人体跟随小车(yolov5、目标检测)
- 前言
- 最终结果
- 接线
- 实现
- 注意
前言
上板运行的后处理使用cython封装了,由于每个版本的yolo输出的形状不一样,这里只能用yolov5-6.2这个版本。
①训练自己的模型并部署于旭日x3派参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_71523511/article/details/136546588/部署官方权重文件
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_71523511/article/details/136823320/部署自己训练的安全帽识别权重文件
②通过40pin引脚驱动减速电机参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_71523511/article/details/136722608/视觉循迹小车
最终结果
跟随人体前进,当距离过近时会停车(没有使用深度相机,无法直接获取距离信息,简单根据检测框与图像的比值来确定是否停车),检测不到人时也会停车。根据目标(在这里是目标框中心的 x 坐标)与设定值(320)之间的偏差计算(PID)得到相应占空比驱动差速车轮。
人体跟随小车
接线
这里使用物理引脚编号:

旭日x3派连接TB6612驱动电机:
11、13引脚接AIN1、AIN2;15、16引脚接BIN1、BIN2;32引脚接PWMA;33引脚接PWMB引脚。TB6612的VCC接3.3v,VM和STBY接5V,有条件的VM可以接7-12V;AO1、AO2接左电机的正负极;BO1、BO2接右电机的正负极。
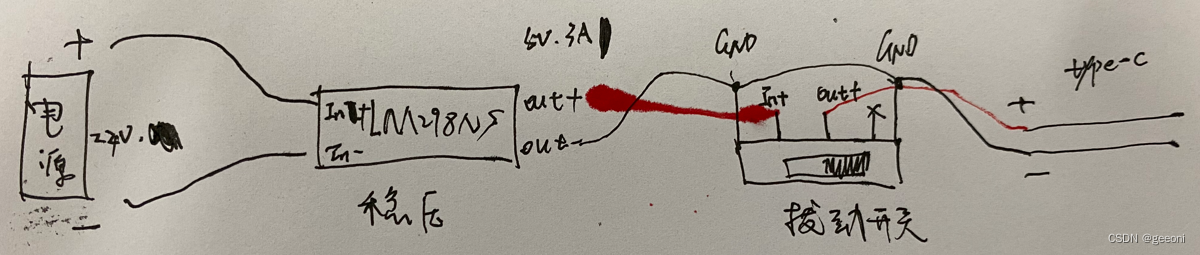
供电连线:
旭日x3派1.0板卡只能使用tpye-c口进行供电,2.0还可以使用40pin引脚中的5v引脚供电,推荐使用5v3a电源,否则板卡可能无法启动。
电源模块使用实验室的锂电池模组:额定输出电压为24V,3000mah,3c:

稳压模块使用LM2596S,将输出电压调至5V,买带有数表显示的就不用万用表测了:
开关使用拨动开关:
将type-c的usb端剪了就可以看到里面有几根线,红黑就是供电线,这要与电源连接,上面几个部分的连线如下:
最好买粗的硅胶线来进行电源部分的连线,杜邦线没法传那么大的电流:
实现
通过前言中的部署相关博客得到bin文件之后,需要将如下文件放入板端(在前言的参考博客中有下载链接)
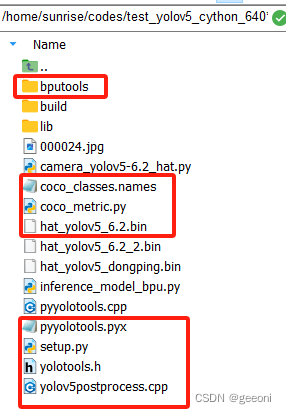
以下跟随代码仅供参考:
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os
from hobot_dnn import pyeasy_dnn as dnn
from bputools.format_convert import imequalresize, bgr2nv12_opencv
import Hobot.GPIO as GPIO
import lib.pyyolotools as yolotools
class CTRL():
def __init__(self, in1, in2, in3, in4, pa, pb):
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setup(in1, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(in2, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(in3, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(in4, GPIO.OUT)
self.in1 = in1
self.in2 = in2
self.in3 = in3
self.in4 = in4
self.PWMA = GPIO.PWM(pa, 48000)
self.PWMB = GPIO.PWM(pb, 48000)
def drive(self, FL, FR):
if FL >= 0:
GPIO.output(self.in3, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(self.in4, GPIO.LOW)
elif FL < 0:
GPIO.output(self.in4, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(self.in3, GPIO.LOW)
if FR >= 0:
GPIO.output(self.in1, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(self.in2, GPIO.LOW)
elif FR < 0:
GPIO.output(self.in2, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(self.in1, GPIO.LOW)
