Spring Boot REST API - CRUD 操作
这里主要提一下 spring boot 创建 rest api,并对其进行 CRUD 操作
jackson & gson
目前浏览器和服务端主流的交互方式是使用 JSON(JavaScript Object Notation),但是 JSON 没有办法直接和 Java 的 POJO 创建对应关系,因此就需要一些库去实现这个转换的功能:
- 将 JSON 转换成 Java POJO
- 将 Java POJO 转化成 JSON
- 实现序列化和反序列化
目前比较主流的两个库是 jackson 和 gson,这里选用 jackson,不需要做任何的配置,spring 默认使用 jackson,并且在默认情况下使用 setter/getter 对 POJO 的属性进行赋值
POM
项目依旧使用 spring initializer 创建,这里是额外需要勾选的两个库:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
其中 lombok 可选,我只是懒得写 boilerplate code 所以直接安装了 lombok,配制方法在 Intellij 安装配置 lombok,这里不多赘述。如果 IDE 没有配置 lombok 可能会导致这个工具没法用
创建一个 rest controller
实现如下:
package com.example.demo.rest;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class DemoRestController {
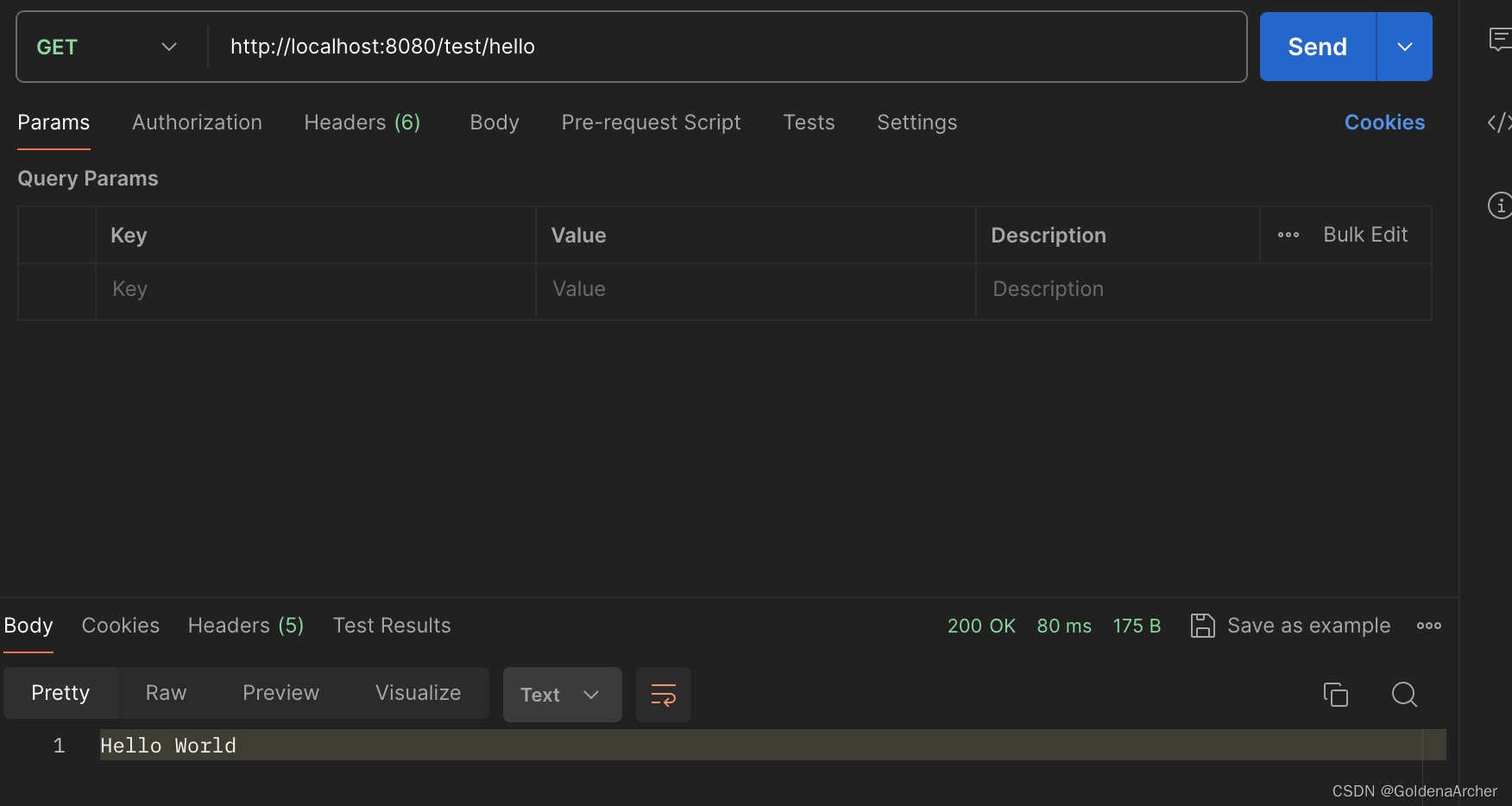
// add code for the "/hello" endpoint
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello World";
