共享内存是操作系统在内存中开辟一块空间,通过页表与共享区建立映射关系,使两个进程看到同一份资源,实现进程间通信。

1、创建共享内存
参数:第一个参数为key,一般使用ftok()函数生成,key值不能冲突,标识共享内存的唯一性
第二个参数 size 表示要创建的共享内存的大小。(会向上取整至4KB的整数倍)
第三个参数为标志位,用IPC_CREAT表示如果共享内存不存在就创建,存在就获取。另一个为IPC_EXCL,单独使用没有意义,要和IPC_CREAT配合使用.(IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL)表示如果共享内存不存在就创建,存在就出错返回。还可以在后面加上 | mode 表示设置mode权限
 可以看到库里面定义的后三位为0,所以我们用(IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0666)可以设置权限为666.
可以看到库里面定义的后三位为0,所以我们用(IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0666)可以设置权限为666.
返回值:成功则1返回共享内存的 id ;失败返回 -1,并设置错误码。
生成创建共享内存需要的 key:

参数:第一个参数为路径名,第二个参数为一个整数。(两个都可以随便传)
它是根据传入的这两个参数,生产一个key值,只要我们拿到了一样的 pathname 和 proj_id 就能拿到同一个key,就可以用 shmget 拿到同一块共享内存的id,就可以保证两个进程看到同一份资源。
返回值:成功返回一个 key 值,失败返回 -1,并设置错误码。
示例:测试ftok
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
using namespace std;
const char *pathname = "/home/lw/storehouse/process_communication";
const int proj_id = 0x66;
int main()
{
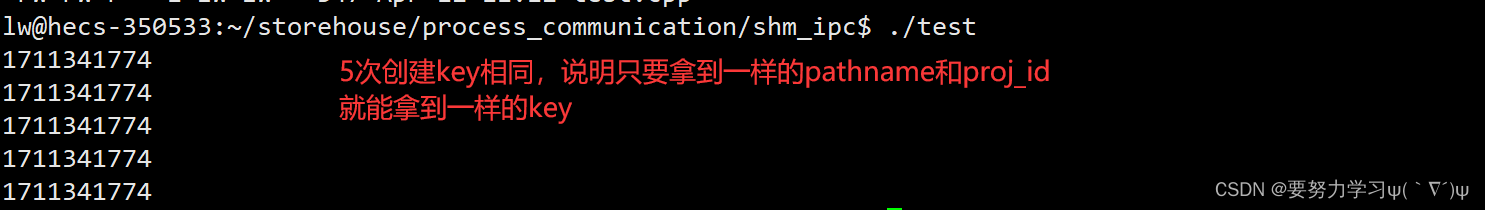
// 创建5次key,验证只有pathname和proj_id相同,key就相同
int i = 5;
while (i--)
{
int key = ftok(pathname, proj_id);
printf("%d\n", key);
}
return 0;
}
示例:测试shmget
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
using namespace std;
const char *pathname = "/home/lw/storehouse/process_communication";
const int proj_id = 0x66;
int main()
{
int key = ftok(pathname, proj_id);
printf("%d\n", key);
shmget(key, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0666);
return 0;
}
可以看到创建成功。
有关共享内存的命令:
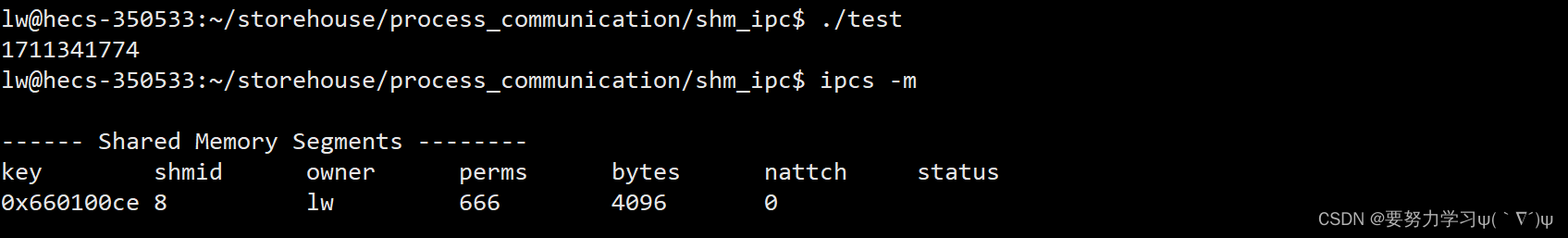
1、ipcs -m :可以看到创建出的共享内存的信息。
key:key值;shmid:共享内存的id;owner:创建者;perms:权限;
bytes:大小;nattch:附接数(附接可以看下文);status:状态。
2、ipcrm -m 【shmid】:删除 id 为 shmid 的共享内存。
2、挂接上地址空间
我们在内存中开辟了内存,之后就需要挂接上我们的地址空间,让它与页表建立映射关系,连到我们的共享区。

参数:第一个参数:shmid 为 shmget() 创建共享内存时返回的 id。
第二个参数:shmaddr 为一个地址,代表你想把共享内存映射到哪个地址上。我们一般设为nullptr,让操作系统帮我们选择。
第三个参数:标志位,一般设为0,表示正常读写。
返回值:成功就返回已经构建好映射的虚拟地址;失败返回(void*) -1。
示例:使用shmat
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
const char *pathname = "/home/lw/storehouse/process_communication";
const int proj_id = 0x66;
int main()
{
// 创建key
key_t key = ftok(pathname, proj_id);
printf("%d\n", key);
// 创建共享内存
int shmid = shmget(key, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if(shmid < 0)
