为了使主程代码不受阻塞之苦,一般使用异步编程,而异步编程架构在JDK1.5便已有了雏形,主要通过Future和Callable实现,但其操作方法十分繁琐,想要异步获取结果,通常要以轮询的方式去获取结果,具体如下:
public static void testFuture1() throws Exception {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//定义一个异步任务
Future<String> future = executorService.submit(()->{
Thread.sleep(3000);
return "Future异步请求方法";
});
//轮询获取结果,耗费的CPU资源
while (true){
if(future.isDone()) {
System.out.println(future.get());
break;
}
}
}在JDK8后首次引入的CompletableFuture,简化异步编程复杂性,提供了函数式编程让代码更加简洁,可以在任务完成后做对应的callback回调处理。接下来,我带你一步步了解并掌握CompletableFuture。
什么是CompletableFuture
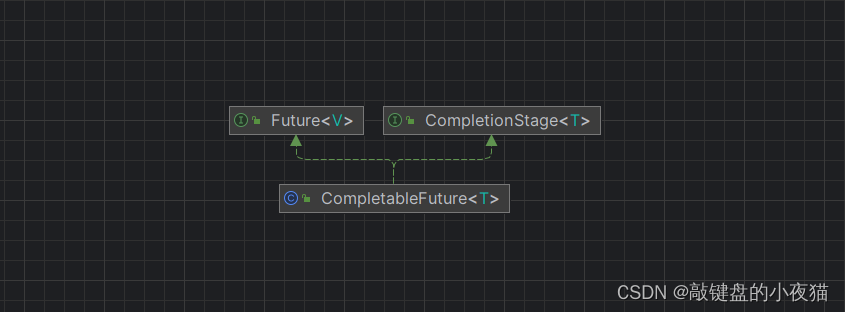
在项目开发中,由于业务规划逻辑的原因,业务需要从多个不同的地方获取数据,然后汇总处理为最终的结果,再返回给请求的调用方,就是聚合信息处理类的处理逻辑。如果常用串行请求,则接口响应时间长;那么利用CompletableFuture则可以大大提升性能。针对多任务,需要进行任务编排调度,也可以使用CompletableFuture进行完成。
其内部就是实现了Future和CompletionStage接口,相当于一个Task编排工具。
Future表示了其异步计算的结果,它提供了检查计算是否完成的方法,以等待计算的完成。计算完成后只能使用 get 方法来获取结果,有cancel、get、isDone、isCancelled等方法。
CompletionStage是Java8新增接口,用于异步执行中的阶段处理,CompletableFuture就是其中的一个实现类。负责对任务处理可以构造一条结果传递链,在结果传递过程中任何一个CompletionStage都可以对结果进行处理,包括异常处理、类型转换,可以构造非常简单的传递链也可以构造很复杂的传递链,几个CompletionStage可以串联起来,一个完成的阶段可以触发下一阶段的执行。
当前的Task到底由那个Thread执行,使用的不好可能会有性能问题, 根据CompletableFuture的方法命名可以掌握。
xxxx():表示该方法将继续在当前执行CompletableFuture的方法线程中执行;
xxxxAsync():表示异步,在线程池中执行。在没有指定线程池的情况下,使用的是CompletableFuture内部的线程池 ForkJoinPool ,线程数默认是 CPU 的核心数。一般不要所有业务共用一个线程池,避免有任务执行一些很慢的 I/O 操作,会导致线程池中所有线程都阻塞在 I/O 操作上,从而造成线程饥饿,影响整个系统的性能。
方法API
CompletableFuture静态方法,执行异步任务的API
//无返回值,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
//无返回值,可以自定义线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
//有返回值,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
//有返回值,可以自定义线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)CompletableFuture对象,获取结果的API
//如果返回值没有返回,一直阻塞
V get()
//设置等待超时的时间
V get(long timeout,Timeout unit);
//有返回值就返回, 线程抛出异常就返回设置的默认值
T getNow(T defaultValue);CompletableFuture对象,其他重点API
//方法无返回值,当前任务正常完成以后执行,当前任务的执行结果可以作为下一任务的输入参数
thenAccept
//方法有返回值,当前任务正常完成以后执行,当前任务的执行的结果会作为下一任务的输入参数
thenApply
//对不关心上一步的计算结果,执行下一个操作
thenRun异步编程具体代码
public class CompletableFutureDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
testFuture3();
System.out.println("主线程操作其他----");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("主线程执行完成");
}
//简单案例
public static void testFuture2() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//有返回值,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) { }
return "supplyAsync";
});
System.out.println("future1返回值:" + future1.get()); //输出 supplyAsync
}
//任务编排案例,有返回值
public static void testFuture3() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
//有返回值,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) { }
System.out.println("执行任务一");
return "supplyAsync";
});
System.out.println("future1返回值:" + future1.get()); //输出 supplyAsync
//有返回值,当前任务正常完成以后执行,当前任务的执行的结果会作为下一任务的输入参数
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = future1.thenApply((element) -> {
System.out.println("入参:"+element);
System.out.println("执行任务二");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(6);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return "thenApply";
});
System.out.println("future2返回值:" + future2.get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
//任务编排案例,无返回值
public static void testFuture4() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
//有返回值,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) { }
System.out.println("执行任务一");
return "supplyAsync";
});
//无返回值,当前任务正常完成以后执行,当前任务的执行结果可以作为下一任务的输入参数
CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = future1.thenAccept((element) -> {
System.out.println("入参:"+element);
System.out.println("执行任务二");
});
//System.out.println("future2返回值:" + future2.get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("future2返回值:" + future2.get());
}
}CompletableFuture嵌套案例
日常的任务中,通常定义的方法都会返回 CompletableFuture 类型,方便后续操作,然后将该任务的执行结果Future作为方法入参然后执行指定的方法, 返回一个新的CompletableFuture任务它们之间存在着业务逻辑上的先后顺序。thenCompose用来连接两个CompletableFuture,是生成一个新的CompletableFuture,用于组合多个CompletableFuture,也可以使用 thenApply() 方法来描述关系,但返回的结果就会发生 CompletableFuture 的嵌套,CompletableFuture<CompletableFuture< Product >> 这样的情况,需要get两次
具体代码
public class Product {
private int id;
private String title;
private String detail;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getDetail() {
return detail;
}
public void setDetail(String detail) {
this.detail = detail;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product{" +
