实现功能:
1:敌人的绵绵不断的前进,拿着各种各样的武器(叉子,斧头,宝剑),挥动武器攻击我方城堡,对我方城堡造成伤害!
2:我方城堡发现敌人可手动点击鼠标左键来发起子弹攻击,对日人造成致命伤害,让其死亡!
3:完备的数据显示,攻击敌人获取金币,累计得分,当前管卡的级别,我方城堡生命值的显示等等,击杀敌人获取的金币可以兑换额外属性来装备回复加强我方堡垒!
4:项目的布局界面优美干净,结合添加的纯音乐游戏背景和攻击音效以及实时的动画显示(如我方城堡的外观会随着我方城堡生命值的降低而发生改变,也就是变得会破败一些等等)以此让项目更加具有可玩性!
5:拿该项目练手或者作为一个python简单的课程设计也是一个可以的选择!
6:项目总代码700行左右
用到的编程知识:
python基础,os文件读写,pygame模块以及面向对象思想!
代码如下:
enemy.py类文件(100行代码左右)
import pygame
class Enemy(pygame.sprite.Sprite):
def __init__(self, health, animation_list, x, y, speed):
pygame.sprite.Sprite.__init__(self)
self.alive = True
self.speed = speed
self.health = health
self.last_attack = pygame.time.get_ticks()
self.attack_cooldown = 1000
self.animation_list = animation_list
self.frame_index = 0
self.action = 0#0: walk, 1: attack, 2: death
self.update_time = pygame.time.get_ticks()
#select starting image
self.image = self.animation_list[self.action][self.frame_index]
self.rect = pygame.Rect(0, 0, 25, 40)
self.rect.center = (x, y)
def update(self, surface, target, bullet_group):
if self.alive:
#check for collision with bullets
if pygame.sprite.spritecollide(self, bullet_group, True):
#lower enemy health
self.health -= 25
#check if enemy has reached the castle
if self.rect.right > target.rect.left:
self.update_action(1)
#move enemy
if self.action == 0:
#update rectangle position
self.rect.x += self.speed
#attack
if self.action == 1:
#check if enough time has passed since last attack
if pygame.time.get_ticks() - self.last_attack > self.attack_cooldown:
target.health -= 25
if target.health < 0:
target.health = 0
self.last_attack = pygame.time.get_ticks()
#check if health has dropped to zero
if self.health <= 0:
target.money += 100
target.score += 100
self.update_action(2)#death
self.alive = False
self.update_animation()
#draw image on screen
surface.blit(self.image, (self.rect.x - 10, self.rect.y - 15))
def update_animation(self):
#define animation cooldown
ANIMATION_COOLDOWN = 50
#update image depending on current action
self.image = self.animation_list[self.action][self.frame_index]
#check if enough time has passed since the last update
if pygame.time.get_ticks() - self.update_time > ANIMATION_COOLDOWN:
self.update_time = pygame.time.get_ticks()
self.frame_index += 1
#if the animation has run out then reset back to the start
