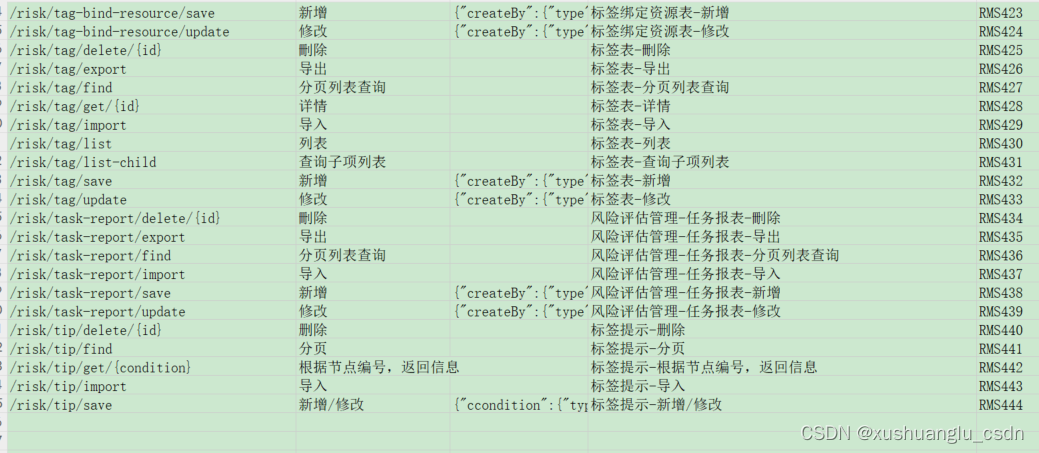
1. 新建run.py文件,并定义相关接口:
import numpy as np
from scipy.fftpack import fft
def str_add(str1,str2):
return int(str1) + int(str2)
def my_sort(data):
data.sort()
return data
def aw_fft(data, Fs):
N = len(data)
result = np.abs(fft(x=data, n=N) / N) * 2
axisFreq = np.arange(int(N / 2)) * Fs / N
result = result[range(int(N / 2))]
idx = np.argmax(result)
return axisFreq[idx]
2. 将run.py文件拷入c++工程目录下:
- 项目->属性->VC++目录->包含目录->添加python头文件路径(C:\Python38\include);
- 链接器->常规->附加库目录->添加python库路径(C:\Python38\libs);
- 链接器->输入->输入python38.lib;
2.1 c++中直接运行python代码
#include <Python.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 初始化Python解释器
Py_Initialize();
// 检查初始化是否成功
if (!Py_IsInitialized()) {
return -1;
}
// 直接运行Python代码
PyRun_SimpleString("import numpy as np\n");
PyRun_SimpleString("print(np.sort(np.array([3,2,5,8,1])))");
// 结束python运行环境
Py_Finalize();
}
2.2 c++中调run.py中的str_add接口
#include <Python.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
PyObject* pModule;
PyObject* pFun;
PyObject* pResult;
PyObject* pArgs;
// 初始化Python解释器
Py_Initialize();
// 检查初始化是否成功
if (!Py_IsInitialized()) {
return -1;
}
// 定位到python脚本所在目录
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys\n");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('.')\n");
// 导入py文件,文件名即可,不需要带后缀.py
pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("run");
if (!pModule) {
printf("error1\n");
exit(0);
}
// 获取模块中函数
pFun = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "str_add");
if (!pFun) {
printf("error2\n");
exit(0);
}
// 创建参数
string s1 = "33";
string s2 = "66";
pArgs = Py_BuildValue("(ss)", s1.c_str(), s2.c_str());
// 调用函数
pResult = PyObject_CallFunction(pFun, "O", pArgs);
int res = PyLong_AsLong(pResult);
printf("result=%d\n", res);
// 使用结束后,释放掉这些Python对象
Py_DECREF(pModule);
Py_DECREF(pFun);
Py_DECREF(pResult);
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
// 结束python运行环境
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}
2.3 c++中调run.py中的my_sort接口
#include <Python.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
PyObject* pModule;
PyObject* pFun;
PyObject* pResult;
PyObject* pArgs;
// 初始化Python解释器
Py_Initialize();
// 检查初始化是否成功
if (!Py_IsInitialized()) {
return -1;
}
// 定位到python脚本所在目录
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys\n");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('.')\n");
// 导入py文件,文件名即可,不需要带后缀.py
pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("run");
if (!pModule) {
printf("error1\n");
exit(0);
}
// 获取模块中函数
pFun = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "my_sort");
// 创建参数
pArgs = Py_BuildValue("[i,i,i,i,i]", 4,2,6,3,1);
pResult = PyObject_CallFunction(pFun, "O", pArgs);
printf("result=%d\n", PyList_Size(pResult));
for (int i = 0; i < PyList_Size(pResult); i++) {
PyObject* b = PyList_GetItem(pResult, i);
int bi = _PyLong_AsInt(b);
cout << bi << endl;
}
// 使用结束后,释放掉这些Python对象
Py_DECREF(pModule);
Py_DECREF(pFun);
Py_DECREF(pResult);
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
// 结束python运行环境
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}
2.4 c++中调run.py中的aw_fft接口
#include <Python.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
PyObject* pModule;
PyObject* pFun;