self.PWMA.ChangeDutyCycle(abs(FR))
self.PWMB.ChangeDutyCycle(abs(FL))
self.PWMA.start(abs(FR))
self.PWMB.start(abs(FL))
def stop(self):
GPIO.output(self.in1, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(self.in2, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(self.in3, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(self.in4, GPIO.LOW)
self.PWMA.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
self.PWMB.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
self.PWMA.start(0)
self.PWMB.start(0)
def clean(self):
self.PWMB.stop()
self.PWMA.stop()
GPIO.cleanup()
class PIDController():
def __init__(self,KP,KI,KD,setpoint):
self.KP = KP
self.KI = KI
self.KD = KD
self.setpoint = setpoint
self.prev_error = 0
self.integral = 0
def update(self,current_value):
error = self.setpoint - current_value
self.integral += error
derivative = error - self.prev_error
output = self.KP * error + self.KI *self.integral + self.KD * derivative
self.prev_error = error
return output
def get_hw(pro):
if pro.layout == "NCHW":
return pro.shape[2], pro.shape[3]
else:
return pro.shape[1], pro.shape[2]
def format_yolov5(frame):
row, col, _ = frame.shape
_max = max(col, row)
result = np.zeros((_max, _max, 3), np.uint8)
result[0:row, 0:col] = frame
return result
# 加载模型和设置参数
model_path = 'hat_yolov5_6.2_2.bin'
classes_name_path = 'coco_classes.names'
models = dnn.load(model_path)
model_h, model_w = get_hw(models[0].inputs[0].properties)
print("Model Height:", model_h, "Model Width:", model_w)
thre_confidence = 0.4
thre_score = 0.25
thre_nms = 0.45
colors = [(255, 255, 0), (0, 255, 0), (0, 255, 255), (255, 0, 0)]
# 打开摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(8) # 使用第一个摄像头(如果有多个摄像头,可能需要更改参数)
Ctrl = CTRL(11, 13, 16, 15, 32, 33) # 设置管脚
pidController = PIDController(KP=0.12,KI=0.001,KD=0.12,setpoint=320)
Ctrl.drive(25, 25) # 小车的始发运动
# 主循环:读取帧,进行目标检测,显示结果
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read() # 读取一帧图像
if not ret:
print("Error: Couldn't capture frame")
break
inputImage = format_yolov5(frame)
img = imequalresize(inputImage, (model_w, model_h))
nv12 = bgr2nv12_opencv(img)
t1 = cv2.getTickCount()
outputs = models[0].forward(nv12)
t2 = cv2.getTickCount()
outputs = outputs[0].buffer
#print('Inference time: {0} ms'.format((t2 - t1) * 1000 / cv2.getTickFrequency()))
