用栈实现队列:
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 推到队列的末尾int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek()返回队列开头的元素boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回true;否则,返回false
1.题解:
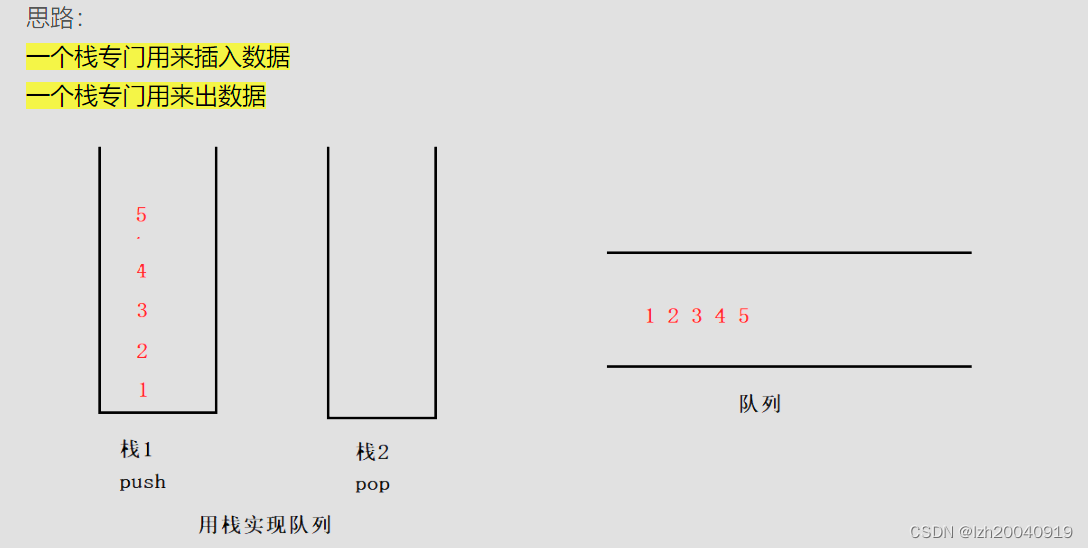
通过两个栈的配合实现队列的基本功能,下面先实现栈的基本功能
栈: (前面文章介绍过栈的实现,这里就不过多阐述)
typedef int StackDataType;
typedef struct Stack {
StackDataType* head;
int capacity;
int size;
}Stack;
//创建栈
Stack* StackCreate() {
Stack* tmp = (Stack*)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
tmp->head = NULL;
tmp->capacity = tmp->size = 0;
return tmp;
}
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack*tmp,StackDataType x) {
if (tmp->capacity == tmp->size) {
int newcapacity = tmp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * tmp->capacity;
StackDataType* cur = (StackDataType*)realloc(tmp->head, newcapacity * sizeof(StackDataType));
if (cur == NULL) {
perror("StackPush:malloc");
exit;
}
tmp->head = cur;
tmp->capacity = newcapacity;
}
tmp->head[tmp->size] = x;
tmp->size++;
}
//出栈
StackDataType StackPop(Stack*tmp) {
if (tmp->size == 0) {
perror("StackPop:NULL");
exit;
}
StackDataType s = tmp->head[tmp->size - 1];
tmp->size--;
return s;
}
//栈的销毁
void StackDestroy(Stack*tmp) {
free(tmp->head);
tmp->head = NULL;
tmp->capacity = tmp->size = 0;
free(tmp);
tmp = NULL;
}2.基于栈实现队列基本功能:
入队列:
根据上图思路,一个栈(stack1)存储数据,一个栈(stack2)出数据。
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
StackPush(obj->stack1, x);
}出队列:
出队列就涉及到判断出数据的那个栈(stack2)是否有数据(栈判空(StackEmpty))
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
if (obj->stack2->size == 0) {
while (obj->stack1->size != 0) {
StackPush(obj->stack2, StackPop(obj->stack1));
}
}
return StackPop(obj->stack2);
}返回队列顶部元素:
同样涉及判空问题,因为该功能仅和出队列少了最后删除元素
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
if (obj->stack2->size == 0) {
if (obj->stack1->size == 0) {
perror("Peek:NULL");
exit;
}
return obj->stack1->head[0];
}
return obj->stack2->head[obj->stack2->size - 1];
}判空:
stack1与stack2均为空
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
return obj->stack1->size == 0 && obj->stack2->size == 0;
}3.完整代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int StackDataType;
typedef struct Stack {
StackDataType* head;
int capacity;
int size;
}Stack;
Stack* StackCreate() {
Stack* tmp = (Stack*)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
tmp->head = NULL;
tmp->capacity = tmp->size = 0;
return tmp;
}
void StackPush(Stack*tmp,StackDataType x) {
if (tmp->capacity == tmp->size) {
int newcapacity = tmp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * tmp->capacity;
StackDataType* cur = (StackDataType*)realloc(tmp->head, newcapacity * sizeof(StackDataType));
if (cur == NULL) {
perror("StackPush:malloc");
exit;
}
tmp->head = cur;
tmp->capacity = newcapacity;
}
tmp->head[tmp->size] = x;
tmp->size++;
}
StackDataType StackPop(Stack*tmp) {
if (tmp->size == 0) {
perror("StackPop:NULL");
exit;
}
StackDataType s = tmp->head[tmp->size - 1];
tmp->size--;
return s;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack*tmp) {
free(tmp->head);
tmp->head = NULL;
tmp->capacity = tmp->size = 0;
free(tmp);
tmp = NULL;
}
typedef struct Queue{
Stack* stack1;
Stack* stack2;
}MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* queue = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
queue->stack1 = StackCreate();
queue->stack2 = StackCreate();
return queue;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
StackPush(obj->stack1, x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
if (obj->stack2->size == 0) {
while (obj->stack1->size != 0) {
StackPush(obj->stack2, StackPop(obj->stack1));
}
}
return StackPop(obj->stack2);
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
if (obj->stack2->size == 0) {
if (obj->stack1->size == 0) {
perror("Peek:NULL");
exit;
}
return obj->stack1->head[0];
}
return obj->stack2->head[obj->stack2->size - 1];
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
return obj->stack1->size == 0 && obj->stack2->size == 0;
}








![buuctf——[ZJCTF 2019]NiZhuanSiWei](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/43952c145755420cbbb606e89c3c318e.png)