文章目录
- 一、概览
- 加载
- Transformations
- 将所有内容放在一起
- 抽象
- 二、文档/节点概览
- 1、概念
- 2、使用模式
- 文件
- 节点
- 三、定义和定制文档
- 1、定义文档
- 2、自定义文档
- 2.1 元数据
- 2.2 自定义id
- 2.3 高级 - 元数据定制
- 1)自定义LLM元数据文本
- 2)自定义嵌入元数据文本
- 3)自定义元数据格式
- 2.4 概括
- 2.5 高级 - 自动元数据提取
- 四、使用节点
- 自定义ID
- 五、元数据提取使用模式
- 资源
- 六、简单目录阅读器
- 1、支持的文件类型
- 2、用法
- 2.1 从子目录读取
- 2.2 加载文件时对其进行迭代
- 2.3 限制加载的文件
- 2.4 指定文件编码
- 2.5 提取元数据
- 2.6 扩展到其他文件类型
- 2.7 对外部文件系统的支持
- 七、数据连接器 (LlamaHub) 概览
- 1、概念
- 2、LlamaHub
- 3、使用模式
- 4、模块
- 八、LlamaParse
- 1、入门
- 2、与使用`SimpleDirectoryReader`
- 3、例子
- 4、服务条款 & 模块指南
- 九、节点解析器使用模式
- 1、入门使用
- 1.1 独立使用
- 1.2 转换用法
- 1.3 索引使用
- 十、节点解析器模块
- 1、基于文件的节点解析器
- 1.1 简单文件节点解析器
- 1.2 HTML节点解析器
- 1.3 JSONNode解析器
- 1.4 MarkdownNode解析器
- 2、文本分割器
- 2.1 代码分割器
- 2.2 Langchain节点解析器
- 2.3 分句器
- 2.4 句子窗口节点解析器
- 2.5 语义分割器节点解析器
- 2.6 令牌文本分割器
- 3、基于关系的节点解析器
- 层次节点解析器
- 十一、Ingestion Pipeline
- 1、使用模式
- 2、连接到矢量数据库
- 3、计算管道中的嵌入
- 4、缓存
- 本地缓存管理
- 远程缓存管理
- 5、异步支持
- 6、文件管理
- 7、并行处理
- 8、模块
- 十二、转换
- 1、使用模式
- 2、与索引结合
- 3、自定义转换
本文翻译整理自:https://docs.llamaindex.ai/en/stable/module_guides/loading/
一、概览
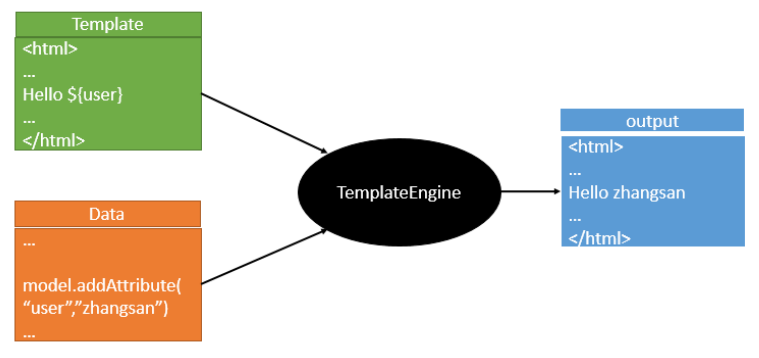
LlamaIndex 中数据摄取的关键是加载和转换。
加载文档后,您可以通过转换和输出节点来处理它们。
一旦您在“理解”部分了解了加载数据的基础知识,您就可以继续阅读以了解更多信息:
加载
- SimpleDirectoryReader,我们的内置加载器,用于从本地目录加载各种文件类型
- LlamaParse,LlamaIndex 的 PDF 解析官方工具,作为托管 API 提供。
- LlamaHub,我们的数百个数据加载库的注册表,用于从任何来源提取数据
Transformations
这包括拆分文本等常见操作。
- 节点解析器使用模式,向您展示如何使用我们的节点解析器
- 节点解析器模块,显示我们的文本分割器(句子、标记、HTML、JSON)和其他解析器模块。
将所有内容放在一起
- 摄取管道允许您设置可重复的、缓存优化的过程来加载数据。
抽象
- 文档和节点对象以及如何针对更高级的用例自定义它们
二、文档/节点概览
1、概念
Document 和 Node 对象是 LlamaIndex 中的核心抽象。
文档是任何数据源的通用容器 - 例如,PDF、API 输出或从数据库检索的数据**。
**它们可以手动构建,也可以通过我们的数据加载器自动创建。
默认情况下,文档存储文本以及一些其他属性。
下面列出了其中一些。
metadata- 可附加到文本的注释字典。relationships- 包含与其他文档/节点的关系的字典。
注意:我们提供了允许文档存储图像的测试版支持,并正在积极致力于改进其多模式功能。
节点表示源文档的一个“块”,无论是文本块、图像还是其他块。
与文档类似,它们包含元数据以及与其他节点的关系信息。
节点是 LlamaIndex 中的一等公民。
您可以选择直接定义节点及其所有属性。
您还可以选择通过我们的NodeParser类将源文档“解析”为节点。
默认情况下,从文档派生的每个节点都将从该文档继承相同的元数据(例如,文档中归档的“file_name”被传播到每个节点)。
2、使用模式
以下是一些开始使用文档和节点的简单片段。
文件
from llama_index.core import Document, VectorStoreIndex
text_list = [text1, text2, ...]
