01.idea中创建一个maven管理的空项目
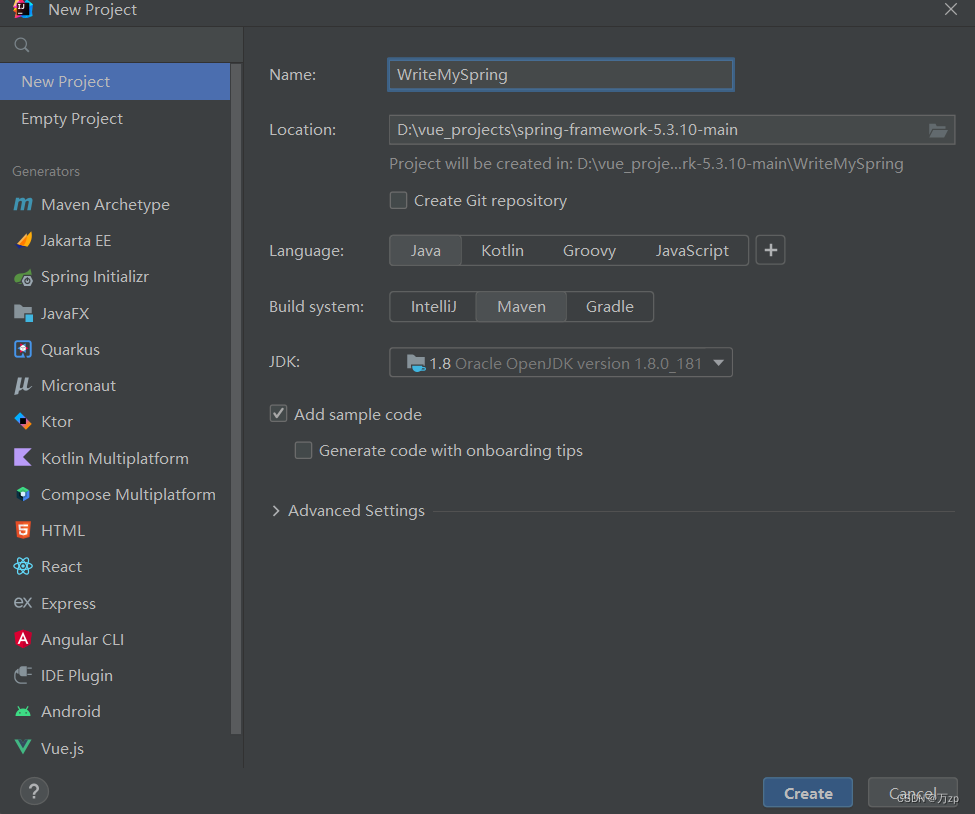
02.模拟创建出spring容器类,这里叫wzpApplicationContext,创建的时候会自动加载配置类的数据:
这里wzpApplicationContext对标的是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
public class wzpApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
public wzpApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
}
}
模拟出容器类要扫描的配置类Appconfig
public class Appconfig {
}
在test中去测试这些创建的类
public class Mytest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
wzpApplicationContext wzpApplicationContext=new wzpApplicationContext(Appconfig.class);
}
}
03.在wzpApplicationContext 添加getbean函数,获取spring容器中的bean
public Object getBean(String beanName) {
return null;
}
创建服务类UserService
public class UserService {
}
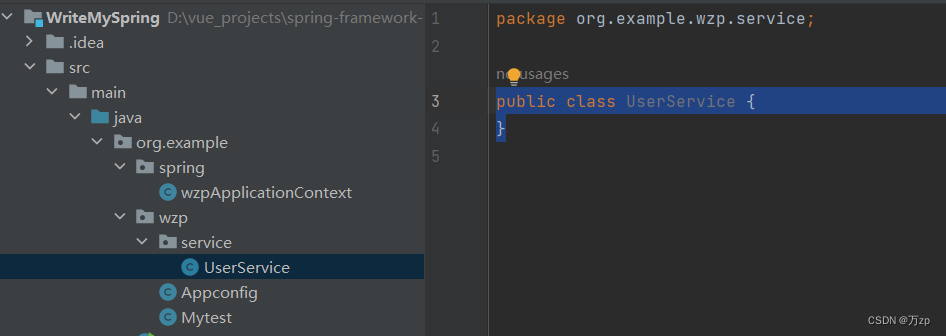
在测试test中运行getbean方法
public class Mytest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
wzpApplicationContext wzpApplicationContext=new wzpApplicationContext(Appconfig.class);
UserService userService= (UserService)wzpApplicationContext.getBean("UserService");
}
}
04.在服务类中写一些方法,等会看一下是不是可以运行
public class UserService {
public void test(){
System.out.println("test");
}
}
此时在test中:
public class Mytest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
wzpApplicationContext wzpApplicationContext=new wzpApplicationContext(Appconfig.class);
UserService userService= (UserService)wzpApplicationContext.getBean("UserService");
userService.test();
}
}
05.写几个自定义的注解
比如说,spring容器中的扫描,需要注解@ComponentScan
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface ComponentScan {
String value() default "";
}
解释一下:
Target 注解是说,这个注解主要用在哪一个区域,TYPE表示类,FIELD表示属性,METHOD表示方法。
Rentention 注解是说,这个注解在那个阶段使用,RUNTIME是在类加载阶段使用
然后模仿spring去用:
@ComponentScan("org.example.wzp.service")
public class Appconfig {
}
再创建一个注解:@Component
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Component {
String value() default "";
}
在服务类中去使用:
@Component
public class UserService {
public void test(){
System.out.println("test");
}
}
06.实现扫描的功能
现在只是写了几个注解,具体的功能代码还没有写,接下来就是扫描的代码
回想spring框架,是创建spring容器的时候,就会自动创建bean
所以,扫描的具体实现代码就应该在构造函数中写
//判断类上是不是有注解ComponentScan
if(configClass.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class)){
//获取注解对象
ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan)configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
//获取注解对象上的value,这里也就是path
String path = componentScan.value();
//文件的路径是/,而获取到的是带有.的包名
path=path.replace(".","/");
//获取当前的类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = wzpApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