if self.frame_index >= len(self.animation_list[self.action]):
if self.action == 2:
self.frame_index = len(self.animation_list[self.action]) - 1
else:
self.frame_index = 0
def update_action(self, new_action):
#check if the new action is different to the previous one
if new_action != self.action:
self.action = new_action
#update the animation settings
self.frame_index = 0
self.update_date = pygame.time.get_ticks()
castle.py类文件(500行代码左右)
# 导入库
import pygame
import math
import os
import sys
import random
import button
from pygame import mixer
# 初始化pygame
pygame.init()
# 定义游戏窗口高度和宽度
SCREEN_WIDTH = 800
SCREEN_HEIGHT = 600
# 加载背景音乐
pygame.mixer.music.load("sound/bjmusic.WAV")
pygame.mixer.music.set_volume(0.3)
jump_fx = pygame.mixer.Sound("sound/bullet.wav")
jump_fx.set_volume(0.5)
# 创建游戏窗口
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT))
pygame.display.set_caption("城堡防卫战")
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
FPS = 60
# 定义游戏变量
level = 1
high_score = 0
level_difficulty = 0
target_difficulty = 1000
DIFFICULTY_MULTIPLIER = 1.1
game_over = False
next_level = False
ENEMY_TIMER = 1000
last_enemy = pygame.time.get_ticks()
enemies_alive = 0
max_towers = 4
TOWER_COST = 5000
# 定义炮塔位置的列表
tower_positions = [
[SCREEN_WIDTH - 250, SCREEN_HEIGHT - 200],
[SCREEN_WIDTH - 200, SCREEN_HEIGHT - 150],
[SCREEN_WIDTH - 150, SCREEN_HEIGHT - 150],
[SCREEN_WIDTH - 100, SCREEN_HEIGHT - 150]
]
# 加载最高分
if os.path.exists('socre.txt'):
with open('socre.txt', 'r') as file:
high_score = int(file.read())
# 定义颜色
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
GREY = (100, 100, 100)
# 定义字体
font = pygame.font.SysFont('华文彩云', 30)
font_60 = pygame.font.SysFont('华文行楷', 60)
# 加载图片
bg = pygame.image.load('img/bg.png').convert_alpha()
# 城堡
castle_img_100 = pygame.image.load('img/castle/castle_100.png').convert_alpha()
castle_img_50 = pygame.image.load('img/castle/castle_50.png').convert_alpha()
castle_img_25 = pygame.image.load('img/castle/castle_25.png').convert_alpha()
# 炮塔
tower_img_100 = pygame.image.load('img/tower/tower_100.png').convert_alpha()
tower_img_50 = pygame.image.load('img/tower/tower_50.png').convert_alpha()
tower_img_25 = pygame.image.load('img/tower/tower_25.png').convert_alpha()
# 子弹图像
bullet_img = pygame.image.load('img/bullet.png').convert_alpha()
b_w = bullet_img.get_width()
b_h = bullet_img.get_height()