documents = [Document(text=t) for t in text_list]
# build index
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
节点
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
# load documents
...
# parse nodes
parser = SentenceSplitter()
nodes = parser.get_nodes_from_documents(documents)
# build index
index = VectorStoreIndex(nodes)
三、定义和定制文档
1、定义文档
文档可以通过数据加载器自动创建,也可以手动构建。
默认情况下,我们所有的数据加载器(包括 LlamaHub 上提供的数据加载器)都Document通过该函数返回对象load_data。
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data").load_data()
您还可以选择手动构建文档。 LlamaIndex 公开该Document结构。
from llama_index.core import Document
text_list = [text1, text2, ...]
documents = [Document(text=t) for t in text_list]
为了加快原型设计和开发速度,您还可以使用一些 默认文本快速创建文档:
document = Document.example()
2、自定义文档
本节介绍自定义Document对象的各种方法。
由于该Document对象是我们对象的子类TextNode,因此所有这些设置和详细信息TextNode也适用于该对象类。
2.1 元数据
文档还提供了包含有用元数据的机会。
使用metadata每个文档上的字典,可以包含附加信息来帮助通知响应并跟踪查询响应的来源。
此信息可以是任何内容,例如文件名或类别。
如果您要与矢量数据库集成,请记住,某些矢量数据库要求键必须是字符串,并且值必须是平面( 、str或float)int。
每个文档的字典中设置的任何信息metadata都将显示在metadata从该文档创建的每个源节点的 中。
此外,此信息包含在节点中,使索引能够在查询和响应中利用它。
默认情况下,元数据会注入到嵌入和 LLM 模型调用的文本中。
有几种方法可以设置此词典:
1、在文档构造函数中:
document = Document(
text="text",
metadata={"filename": "<doc_file_name>", "category": "<category>"},
)
2、文档创建后:
document.metadata = {"filename": "<doc_file_name>"}
3、SimpleDirectoryReader使用和挂钩自动设置文件名file_metadata。
这将自动在每个文档上运行挂钩来设置metadata字段:
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
filename_fn = lambda filename: {"file_name": filename}
# automatically sets the metadata of each document according to filename_fn
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(
"./data", file_metadata=filename_fn
).load_data()
2.2 自定义id
正如文档管理部分中详细介绍的,它 doc_id 用于实现索引中文档的高效刷新。
使用 时SimpleDirectoryReader,您可以自动将 doc 设置doc_id为每个文档的完整路径:
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data", filename_as_id=True).load_data()
print([x.doc_id for x in documents])
您也可以直接设置任何Document 的 doc_id
document.doc_id = "My new document id!"
注意:ID 也可以通过Document 对象上的node_id或id_属性来设置,类似于TextNode对象。
2.3 高级 - 元数据定制
上面提到的一个关键细节是,默认情况下,您设置的任何元数据都包含在嵌入生成和 LLM 中。
1)自定义LLM元数据文本
通常,文档可能有许多元数据键,但您可能不希望所有这些键 在响应合成期间 对 LLM 可见。
在上面的例子中,我们可能不希望法学硕士阅读file_name我们的文档。
但是,其中file_name可能包含有助于生成更好嵌入的信息。
这样做的一个关键优势是在不改变法学硕士最终阅读内容的情况下偏向检索的嵌入。
我们可以像这样排除它:
document.excluded_llm_metadata_keys = ["file_name"]
get_content()然后,我们可以使用该函数并指定来测试 LLM 实际上最终会读取什么内容MetadataMode.LLM:
from llama_index.core.schema import MetadataMode
print(document.get_content(metadata_mode=MetadataMode.LLM))
2)自定义嵌入元数据文本
与定制LLM可见的元数据类似,我们也可以定制嵌入可见的元数据。
在这种情况下,您可以专门排除嵌入模型可见的元数据,以防您不希望特定文本使嵌入产生偏差。
document.excluded_embed_metadata_keys = ["file_name"]
get_content()然后,我们可以使用该函数并指定来测试嵌入模型最终实际读取的内容MetadataMode.EMBED:
from llama_index.core.schema import MetadataMode
print(document.get_content(metadata_mode=MetadataMode.EMBED))
3)自定义元数据格式
正如您现在所知,当发送到 LLM 或嵌入模型时,元数据会被注入到每个文档/节点的实际文本中。
默认情况下,此元数据的格式由三个属性控制:
Document.metadata_seperator-> 默认 ="\n"
连接元数据的所有键/值字段时,此字段控制每个键/值对之间的分隔符。
Document.metadata_template-> 默认 ="{key}: {value}"
此属性控制元数据中每个键/值对的格式。
这两个变量key和value字符串键是必需的。
Document.text_template-> 默认 ={metadata_str}\n\n{content}
