文章目录
- priority_queue的介绍
- 库中priority_queue的使用
- 什么叫仿函数?
- 模拟实现prioprity_queue类
priority_queue的介绍
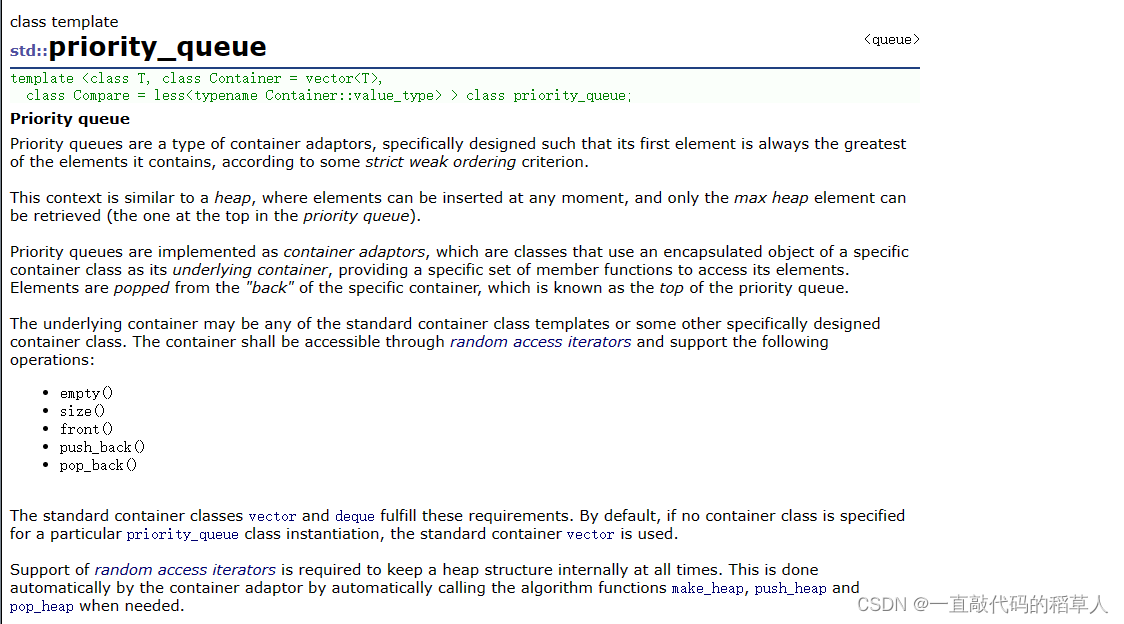
解释以上内容
- priority_queue(优先级队列)跟stack、queue一样,都是一种容器适配器,根据严格的弱排序标准,它的第一个元素总是它所包含的元素中最大或者最小的(默认最大)。
- .优先队列的底层数据结构是用堆来实现的。
- 作为容器适配器,priority_queue默认是由 vector类
来实现的。优先队列(堆)这种数据结构需要快速随机访问元素的能力。除了vector,deque类也可以用来作为优先队列的底层容器。严格来说,只要满足以下能力的容器都可以作为优先队列的底层容器:
(1)empty():检测容器是否为空
(2)size():返回容器中有效元素个数
(3)front():返回容器中第一个元素的引用
(4)push_back():在容器尾部插入元素
(5)pop_back():删除容器尾部元素
库中priority_queue的使用
虽然我们将priority_queue称为优先队列,但是其本质就是堆,而堆的本质又是一颗完全二叉树。所以,我们需要一种符合以上这些数据结构所有特点的容器来存储元素。vector就显得非常合适。可以用下标映射节点的父子关系,高效尾删,快速随机访问。
现在我们来看库中priority_queue主要有哪些功能吧
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
| priority_queue()和priority_queue(first, last) | 构造一个空的优先队列 |
| empty() | 检测优先级队列是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
| top() | 返回堆顶元素的值,即当前优先队列中的最大值或者最小值 |
| push(val) | 在优先队列中插入val,并且调整优先队列 |
| pop() | 弹出堆顶元素,即优先队列的最大值或者最小值 |
1.使用演示:创建大堆,默认就是最大堆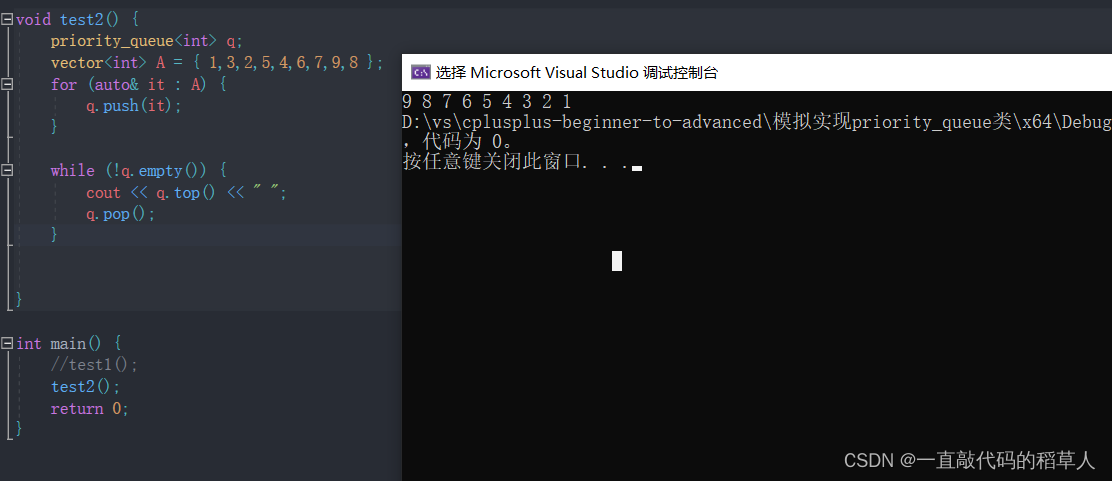
2.使用演示:创建最小堆, 将第三个模板参数换成greater比较方式
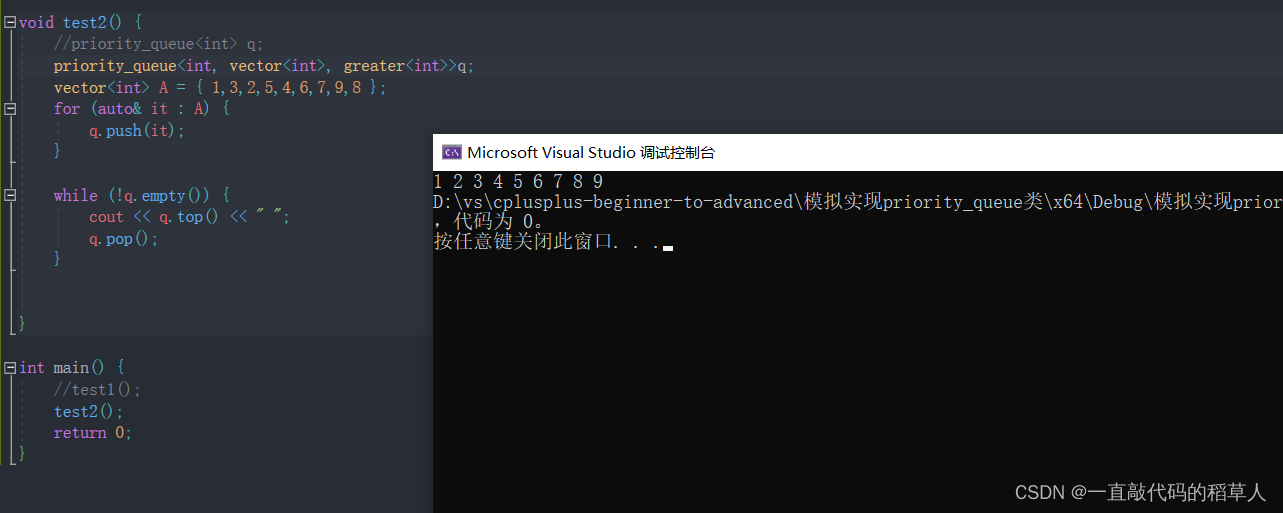
其中,greater是一个类模板,实例化出来之后可以当函数一样使用(仿函数)。greater里面控制了比较对象的关系,是一个比较剂。
什么叫仿函数?
仿函数又叫函数对象。本质是一个类实例化出来的对象,因为重载了()我们可以像使用函数一样使用其operator()。
比如下面就是一个仿函数:
class fun {
public:
int operator()(int& A, int& B) {
return A + B;
}
};
我们可以创建一个fun类来调用operator():
class fun {
public:
int operator()(int& A, int& B) {
return A + B;
}
};
void test3() {
fun f;
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
cout << f(a, b) << endl;
}
借用模板之后,仿函数比普通函数显得更加灵活。
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>>中的greater其实就是一个函数对象,通过实例化int类型,来控制两个int类型变量的顺序关系。
模拟实现greater类:
template<class T>
class Greater {
public:
bool operator()(T& A, T& B) {
return A > B;
}
};
当我们将greater作为第三个参数传递给priority_queue时,二叉树的父子节点的关系也就确定了,即确定了优先级。
那为什么默认是小堆呢?
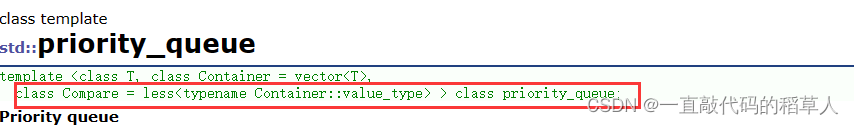
这是因为priority_queue的第三个参数的缺省值设置成了less,而less其实就是一个仿函数,控制了堆顶元素永远是最小值。
当然,我们同样可以不用仿函数做参数,用一个函数指针也可以达到一样的效果。
值得注意的是,如果priority_queue的元素是自定义类型,那我们需要在自定义类型中提供比较运算符的重载,以便达到我们想要的目的。
给出以下代码示例:
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
void TestPriorityQueue()
{
// 大堆,需要用户在自定义类型中提供<的重载
priority_queue<Date> q1;
q1.push(Date(2018, 10, 29));
q1.push(Date(2018, 10, 28));
q1.push(Date(2018, 10, 30));
cout << q1.top() << endl;
// 如果要创建小堆,需要用户提供>的重载
priority_queue<Date, vector<Date>, greater<Date>> q2;
q2.push(Date(2018, 10, 29));
q2.push(Date(2018, 10, 28));
q2.push(Date(2018, 10, 30));
cout << q2.top() << endl;
}
模拟实现prioprity_queue类
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
template<class T>
class Less {
public:
bool operator()(T& A, T& B) {
return A < B;
}
};
template<class T>
class Greater {
public:
bool operator()(T& A, T& B) {
return A > B;
}
};
template<class T,class Container=std::vector<T>, class Compare = Less<T> >
class priority_queue {
public:
int size() {
return _con.size();
}
bool empty() {
return _con.empty();
}
void adjust_up(int n) {
int child = n;
int father = (n - 1) / 2;
Compare com;
while (child >= 0) {
if (com(_con[father], _con[child])) {
std::swap(_con[father], _con[child]);
child = father;
father = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
void adjust_down(int n) {
int father = n;
int child = father * 2 + 1;
Compare com;
while (child < size()) {
if (child + 1 < size() && com(_con[child ],_con[child+1])) {
child++;
}
if (com(_con[father], _con[child])) {
std::swap(_con[father], _con[child]);
father = child;
child = child * 2 + 1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
void push(const T& val) {
_con.push_back(val);
adjust_up(_con.size()-1);
}
T& top() {
return _con[0];
}
void pop() {
std::swap(_con[0], _con[size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
adjust_down(0);
}
T& operator[](size_t n) {
return _con[n];
}
private:
Container _con;
};
![[leetcode] all-nodes-distance-k-in-binary-tree 二叉树中所有距离为 K 的结点](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/6d8eceafdb9b46a6888119f7de3829bd.png)