解题方案
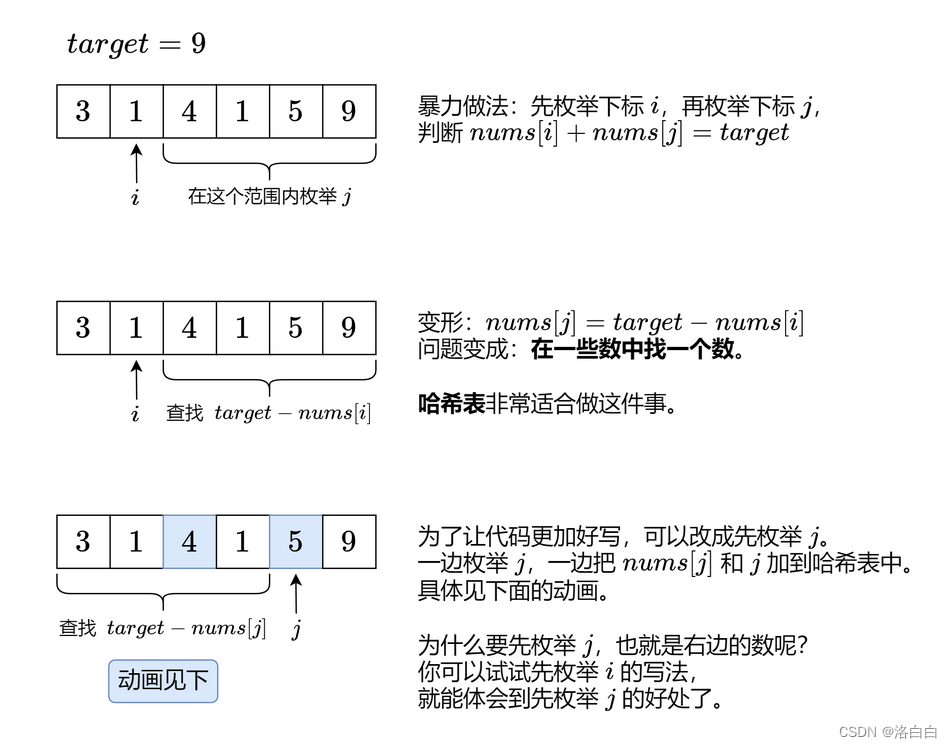
解法一
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
for i, x in enumerate(nums): # x=nums[i]
for j in range(i + 1, len(nums)): # 枚举 i 右边的 j
if x + nums[j] == target: # 满足要求
return [i, j] # 返回两个数的下标
# 这里无需 return,因为题目保证有解
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n2)\mathcal{O}(n^2)O(n2),其中 nnn 为 nums\textit{nums}nums 的长度。
空间复杂度:O(1)\mathcal{O}(1)O(1)。仅用到若干额外变量。
解法二
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
idx = {} # 创建一个空哈希表(字典)
for j, x in enumerate(nums): # x=nums[j]
if target - x in idx: # 在左边找 nums[i],满足 nums[i]+x=target
return [idx[target - x], j] # 返回两个数的下标
idx[x] = j # 保存 nums[j] 和 j
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n)\mathcal{O}(n)O(n),其中 nnn 为 nums\textit{nums}nums 的长度。
空间复杂度:O(n)\mathcal{O}(n)O(n)。哈希表需要 O(n)\mathcal{O}(n)O(n) 的空间。
相比暴力做法,哈希表消耗了内存空间,减少了运行时间,这就是「空间换时间」。
来源:灵茶山艾府
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum/solutions/2326193/dong-hua-cong-liang-shu-zhi-he-zhong-wo-0yvmj/