metadata_seperator使用和将元数据转换为字符串后metadata_template,此模板将控制元数据与文档/节点的文本内容连接时的外观。
和字符串metadata键content是必需的。
2.4 概括
了解了这一切后,让我们使用所有这些功能创建一个简短的示例:
from llama_index.core import Document
from llama_index.core.schema import MetadataMode
document = Document(
text="This is a super-customized document",
metadata={
"file_name": "super_secret_document.txt",
"category": "finance",
"author": "LlamaIndex",
},
excluded_llm_metadata_keys=["file_name"],
metadata_seperator="::",
metadata_template="{key}=>{value}",
text_template="Metadata: {metadata_str}\n-----\nContent: {content}",
)
print(
"The LLM sees this: \n",
document.get_content(metadata_mode=MetadataMode.LLM),
)
print(
"The Embedding model sees this: \n",
document.get_content(metadata_mode=MetadataMode.EMBED),
)
2.5 高级 - 自动元数据提取
我们有使用法学硕士本身来执行元数据提取的初始示例。
***
四、使用节点
节点代表源文档的“块”,无论是文本块、图像还是更多。
它们还包含元数据以及与其他节点和索引结构的关系信息。
节点是 LlamaIndex 中的一等公民。
您可以选择直接定义节点及其所有属性。
您还可以选择通过我们的NodeParser类将源文档“解析”为节点。
例如,你可以这样做
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
parser = SentenceSplitter()
nodes = parser.get_nodes_from_documents(documents)
您还可以选择手动构造 Node 对象并跳过第一部分。例如:
from llama_index.core.schema import TextNode, NodeRelationship, RelatedNodeInfo
node1 = TextNode(text="<text_chunk>", id_="<node_id>")
node2 = TextNode(text="<text_chunk>", id_="<node_id>")
# set relationships
node1.relationships[NodeRelationship.NEXT] = RelatedNodeInfo(
node_id=node2.node_id
)
node2.relationships[NodeRelationship.PREVIOUS] = RelatedNodeInfo(
node_id=node1.node_id
)
nodes = [node1, node2]
如果需要,该类RelatedNodeInfo还可以存储其他内容:metadata
node2.relationships[NodeRelationship.PARENT] = RelatedNodeInfo(
node_id=node1.node_id, metadata={"key": "val"}
)
自定义ID
每个节点都有一个node_id属性,如果没有手动指定,该属性会自动生成。
该 ID 可用于多种目的;这包括能够更新存储中的节点、能够定义节点之间的关系(通过IndexNode)等等。
您还可以直接获取和设置node_idany TextNode。
print(node.node_id)
node.node_id = "My new node_id!"
五、元数据提取使用模式
您可以使用法学硕士通过我们的模块自动提取元数据Metadata Extractor。
我们的元数据提取器模块包括以下“特征提取器”:
SummaryExtractor- 自动提取一组节点的摘要QuestionsAnsweredExtractor- 提取每个节点可以回答的一组问题TitleExtractor- 提取每个节点上下文的标题EntityExtractor- 提取每个节点内容中提到的实体(即地名、人物、事物的名称)
然后您可以Metadata Extractor使用我们的节点解析器链接 s:
from llama_index.core.extractors import (
TitleExtractor,
QuestionsAnsweredExtractor,
)
from llama_index.core.node_parser import TokenTextSplitter
text_splitter = TokenTextSplitter(
separator=" ", chunk_size=512, chunk_overlap=128
)
title_extractor = TitleExtractor(nodes=5)
qa_extractor = QuestionsAnsweredExtractor(questions=3)
# assume documents are defined -> extract nodes
from llama_index.core.ingestion import IngestionPipeline
pipeline = IngestionPipeline(
transformations=[text_splitter, title_extractor, qa_extractor]
)
nodes = pipeline.run(
documents=documents,
in_place=True,
show_progress=True,
)
或插入索引:
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents, transformations=[text_splitter, title_extractor, qa_extractor]
)
资源
- SEC Documents Metadata Extraction
- LLM Survey Extraction
- Entity Extraction
- Marvin Metadata Extraction
- Pydantic Metadata Extraction
六、简单目录阅读器
SimpleDirectoryReader是将本地文件中的数据加载到 LlamaIndex 的最简单方法。
对于生产用例,您更有可能希望使用LlamaHub上提供的众多 Reader 之一,但这SimpleDirectoryReader是一个很好的入门方式。