}
}
效果如下:
这里几个注解的用途如下:
-
@RestController告知 spring boot 这是一个 restful api 的 controller是传统 spring mvc 里
@Controller+@ResponseBody的结合 -
@RequestMapping这个注解 spring mvc 里就有,表示处理的所有 rest api 都会 map 到
/test这个路径下 -
@GetMapping表示这里会接受一个 HTTP 的 Get 请求,对应的路径是
/hello比较新版本的 sping mvc 也应该有这个注解
POJO
这里就是非常简单的定义一个 java class:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Student {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
}
其中三个注解来自于 lombok
Rest Controller 实现
CRUD 的实现,关于具体的 API 设计结尾处会稍微提一下
获取全部学生
实现如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class StudentRestController {
// define endpoint for "/students" - return a list of students
@GetMapping("/students")
public List<Student> getStudents() {
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student("Peter", "Parker"));
students.add(new Student("Stephen", "Strange"));
students.add(new Student("Steve", "Rodgers"));
return students;
}
}
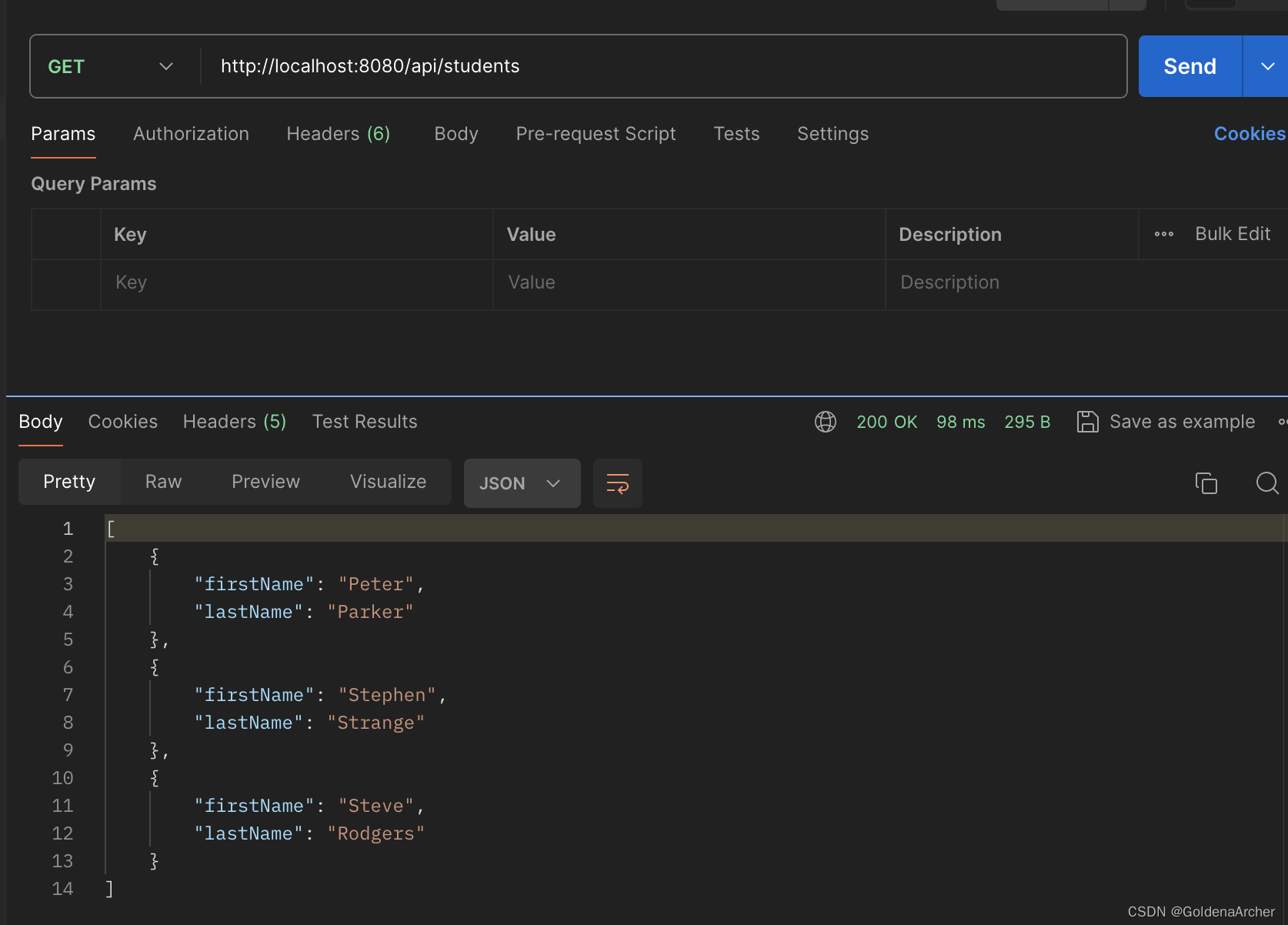
这里没有连接数据库,所以用一个 ArrayList 放所有的对象,并进行返回。可以看到返回值是一个正常的 JSON
路径变量 Path Variables
path variable 是一种可以从 URL 路径中获取变量的方式,如 client 可以调用这个路径: /api/students/{studentId}, 那么 studentId 就是路径变量
简单重构
开始之前先做一下简单重构,这样可以不用反复创建新的 ArrayList:
public class StudentRestController {
private List<Student> students;
// define @PostConstruct to load the student data, it will only load data once
@PostConstruct
public void loadData() {
this.students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student("Peter", "Parker"));
students.add(new Student("Stephen", "Strange"));
students.add(new Student("Steve", "Rodgers"));
}
// define endpoint for "/students" - return a list of students
@GetMapping("/students")
public List<Student> getStudents() {
return students;
}
}
