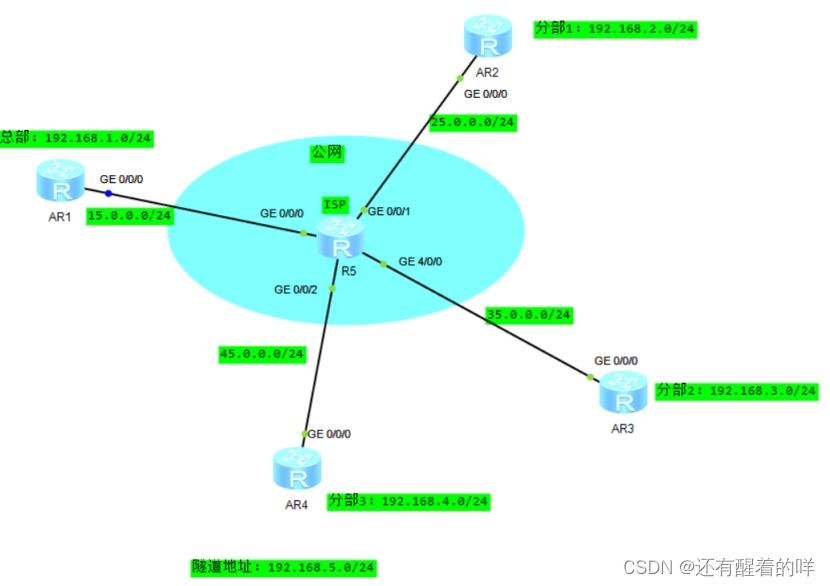
第一步:在任意一个目录下创建功能包
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_cmake ros2_demo --dependencies rclcpp std_msgs
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_python learning_pkg_python # Pythonros2命令中:
pkg:表示功能包相关的功能;
create:表示创建功能包;
build-type:表示新创建的功能包是C++还是Python的,如果使用C++或者C,那这里就跟ament_cmake,如果使用Python,就跟ament_python
package_name:新建功能包的名字。比如在终端中分别创建C++和Python版本的功能包:
第二步:确定功能包,会在当前目录下生成一个名为ros2_demo的功能包。目录架构如下:

1、c/c+++功能包
首先看下C++类型的功能包,其中必然存在两个文件:package.xml和CMakerLists.txt。
package.xml文件的主要内容如下,包含功能包的版权描述,和各种依赖的声明。

CMakeLists.txt文件是编译规则,C++代码需要编译才能运行,所以必须要在该文件中设置如何编译,使用CMake语法。
第三步:在src目录下创建节点文件sub_node.cpp
#include <chrono>
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
/* This example creates a subclass of Node and uses a fancy C++11 lambda
* function to shorten the timer syntax, at the expense of making the
* code somewhat more difficult to understand at first glance if you are
* unaccustomed to C++11 lambda expressions. */
class MinimalTimer : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
MinimalTimer(): Node("minimal_timer")
{
auto timer_callback = [this]()-> void { RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(),"Hello, world!");};
timer_ = create_wall_timer(500ms, timer_callback);
}
private:
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
};
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
rclcpp::spin(std::make_shared<MinimalTimer>());
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
第四步:修改CMakeLists.txt
在CMakeLists.txt中添加
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(std_msgs REQUIRED)添加可执行文件的名字为sub_node
add_executable(sub_node src/sub_node.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(sub_node rclcpp std_msgs)添加 install(TARGETS…) 把可执行文件安装到install去
install(TARGETS
sub_node
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME})第五步:编译运行
1、编译节点
colcon build --packages-select ros2_demo
source install/setup.bash 注意
1、为了防止build出来的文件污染原工程文件结构。尽量在ros2_demo所在包(文件夹)同级目录下编译。
2、需要编译成功后需要source install/setup.bash,不然找不到ros2-demo包中的可执行文件sub_node。
2、运行节点
ros2 run ros2_demo sub_node