bullet_img = pygame.transform.scale(bullet_img, (int(b_w * 0.075), int(b_h * 0.075)))
# 创建敌人类
class Enemy(pygame.sprite.Sprite):
def __init__(self, health, animation_list, x, y, speed):
super().__init__()
self.alive = True
self.speed = speed
self.health = health
self.last_attack = pygame.time.get_ticks()
self.attack_cooldown = 1000
self.animation_list = animation_list
self.frame_index = 0
self.action = 0
self.update_time = pygame.time.get_ticks()
# 选择动画开始的图片
self.image = self.animation_list[self.action][self.frame_index]
self.rect = pygame.Rect(0, 0, 25, 40)
self.rect.center = (x, y)
def update(self, surface, target, bullet_group):
if self.alive:
# 检查敌人与子弹的碰撞
if pygame.sprite.spritecollide(self, bullet_group, True):
# 减少健康
self.health -= 25
# 检查敌人是否已经到达城堡
if self.rect.right > target.rect.left:
self.update_action(1)
# 移动敌人
if self.action == 0:
self.rect.x += 1
# 攻击城堡
if self.action == 1:
# 检测冷却时间
if pygame.time.get_ticks() - self.last_attack > self.attack_cooldown:
target.health -= 25
if target.health < 0:
target.health = 0
self.last_attack = pygame.time.get_ticks()
# 检查敌人血条是否为0
if self.health <= 0:
target.money += 100
target.score += 100
self.update_action(2)
self.alive = False
# 调用更新动画
self.update_animation()
# 绘制敌人
# pygame.draw.rect(surface, (255, 255, 255), self.rect, 1)
surface.blit(self.image, (self.rect.x - 10, self.rect.y - 15))
def update_animation(self):
# 定义动画冷却时间
ANIMATION_COOLDOWN = 50
# 根据选择的冬瓜更新帧
self.image = self.animation_list[self.action][self.frame_index]
# 判断多久更新一次帧
if pygame.time.get_ticks() - self.update_time > ANIMATION_COOLDOWN:
self.update_time = pygame.time.get_ticks()
self.frame_index += 1
# 检查帧数不能超过最大帧数
if self.frame_index >= len(self.animation_list[self.action]):
if self.action == 2:
self.frame_index = len(self.animation_list[self.action]) - 1
else:
self.frame_index = 0
def update_action(self, new_action):
# 检查新动作与上一个动作是否相同
if new_action != self.action:
self.action = new_action
# 更新动画重置
self.frame_index = 0
self.update_time = pygame.time.get_ticks()
# 加载敌人列表
enemy_animations = []
enemy_tpyes = ['knight', 'goblin', 'purple_goblin', 'red_goblin']
enemy_health = [75, 100, 125, 150]
animation_types = ['walk', 'attack', 'death']
for enemy in enemy_tpyes:
# 加载动画列表
animation_list = []
for animation in animation_types:
# 创建临时列表
temp_list = []