//根据类加载器获取编译完成的target的class文件夹的路径
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
//根据路径,获取文件
File file=new File(resource.getFile());
//因为扫描的是包,所以大概率是一个目录
if (file.isDirectory()){
//获取目录中的文件集合
for (File f:file.listFiles()){
//获取文件的绝对路径
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
//截取从org到class
String org = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.indexOf("org"), absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
//由于是文件路径,要转换回来,把\变成 . 包名,好让类加载器加载得到类的对象
String classpath = org.replace("\\", ".");
//加载器加载后,得到一个类对象
Class<?> aClass = classLoader.loadClass(classpath);
//判断是不是类上存在Component注解
if(aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){
//判断是不是单例模式,要看自定义的注解Scope
if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)){
Scope scopeAnnotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Scope.class);
String value = scopeAnnotation.value();
if (value.equals("singleton")){
//创建单例模式的bean
}
else{
//多例模式
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
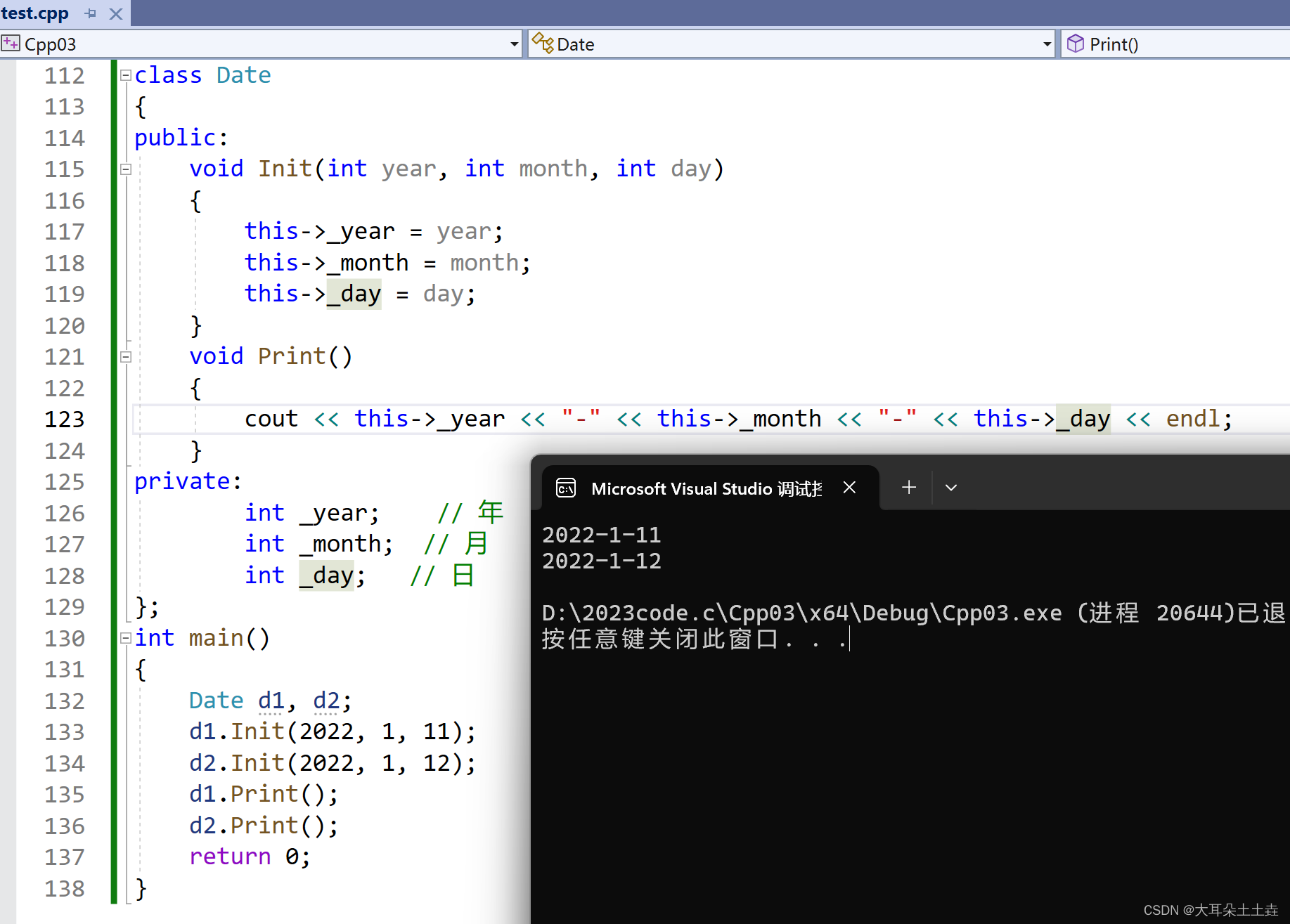
创建一个注解 Scope
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Scope {
String value() default "";
}
在服务类上使用,如果是单例,就写singleton,如果是多例,就写prototype
例如:服务类UserService ,这里声明是单例模式
@Component("UserService")
@Scope("singleton")
public class UserService {
public void test(){
System.out.println("test");
}
}
07.优化设计,把类上注解的许多信息都放入到一个对象中的话,直接去读取这个类的属性就好了
创建一个BeanDefinition
public class BeanDefinition {
private Class type;
private String scope;
private Boolean isLazy;
public Class getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(Class type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getScope() {
return scope;
}
public void setScope(String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
}
public Boolean getLazy() {
return isLazy;
}
public void setLazy(Boolean lazy) {
isLazy = lazy;
}
}
再次优化扫描
//判断是不是类上存在Component注解
if(aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){
Component componentAnnotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String name = componentAnnotation.value();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition=new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setType(aClass);
//判断是不是单例模式,要看自定义的注解Scope
if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)){
Scope scopeAnnotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Scope.class);
String value = scopeAnnotation.value();
beanDefinition.setScope(value);
if (value.equals("singleton")){
//创建单例模式的bean
