leetcode面试题 02.07. 链表相交
- 1 题目
- 2 思路
- 2.1 思路一
- 2.2 思路二(强推--5行代码)
- 3 代码
- 3.1 C++版本
- 3.1.1思路一:
- 3.1.2 思路二
- 3.2 C版本
- 3.2.1 思路一
- 3.2.2 思路二
- 3.3 Java版本
- 3.3.1 思路一
- 3.3.2 思路二
- 3.4 JavaScript版本
- 4 总结
1 题目
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
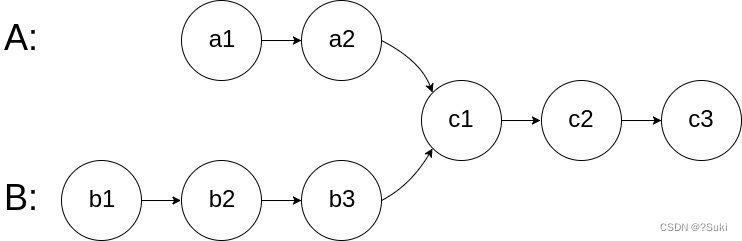
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例 1:
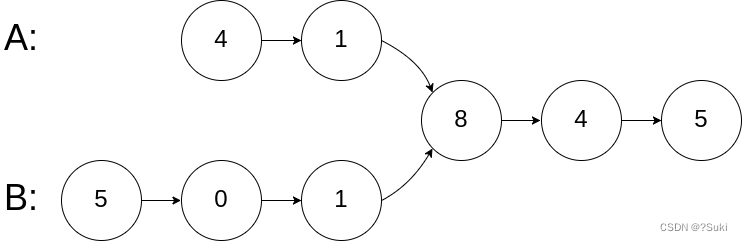
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at ‘8’
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
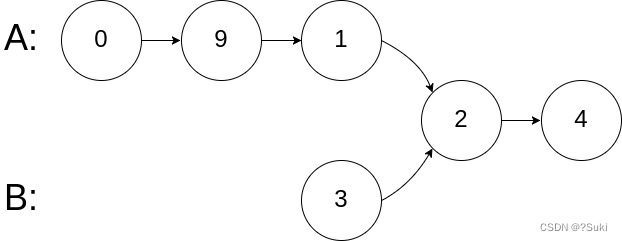
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Intersected at ‘2’
解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
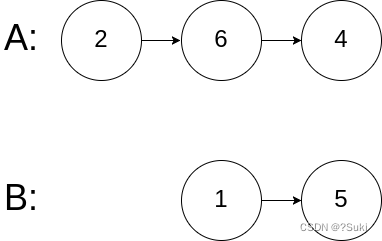
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
listA 中节点数目为 m
listB 中节点数目为 n
0 <= m, n <= 3 * 104
1 <= Node.val <= 105
0 <= skipA <= m
0 <= skipB <= n
如果 listA 和 listB 没有交点,intersectVal 为 0
如果 listA 和 listB 有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA + 1] == listB[skipB + 1]
2 思路
2.1 思路一
简单来说,就是求两个链表交点节点的指针。 这里同学们要注意,交点不是数值相等,而是指针相等。
为了方便举例,假设节点元素数值相等,则节点指针相等。
看如下两个链表,目前curA指向链表A的头结点,curB指向链表B的头结点:
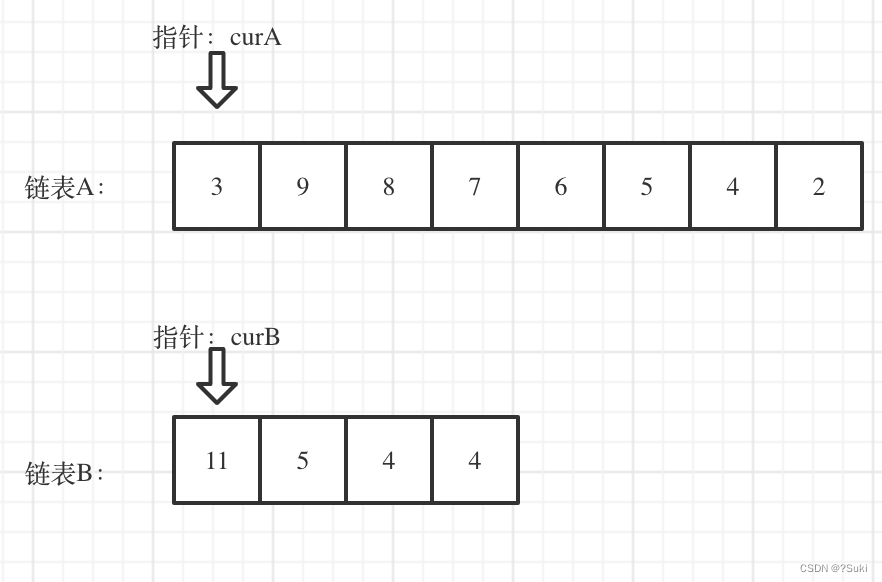
我们求出两个链表的长度,并求出两个链表长度的差值,然后让curA移动到,和curB 末尾对齐的位置,如图:
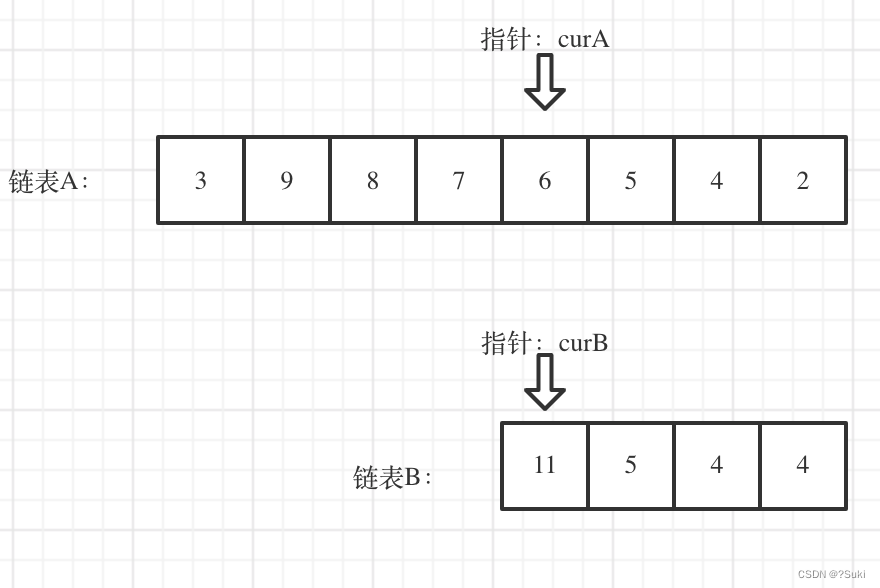
此时我们就可以比较curA和curB是否相同,如果不相同,同时向后移动curA和curB,如果遇到curA == curB,则找到交点。
否则循环退出返回空指针。
2.2 思路二(强推–5行代码)
非常逻辑的一种思路:
打个简单的比方,把这两个链表看作是两条路,两条路有汇合点
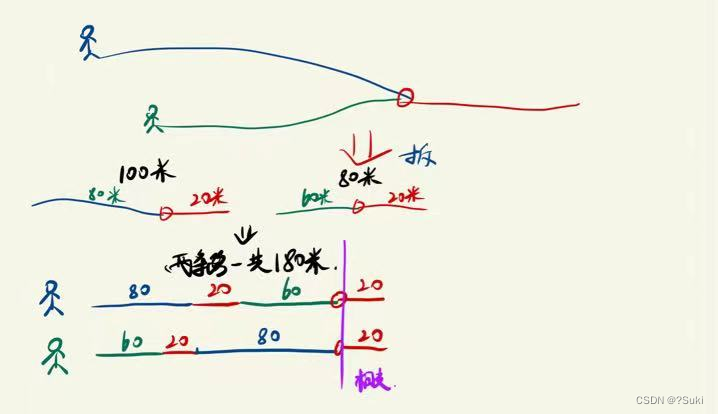
大家结合图可以看出,小蓝走完它对应的路后,再从小绿的起点开始走;
小绿走完它对应的路后,再从小蓝的起点走,这样一定会相遇(图中紫色)
看代码:
如果还在不清楚的可以用自己的两个手指头模拟一下这个过程:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode *curA = headA, *curB = headB;
while (curA != curB) {
curA = curA?curA->next:headB;
curB = curB?curB->next:headA;
}
return curA; //return curB;
}
};
3 代码
3.1 C++版本
