多线程补充
等待唤醒机制
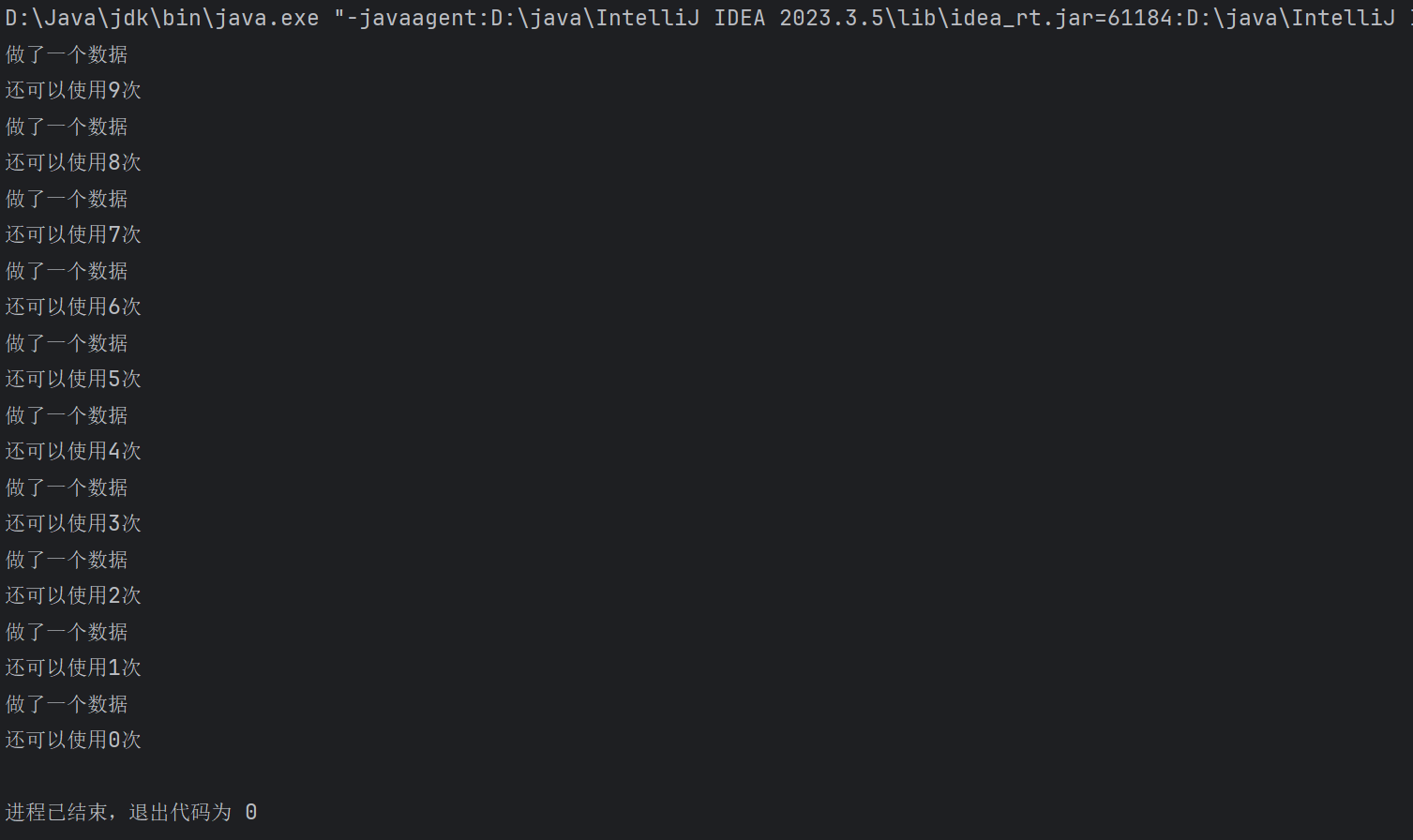
现在有两条线程在运行,其中一条线程可以创造一个特殊的数据供另一条线程使用,但这个数据的创建也有要求:在同一时间只允许有一个这样的特殊数据,那么我们要怎样去完成呢?如果用普通的多线程在理想环境下(也就是两个线程分别每个抢到一次)可以完成,但是很多时候没有这么美好,如果任意一个线程连续运行就会发生错误。我们可以让线程在运行的时候去判断这个特殊数据是否存在,然后再去根据这个结果去运行程序或是放弃占用CPU让另一个线程运行就行了。
例子:


public class dask {
//有就是1,没有就是0;
public static int food=0;
//消耗十次
public static int sum=10;
public static Object lock=new Object();
}public class cread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
synchronized (dask.lock){
if(dask.sum==0&&dask.food==0) {
break;
} else {
if(dask.food==0){
dask.food=1;
System.out.println("做了一个数据");
dask.lock.notifyAll();
}
else{
try {
dask.lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
public class food implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
synchronized (dask.lock){
if(dask.sum==0&&dask.food==0) {
break;
} else {
if(dask.food==1){
dask.sum--;
dask.food=0;
System.out.println("还可以使用"+dask.sum+"次");
dask.lock.notifyAll();
}
else{
try {
dask.lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
food food=new food();
Thread thread=new Thread(food);
thread.start();
cread cread=new cread();
Thread thread1=new Thread(cread);
thread1.start();
}
}
网络编程
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TCPin implements Runnable{
private final Socket socket;
private final String name;
public TCPin(Socket socket, String name) {
this.socket = socket;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
TCPout tcPout=new TCPout(socket,name);
Thread thread= new Thread(tcPout);
thread.start();
char []chars=new char[1000];
while(true){
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader= null;
try {
inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
int x;
try {
x=inputStreamReader.read(chars);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(new String(chars,0,x));
}
}
}import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TCPout implements Runnable{
private final Socket socket;
private final String name;
public TCPout(Socket socket, String name) {
this.socket = socket;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
OutputStream outputStream= null;
try {
outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
while(true){
String s=name+":\t"+scanner.nextLine();
try {
outputStream.write(s.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TCPclient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 1080);
TCPin tcPin=new TCPin(socket,"用户1");
tcPin.run();
}
}import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TCPclient1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 1080);
TCPin tcPin=new TCPin(socket,"用户2");
tcPin.run();
}
}import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.Socket;
public class serverin implements Runnable{
private final Socket socket;
private final String name;
public serverin(Socket socket, String name) {
this.socket = socket;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
char []chars=new char[1000];
while(true){
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader= null;
try {
inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
int x;
try {
x=inputStreamReader.read(chars);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(new String(chars,0,x));
}
}
}import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TCPserver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(1080);
ArrayList<Socket> s=new ArrayList<>();
int x=0;
while(true){
Socket socket=serverSocket.accept();
s.add(socket);
System.out.println(x);
Thread thread=new Thread(new serverin(socket,"服务器"));
thread.start();
x++;
if(x==2)
break;
}
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
OutputStream outputStream= null;
while(true) {
String b = "服务器" + ":\t" + scanner.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
try {
outputStream = s.get(i).getOutputStream();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
outputStream.write(b.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}该程序实现了多个客户端与服务端的多次通信。