1、支持的文件类型
默认情况下,SimpleDirectoryReader将尝试读取它找到的任何文件,并将它们全部视为文本。
除了纯文本之外,它还明确支持以下文件类型,这些文件类型是根据文件扩展名自动检测的:
- .csv - 逗号分隔值
- .docx - Microsoft Word
- .epub - EPUB 电子书格式
- .hwp - 韩文文字处理器
- .ipynb - Jupyter 笔记本
- .jpeg、.jpg - JPEG 图像
- .mbox - MBOX 电子邮件存档
- .md-Markdown
- .mp3、.mp4 - 音频和视频
- .pdf - 便携式文档格式
- .png - 便携式网络图形
- .ppt、.pptm、.pptx - Microsoft PowerPoint
您可能希望在这里找到的一种文件类型是 JSON;为此,我们建议您使用我们的JSON Loader。
2、用法
最基本的用法是传递 an input_dir,它将加载该目录中所有支持的文件:
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
reader = SimpleDirectoryReader(input_dir="path/to/directory")
documents = reader.load_data()
如果从目录加载多个文件,也可以通过并行处理加载文档。
请注意,在 Windows 和 Linux/MacOS 计算机上使用时存在差异multiprocessing,整个文档对此进行了解释multiprocessing(例如,请参阅此处)。
最终,Windows 用户可能会看到较少的性能提升或没有性能提升,而 Linux/MacOS 用户在加载完全相同的文件集时会看到这些提升。
...
documents = reader.load_data(num_workers=4)
2.1 从子目录读取
默认情况下,SimpleDirectoryReader只会读取目录顶层的文件。
要从子目录中读取,请设置recursive=True:
SimpleDirectoryReader(input_dir="path/to/directory", recursive=True)
2.2 加载文件时对其进行迭代
您还可以使用该iter_data()方法在文件加载时对其进行迭代和处理
reader = SimpleDirectoryReader(input_dir="path/to/directory", recursive=True)
all_docs = []
for docs in reader.iter_data():
# <do something with the documents per file>
all_docs.extend(docs)
2.3 限制加载的文件
您可以传递文件路径列表,而不是传递所有文件:
SimpleDirectoryReader(input_files=["path/to/file1", "path/to/file2"])
或者您可以使用以下命令传递要排除的文件路径列表exclude:
SimpleDirectoryReader(
input_dir="path/to/directory", exclude=["path/to/file1", "path/to/file2"]
)
您还可以设置required_exts文件扩展名列表以仅加载具有这些扩展名的文件:
SimpleDirectoryReader(
input_dir="path/to/directory", required_exts=[".pdf", ".docx"]
)
您可以设置要加载的最大文件数num_files_limit:
SimpleDirectoryReader(input_dir="path/to/directory", num_files_limit=100)
2.4 指定文件编码
SimpleDirectoryReader期望对文件进行utf-8编码,但您可以使用参数覆盖它encoding:
SimpleDirectoryReader(input_dir="path/to/directory", encoding="latin-1")
2.5 提取元数据
您可以指定一个函数,该函数将读取每个文件并提取附加到Document每个文件的结果对象的元数据,方法是将函数传递为file_metadata:
def get_meta(file_path):
return {"foo": "bar", "file_path": file_path}
SimpleDirectoryReader(input_dir="path/to/directory", file_metadata=get_meta)
该函数应采用单个参数(文件路径)并返回元数据字典。
2.6 扩展到其他文件类型
您可以SimpleDirectoryReader通过将文件扩展名字典传递给BaseReaderas的实例来扩展读取其他文件类型file_extractor。
BaseReader 应该读取文件并返回文档列表。
例如,要添加对.myfile文件的自定义支持:
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
from llama_index.core.readers.base import BaseReader
from llama_index.core import Document
class MyFileReader(BaseReader):
def load_data(self, file, extra_info=None):
with open(file, "r") as f:
text = f.read()
# load_data returns a list of Document objects
return [Document(text=text + "Foobar", extra_info=extra_info or {})]
reader = SimpleDirectoryReader(
input_dir="./data", file_extractor={".myfile": MyFileReader()}
)
documents = reader.load_data()
print(documents)
请注意,此映射将覆盖您指定的文件类型的默认文件提取器,因此如果您想支持它们,则需要将它们添加回来。
2.7 对外部文件系统的支持
与其他模块一样,它SimpleDirectoryReader采用一个可选fs参数,可用于遍历远程文件系统。
这可以是协议实现的任何文件系统对象fsspec。
该fsspec协议具有针对各种远程文件系统的开源实现,包括AWS S3、Azure Blob 和 DataLake、Google Drive、SFTP等。
这是连接到 S3 的示例:
from s3fs import S3FileSystem
s3_fs = S3FileSystem(key="...", secret="...")