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
else{
//多例模式
}
}
}
在wzpApplicationContext 中添加一个属性,map集合
public class wzpApplicationContext {
//配置类
private Class configClass;
//存放BeanDefinition
private Map<String,BeanDefinition> BeanDefinitionMap =new HashMap<>();
}
把刚刚创建的BeanDefinition放入到map集合中:
if(aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){
Component componentAnnotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String name = componentAnnotation.value();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition=new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setType(aClass);
//判断是不是单例模式,要看自定义的注解Scope
if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)){
Scope scopeAnnotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Scope.class);
String value = scopeAnnotation.value();
beanDefinition.setScope(value);
if (value.equals("singleton")){
//创建单例模式的bean
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
else{
//多例模式
}
BeanDefinitionMap.put(name,beanDefinition);
}
}
最后总的代码抽象此外一个方法:
public wzpApplicationContext(Class configClass) throws ClassNotFoundException {
this.configClass = configClass;
//判断类上是不是有注解ComponentScan
scan(configClass);
}
private void scan(Class configClass) throws ClassNotFoundException {
if(configClass.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class)){
//获取注解对象
ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
//获取注解对象上的value,这里也就是path
String path = componentScan.value();
//文件的路径是/,而获取到的是带有.的包名
path.replace(".","/");
//获取当前的类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = wzpApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
//根据类加载器获取编译完成的target的class文件夹的路径
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
//根据路径,获取文件
File file=new File(resource.getFile());
//因为扫描的是包,所以大概率是一个目录
if (file.isDirectory()){
//获取目录中的文件集合
for (File f:file.listFiles()){
//获取文件的绝对路径
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
//截取从org到class
String org = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.indexOf("org"), absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
//由于是文件路径,要转换回来,把\变成 . 包名,好让类加载器加载得到类的对象
String classpath = org.replace("\\", ".");
//加载器加载后,得到一个类对象
Class<?> aClass = classLoader.loadClass(classpath);
//判断是不是类上存在Component注解
if(aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){
Component componentAnnotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String name = componentAnnotation.value();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition=new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setType(aClass);