# 定义帧数
num_of_frames = 20
for i in range(num_of_frames):
img = pygame.image.load(f'img/enemies/{enemy}/{animation}/{i}.png').convert_alpha()
e_w = img.get_width()
e_h = img.get_height()
img = pygame.transform.scale(img, (int(e_w * 0.2), int(e_h * 0.2)))
temp_list.append(img)
animation_list.append(temp_list)
enemy_animations.append(animation_list)
# 加载按钮图片
repair_img = pygame.image.load('img/repair.png').convert_alpha()
armour_img = pygame.image.load('img/armour.png').convert_alpha()
# 在屏幕上输出文本信息
def draw_text(text, font, text_color, x, y):
img = font.render(text, True, text_color)
screen.blit(img, (x, y))
# 定义一个显示状态的函数
def show_info():
draw_text('钱数:' + str(castle.money), font, GREY, 10, 10)
draw_text('分数:' + str(castle.score), font, GREY, 180, 10)
draw_text('最分数:' + str(high_score), font, GREY, 180, 50)
draw_text('级别:' + str(level), font, GREY, SCREEN_WIDTH // 2, 10)
draw_text('健康:' + str(castle.health) + "/" + str(castle.max_health), font, GREY, SCREEN_WIDTH - 230, SCREEN_HEIGHT - 50)
draw_text('1000', font, GREY, SCREEN_WIDTH - 250, 70)
draw_text(str(TOWER_COST), font, GREY, SCREEN_WIDTH - 150, 70)
draw_text('500', font, GREY, SCREEN_WIDTH - 70, 70)
# 城堡类
class Castle():
def __init__(self, image100, image50, image25, x, y, scale):
self.health = 1000
self.max_health = self.health
self.fired = False
self.money = 0
self.score = 0
width = image100.get_width()
height = image100.get_height()
self.image100 = pygame.transform.scale(image100, (int(width * scale), int(height * scale)))
self.image50 = pygame.transform.scale(image50, (int(width * scale), int(height * scale)))
self.image25 = pygame.transform.scale(image25, (int(width * scale), int(height * scale)))
self.rect = self.image100.get_rect()
self.rect.x = x
self.rect.y = y
def shoot(self):
pos = pygame.mouse.get_pos()
x_dist = pos[0] - self.rect.midleft[0]
y_dist = -(pos[1] - self.rect.midleft[1])
self.angle = math.degrees(math.atan2(y_dist, x_dist))
# 在该位置点击鼠标
if pygame.mouse.get_pressed()[0] and self.fired == False and pos[1] > 70:
self.fired = True
bullet = Bullet(bullet_img, self.rect.midleft[0], self.rect.midleft[1], self.angle)
bullet_group.add(bullet)
jump_fx.play()
# 重置鼠标点击
if pygame.mouse.get_pressed()[0] == False:
self.fired = False
def draw(self):
# 根据血量判断加载那张图片
if self.health <= 250:
self.image = self.image25
elif self.health <= 500:
self.image = self.image50
else:
self.image = self.image100
screen.blit(self.image, self.rect)
def repair(self):
if self.money >= 1000 and self.health < self.max_health:
self.health += 500
self.money -= 1000
if castle.health > castle.max_health:
castle.health = castle.max_health
def armour(self):
if self.money >= 500:
self.max_health += 250
self.money -= 500
# 炮塔类
class Tower(pygame.sprite.Sprite):
def __init__(self, image100, image50, image25, x, y, scale):
super().__init__()
self.got_target = False
self.angle = 0
self.last_shot = pygame.time.get_ticks()
width = image100.get_width()
height = image100.get_height()
self.image100 = pygame.transform.scale(image100, (int(width * scale), int(height * scale)))
self.image50 = pygame.transform.scale(image50, (int(width * scale), int(height * scale)))
self.image25 = pygame.transform.scale(image25, (int(width * scale), int(height * scale)))
self.image = self.image100
self.rect = self.image100.get_rect()
self.rect.x = x
self.rect.y = y
def update(self, enemy_group):
self.got_target = False
for e in enemy_group:
if e.alive:
target_x, target_y = e.rect.midbottom
self.got_target = True
break
if self.got_target:
x_dist = target_x - self.rect.midleft[0]
y_dist = -(target_y - self.rect.midleft[1])
self.angle = math.degrees(math.atan2(y_dist, x_dist))
# pygame.draw.line(screen, WHITE, (self.rect.midleft[0], self.rect.midleft[1]), (target_x, target_y))
shot_cooldown = 1000
# 开火
if pygame.time.get_ticks() - self.last_shot > shot_cooldown:
self.last_shot = pygame.time.get_ticks()
bullet = Bullet(bullet_img, self.rect.midleft[0], self.rect.midleft[1], self.angle)
bullet_group.add(bullet)
# 根据城堡血量判断加载那张图片
if castle.health <= 250:
self.image = self.image25
elif castle.health <= 500:
self.image = self.image50
else:
self.image = self.image100
# 创建子弹类
class Bullet(pygame.sprite.Sprite):
def __init__(self, image, x, y, angle):
super().__init__()
self.image = image
self.rect = self.image.get_rect()
self.rect.x = x
self.rect.y = y
self.angle = math.radians(angle) # 角度转换为弧度
self.speed = 10
# 根据角度计算水平和垂直的速度
self.dx = math.cos(self.angle) * self.speed
self.dy = -(math.sin(self.angle) * self.speed)
def update(self):
# 检测子弹是否已经超出窗口
if self.rect.right < 0 or self.rect.left > SCREEN_WIDTH or self.rect.bottom < 0 or self.rect.top > SCREEN_HEIGHT:
self.kill()
# 移动子弹
self.rect.x += self.dx
self.rect.y += self.dy
# 创建十字准心
class Crosshair():
def __init__(self, scale):
image = pygame.image.load("img/crosshair.png").convert_alpha()
width = image.get_width()
height = image.get_height()
self.image = pygame.transform.scale(image, (int(width * scale), int(height * scale)))
self.rect = self.image.get_rect()
# 隐藏鼠标指针
pygame.mouse.set_visible(False)
def draw(self):
mx, my = pygame.mouse.get_pos()
self.rect.center = (mx, my)
screen.blit(self.image, self.rect)
# 创建城堡
castle = Castle(castle_img_100, castle_img_50, castle_img_25, SCREEN_WIDTH - 250, SCREEN_HEIGHT - 300, 0.2)
# 实例化十字准心
crosshair = Crosshair(0.025)
# 创建按钮
repair_button = button.Button(SCREEN_WIDTH - 240, 10, repair_img, 0.5)
tower_button = button.Button(SCREEN_WIDTH - 130, 10, tower_img_100, 0.1)
armour_button = button.Button(SCREEN_WIDTH - 75, 10, armour_img, 1.5)
# 创建组
bullet_group = pygame.sprite.Group()
enemy_group = pygame.sprite.Group()
tower_group = pygame.sprite.Group()
# 穿件临时塔
# tower = Tower(tower_img_100, tower_img_50, tower_img_25, SCREEN_WIDTH - 350, SCREEN_HEIGHT - 200, 0.2)
# tower_group.add(tower)
# 游戏循环显示窗口
pygame.mixer.music.unpause()
pygame.mixer.music.play(-1)
run = True
while run:
clock.tick(FPS)
if game_over == False:
screen.blit(bg, (0, 0))
# 显示城堡
castle.draw()
castle.shoot()
# 显示炮塔
tower_group.draw(screen)
tower_group.update(enemy_group)
# 显示十字准心
crosshair.draw()
# 绘制子弹到屏幕
bullet_group.update()
bullet_group.draw(screen)
# 绘制敌人
enemy_group.update(screen, castle, bullet_group)
# 显示详细信息
show_info()
# 显示按钮 修理和铠甲按钮
if repair_button.draw(screen):
castle.repair()
if tower_button.draw(screen):
# 检查是否有足够的金钱来建造炮塔
if castle.money >= TOWER_COST and len(tower_group) < max_towers:
tower = Tower(tower_img_100,
tower_img_50,
tower_img_25,
tower_positions[len(tower_group)][0],
tower_positions[len(tower_group)][1],
0.2)
tower_group.add(tower)
# 减去消耗的金钱数
castle.money -= TOWER_COST
if armour_button.draw(screen):
castle.armour()
# 创建不同的敌人
if level_difficulty < target_difficulty:
if pygame.time.get_ticks() - last_enemy > ENEMY_TIMER:
# 创建敌人实例
e = random.randint(0, len(enemy_tpyes) - 1)
enemy = Enemy(enemy_health[e], enemy_animations[e], -100, SCREEN_HEIGHT - 100, 1)
enemy_group.add(enemy)
last_enemy = pygame.time.get_ticks()
level_difficulty += enemy_health[e]