bucket_name = "my-document-bucket"
reader = SimpleDirectoryReader(
input_dir=bucket_name,
fs=s3_fs,
recursive=True, # recursively searches all subdirectories
)
documents = reader.load_data()
print(documents)
可以在此处找到完整的示例笔记本。
七、数据连接器 (LlamaHub) 概览
1、概念
数据连接器(又名Reader)将来自不同数据源和数据格式的数据提取为简单的Document表示形式(文本和简单元数据)。
提示
获取数据后,您可以在顶部构建索引,使用查询引擎提出问题,并使用聊天引擎进行对话。
2、LlamaHub
我们的数据连接器通过LlamaHub 🦙提供。
LlamaHub 是一个开源存储库,包含数据加载器,您可以轻松地将其插入任何 LlamaIndex 应用程序中。

3、使用模式
简单使用:
from llama_index.core import download_loader
from llama_index.readers.google import GoogleDocsReader
loader = GoogleDocsReader()
documents = loader.load_data(document_ids=[...])
每个数据加载器都包含一个“用法”部分,显示如何使用该加载器。
使用每个加载程序的核心是一个download_loader函数,它将加载程序文件下载到您可以在应用程序中使用的模块中。
用法示例:
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, download_loader
from llama_index.readers.google import GoogleDocsReader
gdoc_ids = ["1wf-y2pd9C878Oh-FmLH7Q_BQkljdm6TQal-c1pUfrec"]
loader = GoogleDocsReader()
documents = loader.load_data(document_ids=gdoc_ids)
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
query_engine.query("Where did the author go to school?")
4、模块
一些示例数据连接器:
- 本地文件目录(
SimpleDirectoryReader)。
可以支持解析多种文件类型:.pdf、.jpg、.png、.docx等。 - 概念(
NotionPageReader) - 谷歌文档(
GoogleDocsReader) - 松弛(
SlackReader) - 不和谐(
DiscordReader) - Apify 演员(
ApifyActor)。
可以抓取网页、抓取网页、提取文本内容、下载文件,包括.pdf、.jpg、.png、.docx等。
有关更多详细信息,请参阅模块指南。
八、LlamaParse
LlamaParse 是由 LlamaIndex 创建的 API,用于使用 LlamaIndex 框架高效解析和表示文件,以便进行高效检索和上下文增强。
LlamaParse 直接与LlamaIndex集成。
目前免费提供。今天就尝试一下吧!
**注意:**目前仅支持 PDF 文件。
1、入门
首先,登录并从 获取 api-key https://cloud.llamaindex.ai。
然后,确保您安装了最新的 LlamaIndex 版本。
**注意:**如果您从 v0.9.X 升级,我们建议您遵循我们的迁移指南,并首先卸载以前的版本。
pip uninstall llama-index # run this if upgrading from v0.9.x or older
pip install -U llama-index --upgrade --no-cache-dir --force-reinstall
最后,安装包:
pip install llama-parse
现在您可以运行以下命令来解析您的第一个 PDF 文件:
import nest_asyncio
nest_asyncio.apply()
from llama_parse import LlamaParse
parser = LlamaParse(
api_key="llx-...", # can also be set in your env as LLAMA_CLOUD_API_KEY
result_type="markdown", # "markdown" and "text" are available
verbose=True,
)
# sync
documents = parser.load_data("./my_file.pdf")
# sync batch
documents = parser.load_data(["./my_file1.pdf", "./my_file2.pdf"])
# async
documents = await parser.aload_data("./my_file.pdf")
# async batch
documents = await parser.aload_data(["./my_file1.pdf", "./my_file2.pdf"])
2、与使用SimpleDirectoryReader
您还可以将解析器集成为默认 PDF 加载器SimpleDirectoryReader:
import nest_asyncio
nest_asyncio.apply()
from llama_parse import LlamaParse
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
parser = LlamaParse(
api_key="llx-...", # can also be set in your env as LLAMA_CLOUD_API_KEY
result_type="markdown", # "markdown" and "text" are available
verbose=True,
)
file_extractor = {".pdf": parser}
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(
"./data", file_extractor=file_extractor
).load_data()
完整的文档可以在LlamaIndex DocumentationSimpleDirectoryReader上找到。
3、例子
可以在示例文件夹中找到几个端到端索引示例
- 入门
- 高级 RAG 示例
- 原始 API 使用情况
4、服务条款 & 模块指南
请参阅此处的服务条款:https://github.com/run-llama/llama_parse/blob/main/TOS.pdf
模块指南:https://docs.llamaindex.ai/en/stable/module_guides/loading/connector/modules/
九、节点解析器使用模式
节点解析器是一个简单的抽象,它获取文档列表,并将它们分块为Node对象,这样每个节点都是父文档的特定块。
当文档被分解为节点时,它的所有属性都被继承到子节点(即metadata,文本和元数据模板等)。
您可以在此处Node阅读有关和Document属性的更多信息。
1、入门使用
1.1 独立使用
节点解析器可以单独使用:
from llama_index.core import Document
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
node_parser = SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=1024, chunk_overlap=20)
nodes = node_parser.get_nodes_from_documents(
[Document(text="long text")], show_progress=False
)
1.2 转换用法
节点解析器可以包含在具有摄取管道的任何转换集中。
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
from llama_index.core.ingestion import IngestionPipeline
from llama_index.core.node_parser import TokenTextSplitter
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data").load_data()
pipeline = IngestionPipeline(transformations=[TokenTextSplitter(), ...])
nodes = pipeline.run(documents=documents)
1.3 索引使用
transformations或者在使用以下命令构建索引时自动使用的内部设置或全局设置.from_documents():
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader, VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data").load_data()
# global
from llama_index.core import Settings
Settings.text_splitter = SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=1024, chunk_overlap=20)
# per-index
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
transformations=[SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=1024, chunk_overlap=20)],
)
十、节点解析器模块
1、基于文件的节点解析器
有几个基于文件的节点解析器,它们将根据正在解析的内容类型(JSON、Markdown 等)创建节点
最简单的流程是将FlatFileReader与结合起来SimpleFileNodeParser,自动为每种类型的内容使用最佳节点解析器。
然后,您可能希望将基于文件的节点解析器与基于文本的节点解析器链接起来,以考虑文本的实际长度。
1.1 简单文件节点解析器
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SimpleFileNodeParser
from llama_index.readers.file import FlatReader
from pathlib import Path
md_docs = FlatReader().load_data(Path("./test.md"))
parser = SimpleFileNodeParser()
md_nodes = parser.get_nodes_from_documents(md_docs)
1.2 HTML节点解析器
该节点解析器用于beautifulsoup解析原始 HTML。
默认情况下,它将解析 HTML 标记的选定子集,但您可以覆盖它。
默认标签是:["p", "h1", "h2", "h3", "h4", "h5", "h6", "li", "b", "i", "u", "section"]
from llama_index.core.node_parser import HTMLNodeParser
parser = HTMLNodeParser(tags=["p", "h1"]) # optional list of tags
nodes = parser.get_nodes_from_documents(html_docs)
1.3 JSONNode解析器
解析JSONNodeParser原始 JSON。
from llama_index.core.node_parser import JSONNodeParser
parser = JSONNodeParser()
nodes = parser.get_nodes_from_documents(json_docs)
1.4 MarkdownNode解析器
解析MarkdownNodeParser原始 Markdown 文本。
from llama_index.core.node_parser import MarkdownNodeParser
parser = MarkdownNodeParser()
nodes = parser.get_nodes_from_documents(markdown_docs)
2、文本分割器
2.1 代码分割器
根据编写的语言分割原始代码文本。
在此处查看支持语言的完整列表。
from llama_index.core.node_parser import CodeSplitter
splitter = CodeSplitter(
language="python",
chunk_lines=40, # lines per chunk
chunk_lines_overlap=15, # lines overlap between chunks
max_chars=1500, # max chars per chunk
)
nodes = splitter.get_nodes_from_documents(documents)
2.2 Langchain节点解析器
您还可以使用节点解析器包装来自 langchain 的任何现有文本分割器。
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from llama_index.core.node_parser import LangchainNodeParser
parser = LangchainNodeParser(RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter())
nodes = parser.get_nodes_from_documents(documents)
2.3 分句器
尝试SentenceSplitter在尊重句子边界的同时分割文本。
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
splitter = SentenceSplitter(
chunk_size=1024,
chunk_overlap=20,
)
nodes = splitter.get_nodes_from_documents(documents)
2.4 句子窗口节点解析器
它SentenceWindowNodeParser与其他节点解析器类似,不同之处在于它将所有文档拆分为单独的句子。
生成的节点还包含元数据中每个节点周围的句子“窗口”。
请注意,此元数据对 LLM 或嵌入模型不可见。
这对于生成具有非常特定范围的嵌入最有用。
然后,结合 a MetadataReplacementNodePostProcessor,您可以在将节点发送到 LLM 之前将句子替换为其周围的上下文。
下面是使用默认设置设置解析器的示例。
在实践中,您通常只想调整句子的窗口大小。
import nltk
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceWindowNodeParser
node_parser = SentenceWindowNodeParser.from_defaults(
# how many sentences on either side to capture
window_size=3,
# the metadata key that holds the window of surrounding sentences
window_metadata_key="window",
# the metadata key that holds the original sentence
original_text_metadata_key="original_sentence",
)
可以在此处结合MetadataReplacementNodePostProcessor找到完整的示例。
2.5 语义分割器节点解析器
“语义分块”是 Greg Kamradt 在他的关于 5 个级别的嵌入分块的视频教程中提出的一个新概念:https://youtu.be/8OJC21T2SL4?t=1933。
语义分割器不是使用固定块大小对文本进行分块,而是使用嵌入相似性自适应地选择句子之间的断点。
这确保了“块”包含语义上彼此相关的句子。
我们将其改编成 LlamaIndex 模块。
看看下面我们的笔记本!