//判断是不是单例模式,要看自定义的注解Scope
if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)){
Scope scopeAnnotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Scope.class);
String value = scopeAnnotation.value();
beanDefinition.setScope(value);
if (value.equals("singleton")){
//创建单例模式的bean
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
else{
//多例模式
}
BeanDefinitionMap.put(name,beanDefinition);
}
}
}
}
}
}
08.扫描完了,开始写createbean方法了
在扫描之后调用:
用for循环
public class wzpApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
private Map<String,BeanDefinition> BeanDefinitionMap =new HashMap<>();
public wzpApplicationContext(Class configClass) throws ClassNotFoundException {
this.configClass = configClass;
//判断类上是不是有注解ComponentScan
scan(configClass);
for (Map.Entry<String, BeanDefinition> entry : BeanDefinitionMap.entrySet()){
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = entry.getValue();
String beanName = entry.getKey();
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton"))
{
//在这里调用createbean,创建单例
Object bean= createBean(beanName,beanDefinition);
}
}
}
09.在wzpApplicationContext 创建createBean
private Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
return null;
}
10.创建的bean要保存到容器
在wzpApplicationContext 创建一个属性 Map<String,Object> singletonObjectsMap,这个用来保存创建的单例bean
//保存单例的地方,Map集合
private Map<String,Object> singletonObjectsMap =new HashMap<>();
此时的for循环
for (Map.Entry<String, BeanDefinition> entry : BeanDefinitionMap.entrySet()){
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = entry.getValue();
String beanName = entry.getKey();
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton"))
{
//创建单例
Object bean= createBean(beanName,beanDefinition);
//保存单例到容器中
singletonObjectsMap.put(beanName,bean);
}
}
11.什么时候调用这个getbean方法
先从BeanDefinitionMap获取已经扫描完了beanDefinition,如果有的话,那表示在扫描的包中,有这个类,再判断是不是单例模式,如果没有的话,那就说明没有这样的类,抛出异常。
public Object getBean(String beanName) throws Exception {
if (!BeanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton"))
{
//单例
}else{
//原型
}
return null;
}
这里是获取bean,单例从容器中获取
singletonObjectsMap.get(beanName)
原型(多例)就马上创建一个bean
createBean(beanName, beanDefinition);
这个时候的getBean方法
public Object getBean(String beanName) throws Exception {
if (!BeanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton"))
{
//单例
return singletonObjectsMap.get(beanName);
}else{
//原型
Object bean = createBean(beanName, beanDefinition);
return bean;
}
}
12.如何创建bean呢,用反射 newInstance()
private Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getType();