@PostConstruct 是 JavaEE 的规范之一,会在容器初始化后当前 bean 后被调用,且只会被调用一次,因此这里用来实现数据的赋值
路径变量实现
实现比较粗暴,直接获取对应下标的值:
// define ent point for "students/{studentId}" - return student at index
@GetMapping("/students/{studentId}")
// by default, param should match
public Student getStudent(@PathVariable int studentId) {
return this.students.get(studentId);
}
实现效果如下:
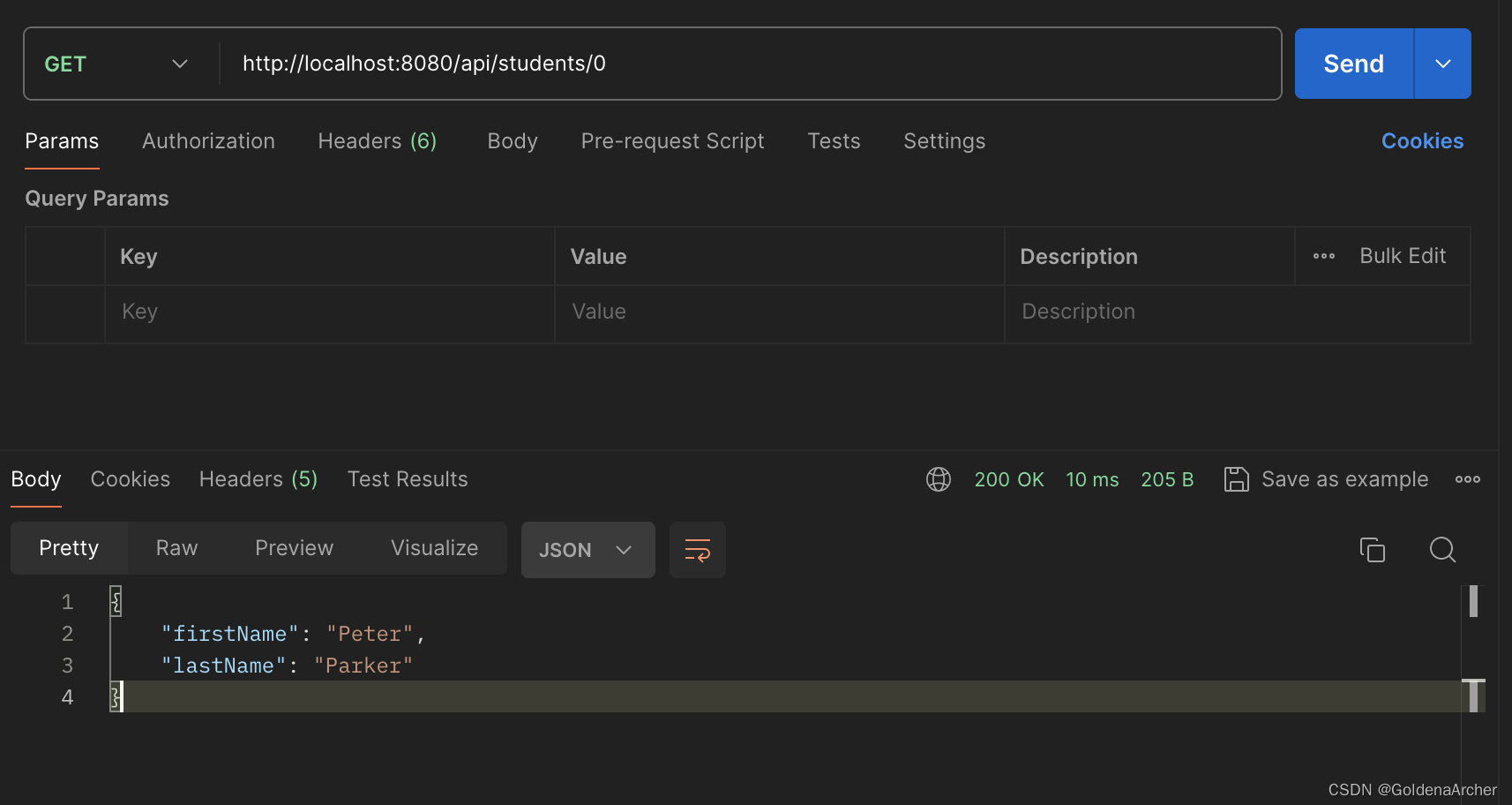
⚠️:函数中的变量名和路径变量中的名称应当保持一致
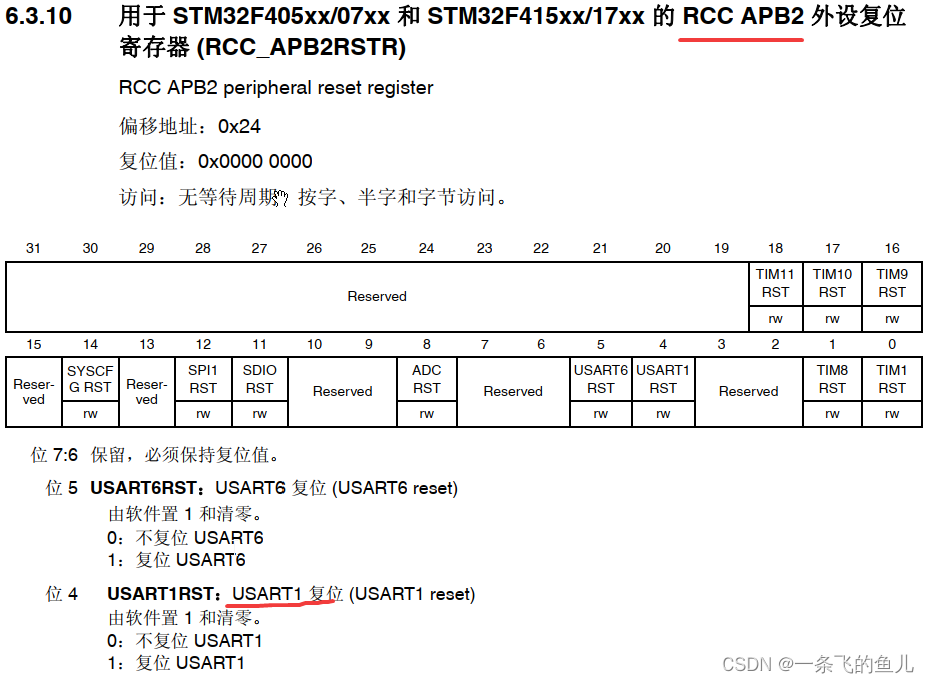
异常处理
假设 studentId 并不是一个合法的参数,如 ArrayList 中只有三条数据,但是提供的 id 为 99,或者提供的不是数字,而是字符串,那么就会出现对应的异常:
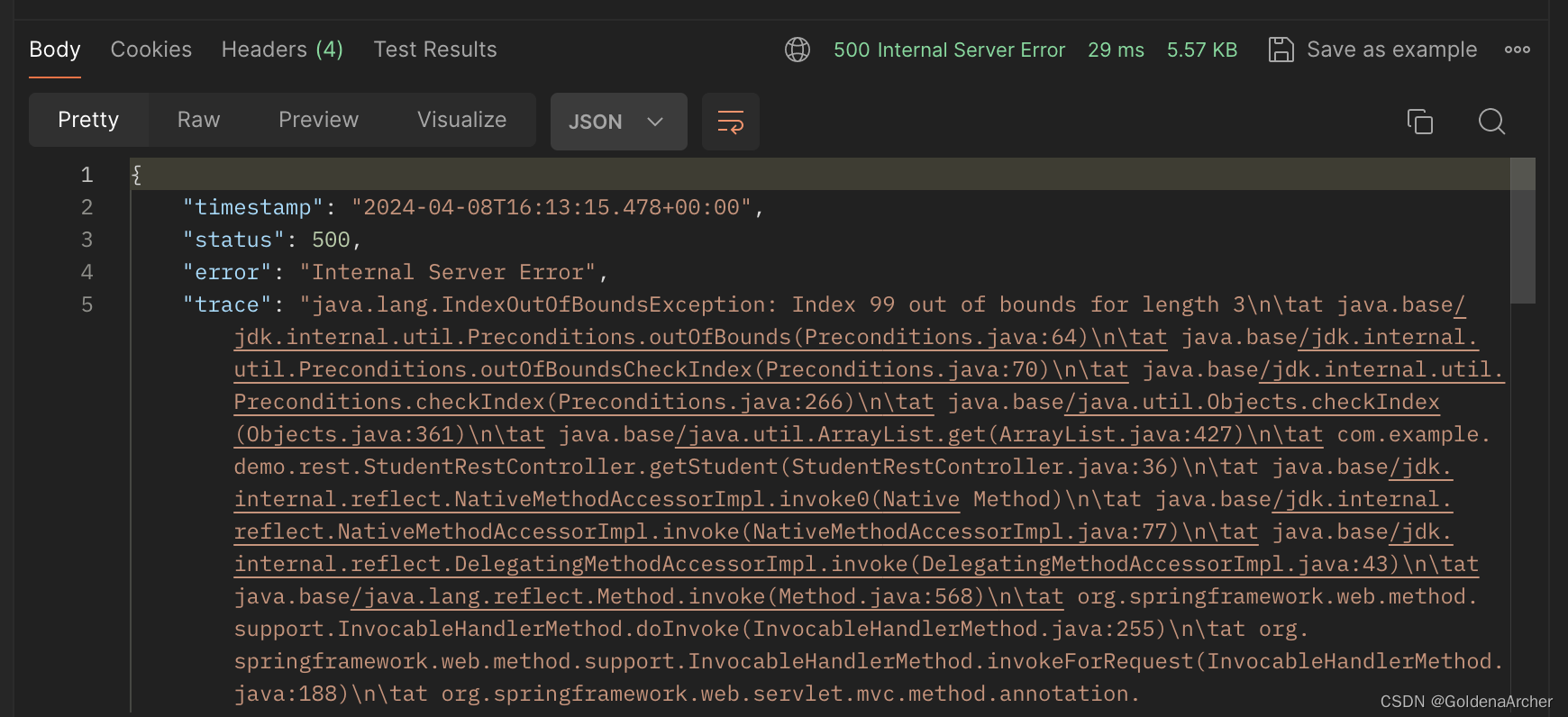
这种情况下,用户其实并不需要了解这么多的信息,ta 可能只需要知道传过去的 id 不对,数据库找不到对应的数据即可。spring mvc 也提供了一个 @ExceptionHandler 去处理报错信息。实现方法如下:
- 创建对应的 error response POJO
- 创建对应的 exception 类
- 更新对应的 rest 实现,抛出在第 2 步里实现的 exception
- 使用
@ExceptionHandler捕获对应异常,并且返回一个对应的ResponseEntity<T>, 其中T为第 1 步里创建的 POJO,jackson 会将其转换成对应的 JSON 对象