"id=" + id +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", detail='" + detail + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public class ProductDetailService {
private static final Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
static {
map.put(1,"java-详情");
map.put(2,"python-详情");
map.put(3,"c#-详情");
map.put(4,"spring-详情");
map.put(5,"springboot-详情");
map.put(6,"harbor-详情");
map.put(7,"mybatis-详情");
}
public String getById(int id){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("DetailService # getById方法运行线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return map.get(id);
}
}
public class ProductService {
private static final Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
static {
map.put(1,"java");
map.put(2,"python");
map.put(3,"c#");
map.put(4,"spring");
map.put(5,"springboot");
map.put(6,"harbor");
map.put(7,"mybatis");
}
public String getById(int id){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("ProductService # getById方法运行线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return map.get(id);
}
}
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
testComposeFuture();
}
//之前的方案, 方法的返回值也是CompletableFuture,则会出现嵌套
public static void testEmbedFuture() throws Exception {
ProductService productService = new ProductService();
ProductDetailService detailService = new ProductDetailService();
int id = 1;
CompletableFuture<CompletableFuture<Product>> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String title = productService.getById(id);
Product product = new Product();
product.setTitle(title);
product.setId(id);
System.out.println("步骤1:主线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()+",获取产品信息:"+ product);
return product;
}).thenApply(new Function<Product, CompletableFuture<Product>>() {
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Product> apply(Product product) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//用到了上个线程的返回值
String detail = detailService.getById(product.getId());
product.setDetail(detail);
System.out.println("步骤2:主线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()+",获取产品信息:"+ product);
return product;
});
}
});
System.out.println("线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 结果:" + future.get().get().toString());
}
//现在的方案
public static void testComposeFuture() throws Exception {
ProductService productService = new ProductService();
ProductDetailService detailService = new ProductDetailService();
int id = 1;
CompletableFuture<Product> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String title = productService.getById(id);
Product product = new Product();
product.setTitle(title);
product.setId(id);
System.out.println("步骤1:主线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()+",获取产品信息:"+ product);
return product;
})
.thenCompose(product -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String detail = detailService.getById(product.getId());
product.setDetail(detail);
System.out.println("步骤2:主线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()+",获取产品信息:"+ product);
return product;
}));
System.out.println("线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() +
" 结果:" + future.get().toString());
}
}
thenCombine合并CompletableFuture案例
需要请求两个个接口,然后把对应的CompletableFuture进行合并,返回一个新的CompletableFuture
具体代码
public static void testFuture6() throws Exception {
ProductService productService = new ProductService();
ProductDetailService detailService = new ProductDetailService();
int id = 1;
//第1个任务
CompletableFuture<Product> baseProductFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String title = productService.getById(id);
Product product = new Product();
product.setTitle(title);
product.setId(id);
return product;
});
//第2个任务
CompletableFuture<Product> detailProductFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String detail = detailService.getById(id);
Product product = new Product();
product.setDetail(detail);
product.setId(id);
return product;
});
//将上面2个任务的返回结果baseProduct和detailProduct合并,返回新的包括全部的
CompletableFuture<Product> resultFuture = baseProductFuture
.thenCombine(detailProductFuture,
new BiFunction<Product, Product, Product>() {
@Override
public Product apply(Product base, Product detail) {
base.setDetail(detail.getDetail());
return base;
}
}
);
System.out.println("线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() +
" 结果:" + resultFuture.get().toString());
}多个CompletableFuture任务组合调度
前面学习处理两个 Future 的关系,如果超过两个Future,如何处理他们的一些聚合关系呢?