3.1.1思路一:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode* curA = headA;
ListNode* curB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (curA != NULL) { // 求链表A的长度
lenA++;
curA = curA->next;
}
while (curB != NULL) { // 求链表B的长度
lenB++;
curB = curB->next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
// 让curA为最长链表的头,lenA为其长度
if (lenB > lenA) {
swap (lenA, lenB);
swap (curA, curB);
}
// 求长度差
int gap = lenA - lenB;
// 让curA和curB在同一起点上(末尾位置对齐)
while (gap--) {
curA = curA->next;
}
// 遍历curA 和 curB,遇到相同则直接返回
while (curA != NULL) {
if (curA == curB) {
return curA;
}
curA = curA->next;
curB = curB->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n + m)
空间复杂度:O(1)
3.1.2 思路二
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode *curA = headA, *curB = headB;
while (curA != curB) {
curA = curA?curA->next:headB;
curB = curB?curB->next:headA;
}
return curA; //return curB;
}
};
3.2 C版本
3.2.1 思路一
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode *l = NULL, *s = NULL;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0, gap = 0;
// 求出两个链表的长度
s = headA;
while (s) {
lenA ++;
s = s->next;
}
s = headB;
while (s) {
lenB ++;
s = s->next;
}
// 求出两个链表长度差
if (lenA > lenB) {
l = headA, s = headB;
gap = lenA - lenB;
} else {
l = headB, s = headA;
gap = lenB - lenA;
}
// 尾部对齐
while (gap--) l = l->next;
// 移动,并检查是否有相同的元素
while (l) {
if (l == s) return l;
l = l->next, s = s->next;
}
return NULL;
}
3.2.2 思路二
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
struct ListNode *curA = headA, *curB = headB;
while (curA != curB) {
curA = curA?curA->next:headB;
curB = curB?curB->next:headA;
}
return curA; //return curB;
}
3.3 Java版本
3.3.1 思路一
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (curA != null) { // 求链表A的长度
lenA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