定义 error res pojo
实现如下,非常简单:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class StudentErrorResponse {
private String message;
private int status;
private long timeStamp;
}
依旧使用 Lombok 解决大部分的问题
创建 custom exception
这里实现的是 not found exception,因为没有用默认参数,也没有用全参,所以没有使用 Lombok
public class StudentNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
public StudentNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public StudentNotFoundException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public StudentNotFoundException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
抛出异常
// define ent point for "students/{studentId}" - return student at index
@GetMapping("/students/{studentId}")
public Student getStudent(@PathVariable int studentId) {
// check the studentId against list size
if (studentId >= this.students.size() || studentId < 0) {
throw new StudentNotFoundException(("Student id not found - " + studentId));
}
return this.students.get(studentId);
}
这里主要处理的是 index out of bound 的异常,如果参数类型不对则需要 overload 方法:
捕获异常
使用 ExceptionHandler 去捕获对应的异常,并且将 error code 修改成 404,表示无法根据当前 id 获取对应数据
// add the exception handler
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<StudentErrorResponse> handleException(StudentNotFoundException exec) {
// create a studentErrorResponse
StudentErrorResponse error = new StudentErrorResponse();
error.setStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value());
error.setMessage(exec.getMessage());
error.setTimeStamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
// return ResponseEntity
return new ResponseEntity<>(error, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
显示结果如下:
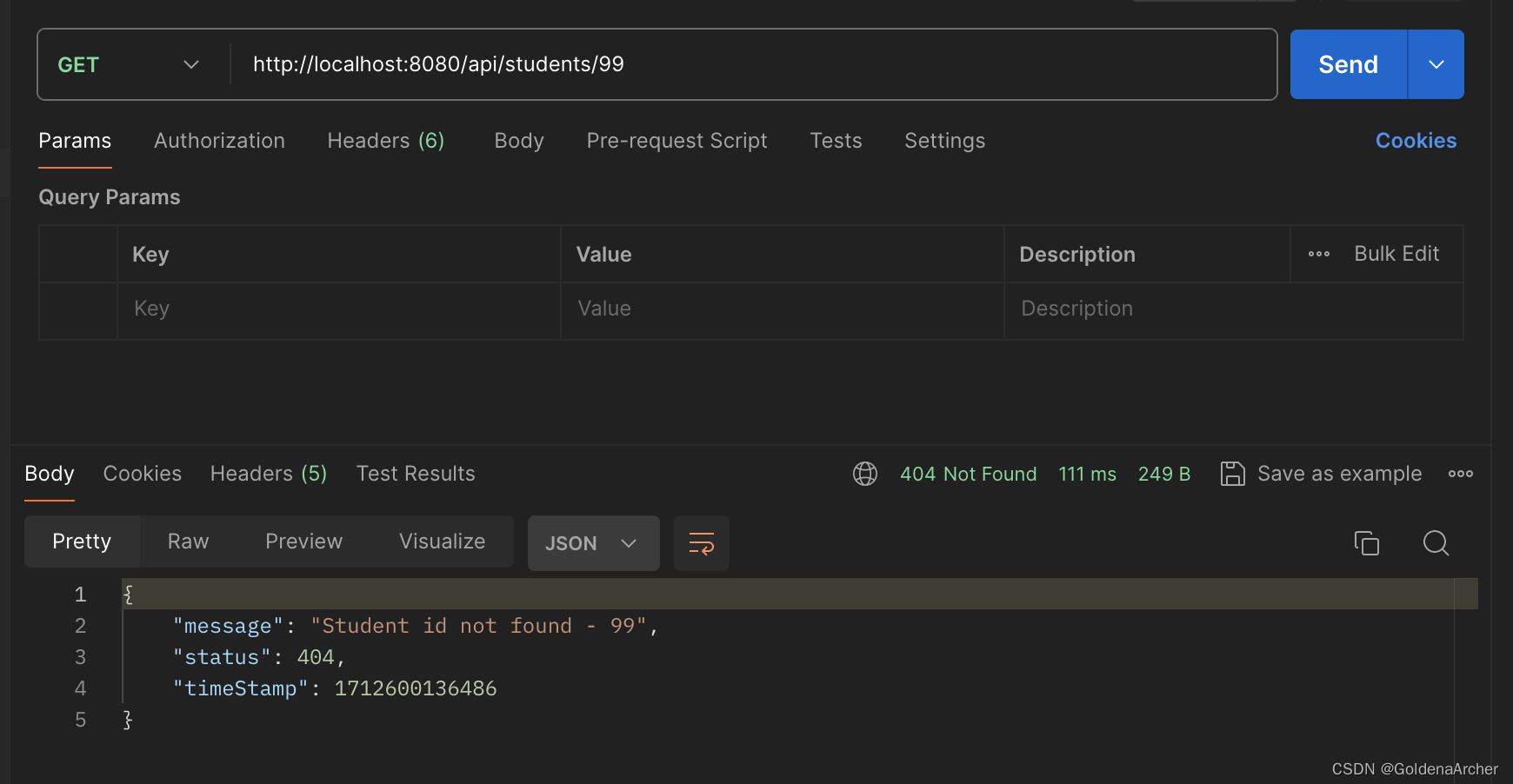