{
printf("shmget fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return errno;
}
printf("shmget success, shmid = %d\n", shmid);
// 挂接上共享区
char* shmaddr = (char*)shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if((long)shmaddr == -1)
{
printf("shmat fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return errno;
}
printf("shmat success\n");
// 让我们有时间输命令,看到挂接数+1
sleep(10);
return 0;
}
3、使用
挂接上地址空间后,就可以使用共享内存了。我们使用共享内存不用向管道一样读写,可以把 shmat() 返回的地址看做我们自己 malloc 出的空间来使用。
示例:
客户端:写数据
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 创建key
key_t key = ftok("/home/lw/storehouse/process_communication", 0x66);
printf("%d\n", key);
// 创建共享内存
int shmid = shmget(key, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if(shmid < 0)
{
printf("shmget fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return errno;
}
printf("shmget success, shmid = %d\n", shmid);
// 挂接上共享区
char* shmaddr = (char*)shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if((long)shmaddr == -1)
{
printf("shmat fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return errno;
}
printf("shmat success\n");
// client 写数据, 从A写到Z
memset(shmaddr, 0, 4096);
for(char ch = 'A'; ch <= 'Z'; ++ch)
{
shmaddr[ch-'A'] = ch;
}
return 0;
}服务端:读数据
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 创建key
key_t key = ftok("/home/lw/storehouse/process_communication", 0x66);
printf("%d\n", key);
// 创建共享内存
int shmid = shmget(key, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if(shmid < 0)
{
printf("shmget fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return errno;
}
printf("shmget success, shmid = %d\n", shmid);
// 挂接上共享区
char* shmaddr = (char*)shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if((long)shmaddr == -1)
{
printf("shmat fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return errno;
}
printf("shmat success\n");
// 服务端读取
sleep(1);
printf("server 读取数据: %s\n", shmaddr);
return 0;
}
4、去挂接
我们使用完以后需要将共享内存与我们的共享区去挂接。
 参数:shmaddr 表示挂接时拿到的虚拟地址。
参数:shmaddr 表示挂接时拿到的虚拟地址。
返回值:成功为0;失败返回 -1,错误码被设置。
服务端示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 创建key
key_t key = ftok("/home/lw/storehouse/process_communication", 0x66);