注意事项:
- 正则表达式主要适用于英语句子
- 您可能必须调整断点百分位数阈值。
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SemanticSplitterNodeParser
from llama_index.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbedding
embed_model = OpenAIEmbedding()
splitter = SemanticSplitterNodeParser(
buffer_size=1, breakpoint_percentile_threshold=95, embed_model=embed_model
)
完整的示例可以在我们的使用指南SemanticSplitterNodeParser中找到。
2.6 令牌文本分割器
尝试TokenTextSplitter根据原始令牌计数拆分为一致的块大小。
from llama_index.core.node_parser import TokenTextSplitter
splitter = TokenTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1024,
chunk_overlap=20,
separator=" ",
)
nodes = splitter.get_nodes_from_documents(documents)
3、基于关系的节点解析器
层次节点解析器
该节点解析器将节点分块为分层节点。
这意味着单个输入将被分块为多个块大小的层次结构,每个节点都包含对其父节点的引用。
与 结合使用时AutoMergingRetriever,这使我们能够在检索到大多数子节点时自动用其父节点替换检索到的节点。
此过程为法学硕士提供了更完整的响应综合背景。
from llama_index.core.node_parser import HierarchicalNodeParser
node_parser = HierarchicalNodeParser.from_defaults(
chunk_sizes=[2048, 512, 128]
)
可以在此处结合AutoMergingRetriever找到完整的示例。
十一、Ingestion Pipeline
An使用应用于输入数据IngestionPipeline的概念。
Transformations这些Transformations将应用于您的输入数据,并且结果节点将被返回或插入到向量数据库(如果给定)中。
每个节点+转换对都会被缓存,因此使用相同节点+转换组合的后续运行(如果缓存已持久)可以使用缓存的结果并节省时间。
IngestionPipeline要查看使用的交互式示例,请查看RAG CLI。
1、使用模式
最简单的用法是实例化IngestionPipeline如下:
from llama_index.core import Document
from llama_index.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbedding
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
from llama_index.core.extractors import TitleExtractor
from llama_index.core.ingestion import IngestionPipeline, IngestionCache
# create the pipeline with transformations
pipeline = IngestionPipeline(
transformations=[
SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=25, chunk_overlap=0),
TitleExtractor(),
OpenAIEmbedding(),
]
)
# run the pipeline
nodes = pipeline.run(documents=[Document.example()])
请注意,在现实场景中,您可以从SimpleDirectoryReaderLlama Hub 或其他读者处获取文档。
2、连接到矢量数据库
运行摄取管道时,您还可以选择自动将生成的节点插入到远程向量存储中。
然后,您可以稍后从该向量存储构建索引。
from llama_index.core import Document
from llama_index.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbedding
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
from llama_index.core.extractors import TitleExtractor
from llama_index.core.ingestion import IngestionPipeline
from llama_index.vector_stores.qdrant import QdrantVectorStore
import qdrant_client
client = qdrant_client.QdrantClient(location=":memory:")
vector_store = QdrantVectorStore(client=client, collection_name="test_store")
pipeline = IngestionPipeline(
transformations=[
SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=25, chunk_overlap=0),
TitleExtractor(),
OpenAIEmbedding(),
],
vector_store=vector_store,
)
# Ingest directly into a vector db
pipeline.run(documents=[Document.example()])
# Create your index
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_vector_store(vector_store)
3、计算管道中的嵌入
请注意,在上面的示例中,嵌入是作为管道的一部分进行计算的。
如果您将管道连接到向量存储,则嵌入必须是管道的一个阶段,否则稍后的索引实例化将失败。
如果您不连接到向量存储,即仅生成节点列表,则可以省略管道中的嵌入。
4、缓存
在 中IngestionPipeline,每个节点+转换组合都被散列并缓存。
这可以节省使用相同数据的后续运行的时间。
以下部分描述了有关缓存的一些基本用法。
本地缓存管理
一旦有了管道,您可能需要存储和加载缓存。
# save
pipeline.persist("./pipeline_storage")
# load and restore state
new_pipeline = IngestionPipeline(
transformations=[
SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=25, chunk_overlap=0),
TitleExtractor(),
],
)
new_pipeline.load("./pipeline_storage")
# will run instantly due to the cache
nodes = pipeline.run(documents=[Document.example()])
如果缓存太大,可以清除它
# delete all context of the cache
cache.clear()
远程缓存管理
我们支持多个远程存储后端的缓存
RedisCacheMongoDBCacheFirestoreCache
这里作为使用的示例RedisCache:
from llama_index.core import Document
from llama_index.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbedding
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
from llama_index.core.extractors import TitleExtractor
from llama_index.core.ingestion import IngestionPipeline, IngestionCache
from llama_index.core.ingestion.cache import RedisCache
pipeline = IngestionPipeline(
transformations=[
SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=25, chunk_overlap=0),
TitleExtractor(),
OpenAIEmbedding(),
],
cache=IngestionCache(
cache=RedisCache(
redis_uri="redis://127.0.0.1:6379", collection="test_cache"
)
),
)
# Ingest directly into a vector db
nodes = pipeline.run(documents=[Document.example()])
在这里,不需要持久步骤,因为当您进入指定的远程集合时,所有内容都会被缓存。
5、异步支持
还IngestionPipeline支持异步操作
nodes = await pipeline.arun(documents=documents)
6、文件管理
将 附加docstore到摄取管道将启用文档管理。
使用document.doc_id或node.ref_doc_id作为接地点,摄取管道将主动查找重复文档。
它的工作原理是:
- 存储地图
doc_id->document_hash - 如果附加了矢量存储:
- 如果检测到重复项
doc_id,并且哈希已更改,则将重新处理并更新插入文档 - 如果检测到重复
doc_id且哈希未更改,则跳过该节点 - 如果仅未附加矢量存储:
- 检查每个节点的所有现有哈希值
- 如果发现重复节点,则跳过该节点
- 否则,处理该节点
**注意:**如果我们不附加向量存储,我们只能检查并删除重复的输入。
from llama_index.core.ingestion import IngestionPipeline
from llama_index.core.storage.docstore import SimpleDocumentStore
pipeline = IngestionPipeline(
transformations=[...], docstore=SimpleDocumentStore()
)
在我们的演示笔记本中可以找到完整的演练。
另请查看另一篇使用Redis 作为我们整个摄取堆栈的指南。
7、并行处理
run的方法可以IngestionPipeline用并行进程来执行。
它通过将multiprocessing.Pool批量节点分布到多个处理器来实现这一点。
要使用并行处理执行,请设置num_workers您要使用的进程数:
from llama_index.core.ingestion import IngestionPipeline
pipeline = IngestionPipeline(
transformations=[...],
)
pipeline.run(documents=[...], num_workers=4)
8、模块
- 转型指南
- 先进的摄取管道
- 异步摄取管道
- 文档管理管道
- Redis 摄取管道
- Google Drive 摄取管道
- 并行执行管道
十二、转换
转换是将节点列表作为输入并返回节点列表的过程。
每个实现Transformation基类的组件都有同步__call__()定义和异步acall()定义。
目前,以下组件是Transformation对象:
TextSplitterNodeParserMetadataExtractorEmbeddings模型(查看我们支持的嵌入列表)
1、使用模式
虽然转换最好与 一起使用IngestionPipeline,但它们也可以直接使用。
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
from llama_index.core.extractors import TitleExtractor
node_parser = SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=512)
extractor = TitleExtractor()
# use transforms directly
nodes = node_parser(documents)
# or use a transformation in async
nodes = await extractor.acall(nodes)
2、与索引结合
转换可以传递到索引或整体全局设置中,并将在调用from_documents()或insert()索引时使用。
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.core.extractors import (
TitleExtractor,
QuestionsAnsweredExtractor,
)
from llama_index.core.ingestion import IngestionPipeline
from llama_index.core.node_parser import TokenTextSplitter
transformations = [
TokenTextSplitter(chunk_size=512, chunk_overlap=128),
TitleExtractor(nodes=5),
QuestionsAnsweredExtractor(questions=3),
]
# global
from llama_index.core import Settings
Settings.transformations = [text_splitter, title_extractor, qa_extractor]
# per-index
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents, transformations=transformations
)
3、自定义转换
您可以通过实现基类来自己实现任何转换。
以下自定义转换将删除文本中的所有特殊字符或标点符号。
import re
from llama_index.core import Document
from llama_index.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbedding
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
from llama_index.core.ingestion import IngestionPipeline
from llama_index.core.schema import TransformComponent
class TextCleaner(TransformComponent):
def __call__(self, nodes, **kwargs):
for node in nodes:
node.text = re.sub(r"[^0-9A-Za-z ]", "", node.text)
return nodes
然后可以直接使用它们或在任何IngestionPipeline.
# use in a pipeline
pipeline = IngestionPipeline(
transformations=[
SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=25, chunk_overlap=0),
TextCleaner(),
OpenAIEmbedding(),
],
)
nodes = pipeline.run(documents=[Document.example()])
2024-04-15(一)