文章目录
- 1. 数字统计
- 2. 两个数组的交集
- 3. 点击消除
1. 数字统计
【链接】:数字统计
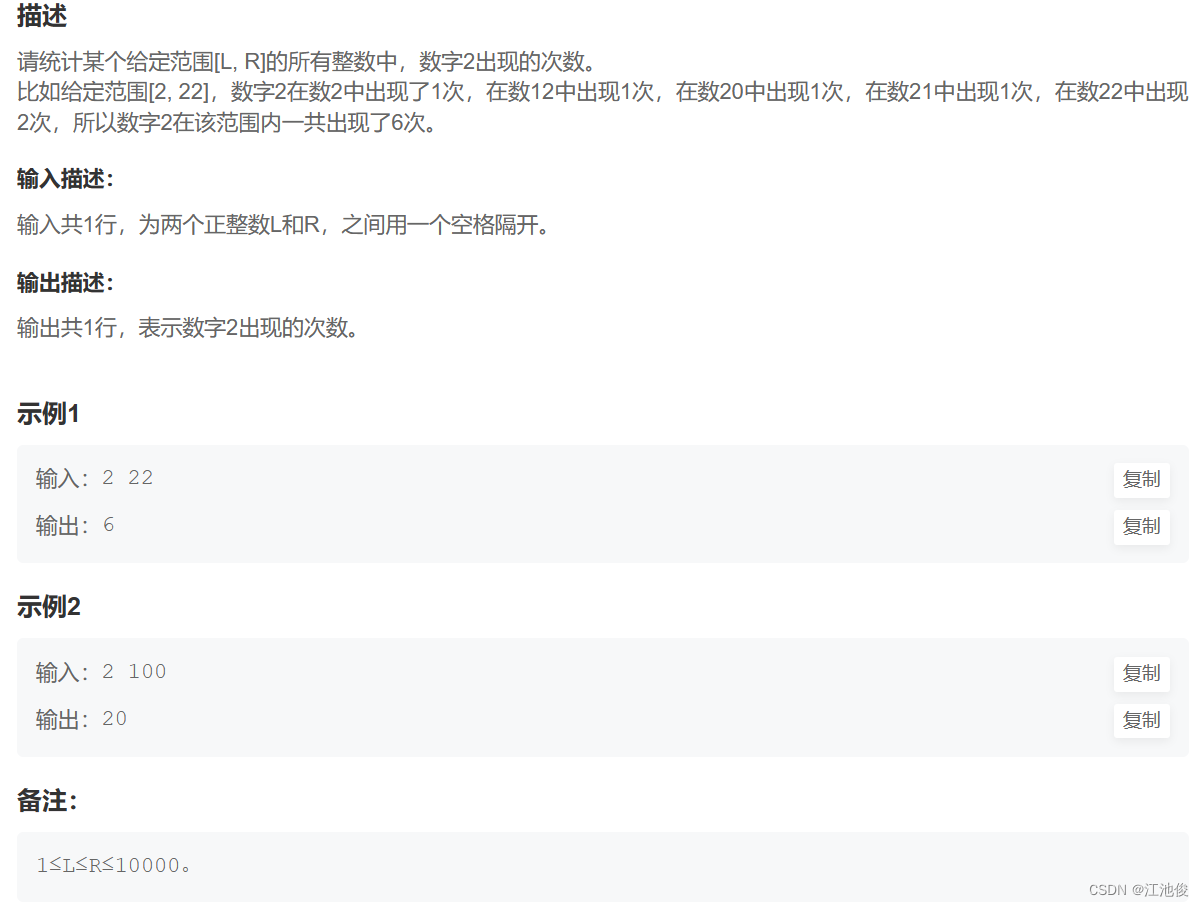
解题思路:模拟,利用数学知识,计算每个数字中2出现的个数。(这里也可以将数字转换成字符串来统计字符’2’出现的个数)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int l,r;
cin>>l>>r;
int ret = 0;
for(int i = l;i <= r;i++)
{
int temp = i;
while(temp)
{
if(temp % 10 == 2) ret++;
temp /= 10;
}
}
cout<<ret<<endl;
return 0;
}
// #include <iostream>
// using namespace std;
// int main() {
// int l,r;
// cin>>l>>r;
// int ret = 0;
// for(int i = l;i <= r;i++)
// {
// string temp = to_string(i);
// for(auto& ch:temp)
// {
// if(ch == '2') ret++;
// }
// }
// cout<<ret<<endl;
// return 0;
// }
2. 两个数组的交集
【链接】:两个数组的交集
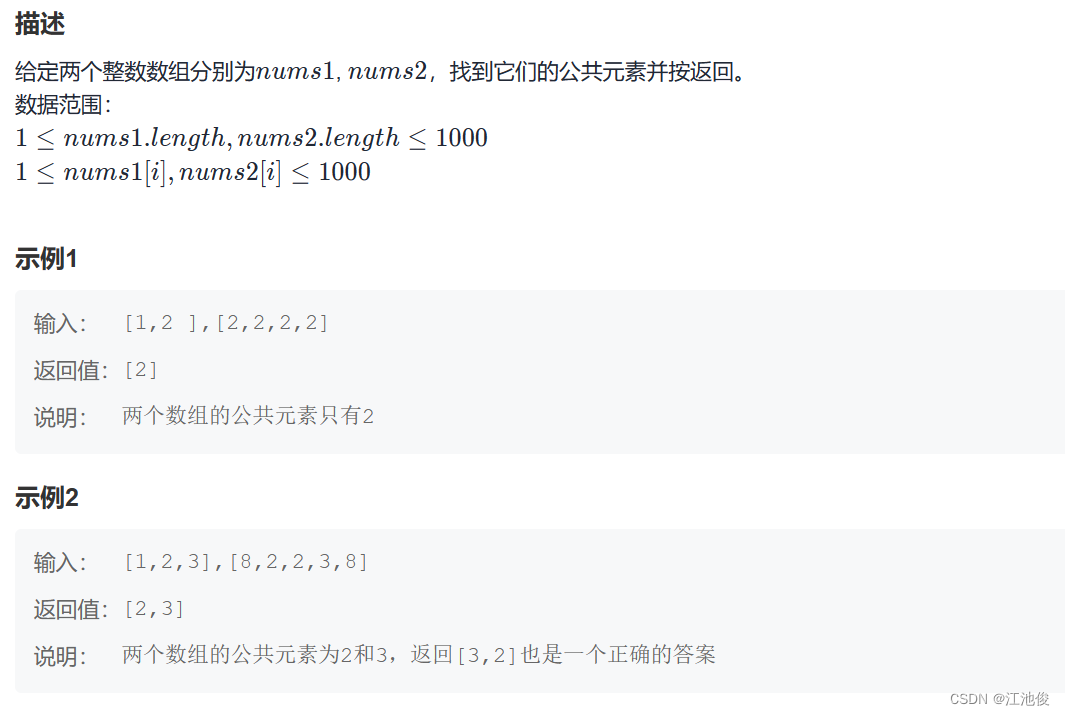