# 检测是所有的的敌人都产生了
if level_difficulty >= target_difficulty:
# 检查有多少敌人仍然是活着的
enemies_alive = 0
for e in enemy_group:
if e.alive == True:
enemies_alive += 1
# 检测如果活着的敌人都被消灭了则当前级别就完成了
if enemies_alive == 0 and next_level == False:
next_level = True
level_reset_time = pygame.time.get_ticks()
# 判断是否进入下一关
if next_level == True:
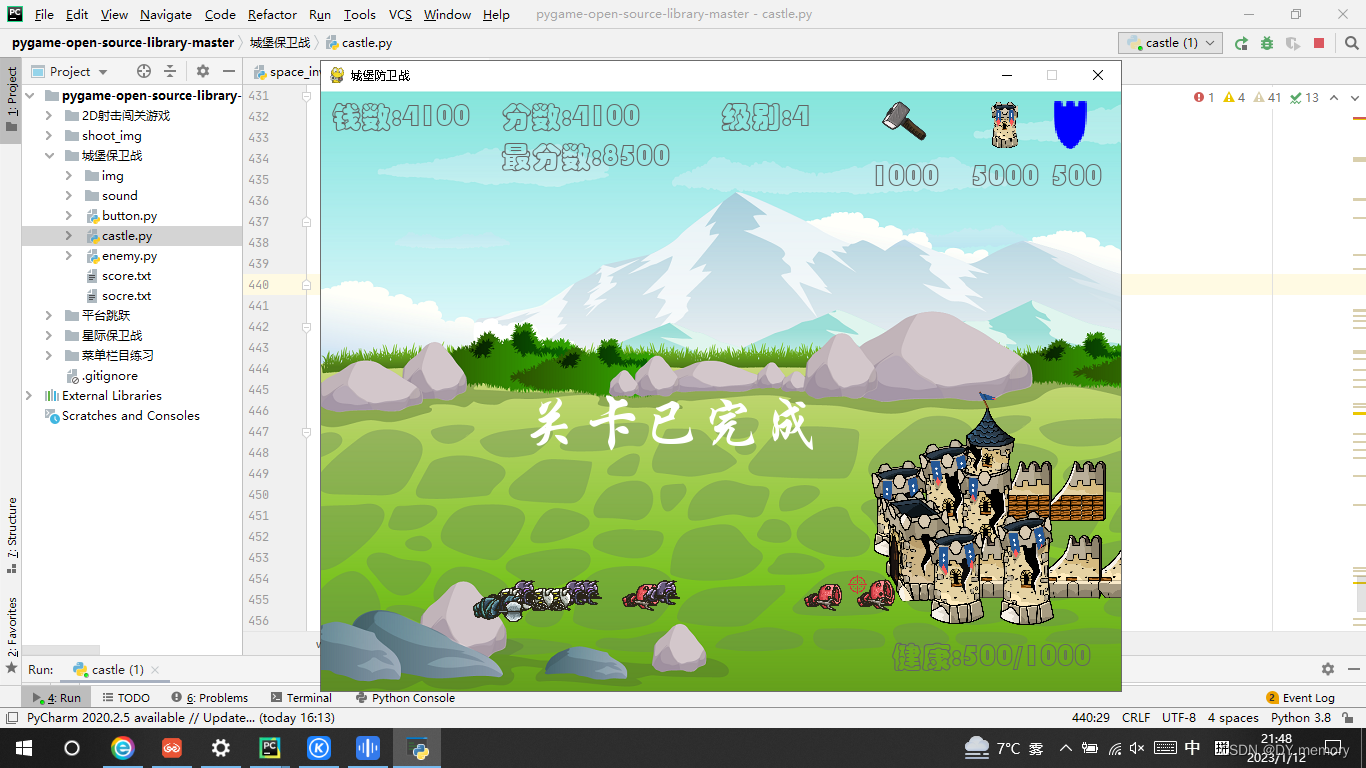
draw_text('关卡已完成', font_60, WHITE, 200, 300)
# 更新最高分
if castle.score > high_score:
high_score = castle.score
with open('socre.txt', 'w') as file:
file.write(str(high_score))
if pygame.time.get_ticks() - level_reset_time > 1500:
next_level = False
level += 1
last_enemy = pygame.time.get_ticks()
target_difficulty *= DIFFICULTY_MULTIPLIER
level_difficulty = 0
enemy_group.empty()
# 检查游戏是否结束
if castle.health <= 0:
game_over = True
else:
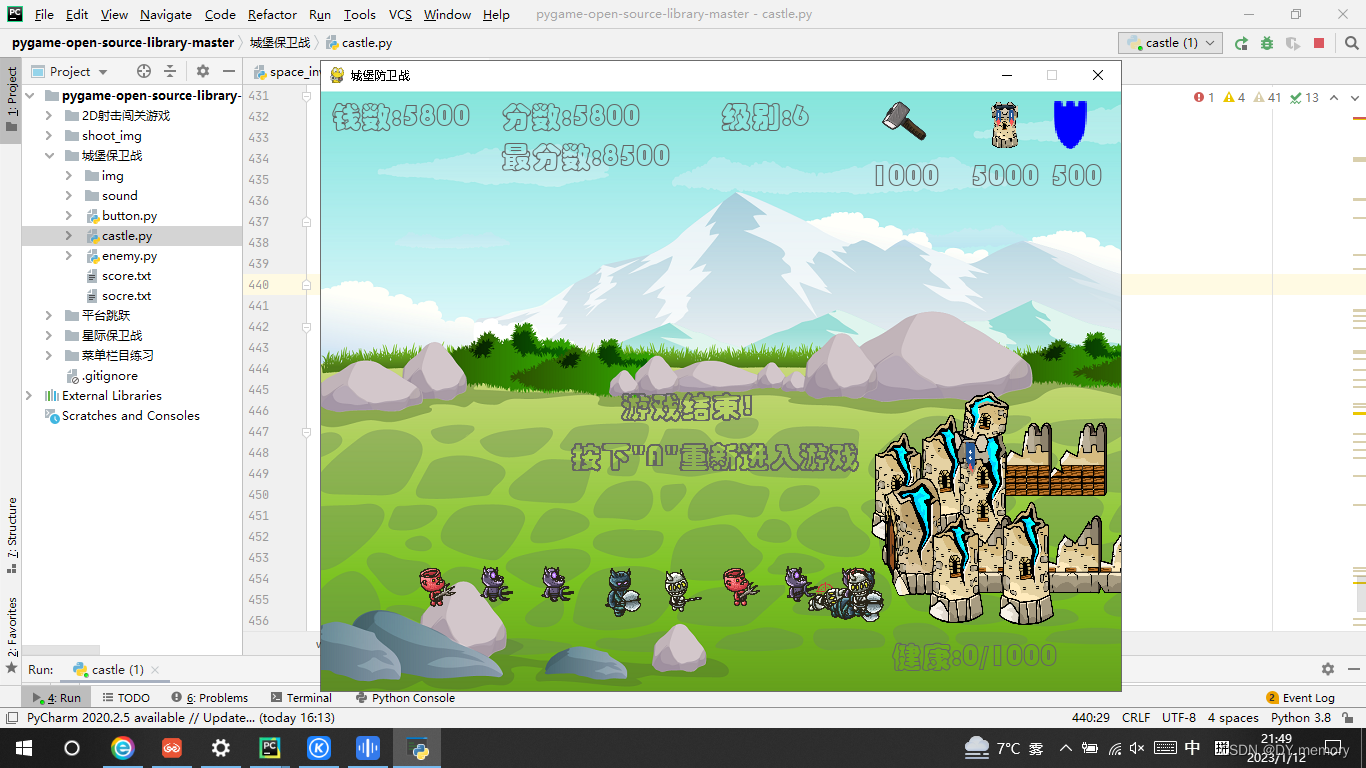
draw_text('游戏结束!', font, GREY, 300, 300)
draw_text('按下"A"重新进入游戏', font, GREY, 250, 350)
pygame.mouse.set_visible(True)
key = pygame.key.get_pressed()
if key[pygame.K_a]:
# 重置游戏
game_over = False
level = 1
target_difficulty = 1000
level_difficulty = 0
last_enemy = pygame.time.get_ticks()
enemy_group.empty()
tower_group.empty()
castle.score = 0
castle.health = 1000
castle.max_health = castle.health
castle.money = 0
pygame.mouse.set_visible(False)
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
run = False
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
pygame.display.update()
button.py类文件(50行代码左右)
import pygame
# 按钮类
class Button():
def __init__(self, x, y, image, scale):
width = image.get_width()
height = image.get_height()
self.image = pygame.transform.scale(image, (int(width * scale), int(height * scale)))
self.rect = self.image.get_rect()
self.rect.topleft = (x, y)
self.clicked = False
def draw(self, surface):
action = False
# 得到鼠标的位置
pos = pygame.mouse.get_pos()
# 检测鼠标指针的碰撞
if self.rect.collidepoint(pos):
if pygame.mouse.get_pressed()[0] == 1 and self.clicked == False:
self.clicked = True
action = True
if pygame.mouse.get_pressed()[0] == 0:
self.clicked = False
# 画按钮到屏幕上
surface.blit(self.image, (self.rect.x, self.rect.y))
return action
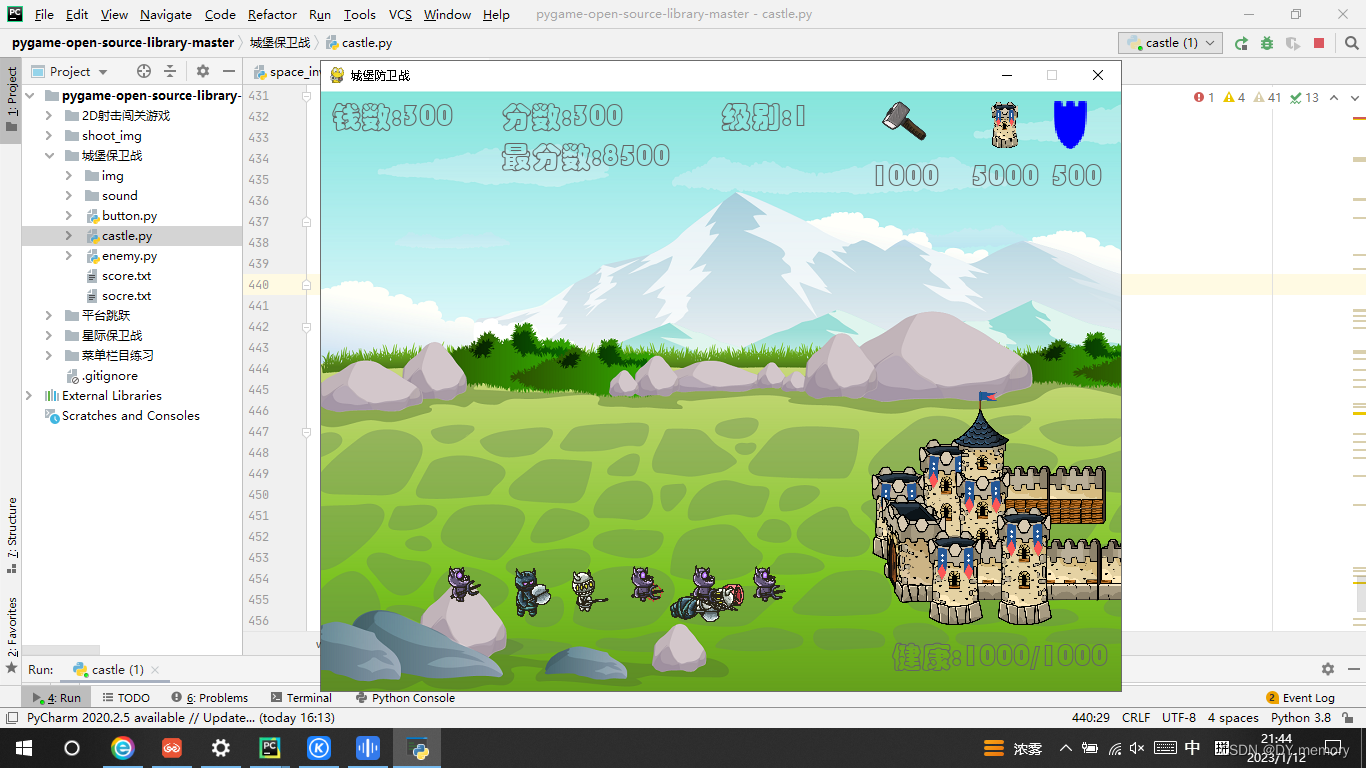
部分运行截图:








![[oeasy]python0045_四种进制_binary_octal_decimal_hexadecimal](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/99a2811d772ee9025f958f0d0b6053b4.png)