Object o = clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
return o;
}
13.测试
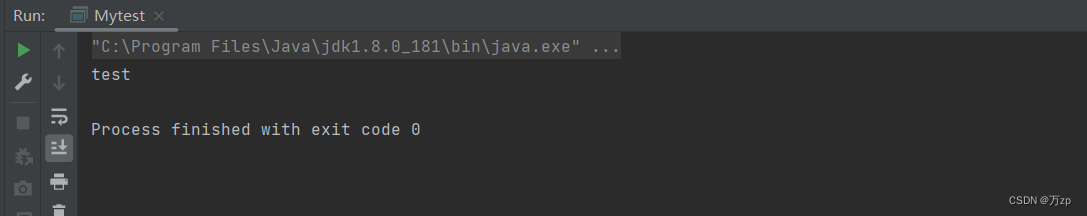
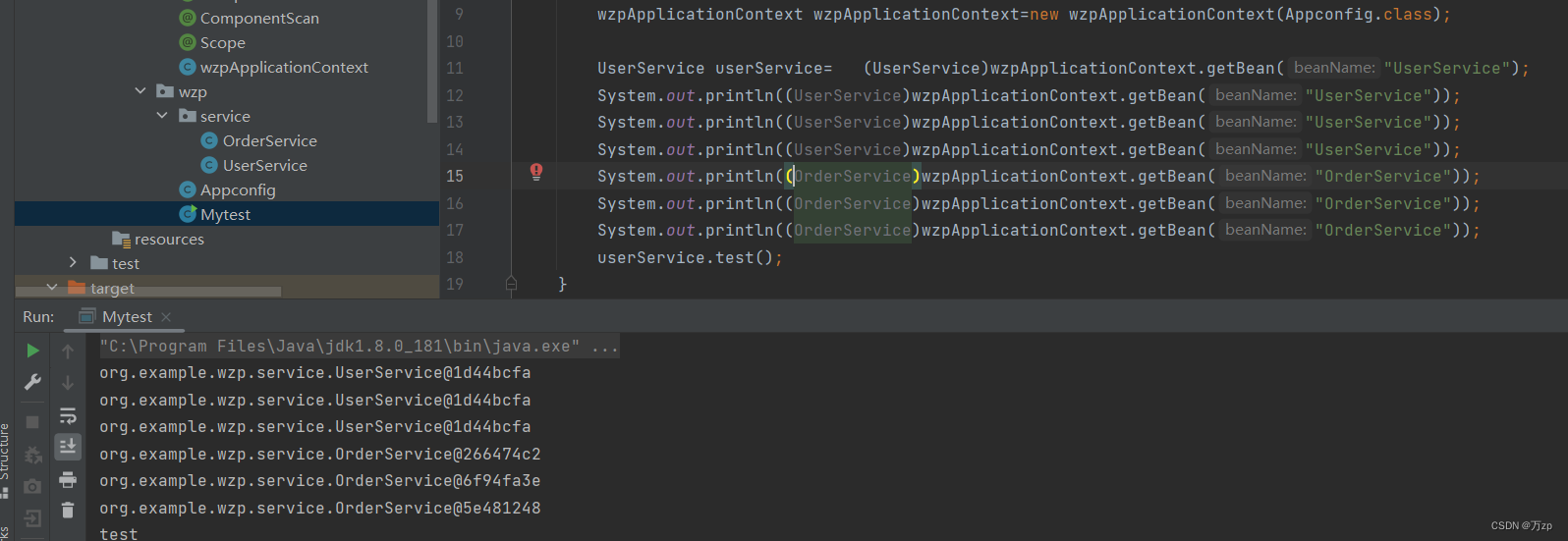
14.创建一个多例
@Component("OrderService")
@Scope("prototype")
public class OrderService
{
}
public class Mytest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
wzpApplicationContext wzpApplicationContext=new wzpApplicationContext(Appconfig.class);
UserService userService= (UserService)wzpApplicationContext.getBean("UserService");
System.out.println((UserService)wzpApplicationContext.getBean("UserService"));
System.out.println((UserService)wzpApplicationContext.getBean("UserService"));
System.out.println((UserService)wzpApplicationContext.getBean("UserService"));
System.out.println((OrderService)wzpApplicationContext.getBean("OrderService"));
System.out.println((OrderService)wzpApplicationContext.getBean("OrderService"));
System.out.println((OrderService)wzpApplicationContext.getBean("OrderService"));
userService.test();
}
}
15.实现依赖注入:也就是@AutoWired注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface AutoWired {
}
在服务类UserService中使用这个自定义的注解:
@Component("UserService")
@Scope("singleton")
public class UserService {
@AutoWired
private OrderService orderService;
public void test(){
System.out.println("test");
}
}
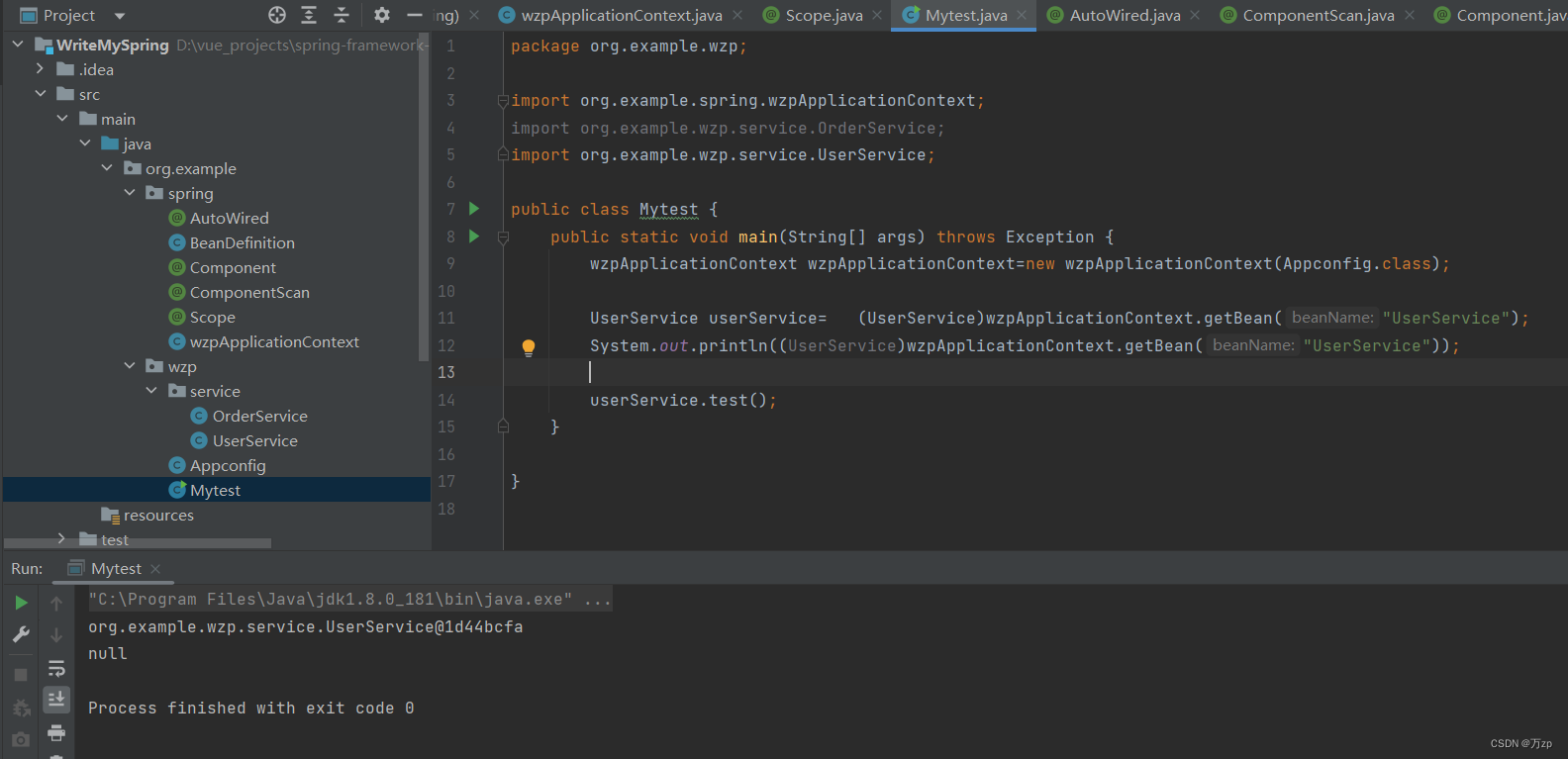
16.测试
结果是null
17.实现依赖注入
在createBean方法中去写:
private Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getType();
Object o = clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
for (Field field : clazz.getDeclaredFields())
{
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(AutoWired.class))
{
//将该对象的可访问标志设置为指定的布尔值。值为true表示当使用该反射对象时应该抑制Java语言访问检查。
//实际上setAccessible是启用和禁用访问安全检查的开关
//由于JDK的安全检查耗时较多.所以通过setAccessible(true)的方式关闭安全检查就可以达到提升反射速度的目的
field.setAccessible(true);
//Field.set()方法的语法:
// set(Object obj, Object value)
// 此时的Field对象表示已经是这个对象的一个属性了 为Field对象属于的变量的属性设置新值(Field代表的属性的新的值)
field.set(o,getBean(field.getName()));
}
}
return o;
}
18.存在一个问题,实现依赖注入的时候,万一那个对象还没有被创建呢,也就是在容器中还没有来得及创建这个类型的bean,要修改getbean方法
public Object getBean(String beanName) throws Exception {
if (!BeanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton"))
{
Object singletOnobjectBean= singletonObjectsMap.get(beanName);
//单例
if (singletOnobjectBean==null){
singletonObjectsMap.put(beanName, createBean(beanName,beanDefinition)) ;
}
return singletOnobjectBean;
}else{
//原型
Object protoTypeBean = createBean(beanName, beanDefinition);
return protoTypeBean;
}
}
19.实现初始化:
要写一个接口:InitializingBean
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet();
}
20.服务类UserService来实现接口:
@Component("UserService")
@Scope("singleton")
public class UserService implements InitializingBean {
@AutoWired
private OrderService orderService;
public void test(){
System.out.println(orderService);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
System.out.println("初始化");
}
}
21.初始化要在创建bean方法中去做啊,所以还是要修改createbean方法:
private Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getType();
Object o = clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
for (Field field : clazz.getDeclaredFields())
{
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(AutoWired.class))
{
//将该对象的可访问标志设置为指定的布尔值。值为true表示当使用该反射对象时应该抑制Java语言访问检查。
//实际上setAccessible是启用和禁用访问安全检查的开关
//由于JDK的安全检查耗时较多.所以通过setAccessible(true)的方式关闭安全检查就可以达到提升反射速度的目的
field.setAccessible(true);
//Field.set()方法的语法:
// set(Object obj, Object value)
// 此时的Field对象表示已经是这个对象的一个属性了 为Field对象属于的变量的属性设置新值(Field代表的属性的新的值)
field.set(o,getBean(field.getName()));
}
}
//初始化
if (o instanceof InitializingBean){
((InitializingBean) o).afterPropertiesSet();
}
return o;
}
22.要实现AOP,也就要实现BeanPostProcessor,这个也是一个接口
package org.example.spring;
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
}
23.写这个接口的实现类,因为要在bean中用,所以加上@Component,表示这个也是一个bean
package org.example.spring;
@Component("wzpBeanPostProcessor")
public class wzpBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor{
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return null;
}
}
24.由于这个bean是用于AOP的,比较特殊,所以在扫描的时候创建比较好
,要修改扫描函数,主要是在扫描类中是否有@Component注解修饰的时候这一部分来写比较好
private void scan(Class configClass) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
if(configClass.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class)){
//获取注解对象
ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
//获取注解对象上的value,这里也就是path
String path = componentScan.value();
//文件的路径是/,而获取到的是带有.的包名
path= path.replace(".","/");
//获取当前的类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = wzpApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
//根据类加载器获取编译完成的target的class文件夹的路径
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
//根据路径,获取文件
File file=new File(resource.getFile());
//因为扫描的是包,所以大概率是一个目录
if (file.isDirectory()){
//获取目录中的文件集合
for (File f:file.listFiles()){
//获取文件的绝对路径
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
//截取从org到class
String org = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.indexOf("org"), absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
//由于是文件路径,要转换回来,把\变成 . 包名,好让类加载器加载得到类的对象
String classpath = org.replace("\\", ".");
//加载器加载后,得到一个类对象
Class<?> aClass = classLoader.loadClass(classpath);
//判断是不是类上存在Component注解
if(aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){
if (BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(aClass)){
BeanPostProcessor BeanPostProcessornewInstance = (BeanPostProcessor)aClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
BeanPostProcessorList.add(BeanPostProcessornewInstance);
}
Component componentAnnotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String name = componentAnnotation.value();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition=new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setType(aClass);
//判断是不是单例模式,要看自定义的注解Scope
if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)){
Scope scopeAnnotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Scope.class);
String value = scopeAnnotation.value();
beanDefinition.setScope(value);
if (value.equals("singleton")){
//创建单例模式的bean
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
else{
//多例模式
}
BeanDefinitionMap.put(name,beanDefinition);
}
}
}
}
}
}
private List<BeanPostProcessor> BeanPostProcessorList=new ArrayList<>();
25.要用这个wzpBeanPostProcessor,主要还是在createbean,这里是初始化后的操作,下面还有一个初始化前的操作
private Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getType();
Object o = clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
for (Field field : clazz.getDeclaredFields())
{
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(AutoWired.class))
{
//将该对象的可访问标志设置为指定的布尔值。值为true表示当使用该反射对象时应该抑制Java语言访问检查。
//实际上setAccessible是启用和禁用访问安全检查的开关
//由于JDK的安全检查耗时较多.所以通过setAccessible(true)的方式关闭安全检查就可以达到提升反射速度的目的
field.setAccessible(true);
//Field.set()方法的语法:
// set(Object obj, Object value)
// 此时的Field对象表示已经是这个对象的一个属性了 为Field对象属于的变量的属性设置新值(Field代表的属性的新的值)
field.set(o,getBean(field.getName()));
}
}
//初始化
if (o instanceof InitializingBean){
((InitializingBean) o).afterPropertiesSet();
}
//AOP
for (BeanPostProcessor b: BeanPostProcessorList){
//初始化后的操作
b.postProcessAfterInitialization(o,beanName);
}
return o;
}
在ceatebean方法
初始化前,初始化,初始化后
//初始化后
for (BeanPostProcessor b: BeanPostProcessorList){
b.postProcessBeforeInitialization(o,beanName);
}
//初始化
if (o instanceof InitializingBean){
((InitializingBean) o).afterPropertiesSet();
}
//初始化后
for (BeanPostProcessor b: BeanPostProcessorList){
b.postProcessAfterInitialization(o,beanName);
}
26.wzpBeanPostProcessor的主要功能是AOP,怎么AOP呢,这里用的是动态代理,还要创建一个接口UserInterface
package org.example.spring;
public interface UserInterface {
void test();
}
服务类再去实现这个接口
@Component("UserService")
@Scope("singleton")
public class UserService implements InitializingBean , UserInterface {
@AutoWired
private OrderService orderService;
public void test(){
System.out.println("hello AOP");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
System.out.println("初始化");
}
}
27.在wzpBeanPostProcessor中去完成AOP,比如说初始化后的postProcessAfterInitialization方法中,做AOP,要针对哪个bean,用if判断:
package org.example.spring;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
@Component("wzpBeanPostProcessor")
public class wzpBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor{
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (beanName.equals("UserService")) {
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(wzpBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//执行AOP的逻辑
System.out.println("hello AOP逻辑在此");
//执行完了AOP的操作,执行原来的切点方法
return method.invoke(bean,args);
}
});
return proxyInstance;
}
return bean;
}
}
在createbean方法中也要修改,因为要接收代理对象
//初始化后
for (BeanPostProcessor b: BeanPostProcessorList){
o= b.postProcessBeforeInitialization(o,beanName);
}
//初始化
if (o instanceof InitializingBean){
((InitializingBean) o).afterPropertiesSet();
}
//初始化后
for (BeanPostProcessor b: BeanPostProcessorList){
o= b.postProcessAfterInitialization(o,beanName);
}
28.实现Aware接口
在 Spring 中,BeanNameAware 接口是一个回调接口,它提供了一个用于设置 Bean 名称的方法。当一个 Bean 实现了 BeanNameAware 接口时,在该 Bean 实例被实例化后,Spring 容器会调用 setBeanName 方法,并将该 Bean 在 Spring 容器中的名称作为参数传递进去。
创建一个BeanNameAware接口:
public interface BeanNameAware {
void setBeanName(String name);
}
在服务类中实现接口:
package org.example.wzp.service;
import org.example.spring.*;
@Component("UserService")
@Scope("singleton")
public class UserService implements InitializingBean , UserInterface ,BeanNameAware {
@AutoWired
private OrderService orderService;
public void test(){
System.out.println("hello AOP");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
System.out.println("初始化");
}
private String beanName;
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
this.beanName=name;
}
}
在createbean函数中:在初始化之前
//Aware接口
if (o instanceof BeanNameAware){
((BeanNameAware) o).setBeanName(beanName);
}
//初始化前
for (BeanPostProcessor b: BeanPostProcessorList){
o= b.postProcessBeforeInitialization(o,beanName);
}
//初始化
if (o instanceof InitializingBean){
((InitializingBean) o).afterPropertiesSet();
}
//初始化后
for (BeanPostProcessor b: BeanPostProcessorList){
o= b.postProcessAfterInitialization(o,beanName);
}