image_width, image_height, _ = inputImage.shape
fx, fy = image_width / model_w, image_height / model_h
t1 = cv2.getTickCount()
class_ids, confidences, boxes = yolotools.pypostprocess_yolov5(outputs[0][:, :, 0], fx, fy,
thre_confidence, thre_score, thre_nms)
t2 = cv2.getTickCount()
#print('Post-processing time: {0} ms'.format((t2 - t1) * 1000 / cv2.getTickFrequency()))
with open(classes_name_path, "r") as f:
class_list = [cname.strip() for cname in f.readlines()]
for (classid, confidence, box) in zip(class_ids, confidences, boxes):
color = colors[int(classid) % len(colors)]
cv2.rectangle(frame, box, color, 2)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (box[0], box[1] - 20), (box[0] + box[2], box[1]), color, -1)
#cv2.putText(frame, str(classid), (box[0], box[1] - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, .5, (0, 0, 0))
cv2.putText(frame, class_list[classid], (box[0], box[1] - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, .5, (0,0,0))
cv2.imshow('frame', frame) # 显示帧
#########################################################################################################################
#car_logical
num_detection = len(boxes)
if num_detection == 0:
print("no_object_stop")
Ctrl.stop()
else:
if classid == 0:
x1,y1 = box[0],box[1]
x2,y2 = box[0] + box[2],box[1] + box[3]
kuang_area = (x2-x1) * (y2-y1)
input_area = 409600
bizhi = kuang_area / input_area
if bizhi > 0.1:
print("too_close_stop")
Ctrl.stop()
else:
x3 = (x2+x1)/2
print("weizhi",x3)
#direct_control
#if x3 < 300:
#print("left")
#Ctrl.drive(20,-20)
#elif x3 > 280 and x3 < 320:
#print("zhixian")
#Ctrl.drive(25,25)
#else:
#print("right")
#Ctrl.drive(-20,20)
#pid_control
pid_output = pidController.update(x3)
if pid_output > 11:
pid_output = 11
if pid_output < -11:
pid_output = -11
Ctrl.drive(25+pid_output, 25-pid_output)
else:
Ctrl.stop()
print("hat_stop")
#########################################################################################################################
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): # 按下 'q' 键退出循环
Ctrl.stop()
break
# 释放资源并关闭窗口
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
注意
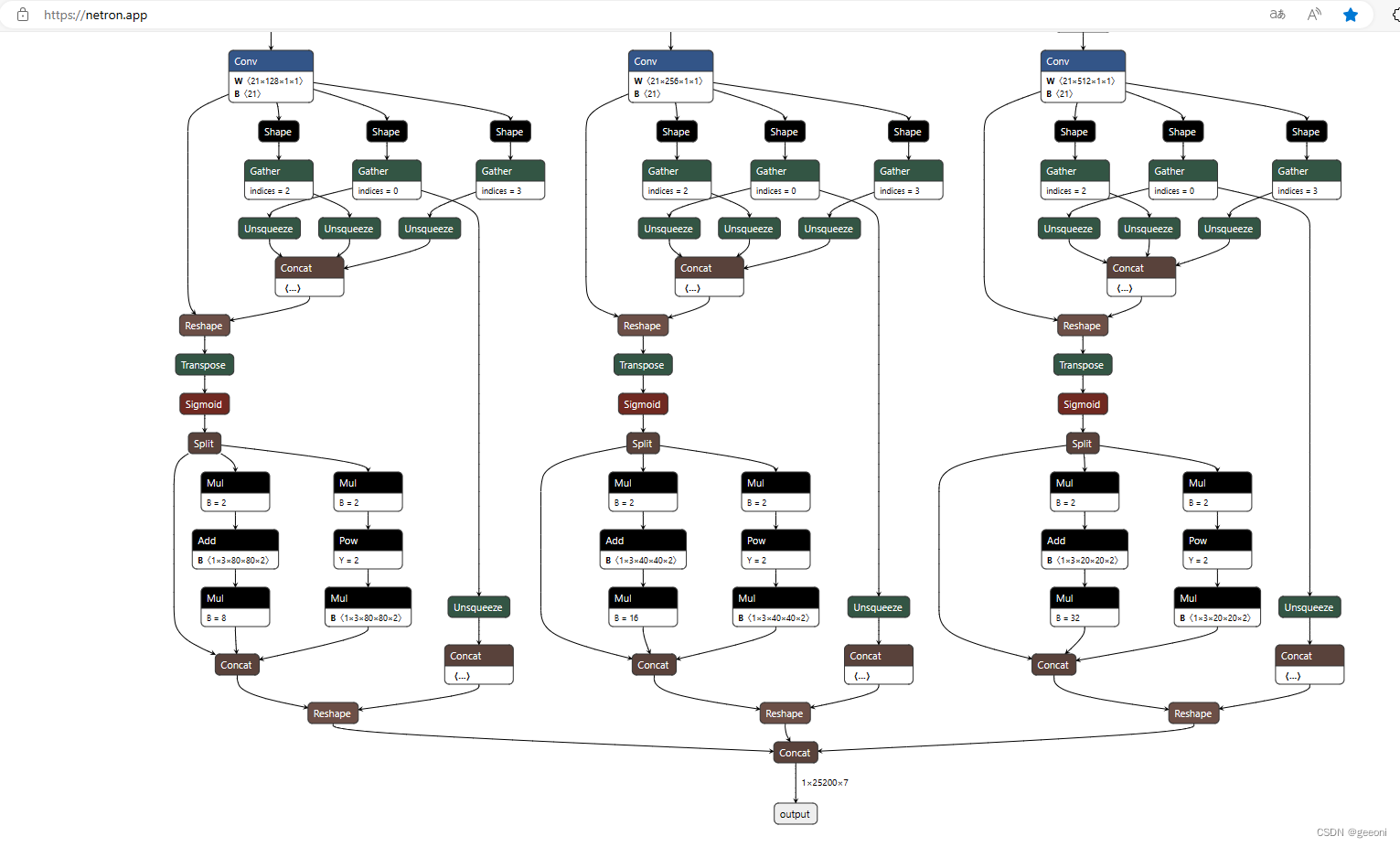
如果模型输出是 1×25200×7 ,代码直接复制就能用。
查看模型结构图网址:https://netron.app/ ,直接打开onnx文件拉到最后就可以看到模型输出: