1.介绍
个人实现的c++开源网络库.
2.软件架构
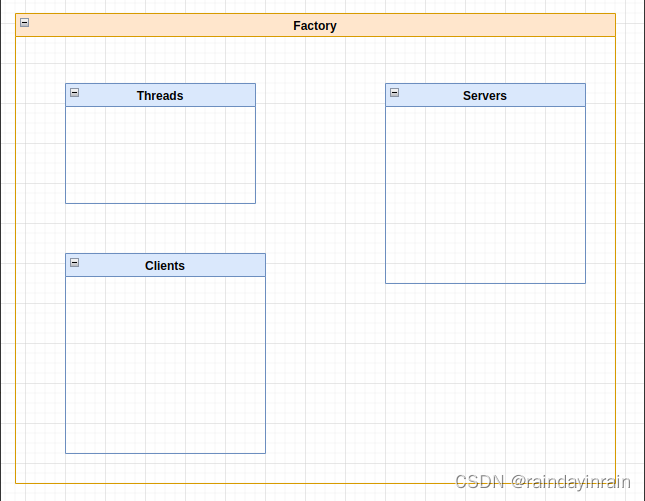
1.结构图
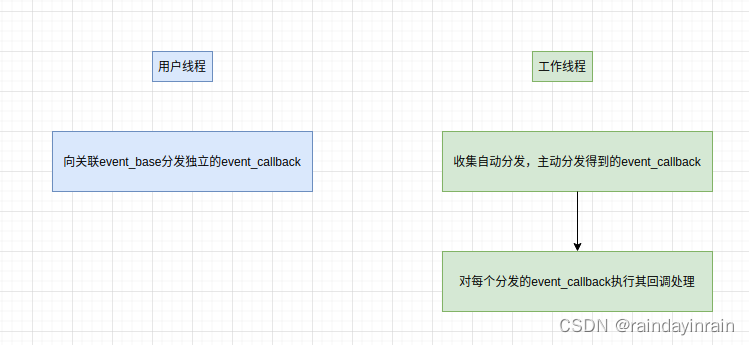
2.基于event的自动分发机制

3.多优先级分发队列,延迟分发队列

内部event服务于通知机制的优先级为0,外部event优先级为1.
当集中处理分发的event_callback时,若激活了更高优先级的event_callback,可在当前event_callback回调处理结束.进入下次时间循环,以便高优先级event_callback及时得到处理.
4.主动分发event_callback来向工作线程提交回调任务
5.通信对象的高效缓存区管理
5.1.以携带管理信息的可变尺寸块作为基础缓存单位

5.2.以可变尺寸块的链式队列构成的缓存区

5.3.块的可复用
对由于消耗而需释放的块,采用缓存而非释放来管理.

释放块时候,依据块容量,释放到缓存指定容量下块的容器.
需要新块时,依据所需容量,先从缓存取块,取不到时,再动态分配新的块.
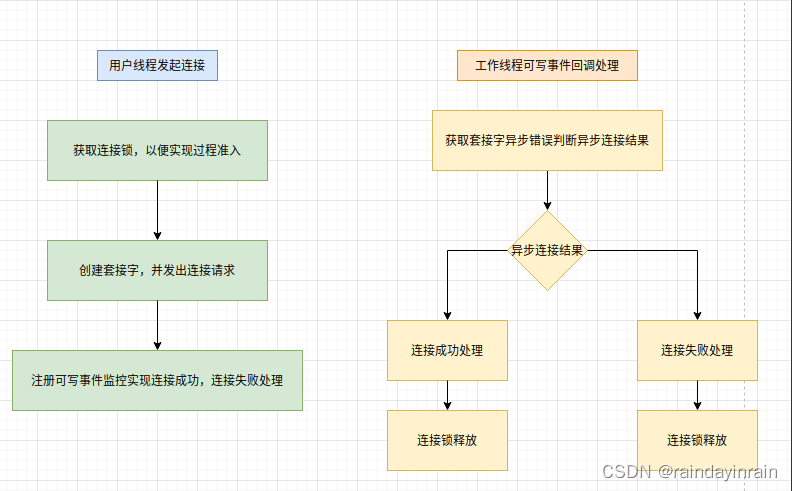
5.4.连接对象的连接管理
采用一个互斥锁,实现连接对象上连接建立过程,连接断开过程至多只有一个并发.
a. 连接过程
b.断开过程
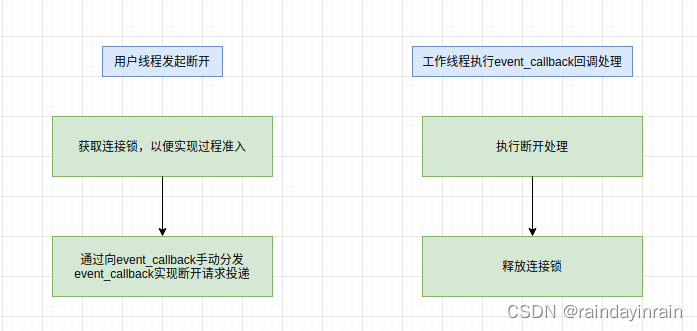
c.断开投递快速响应
设置手动分发event_callback的优先级为0,借助event_callback的多优先级分发队列.可使得当前event_callback回调处理结束,即可开始下轮循环,从而快速处理分发的高优先级的event_callback.
5.5.连接对象高效锁管理
a. 通过连接锁实现连接建立,连接断开的串行化.
b. 可读事件处理,收包回调无锁处理.
因为可读事件及收包回调只在单个工作线程引发,且通过连接建立,连接断开的串行化处理.收包过程及其回调可以实现为无锁的.
c. 通过发送锁实现发送缓存区并发管理
用户线程执行发送,工作线程可写事件执行异步发送分别充当了发送缓存的生产者,消费者.我们用发送互斥锁进行并发管理.
5.6.高效的io复用
a. 采用epoll作为io复用器,其比select,poll在管理大规模事件监控时性能更优异.
b. 只在必要时注册连接对象可写event到event_base.
b.1. 连接建立过程,我们将其注册到event_base,以便实现连接结果异步处理.
b.2. 用户线程向发送缓存写入新数据时,我们将其注册到event_base以便实现数据在可写事件中的异步发送.
b.3. 在异步发送里,判断发送缓存为空时,自动移除可写event.以便减少不必要的事件分发.
5.7.简单易用
a. 以c++实现.
b. 以工厂模式管理资源.
c. 接口定义清晰,详见使用说明.
系统要求
1.支持c++11
2.支持cmake
3.linux系统
安装教程
1.在mynet/build下执行:cmake ../
2.在mynet/build下执行:make
3.在mynet/build/demo下执行:./srv_test开启服务端
4.在mynet/build/demo下执行:./cli_test开启客户端
使用说明
1.客户端demo
#include "ifactory.h"
#include "ilog.h"
#include "iclient.h"
#include "define.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <mutex>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <endian.h>
std::mutex mtx;
std::ofstream logFile("cli_logfile.txt", std::ios_base::out);
void logcb(mynet::LOGLEVEL nLevel, const char *msg){
//if(nLevel == mynet::LOGLEVEL::EVENT_LOG_ERR){
pthread_t thread_id = pthread_self();
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
logFile << "tid:" << (uint32_t)thread_id << " level: " << (int32_t)nLevel << ": msg: " << msg << std::endl;
//}
}
struct Msg1{
int32_t nLen;
int32_t nType;
int32_t nMsg1;
char strName[100];
Msg1(){
nLen = CalculateSize();
nType = 1;
}
static int32_t CalculateSize(){
return 112;
}
void Serialize(char* lpOut){
int32_t nTmpLen = htobe32(nLen);
memcpy(lpOut, (char*)&nTmpLen, 4);
int32_t nTmpType = htobe32(nType);
memcpy(lpOut+4, (char*)&nTmpType, 4);
int32_t nMsg = htobe32(nMsg1);
memcpy(lpOut+8, (char*)&nMsg, 4);
memcpy(lpOut+12, strName, 100);
}
Msg1* DeSerialize(char* lpIn){
Msg1* lpM = new Msg1();
int32_t nTmpLen = *(int32_t*)lpIn;
lpM->nLen = be32toh(nTmpLen);
int32_t nTmpType = *(int32_t*)((char*)lpIn+4);
lpM->nType = be32toh(nTmpType);
int32_t nMsg = *(int32_t*)(lpIn+8);
lpM->nMsg1 = be32toh(nMsg);
memcpy(lpM->strName, lpIn+12, 100);
return lpM;
}
};
struct Msg2{
int32_t nLen;
int32_t nType;
int32_t nMsg2;
char strName1[100];
char strName2[100];
Msg2(){
nLen = CalculateSize();
nType = 2;
}
static int32_t CalculateSize(){
return 212;
}
void Serialize(char* lpOut){
int32_t nTmpLen = htobe32(nLen);
memcpy(lpOut, (char*)&nTmpLen, 4);
int32_t nTmpType = htobe32(nType);
memcpy(lpOut+4, (char*)&nTmpType, 4);
int32_t nMsg = htobe32(nMsg2);
memcpy(lpOut+8, (char*)&nMsg, 4);
memcpy(lpOut+12, strName1, 100);
memcpy(lpOut+112, strName2, 100);
}
Msg2* DeSerialize(char* lpIn){
Msg2* lpM = new Msg2();
int32_t nTmpLen = *(int32_t*)lpIn;
lpM->nLen = be32toh(nTmpLen);
int32_t nTmpType = *(int32_t*)(lpIn+4);
lpM->nType = be32toh(nTmpType);
int32_t nMsg = *(int32_t*)(lpIn+8);
lpM->nMsg2 = be32toh(nMsg);
memcpy(lpM->strName1, lpIn+12, 100);
memcpy(lpM->strName2, lpIn+112, 100);
return lpM;
}
};
class ClientCallback:public mynet::IClientCallback{
public:
virtual ~ClientCallback(){
printf("~ClientCallback\n");
}
virtual void OnEvent(short events){
printf("recv event %d\n", events);
}
virtual void OnMessage(char* lpMsg, int32_t nLen){
printf("msg len:%d\n", nLen);
}
};
int main(){
mynet::SetLogCb(logcb);
mynet::FactoryConfig stConfig;
stConfig.nWorkThreadNum = 1;
mynet::IFactory* lpFac = mynet::CreateFactory(stConfig);
lpFac->Start();
mynet::ClientConfig stCliConfig;
stCliConfig.nConnTimeout = 4;
stCliConfig.nPort = 13142;
strcpy(stCliConfig.strIp, "127.0.0.1");
stCliConfig.nThreadIndex = 0;
ClientCallback stCall;
mynet::IClient* lpCli = lpFac->CreateClient(stCliConfig, &stCall);
int32_t nRet = lpCli->DoConnect(13142, stCliConfig.strIp, 4, true, true);
printf("conn ret %d\n", nRet);
if(nRet != RET_CODE_CONN_SUCC){
return 0;
}
char* lpBuf = (char*)malloc(Msg1::CalculateSize());
for(int32_t i = 0; i < 10; i++){
Msg1 stM1;
stM1.nMsg1 = 11;
strcpy(stM1.strName, "StrName1");
stM1.Serialize(lpBuf);
int32_t nSend = lpCli->SendData(lpBuf, Msg1::CalculateSize());
printf("%d send ret %d\n", i, nSend);
}
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(6));
lpCli->DoDisconnect(true, true);
lpFac->Stop();
mynet::DestroyFactory(lpFac);
return 0;
}
2.服务端demo
#include "ifactory.h"
#include "ilog.h"
#include "iserver.h"
#include "define.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <mutex>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
std::mutex mtx;
std::ofstream logFile("svr_logfile.txt", std::ios_base::out);
void logcb(mynet::LOGLEVEL nLevel, const char *msg){
//if(nLevel == mynet::LOGLEVEL::EVENT_LOG_ERR){
pthread_t thread_id = pthread_self();
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
logFile << "tid:" << (uint32_t)thread_id << " level: " << (int32_t)nLevel << ": msg: " << msg << std::endl;
//}
}
struct Msg1{
int32_t nLen;
int32_t nType;
int32_t nMsg1;
char strName[100];
Msg1(){
nLen = CalculateSize();
nType = 1;
}
static int32_t CalculateSize(){
return 112;
}
void Serialize(char* lpOut){
int32_t nTmpLen = htobe32(nLen);
memcpy(lpOut, (char*)&nTmpLen, 4);
int32_t nTmpType = htobe32(nType);
memcpy(lpOut+4, (char*)&nTmpType, 4);
int32_t nMsg = htobe32(nMsg1);
memcpy(lpOut+8, (char*)&nMsg, 4);
memcpy(lpOut+12, strName, 100);
}
Msg1* DeSerialize(char* lpIn){
Msg1* lpM = new Msg1();
int32_t nTmpLen = *(int32_t*)lpIn;
lpM->nLen = be32toh(nTmpLen);
int32_t nTmpType = *(int32_t*)((char*)lpIn+4);
lpM->nType = be32toh(nTmpType);
int32_t nMsg = *(int32_t*)(lpIn+8);
lpM->nMsg1 = be32toh(nMsg);
memcpy(lpM->strName, lpIn+12, 100);
return lpM;
}
};
struct Msg2{
int32_t nLen;
int32_t nType;
int32_t nMsg2;
char strName1[100];
char strName2[100];
static int32_t CalculateSize(){
return 212;
}
void Serialize(char* lpOut){
int32_t nTmpLen = htobe32(nLen);
memcpy(lpOut, (char*)&nTmpLen, 4);
int32_t nTmpType = htobe32(nType);
memcpy(lpOut+4, (char*)&nTmpType, 4);
int32_t nMsg = htobe32(nMsg2);
memcpy(lpOut+8, (char*)&nMsg, 4);
memcpy(lpOut+12, strName1, 100);
memcpy(lpOut+112, strName2, 100);
}
Msg2* DeSerialize(char* lpIn){
Msg2* lpM = new Msg2();
int32_t nTmpLen = *(int32_t*)lpIn;
lpM->nLen = be32toh(nTmpLen);
int32_t nTmpType = *(int32_t*)(lpIn+4);
lpM->nType = be32toh(nTmpType);
int32_t nMsg = *(int32_t*)(lpIn+8);
lpM->nMsg2 = be32toh(nMsg);
memcpy(lpM->strName1, lpIn+12, 100);
memcpy(lpM->strName2, lpIn+112, 100);
return lpM;
}
};
class ServerCallback:public mynet::IServerCallback{
public:
ServerCallback(){
}
virtual ~ServerCallback(){
printf("~ServerCallback\n");
}
virtual void OnEvent(int32_t nIndex, short events){
printf("index_%d,events_%d\n", nIndex, events);
}
virtual void OnMessage(int32_t nIndex, char* lpMsg, int32_t nLen){
printf("index_%d,len_%d\n", nIndex, nLen);
m_lpSvr->SendData(nIndex, lpMsg, nLen);
}
public:
mynet::IServer* m_lpSvr = nullptr;
};
int main(){
mynet::SetLogCb(logcb);
mynet::FactoryConfig stConfig;
stConfig.nWorkThreadNum = 1;
mynet::IFactory* lpFac = mynet::CreateFactory(stConfig);
lpFac->Start();
mynet::ServerConfig stSvrConfig;
stSvrConfig.nPort = 13142;
stSvrConfig.nListenThreadIndex = 0;
ServerCallback stSvrCallback;
mynet::IServer* lpSvr = lpFac->CreateServer(stSvrConfig, &stSvrCallback);
stSvrCallback.m_lpSvr = lpSvr;
lpSvr->Start();
while(true){
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(6));
}
lpSvr->Stop();
lpFac->Stop();
mynet::DestroyFactory(lpFac);
return 0;
}
后续待处理事项
1.完善各类场景单元测试
2.支持epoll的et模式事件分发
3.制作规范清晰的使用文档
开源地址
1.https://github.com/xubenhao/mynet
2. https://gitee.com/xubenhao2/mynet