方法 allOf 和 anyOf两个函数都是静态函数,参数是变长的 CompletableFuture 的集合,前者是「与」,后者是「或」。
allOf 返回值是 CompletableFuture< Void >类型,因为allOf没有返回值,所以通过thenApply,获取每个 CompletableFuture 的执行结果。
anyOf 只要有任意一个 CompletableFuture 结束,就可以做接下来的事情,不像 allOf 要等待所有的 CompletableFuture 结束,每个 CompletableFuture 的返回值类型都可能不同,无法判断是什么类型, 所以 anyOf 的返回值是 CompletableFuture< Object >类型。
具体代码
public class Test2 {
public static void testAllOf() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1完成");
return "future1";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future2完成");
return "future2";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future3完成");
return "future3";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> all = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2, future3);
//阻塞,直到所有任务结束。
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + LocalDateTime.now() + ":阻塞");
//调用join方法等待全部任务完成
all.join();
if (all.isDone()) {
//一个需要耗时2秒,一个需要耗时3秒,只有当最长的耗时3秒的完成后,才会结束。
System.out.println("全部任务完成");
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + LocalDateTime.now() + ":阻塞结束");
}
public static void testAnyOf() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1完成");
return "future1";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future2完成");
return "future2";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future3完成");
return "future3";
});
CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2, future3);
//阻塞,直到所有任务结束。
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + LocalDateTime.now() + ":阻塞");
//调用join方法等待任务完成
anyOf.join();
if (anyOf.isDone()) {
//一个需要耗时2秒,一个需要耗时3秒,当最短的完成则会结束
System.out.println("全部任务完成:" + anyOf.get());
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + LocalDateTime.now() + ":阻塞结束");
}
}异步编程CompletableFuture案例实战
微服务架构下,接口单一职责,一个页面打开涉及多个模块需要同时调用。由于需要同时建立多个连接,中间会有性能损耗,部分页面需要使用聚合接口,则可以用CompletableFuture聚合多个响应结果一次性返回。该方式可以减少建立连接数量,对于网关和服务端可以处理更多连接。
其缺点也非常明显,如果接口性能差异大,则容易性能好的接口被性能差的拖垮。其次就是需要开发更多接口,数据量大则需要更大的带宽。
具体代码
public class EduService {
public String getRank() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return "rank info";
}
public String getCategory() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return "Category info";
}
public String getBanner() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return "Banner info";
}
public String getVideoCard() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return "Video Card info";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("开始:"+ LocalDateTime.now());
Map<String, String> stringStringMap = homePageAggApi();
System.out.println("结束:"+LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println(stringStringMap.toString());
System.out.println("主线程执行完成");
}
private static final ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
16,
32,
30,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
public static Map<String,String> homePageAggApi() throws Exception {
Map<String,String> homePageInfo = new HashMap<>();
//模拟不同的服务调用
EduService eduService = new EduService();
CompletableFuture<Void> bannerFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
String banner = eduService.getBanner();
homePageInfo.put("banner",banner);
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> categoryFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
String category = eduService.getCategory();
homePageInfo.put("category",category);
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> rankFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
String rank = eduService.getRank();
homePageInfo.put("rank",rank);
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> videoCardFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
String videoCard = eduService.getVideoCard();
homePageInfo.put("videoCard",videoCard);
}, executor);
//join()和get()方法都是阻塞调用它们的线程(通常为主线程)用来获取CompletableFuture异步之后的返回值
CompletableFuture.allOf(bannerFuture,categoryFuture,rankFuture,videoCardFuture)
.get();
return homePageInfo;
}
}