while (curB != null) { // 求链表B的长度
lenB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
// 让curA为最长链表的头,lenA为其长度
if (lenB > lenA) {
//1. swap (lenA, lenB);
int tmpLen = lenA;
lenA = lenB;
lenB = tmpLen;
//2. swap (curA, curB);
ListNode tmpNode = curA;
curA = curB;
curB = tmpNode;
}
// 求长度差
int gap = lenA - lenB;
// 让curA和curB在同一起点上(末尾位置对齐)
while (gap-- > 0) {
curA = curA.next;
}
// 遍历curA 和 curB,遇到相同则直接返回
while (curA != null) {
if (curA == curB) {
return curA;
}
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
3.3.2 思路二
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA = headA, curB = headB;
while (curA != curB) {
if (curA != null) curA = curA.next;
else curA = headB;
if (curB != null) curB = curB.next;
else curB = headA;
}
return curA; //return curB;
}
}
3.4 JavaScript版本
var getListLen = function(head) {
let len = 0, cur = head;
while(cur) {
len++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return len;
}
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
let curA = headA,curB = headB,
lenA = getListLen(headA), // 求链表A的长度
lenB = getListLen(headB);
if(lenA < lenB) { // 让curA为最长链表的头,lenA为其长度
// 交换变量注意加 “分号” ,两个数组交换变量在同一个作用域下时
// 如果不加分号,下面两条代码等同于一条代码: [curA, curB] = [lenB, lenA]
[curA, curB] = [curB, curA];
[lenA, lenB] = [lenB, lenA];
}
let i = lenA - lenB; // 求长度差
while(i-- > 0) { // 让curA和curB在同一起点上(末尾位置对齐)
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curA && curA !== curB) { // 遍历curA 和 curB,遇到相同则直接返回
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return curA;
};
4 总结
总结就是,好好把两个思路的方法看懂。会有很大帮助,尤其是第二个思路,非常巧妙。
By --Suki 2023/1/12






![[ 解决报错篇 ] tomcat 执行 startup.bat 文件报错 -- tomcat 启动失败(安装 java 环境并配置环境变量)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/06b5305ca0b34f88b5eba15e3778d92b.png)