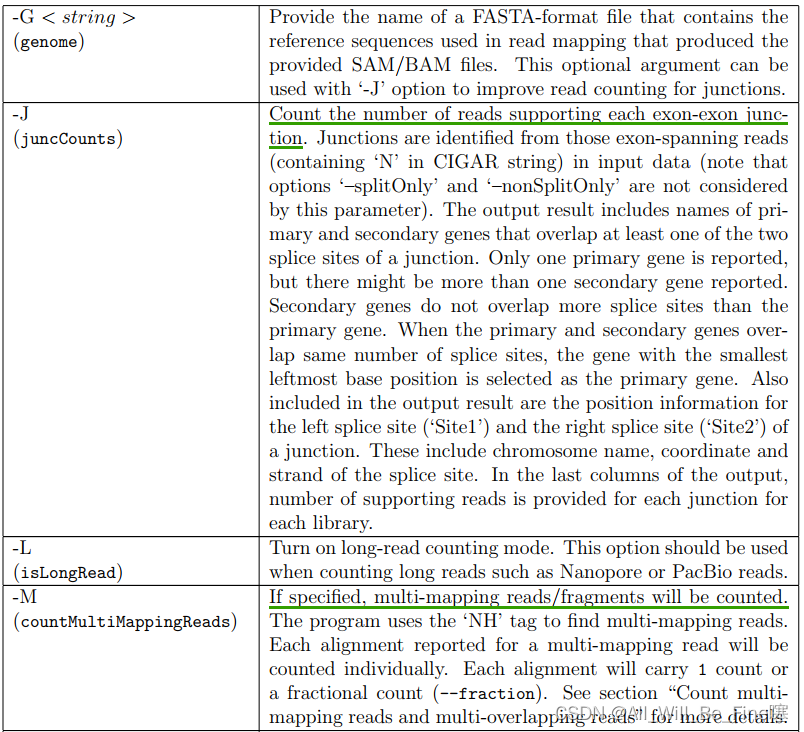
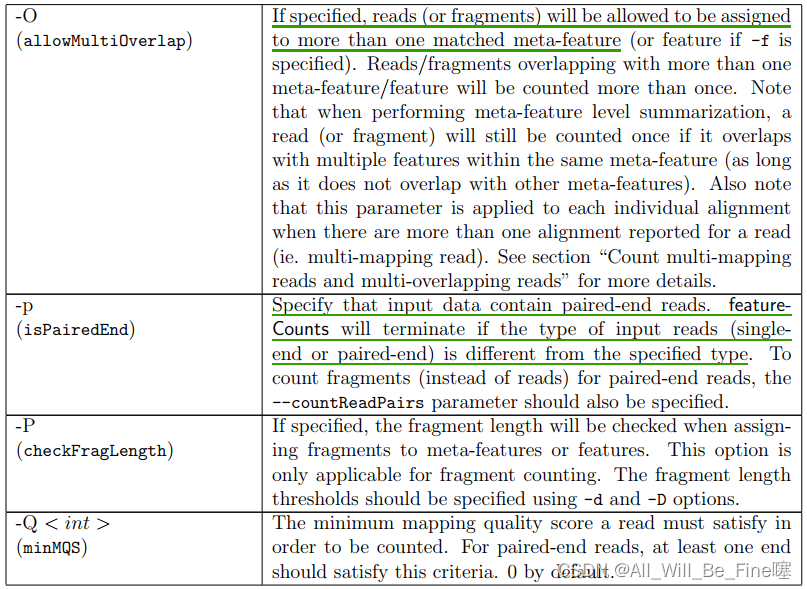
Arguments