解题思路:利用哈希表记录第一个数组中每个元素是否出现,再次遍历第二个数组的元素,如果元素在哈希表出现就将该元素添加到记录最终结果的数组 ret 中,然后将哈希表中该元素删除(对应值改为false即可),遍历完成后,最后结果即在 ret 数组中。
class Solution {
vector<int> ret; // 记录最终结果
bool hash[1010] = {false}; // 哈希表
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
for(auto& x:nums1) // 统计第一个数组
{
hash[x] = true;
}
for(auto& x:nums2) // 遍历第二个数组
{
if(hash[x]) ret.push_back(x);
hash[x] = false;
}
return ret;
}
};
3. 点击消除
【链接】:点击消除
解题思路:利用栈的先进先出特点,并不需要一个真的栈,我们只需要用一个 string 来模拟栈即可,遍历字符串,当栈顶元素与当前遍历到的字符不相等(或者栈为空)时,将该字符加入栈中,否者将栈顶这个相等的字符弹出,继续遍历下一个字符,直到字符串末尾为止。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str,st; // st用来模拟栈
cin>>str;
for(auto& ch:str)
{
if(!st.empty() && st.back() == ch) st.pop_back();
else st += ch;
}
cout<<(st.empty() ? "0" : st)<<endl;
return 0;
}