添加 generic 报错处理
这个时候如果传入 string 的话,抛出的异常还是不太好看:
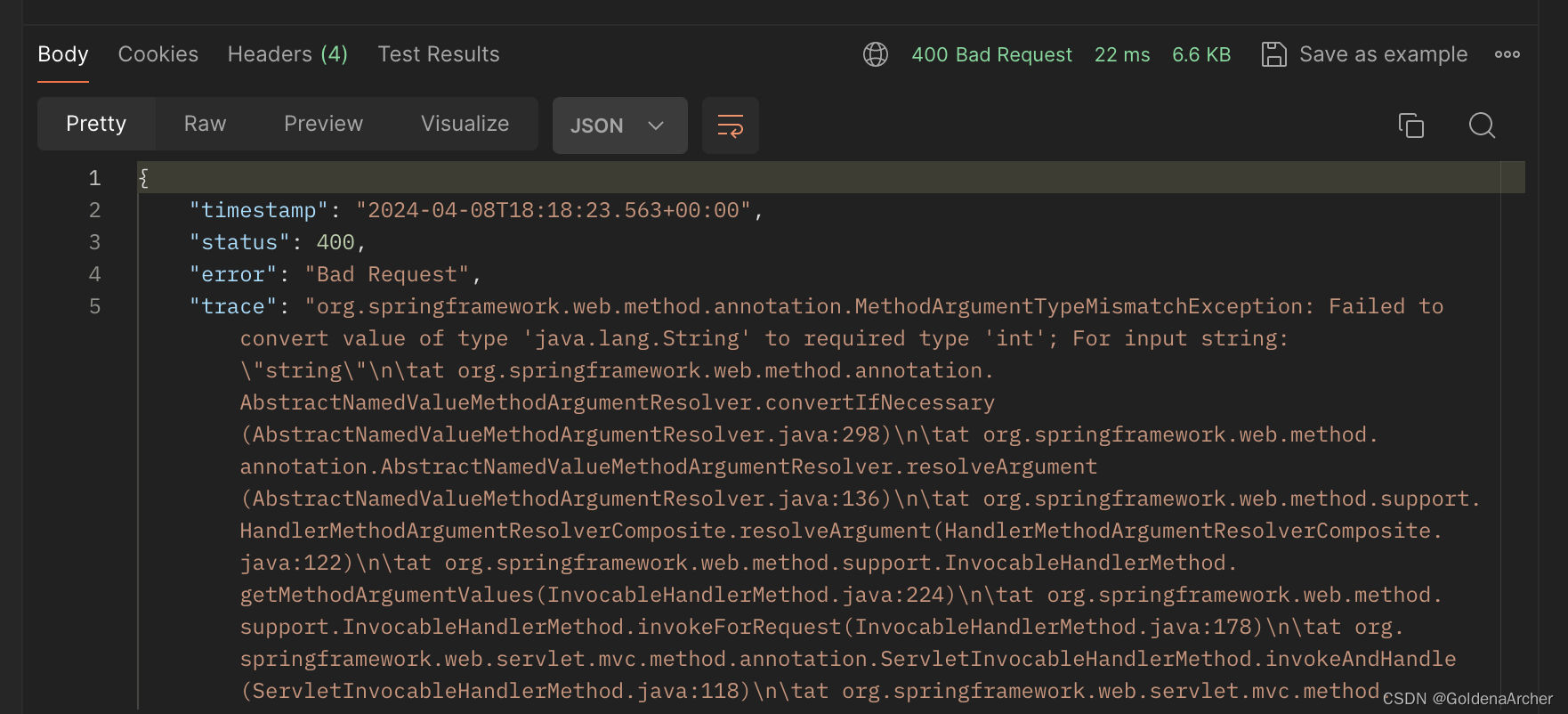
所以这里可以添加一个 generic 的报错信息,表示传进来的参数不对,是 bad request 即可:
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<StudentErrorResponse> handleException(Exception e) {
// create a studentErrorResponse
StudentErrorResponse error = new StudentErrorResponse();
error.setStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
error.setMessage(e.getMessage());
error.setTimeStamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
// return ResponseEntity
return new ResponseEntity<>(error, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
显示结果如下:
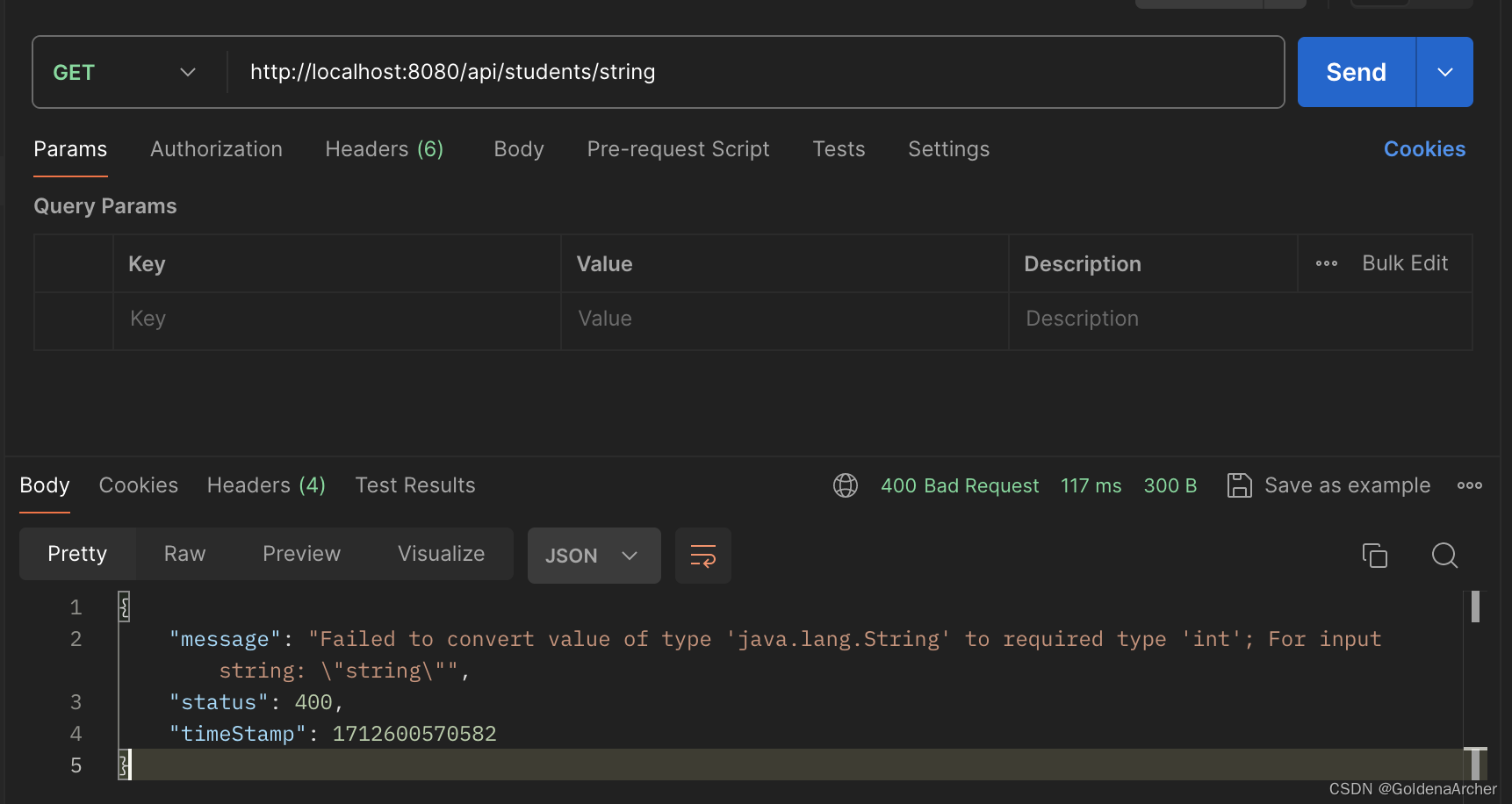
注意这里所有的处理都是在 controller 中实现的:
全局异常处理
这里会使用 @ControllerAdvice 这个注解去实现,这是一个 AOP 的具体实现——即向已经存在的代码中注入新的行为(advice)
这里实现的方式很简单
-
创建一个新的 exception handler class,添加
@ControllerAdvice注解@ControllerAdvice public class StudentRestExceptionHandler {} -
重构
将 controller 中的 exception handling 删掉
同时将 exception handling 贴到
StudentRestExceptionHandler中去
实现后的结构如下:
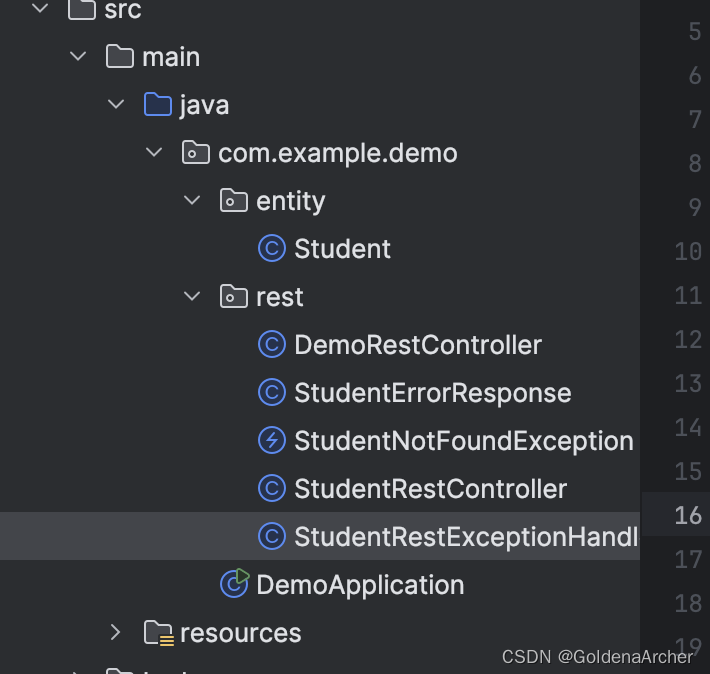
这样这个 handler 就能捕捉全局的报错,如修改一下 DemoRestController 中的代码,使其同样报错,也是可以捕获到的:
API 设计
写一些比较常识性的内容,已经对 RESTful 有了解的可以跳过
设计 API 的时候主要需要考虑三个点:
-
谁会使用这个 API
这个主要看的是目标用户,如这个 API 是会在同一个项目使用?公司内部使用?还是公开项目?
-
API 将会被怎样使用
也就是说 API 的使用情况,如交易系统需要考虑付款、退款(部分退款/全部退款)、查看付款状态
目前来说主流是 RESTful,不过使用 GraphQL 又是不同的情况
-
任务需求是什么
resource 的名称,支持的 HTTP 请求头等
目前来说主流的 API 设计规范如下:
| HTTP Method | Endpoint | CRUD 操作 |
|---|---|---|
| POST | /employee | Create |
| GET | /employee/ | Read |
| GET | /employee/{id} | Read |
| PUT | /employee/{id} | Update |
| DELETE | /employee/{id} | Delete |
之前看到一些比较反常识的操作有一个: /api/deleteEmployee,如果是 delete 的话,应该是 HTTP 使用 DELETE,Endpoint 用 employees