1.两只塔姆沃斯牛(模拟)
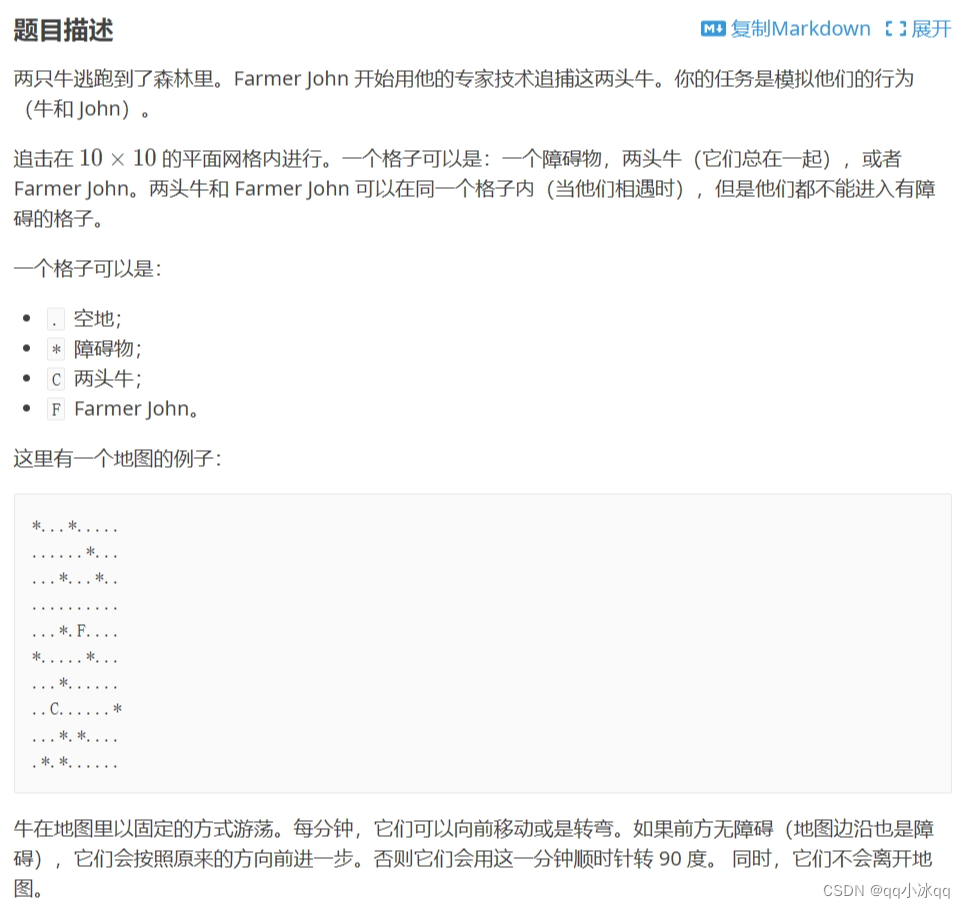

思路:人和牛都记录三个数据,当前坐标和走的方向,如果人和牛的坐标和方向走重复了,那就说明一直在绕圈圈,无解
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
char g[N][N];
int b[N][N][N][N][N][N];
int tx, ty, ex, ey;
struct Point{
int x, y, fang;
}peo, cow;
int ok;
int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int dy[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
void ff(){
int px = peo.x + dx[peo.fang];
int py = peo.y + dy[peo.fang];
int cx = cow.x + dx[cow.fang];
int cy = cow.y + dy[cow.fang];
if(g[px][py] != '*'){
peo.x = px;
peo.y = py;
}else{
peo.fang = (peo.fang + 1) % 4;
}
if(g[cx][cy] != '*'){
cow.x = cx;
cow.y = cy;
}else{
cow.fang = (cow.fang + 1) % 4;
}
}
int main(){
for(int i = 0; i <= 11; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= 11; j++){
g[i][j] = '*';
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= 10; j++){
cin>>g[i][j];
if(g[i][j] == 'F'){
tx = i;
ty = j;
}
if(g[i][j] == 'C'){
ex = i;
ey = j;
}
}
}
// for(int i = 0; i <= 11; i++){
// for(int j = 0; j <= 11; j++){
// cout<<g[i][j];
// }
// cout<<endl;
// }
peo = {tx, ty, 0};
cow = {ex, ey, 0};
int cnt = 0, ok1 = 0, ok2 = 0;
while(!(peo.x == cow.x && peo.y == cow.y)){
cnt++;
ff();
if(b[peo.x][peo.y][peo.fang][cow.x][cow.y][cow.fang] == 1){
ok = 1;
break;
}
b[peo.x][peo.y][peo.fang][cow.x][cow.y][cow.fang] = 1;
}
if(ok == 1) cout<<0;
else cout<<cnt;
return 0;
}
2.宇宙总统(排序)

思路:自定义排序,按照从大到小升序排序
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 25;
pair<string, int> q[N];
int n;
bool cmp(const pair<string, int>& pp, const pair<string, int>& qq){
if(pp.first.size() != qq.first.size()) return pp.first.size() > qq.first.size();
else{
int m = pp.first.size();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
if(pp.first[i] != qq.first[i]){
return pp.first[i] > qq.first[i];
}
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
string x;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin>>x;
q[i] = {x, i};
}
sort(q + 1, q + n + 1, cmp);
cout<<q[1].second<<endl;
cout<<q[1].first;
return 0;
}
3.回文质数(回文数、质数)

思路:先判断回文数,再判断质数,最大的回文质数是 9989899
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int a, b;
// 检查是否回文
int check1(int x){
int res = 0, t = x;
while(t){
res = res * 10 + t % 10;
t /= 10;
}
return res == x;
}
// 检查是否质数
int check2(int x){
if(x < 2) return 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= x / i; i++){
if(x % i == 0){
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
int main(){
cin>>a>>b;
for(int i = a; i <= b; i++){
// 最大的回文质数是 9989899
if(i > 10000000) break;
if(check1(i)){
//cout<<i<<endl;
if(check2(i)){
cout<<i<<endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
4.海底高铁(前缀和、差分)

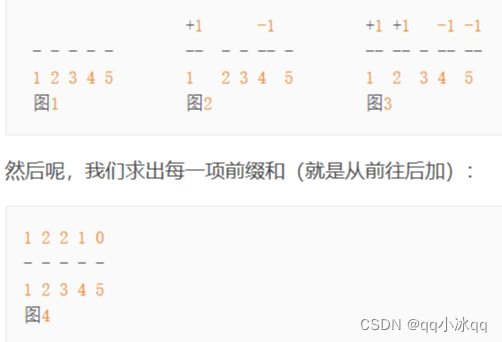
思路:如上,差分标记两个起始地点,然后前缀和求出每个地方需要走多少次,贪心求出买票还是买卡划算
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int p[N], s[N];
int n, m;
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin>>p[i];
if(i > 0){
if(p[i] > p[i - 1]){
s[p[i - 1]]++;
s[p[i]]--;
}else{
s[p[i]]++;
s[p[i - 1]]--;
}
}
}
// 差分数组累加,前缀和
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
s[i] += s[i - 1];
}
int a, b, c;
long long sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
cin>>a>>b>>c;
sum += min(1ll * a * s[i], 1ll * b * s[i] + c);
}
if(m < 2) cout<<0;
else cout<<sum;
return 0;
}
5.KMP(kmp)

#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int ne[N], f[N];
char s[N], p[N];
int n, m;
void kmp(){
ne[1] = 0;
int j = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= m; i++){
while(j > 0 && p[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if(p[i] == p[j + 1]) j++;
ne[i] = j;
}
j = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
while(j > 0 && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if(s[i] == p[j + 1]) j++;
f[i] = j;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(f[i] == m){
cout<<(i - m + 1)<<endl;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
cout<<ne[i]<<" ";
}
}
int main(){
cin>>(s + 1)>>(p + 1);
n = strlen(s + 1);
m = strlen(p + 1);
kmp();
return 0;
}
6.直播获奖(桶排序)

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 610;
int t[N];
int n, w;
int main(){
cin>>n>>w;
int x;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin>>x;
t[x]++;
int sum = 0;
for(int j = 600; j >= 0; j--){
sum += t[j];
if(sum >= max(1, i * w / 100)){
cout<<j<<" ";
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
7.最大子段和(递推)

思路:从开头一直累加,如果小于 0,那就重新开始累加,取最大值
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N];
int n;
int main(){
cin>>n;
int x, res = 0, ans = -1e9;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin>>x;
res += x;
ans = max(ans, res);
if(res < 0) res = 0;
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
8.采药(01背包)

思路:每个物品只能使用一次,时间就是体积
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000 + 10;
int f[N], v[N], w[N];
int n, m;
int main(){
cin>>m>>n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin>>v[i]>>w[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = m; j >= v[i]; j--){
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]);
}
}
cout<<f[m];
return 0;
}
9.疯狂的采药(完全背包)

思路:时间就是体积,完全背包,注意数据范围,背包体积 1e7,最大价值是 1e7 * 1e4 = 1e11
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e7 + 10;
long long f[N], v[N], w[N];
int n, m;
int main(){
cin>>m>>n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin>>v[i]>>w[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = v[i]; j <= m; j++){
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]);
}
}
cout<<f[m];
return 0;
}
10.最大食物链计数(拓扑排序)

思路:求的是路径条数,只有出度为 0 的时候才累加答案
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e3 + 10, mod = 80112002;
vector<int> g[N];
int ru[N], chu[N];
int siz[N];
int n, m;
int cnt;
void ff(){
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(ru[i] == 0){
siz[i] = 1;
q.push(i);
}
}
while(q.size()){
int it = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i : g[it]){
siz[i] = (siz[i] + siz[it]) % mod;
ru[i]--;
if(ru[i] == 0){
if(chu[i] == 0){
cnt = (cnt + siz[i]) % mod;
}else{
q.push(i);
}
}
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
int a, b;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
cin>>a>>b;
g[a].push_back(b);
chu[a]++;
ru[b]++;
}
ff();
cout<<cnt;
return 0;
}
11.装箱问题(01背包)

思路:01 背包,求最大能装下的体积,体积也是价值
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e4 + 10;
int f[N], v[N];
int n, m;
int main(){
cin>>m>>n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin>>v[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = m; j >= v[i]; j--){
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + v[i]);
}
}
cout<<(m - f[m]);
return 0;
}
12.高维正方体(快速幂、逆元)




思路:f[i][j]:i 维立方体中 j 维元素个数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, mod = 1e9 + 7;
int f[N];
int qm(int a, int b){
int res = 1 % mod;
while(b){
if(b & 1) res = 1ll * res * a % mod;
a = 1ll * a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
int a, b;
cin>>a>>b;
f[0] = qm(2, a);
for(int j = 1; j <= b; j++){
f[j] = ((1ll * f[j - 1] * (a + 1 - j)) % mod * qm(2 * j, mod - 2) % mod) % mod;
}
cout<<f[b];
return 0;
}
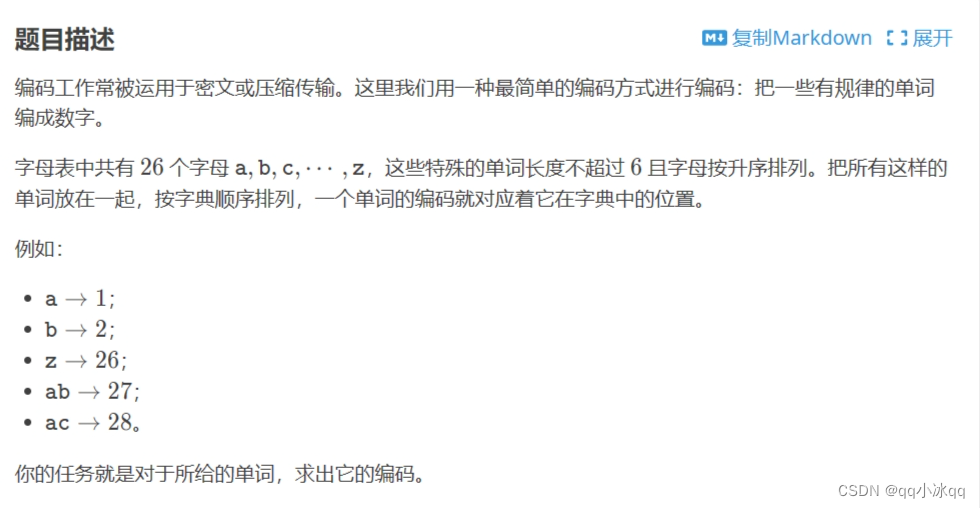
13.编码(计算组合数)


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 30;
int f[N][N];
void init(){
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++){
if(j == 0) f[i][j] = 1;
else f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
}
int main(){
init();
string s;
cin>>s;
int n = s.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){
if(s[i] >= s[i + 1]){
cout<<0;
return 0;
}
}
int ans = 0;
// 加上位数比当前小的
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) ans += f[26][i];
//枚举当前每一位可以有多少种情况
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int m = s[i] - 'a';
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
ans += f[26 - j][n - i - 1];
}
}
// 加上自身
ans++;
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
14.高低位交换(位运算)

思路:无符号整型 unsigned int 是 32 位整型,越界就等于取模了
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
unsigned int n;
cin>>n;
unsigned int res = (n >> 16) + (n << 16);
cout<<res;
return 0;
}
15.合并果子(贪心)

思路:每次取出两个最小的果子合并
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q;
int n;
int main(){
cin>>n;
int x;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin>>x;
q.push(x);
}
long long sum = 0;
while(q.size() > 1){
int a = q.top();
q.pop();
int b = q.top();
q.pop();
sum += a + b;
q.push(a + b);
}
cout<<sum;
return 0;
}
16.陶陶摘苹果(升级版)(贪心)

思路:按照每个苹果所需要的力气升序排序,一个一个摘
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
pair<int, int> q[N];
int n, m, a, b;
bool cmp(const pair<int, int>& pp, const pair<int, int>& qq){
if(pp.second != qq.second) return pp.second < qq.second;
else return pp.first < qq.first;
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
cin>>a>>b;
int x, y;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin>>x>>y;
q[i] = {x, y};
}
sort(q + 1, q + n + 1, cmp);
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(m - q[i].second >= 0 && a + b >= q[i].first){
cnt++;
m -= q[i].second;
}
}
cout<<cnt;
return 0;
}
17.一元三次方程求解(二分)

思路:如果有一个区间左右端点相乘小于等于 0,那么这个区间存在一个零点
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
double a, b, c, d;
double check(double x){
double sum = a * x * x * x + b * x * x + c * x + d;
return sum;
}
int main(){
cin>>a>>b>>c>>d;
int f = 0;
for(int i = -100; i <= 100; i++){
if(f == 3) break;
double l = i - 0.5, r = i + 0.5;
if(check(l) * check(r) <= 0){
if(check(l) >= 0){
while(l + 0.00001 < r){
double mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(check(mid) > 0) l = mid;
else r = mid;
}
}else if(check(l) < 0){
while(l + 0.00001 < r){
double mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(check(mid) < 0) l = mid;
else r = mid;
}
}
f++;
printf("%.2lf ", r);
}
}
return 0;
}
18.八皇后(dfs)
思路:dfs 一个参数,维护每行,然后三个数组维护每一列、正对角线、斜对角线
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 30;
int a[N];
int vis1[N], vis2[N], vis3[N];
int n;
int cnt;
void dfs(int u){
if(u > n){
cnt++;
if(cnt < 4){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(!vis1[i] && !vis2[u + i] && !vis3[i - u + n]){
vis1[i] = vis2[u + i] = vis3[i - u + n] = 1;
a[u] = i;
dfs(u + 1);
vis1[i] = vis2[u + i] = vis3[i - u + n] = 0;
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
dfs(1);
cout<<cnt;
return 0;
}
19.单词接龙(dfs)
思路:dfs 维护当前拼接成功的单词,用 map 记录每个单词用了几次
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 30;
map<string, int> mp;
string s[N];
int n;
int ans;
string check(string s1, string s2){
int len = s1.size();
for(int i = 1; i < len; i++){
if(s1.substr(len - i) == s2.substr(0, i)){
string t = s1 + s2.substr(i);
return t;
}
}
return "加训";
}
void dfs(string ss){
if(ss.size() > ans) ans = ss.size();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(mp[s[i]] == 2) continue;
string t = check(ss, s[i]);
if(t != "加训"){
mp[s[i]]++;
dfs(t);
mp[s[i]]--;
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin>>s[i];
}
char c;
cin>>c;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(s[i][0] == c){
mp[s[i]]++;
dfs(s[i]);
mp[s[i]]--;
}
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
20.约瑟夫问题(取模)

思路:vector 下标从 0 开始,每次前进 m - 1 个位置,到第 n 个位置取模后会变成 0,正好符合条件
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> v;
int n, m;
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) v.push_back(i);
int cnt = 0;
while(v.size()){
cnt = (cnt + m - 1) % v.size();
cout<<v[cnt]<<" ";
v.erase(v.begin() + cnt);
}
return 0;
}
21.队列安排(模拟链表)

思路:结构体模拟双链表
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
struct Point{
int l, r; // 左边和右边的同学
int vis; // 标记是否删除
}q[N];
void add(int i, int j, int f){
// j 插到 i 的右边
if(f == 1){
q[j].r = q[i].r;
q[j].l = i;
q[i].r = j;
q[q[j].r].l = j;
}else{
// j 插到 i 的左边
q[j].r = i;
q[j].l = q[i].l;
q[i].l = j;
q[q[j].l].r = j;
}
}
void init(){
q[0].r = 0, q[0].l = 0;
add(0, 1, 1); // 1 插到 0 的右
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
int k, p;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
cin>>k>>p;
add(k, i, p);
}
cin>>m;
int x;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
cin>>x;
q[x].vis = 1;
}
for(int i = q[0].r; i > 0; i = q[i].r){
if(!q[i].vis) cout<<i<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
22.验证栈序列(模拟栈)

思路:按入栈顺序入栈,如果栈顶和当前 b 数组元素相等,那就弹出,如果入栈结束,栈不为空,说明 b 不是出栈序列
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N], b[N];
int n, q;
int main(){
cin>>q;
while(q--){
cin>>n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin>>a[i];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin>>b[i];
stack<int> q;
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
q.push(a[i]);
while(q.top() == b[cnt]){
q.pop();
cnt++;
if(q.empty()) break;
}
}
if(q.empty()) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
23.马的遍历(bfs)

#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 410;
int g[N][N], vis[N][N], dis[N][N];
int n, m;
int dx[] = {-1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1};
int dy[] = {-2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2};
void bfs(int x, int y){
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
vis[x][y] = 1;
dis[x][y] = 0;
q.push({x, y});
while(q.size()){
auto it = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++){
int a = it.first + dx[i], b = it.second + dy[i];
if(a < 1 || a > n || b < 1 || b > m) continue;
if(vis[a][b]) continue;
vis[a][b] = 1;
dis[a][b] = dis[it.first][it.second] + 1;
q.push({a, b});
}
}
}
int main(){
memset(dis, -1, sizeof(dis));
int x, y;
cin>>n>>m>>x>>y;
bfs(x, y);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
cout<<dis[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
24.01迷宫(dfs)

思路:记录每个点属于哪个连通块,记录每个连通块的点个数
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e3 + 10, M = 1e5 + 10;
char g[N][N];
int vis[N][N];
int mp[M];
int n, m;
int cnt;
int dx[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int dy[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
void dfs(int x, int y, int z){
vis[x][y] = z;
mp[z]++;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if(a < 1 || a > n || b < 1 || b > n) continue;
if(vis[a][b]) continue;
if(g[a][b] == g[x][y]) continue;
dfs(a, b, z);
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
cin>>g[i][j];
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int x, y;
cin>>x>>y;
if(!vis[x][y]){
dfs(x, y, i);
cout<<mp[i]<<endl;
vis[x][y] = i;
}else{
cout<<mp[vis[x][y]]<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
25.村村通(并查集、dfs)

思路:把连通的点放在一个集合,只需要找多少个不连通的集合,需要加的边数就是这个数量减一
// 并查集
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e3 + 10;
int p[N];
int n, m;
int fd(int x){
if(x != p[x]){
p[x] = fd(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
// 合并两个集合
void ff(int x, int y){
int t1 = fd(x);
int t2 = fd(y);
p[t2] = t1;
}
int main(){
while(cin>>n && n != 0){
cin>>m;
int x, y;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
p[i] = i;
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin>>x>>y;
ff(x, y);
}
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(fd(i) == i){
cnt++;
}
}
cnt--;
cout<<cnt<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
// dfs
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e3 + 10;
vector<int> g[N];
int vis[N];
int n, m;
void dfs(int x){
if(!vis[x]);
vis[x] = 1;
for(int y : g[x]){
if(!vis[y]){
dfs(y);
}
}
}
int main(){
while(cin>>n && n != 0){
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
cin>>m;
int x, y;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) g[i].clear();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin>>x>>y;
g[x].push_back(y);
g[y].push_back(x);
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(vis[i]) continue;
dfs(i);
ans++;
}
ans--;
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
26.两数之和(哈希表)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
map<int, int> mp;
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
mp[nums[i]] = i + 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int x = target - nums[i];
if(mp[x] > 0 && i != mp[x] - 1){
return vector<int> {i, mp[x] - 1};
}
}
return vector<int> {0, 0};
}
};
27.盛水最多的容器(双指针)

class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int n = height.size();
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
int ans = 0, res = 0;
while(l < r){
res = min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l);
ans = max(ans, res);
if(height[l] >= height[r]) r--;
else l++;
}
return ans;
}
};
28.最长公共前缀(模拟)

思路:枚举第一个字符串的长度,如果后面不满足相等,那就返回
class Solution {
public:
string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {
if (strs.empty()) return "";
string prefix = "";
for (int i = 0; i < strs[0].size(); ++i) {
char ch = strs[0][i];
for (int j = 1; j < strs.size(); ++j) {
if (i >= strs[j].size() || strs[j][i] != ch) {
return prefix;
}
}
prefix += ch;
}
return prefix;
}
};
29.寻找重复数(哈希、二分、双指针)

双指针思路:数组在 [1, n] 之内,所以慢指针每次走一步,快指针每次走两步,如果有环,肯定会相遇
// 哈希
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
map<int, int> mp;
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
mp[nums[i]]++;
if(mp[nums[i]] == 2) return nums[i];
}
return 666;
}
};
// 二分
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
int l = 1, r = n - 1, ans = -1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cnt += nums[i] <= mid;
}
if (cnt <= mid) {
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
ans = mid;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
// 双指针
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
int slow = 0, fast = 0;
do {
slow = nums[slow];
fast = nums[nums[fast]];
} while (slow != fast);
slow = 0;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = nums[slow];
fast = nums[fast];
}
return slow;
}
};
30.分割数组的最大值(二分答案)

思路:二分这个最大值
class Solution {
public:
int check(vector<int>& nums, int x, int k){
int sum = 0;
int n = nums.size();
int cnt = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(sum + nums[i] <= x){
sum += nums[i];
}else{
sum = nums[i];
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt <= k;
}
int splitArray(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int n = nums.size();
int sum = 0, res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
sum += nums[i];
res = max(res, nums[i]);
}
int l = res - 1, r = sum + 1;
while(l + 1 < r){
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(check(nums, mid, k)) r = mid;
else l = mid;
}
return r;
}
};