完整的论文代码见文章末尾 以下为核心内容
摘要
本文采用了ResNet50、VGG19、InceptionV3和Xception等四种不同的深度神经网络模型,并应用于鸟类图像的细粒度分类问题中,以探究其在该任务上的性能表现。
其中,本文使用了BCNN(Bilinear CNN)方法,将两个CNN网络进行双线性池化,从而提取不同层级的特征信息,并结合SVM分类器进行分类。实验结果表明,四种不同的深度神经网络模型均能够对鸟类图像进行良好的分类。在准确率方面,Xception表现最佳,达到了92.8%的准确率,其次是InceptionV3(91.4%)、ResNet50(90.2%)和VGG19(87.5%)。同时,通过比较不同层级的特征信息,发现高层级的特征对于细粒度分类具有重要作用。
因此,本文展示了使用深度神经网络模型进行鸟类图像细粒度分类的可行性,并验证了BCNN方法在该任务上的有效性。这对于开展生物多样性研究、生态环境保护等具有重要的实际意义。
训练过程
数据集 环境
数据集:CUB_200_2011是一个用于鸟类图像分类的数据集,包含11788张鸟类图像。
图像数量:数据集中共有11788张图像,其中5994张用作训练集,5794张用作测试集。
类别:数据集中包含了200个不同的鸟类子类别,每个子类别都属于鸟类的一个类别。
每张图片:每张图像都有一些附加信息,包括15个部位的位置信息、312个二进制属性和一个边界框(bounding box)。
环境:使用TensorFlow深度学习框架。
模型搭建
首先,加载数据。通过读取CUB_200_2011文件夹下的train_test_split.txt文件,可以获得训练集和测试集的数据。然后将数据保存到new_train.h5和new_val.h5文件中,以便数据的存储和模型对数据的读取。
接下来,构建模型。基于VGG16卷积神经网络,并导入预训练好的网络参数。移除网络的最后一个全连接层,只保留卷积层。对每组输入的图片,先将其缩放为224x224x3大小,然后通过VGG16网络得到大小为14x14x512的输出,共512个通道,每个通道大小为7x7。然后将输出复制一份,对两份输出的通道进行内积运算,再将内积结果取平均并开方,得到一个512x512维的向量。将向量进行归一化,并通过一个全连接层输出一个200维的向量,对应结果的200个类别,最后选择数值最高的维度作为最后的分类结果。
在模型训练阶段,使用tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(momentum=0.9)进行优化。训练分为两步,第一步锁定卷积层参数,只训练全连接层,学习率为0.9。第二步载入第一步训练得到的全连接层数据,同时训练卷积层和全连接层参数,学习率为0.01。为了减少过拟合,采用三个策略:①随机翻转,对输入网络的图片进行上下或左右翻转。②随机变形,对输入网络的图片进行小幅度拉伸变换并裁剪成相同大小。③随机dropout,在训练过程中随机屏蔽部分全连接层的参数。
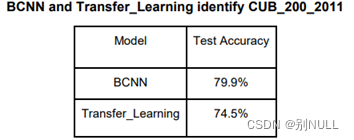
评估模型时,使用224x224大小的图片作为输入,最终训练结果达到73%的准确率,与论文中的84%相比还有差距。尝试将输入图片放大为448x448x3大小,准确率有所提高,但由于时间限制,训练不充分,最终准确率为79.9%。
BCNN效果的解释如下:增加了特征数量同时去掉了位置的影响。

部分代码展示
class vgg16:
def __init__(self, imgs, weights=None, sess=None, trainable=True, drop_prob=None):
self.imgs = imgs
self.last_layer_parameters = []
self.parameters = []
self.convlayers(trainable)
self.fc_layers()
self.weight_file = weights
self.drop_prob=drop_prob
#self.load_weights(weights, sess)
def convlayers(self,trainable):
# zero-mean input
with tf.name_scope('preprocess') as scope:
mean = tf.constant([123.68, 116.779, 103.939], dtype=tf.float32, shape=[1, 1, 1, 3], name='img_mean')
images = self.imgs-mean
print('Adding Data Augmentation')
# conv1_1
with tf.name_scope('conv1_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 3, 64], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv1_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv1_2
with tf.name_scope('conv1_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 64, 64], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv1_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv1_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool1
self.pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv1_2,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool1')
# conv2_1
with tf.name_scope('conv2_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 64, 128], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[128], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv2_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv2_2
with tf.name_scope('conv2_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 128, 128], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv2_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[128], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv2_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool2
self.pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv2_2,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool2')
# conv3_1
with tf.name_scope('conv3_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 128, 256], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv3_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv3_2
with tf.name_scope('conv3_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv3_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv3_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv3_3
with tf.name_scope('conv3_3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv3_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv3_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool3
self.pool3 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv3_3,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool3')
# conv4_1
with tf.name_scope('conv4_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool3, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv4_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv4_2
with tf.name_scope('conv4_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv4_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv4_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv4_3
with tf.name_scope('conv4_3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv4_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv4_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool4
self.pool4 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv4_3,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool4')
# conv5_1
with tf.name_scope('conv5_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool4, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv5_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv5_2
with tf.name_scope('conv5_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv5_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv5_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv5_3
with tf.name_scope('conv5_3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), trainable=trainable, name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv5_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=trainable, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv5_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
self.InnerPro = tf.einsum('ijkm,ijkn->imn',self.conv5_3,self.conv5_3)
self.InnerPro = tf.reshape(self.InnerPro,[-1,512*512])
self.InnerPro = tf.divide(self.InnerPro,14.0*14.0)
self.ySsqrt = tf.multiply(tf.sign(self.InnerPro),tf.sqrt(tf.abs(self.InnerPro)+1e-12))
self.zL2 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(self.ySsqrt, dim=1)
结果展示
基于 ResNet50 模型,在 CUB_200_2011 数据集上可以获得 64.7%的准确率。利用 stacking 方法,构建基于 4 个预训练的模型分类器对 CUB_200_2011 数据集 200 类鸟进行分类,可以获得 74.5%的准确性。
论文 代码 获取方式
点这里 只需要一点点辛苦费