PyObject* pResult;
PyObject* pArgs;
// 初始化Python解释器
Py_Initialize();
// 检查初始化是否成功
if (!Py_IsInitialized()) {
return -1;
}
// 定位到python脚本所在目录
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys\n");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('.')\n");
// 导入py文件,文件名即可,不需要带后缀.py
pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("run");
if (!pModule) {
printf("error1\n");
exit(0);
}
// 获取模块中函数
pFun = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "aw_fft");
if (!pFun) {
printf("error2\n");
exit(0);
}
PyObject* list = PyList_New(1000);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
double temp = sin(2 * 3.14 * 235 * i / 6000);
PyList_SetItem(list, i, PyFloat_FromDouble(temp));
}
PyObject* Fs = Py_BuildValue("i", 6000);
pArgs = PyTuple_Pack(2, list, Fs);
pResult = PyObject_CallFunction(pFun, "O", pArgs);
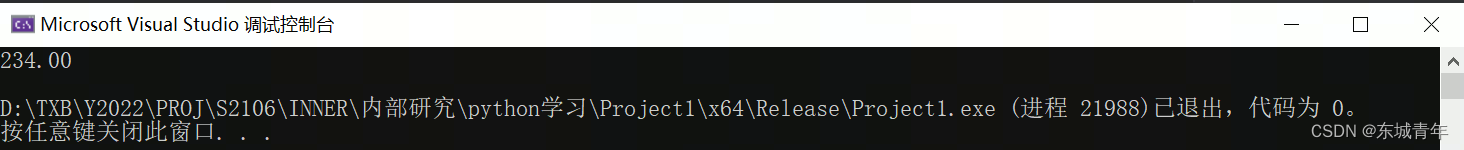
printf("%.2f\n", PyFloat_AsDouble(pResult));
// 使用结束后,释放掉这些Python对象
Py_DECREF(pModule);
Py_DECREF(pFun);
Py_DECREF(pResult);
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
// 结束python运行环境
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}
3. c++中将python接口编译dll文件
在dllmain.cpp中添加如下接口:
#include "utils.h"
#include <Python.h>
#include <iostream>
float aw_fft(const char* py_name, const char* fun_name, double* data, int data_cnts, int Fs)
{
PyObject* pModule;
PyObject* pFun;
PyObject* pArgs;
PyObject* pResult;
// 初始化Python解释器
Py_Initialize();
// 检查初始化是否成功
if (!Py_IsInitialized()) {
return -1;
}
// 定位到脚本所在目录
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys\n");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('.')\n");
// 导入py文件,写文件名即可,不需要带后缀.py
pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("run");
if (!pModule) {
printf("error1\n");
exit(0);
}
// 获取模块中函数
pFun = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "aw_fft");
if (!pFun) {
printf("error2\n");
exit(0);
}
// 创建列表对象
PyObject* list = PyList_New(data_cnts);
for (int i = 0; i < data_cnts; i++) {
PyList_SetItem(list, i, PyFloat_FromDouble(data[i]));
}
// 创建整形对象
PyObject* sample = Py_BuildValue("i", Fs);
// 创建参数
pArgs = PyTuple_Pack(2, list, sample);
// 调用函数
pResult = PyObject_CallFunction(pFun, "O", pArgs);
float result = PyFloat_AsDouble(pResult);
// 释放对象
Py_DECREF(pModule);
Py_DECREF(pFun);
Py_DECREF(pResult);
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
// 结束python运行环境
Py_Finalize();
return result;
}新建utils.h文件:
#define CREATDLL_EXPORTS
#ifdef CREATDLL_EXPORTS
#define DLL_API __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define DLL_API __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
extern "C" DLL_API void add_fun(int a, int b, int& c);
extern "C" DLL_API float aw_fft(const char* py_name, const char* fun_name, double* data, int data_cnts, int Fs);生成解决方案,生成lib和dll文件,将util.h及Dll1.lib和Dll.dll文件拷入c++工程供调用:
#include <iostream>
#include"utils.h"
using namespace std;
#pragma comment (lib, "Dll1.lib")
int main()
{
double data[1000] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
data[i]= sin(2 * 3.14 * 235 * i / 6000);
}
const char* py_name = "run";
const char* fun_name = "aw_fft";
float res = aw_fft(py_name, fun_name, data, 1000, 6000);
cout << res << endl;
}
c++能调用python的接口吗 c++调用python程序