printf("%d\n", key);
// 创建共享内存
int shmid = shmget(key, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if(shmid < 0)
{
printf("shmget fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return errno;
}
printf("shmget success, shmid = %d\n", shmid);
// 挂接上共享区
char* shmaddr = (char*)shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if((long)shmaddr == -1)
{
printf("shmat fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return errno;
}
printf("shmat success\n");
// 服务端读取
sleep(1);
printf("server 读取数据: %s\n", shmaddr);
// 去挂接
shmdt(shmaddr);
printf("去挂接成功\n");
return 0;
}

运行前,我们在命令行输入 while :;do ipcs -m;sleep 1; done 在shell中每隔一秒打印一次共享内存的信息。就可以看到上图,原本客户端和服务端都挂接上了,nattch为2,之后都去挂接就变为0。
5、删除共享内存
当我们要删除共享内存时,使用函数shmctl()

shmctl() 可以用来获取共享内存的属性,也可以用来删除。
参数:shmid 就是共享内存的 id ,cmd 就是选项,填IPC_RMID 表示用来删除共享内存。buf 则是在获取属性时才用到,我们删除共享内存设为 nullptr 即可。
返回值:成功为0;失败为 -1,并设置错误码。
服务端示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 创建key
key_t key = ftok("/home/lw/storehouse/process_communication", 0x66);
printf("%d\n", key);
// 创建共享内存
int shmid = shmget(key, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if(shmid < 0)
{
printf("shmget fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return errno;
}
printf("shmget success, shmid = %d\n", shmid);
// 挂接上共享区
char* shmaddr = (char*)shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if((long)shmaddr == -1)
{
printf("shmat fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return errno;
}
printf("shmat success\n");
// 服务端读取
sleep(2);
printf("server 读取数据: %s\n", shmaddr);
// 去挂接
shmdt(shmaddr);
printf("去挂接成功\n");
// 删除共享内存
sleep(2);
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, nullptr);
printf("删除共享内存成功\n");
return 0;
}
我们在命令行输入 while :;do ipcs -m;sleep 1; done 在shell中每隔一秒打印一次共享内存的信息。可以看到共享内存被我们删除了 。
6、通过管道实现进程间协同
我们在使用共享内存时可以感受到,不管有没有数据,或者数据有没有更新,读端都不会等待,而是直接读,而不像管道一样,读端没数据了会等待写端写。
因此我们可以封装一个管道,实现让写端写好了,读端再读。
做法:我们可以先创建一个命名管道文件,然后把read()封装成Wait(),写端不写,read()就会等待;然后把write()封装成WakeUp(),写端随便写一个字符,读端就会唤醒。用Wait和WakeUp就能控制共享内存的读写。
示例:
我们可以先把管道的创建进行封装,封装到Fifo类里面,构造时创建,析构时删除供服务端使用;
同时把对管道的操作也封装进一个类Sync里面,供服务端和客户端使用。
// Fifo.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <error.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
using namespace std;
#define Mode 0666
#define Path "./fifo"
class Fifo
{
public:
// 构造时创建命名管道
Fifo(const string path = Path)
: _path(path)
{
int n = mkfifo(_path.c_str(), Mode);
if (n < 0)
{
printf("create fifo fail, errno is %d, errinfo is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
}
else
{
printf("create fifo successfully\n");
}
}
// 删除管道文件
~Fifo()
{
unlink(_path.c_str());
printf("destroy fifo successfully\n");
}
private:
string _path;
};
class Sync
{
public:
Sync(const char* Pathname = Path)
:pathname(Pathname)
{}
// 已只读方式打开命名管道
int OpenRD()
{
int fd = open(pathname, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open fifo fail, errno is %d, errinfo is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
return fd;
}
// 已只写方式打开命名管道
int OpenWR()
{
int fd = open(pathname, O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open fifo fail, errno is %d, errinfo is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
return fd;
}
// 当服务器还没读完时,让客户端写等待
bool Wait(int fd)
{
bool ret = true;
uint32_t c = 0;
ssize_t n = read(fd, &c, sizeof(uint32_t));
if (n == 0)
{
ret = false;
}
else if (n < 0)
{
printf("read fail, errno is %d, errinfo is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
return ret;
}
// 服务器读完时,唤醒客户端写
void WakeUp(int fd)
{
uint32_t c = 0;
ssize_t n = write(fd, &c, sizeof(uint32_t));
if (n < 0)
{
printf("write fail, errno is %d, errinfo is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return;
}
}
// 关闭命名管道
void Close(int fd)
{
close(fd);
}
private:
const char* pathname;
};同时将接口封装成函数方便我们使用
// Comm.hpp
// 将key转化为16进制,方便与ipcs -m 查看的信息对比
string ItoH(int x)
{
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "0x%x", x);
return buffer;
}
// 封装ftok,获取key
key_t GetKey()
{
key_t k = ftok(pathname, proj_id);
if(k < 0)
{
printf("get key fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(errno);
}
return k;
}
// 封装shmget,获取shmid
int _CreateShm(key_t key, int size, int flag)
{
int shmid = shmget(key, size, flag);
if(shmid < 0)
{
printf("shmget fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(errno);
}
return shmid;
}
// 给服务器端提供,创建共享内存,已存在出错返回
int CreateShm(key_t key, int size)
{
return _CreateShm(key, size, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0666);
}
// 给客户端提供,获取服务端创建的共享内存的shmid
int GetShm(key_t key, int size)
{
return _CreateShm(key, size, IPC_CREAT);
}
// 封装shmctl,删除共享内存
void DeleteShm(int shmid)
{
int n = shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, nullptr);
if(n < 0)
{
printf("DeleteShm fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(errno);
}
}
// 封装shmat,挂接共享内存
void* ShmAttach(int shmid)
{
void* shmaddr = shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if((long)shmaddr == -1)
{
printf("shm attach fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(errno);
}
return shmaddr;
}
// 封装shmdt,去挂接共享内存
void ShmDetach(const void* shmaddr)
{
int n = shmdt(shmaddr);
if(n == -1)
{
printf("shm detach fail, errno is %d, errstr is %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
return;
}
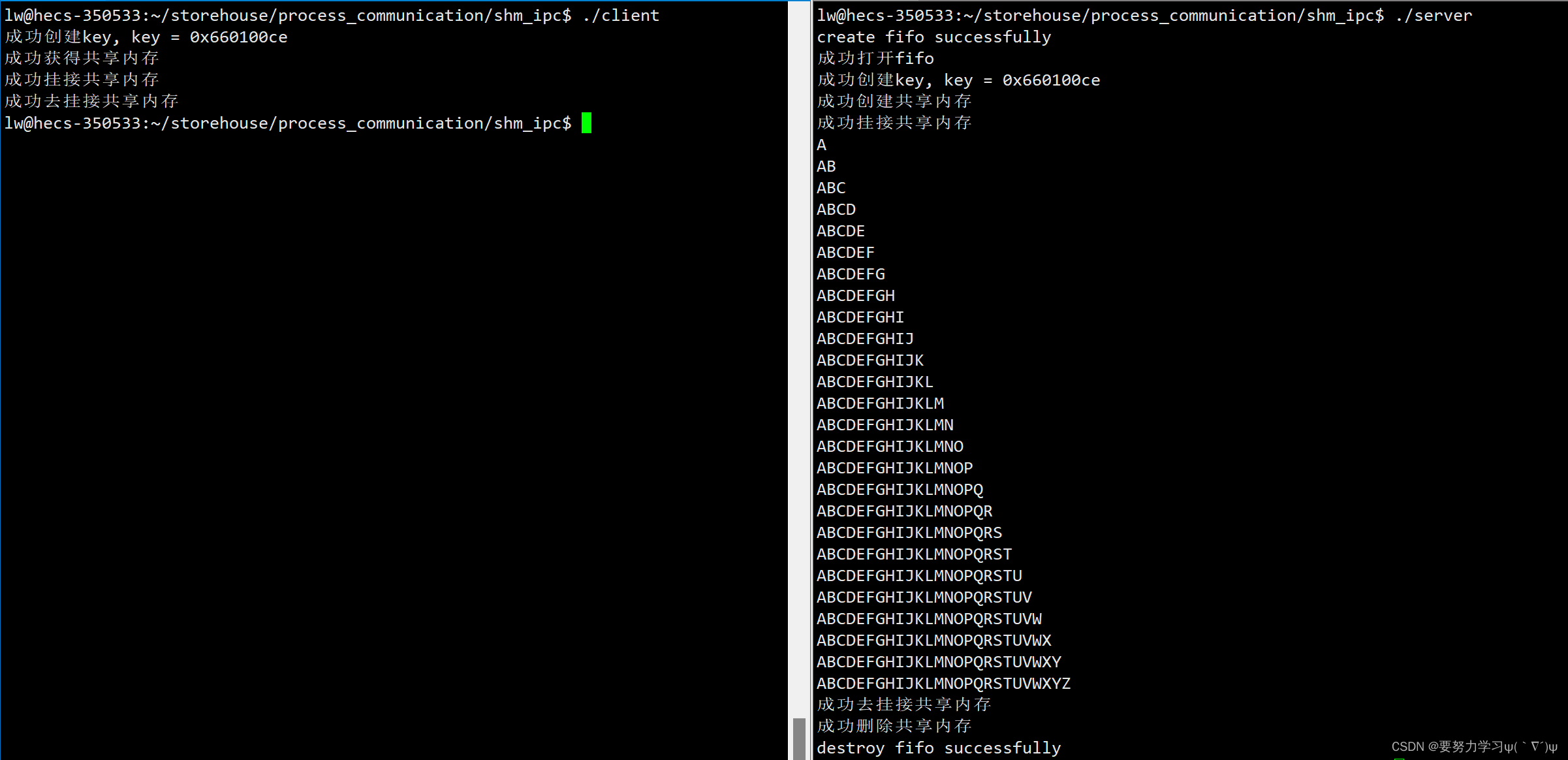
}服务器:1、负责打开、关闭管道
2、负责打开、关闭共享内存
3、负责读取数据
#include "Comm.hpp"
#include "Fifo.hpp"
int main()
{
Fifo fifo;
Sync syn;
int rfd = syn.OpenRD();
printf("成功打开fifo\n");
key_t key = GetKey();
cout << "成功创建key, key = " << ItoH(key) << endl;
const int size = 4096;
sleep(2);
int shmid = CreateShm(key, size);
cout << "成功创建共享内存" << endl;
sleep(2);
char* shmaddr = (char*)ShmAttach(shmid);
cout << "成功挂接共享内存" << endl;
sleep(2);
// 读
while(1)
{
bool ret = syn.Wait(rfd);
if(!ret)
break;
printf("%s\n", shmaddr);
}
ShmDetach((void*)shmaddr);
cout << "成功去挂接共享内存" << endl;
sleep(2);
DeleteShm(shmid);
cout << "成功删除共享内存" << endl;
syn.Close(rfd);
return 0;
}客户端:负责写
#include "Comm.hpp"
#include "Fifo.hpp"
int main()
{
Sync syn;
int wfd = syn.OpenWR();
key_t key = GetKey();
cout << "成功创建key, key = " << ItoH(key) << endl;
const int size = 4096;
sleep(2);
int shmid = GetShm(key, size);
cout << "成功获得共享内存" << endl;
sleep(2);
char* shmaddr = (char*)ShmAttach(shmid);
cout << "成功挂接共享内存" << endl;
sleep(2);
// 写
string str;
for(char ch = 'A'; ch <= 'Z'; ++ch)
{
str += ch;
memcpy(shmaddr, str.c_str(), str.size());
shmaddr[str.size()] = '\0';
//printf("%s\n", shmaddr);
syn.WakeUp(wfd);
usleep(100000);
}
ShmDetach((void*)shmaddr);
cout << "成功去挂接共享内存" << endl;
sleep(2);
syn.Close(wfd);
return 0;
}运行结果: