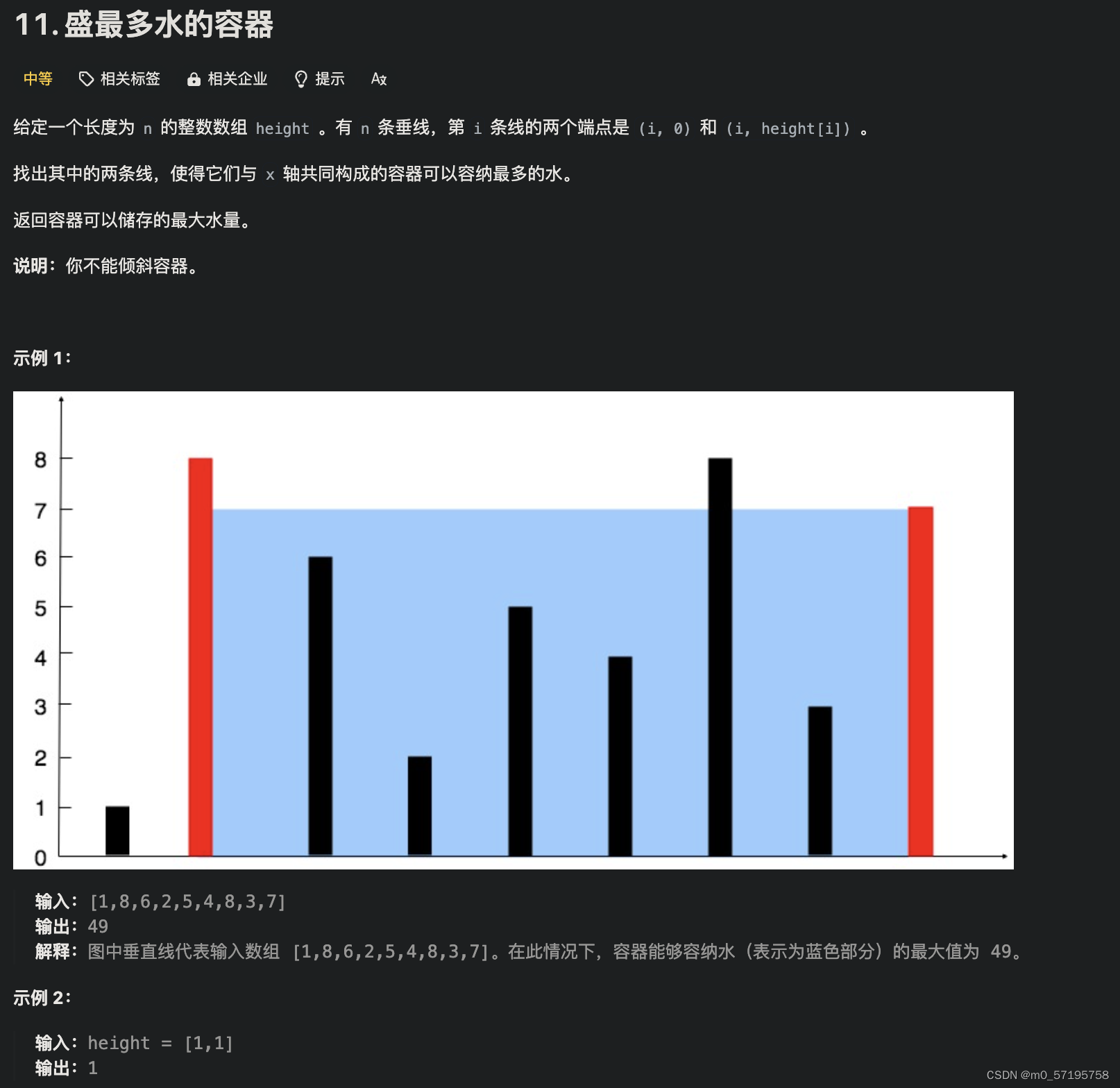
一、前言
目前有一个关于通过STM32F411CEUx的I2S总线接口控制SSS1700芯片进行音频输入输出的研究。
SSS1700 是具有片上振荡器的 3S 高度集成的USB音频控制器芯片 。 SSS1700 功能支持96 KHz 24 位采样率,带外部音频编解码器(24 位/96KHz I2S 输入和输出)并具有内置立体声16/24位ADC、立体声16/24位DAC、耳机驱动、五段硬件均衡器、音频 PLL、USB 时钟振荡器和 USB FS 控制器加上 PHY。(实际个人认为使用基于蓝牙的音频控制芯片来结合STM32等单片机的方案可能更加方便一些,基于USB接口的耳机音响等基本已经退出舞台了,因此使用该类usb芯片个人不是很理解,但也有可能蓝牙被做它用,USB可以通过hub扩展,而蓝牙不容易扩展,具体原因暂时不得而知)
整体的逻辑比较简单:
- 手机通过usb接口将音频数据传输给SSS1700音频芯片,该芯片提供I2S接口,我们MCU通过I2S接口读取该芯片中的音频数据达到录音的效果;
- 如果手机没有放音时,我们MCU通过I2S接口向该音频芯片写入音频内容达到放音的效果。
待验证的扩展功能:
- 音频芯片通过I2S接口读取音频数据的同时是否还可同时通过其它接口读取?
- 手机通过usb接入音频芯片放音时我们是否可以通过I2S接口同步控制音频芯片放音?这个过程理论上芯片是被占用的,是否能像电脑音频混音播放还需要实验一下。
二、资料收集
官方i2s例子:https://www.stmcu.com.cn/Designresource/detail/LAT/710151
https://community.st.com/t5/stm32-mcus-products/pcm-sound-to-pc-gt-stm32f4-microphone/td-p/464908
https://www.st.com/en/embedded-software/stm32cubef4.html#get-software
参考官方HAL库的示例:en.stm32cubef4-v1-28-0\STM32Cube_FW_F4_V1.28.0\Projects\STM32F411E-Discovery\Applications\Audio\Audio_playback_and_record\Src\waveplayer.c
sss1700:https://www.bilibili.com/read/cv21981976/
i2s理解:https://blog.csdn.net/wholetus/article/details/109326191
音频及采样频率:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/101073274
ST-LINK及JLINK等:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/454940732
stm32 usb虚拟串口收发:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_60876665/article/details/122788442
i2s读取录音的重点参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44226356/article/details/125153210
i2s读取的数据发送上位机测试参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/pingwen/p/11794081.html
pcm、pdm:https://blog.csdn.net/u010783226/article/details/130850834
FATFS追加写入:https://blog.csdn.net/ba_wang_mao/article/details/109464436
缓存机制:https://www.cnblogs.com/puyu9499/p/15914090.html
DMA双缓存(比较常见的DMA缓存方式,但是个人更推荐上面缓存机制方式,代码改动小,好理解):https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43336331/article/details/110481985
放音测试参考(测试i2s放音时可以接一个类似设备去听声音):https://blog.csdn.net/sudaroot/article/details/106834893
全双工参考(但是其没有使用DMA回调方式):https://blog.csdn.net/zwl1584671413/article/details/86650062
busy问题:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42254853/article/details/130145214
全双工阻塞方式及异步回调方式使用启发:https://community.st.com/t5/stm32-mcus-products/stm32f411-hal-driver-i2s-full-duplex-ext-sd-issue/td-p/442735
三、I2S接口理解
1、基础概念
- I2S(Inter-IC Sound)总线, 又称集成电路内置音频总线,是飞利浦半导体公司(现为恩智浦半导体公司)针对数字音频设备之间的音频数据传输而制定的一种总线标准。该总线专门用于音频设备之间的数据传输,广泛应用于各种多媒体系统。
- 它为音频应用而设计,是一种电子的串行总线,用于连接电子音频设备。
- 它传输的是PCM音频数据(即脉冲编码调制),PCM音频数据是未经压缩的音频采样数据裸流,它是由模拟信号经过采样、量化、编码转换成的标准数字音频数据。I2S是音频数字化后数据排列的一种格式。
- 声音数字化过程:
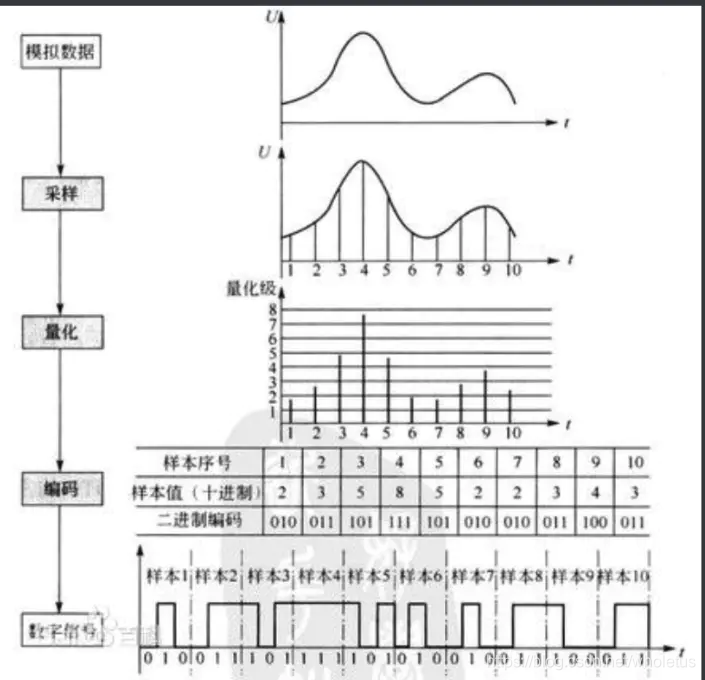
- 转为 PCM 格式三个参数:
声道数、采样位数和采样频率。
- 采样频率:每秒钟取得声音样本的次数。采样频率越高,声音质量越好,还原越真实,但同时它占的资源比较多。
- 采样位数:每个采样点用多少二进制位表示数据范围。量化位数越多,音质越好,数据量也越大。
- 声道数:使用声音通道的个数,有单声道和立体声之分,立体声比单声道数据量翻倍。
- 音频数据量=采样频率×量化位数×声道数/8(字节/秒)
由于PCM数据量比较大,所以一般应用过程中还会对PCM数据进行编码后传输,在播放时再解码(编解码会造成音质损失)。
2、信号线
I2S协议只定义三根信号线:时钟信号SCK、数据信号SD和左右声道选择信号WS。
- 时钟信号 Serial Clock
SCK是模块内的同步信号,从模式时由外部提供,主模式时由模块内部自己产生。 不同厂家的芯片型号,时钟信号叫法可能不同,也可能称BCLK/Bit Clock或SCL/Serial Clock
- 数据信号 Serial Data
**SD是串行数据,在I2S中以二进制补码的形式在数据线上传输。**在WS变化后的第一个SCK脉冲,先传输最高位(MSB, Most Significant Bit)。先传送MSB是因为发送设备和接收设备的字长可能不同,当系统字长比数据发送端字长长的时候,数据传输就会出现截断的现象/Truncated,即如果数据接收端接收的数据位比它规定的字长长的话,那么规定字长最低位(LSB: Least Significant Bit)以后的所有位将会被忽略。如果接收的字长比它规定的字长短,那么空余出来的位将会以0填补。通过这种方式可以使音频信号的最高有效位得到传输,从而保证最好的听觉效果。
√ 根据输入或输出特性,不同芯片上的SD也可能称SDATA、SDIN、SDOUT、DACDAT、ADCDAT等; √ 数据发送既可以同步于SCK的上升沿,也可以是下降沿,但接收设备在SCK的上升沿采样,发送数据时序需考虑
- 左右声道选择信号 Word Select
WS是声道选择信号,表明数据发送端所选择的声道。 当:
√ WS=0,表示选择左声道 √ WS=1,表示选择右声道
WS也称帧时钟,即LRCLK/Left Right Clock。 WS频率等于声音的采样率。WS既可以在SCK的上升沿,也可以在SCK的下降沿变化。从设备在SCK的上升沿采样WS信号。数据信号MSB在WS改变后的第二个时钟(SCK)上升沿有效(即延迟一个SCK),这样可以让从设备有足够的时间以存储当前接收的数据,并准备好接收下一组数据。
另外,有时为使系统间更好地同步,还要传输一个主时钟(MCK),STM32F429x系列控制器固定输出为256* FS。
3、半/全双工及主/从模式
- 支持全双工和半双工通信。(单工数据传输只支持数据在一个方向上传输;半双工数据传输允许数据在两个方向上传输,但是在某一时刻,只允许数据在一个方向上传输,它实际上是一种切换方向的单工通信;全双工数据通信允许数据同时在两个方向上传输,因此,全双工通信是两个单工通信方式的结合,它要求发送设备和接收设备都有独立的接收和发送能力。
- 支持主/从模式。(主模式:就是主CPU作为主机,向从机(挂载器件)发送接收数据。从模式:就是主CPU作为从机,接收和发送主机(挂载器件)数据。而主从机的分别其实是一个触发的作用,主机主动触发,从机只能被动响应触发。)
四、STM32CubeMX配置
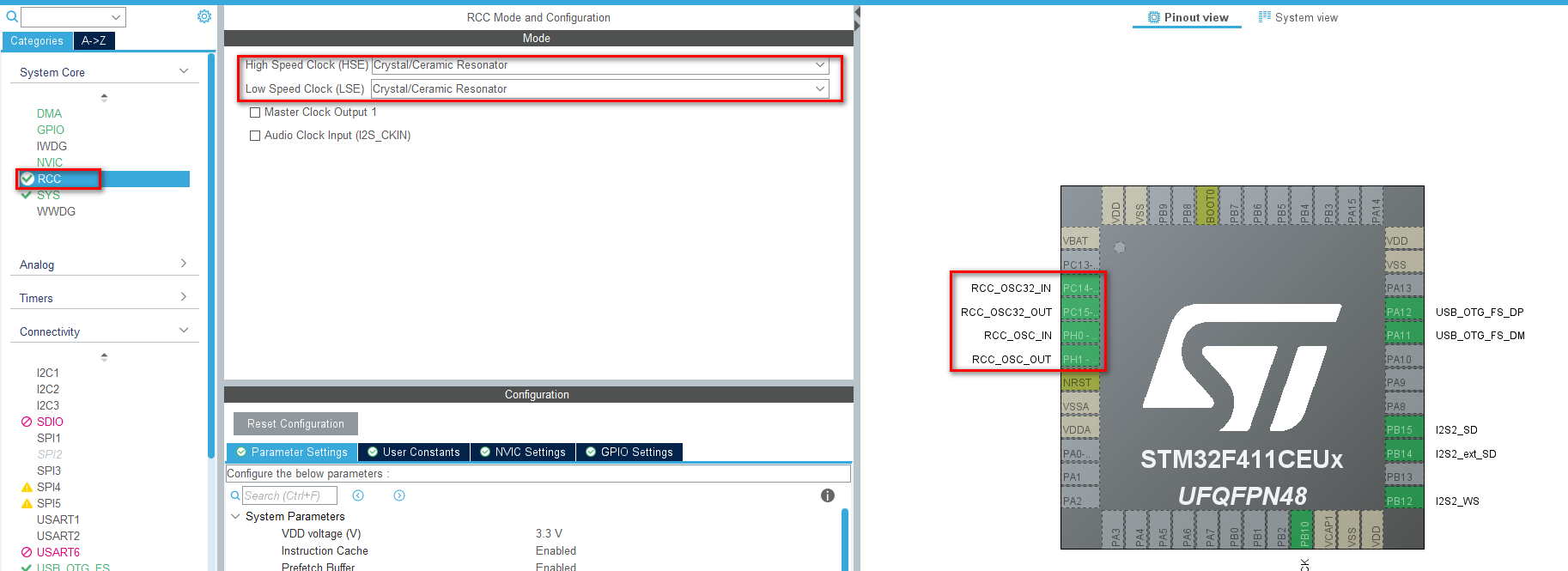
1、配置RCC
根据开发板的晶振配置高速和低速时钟(查看原理图确认对应引脚是否已经配置了对应的晶振):
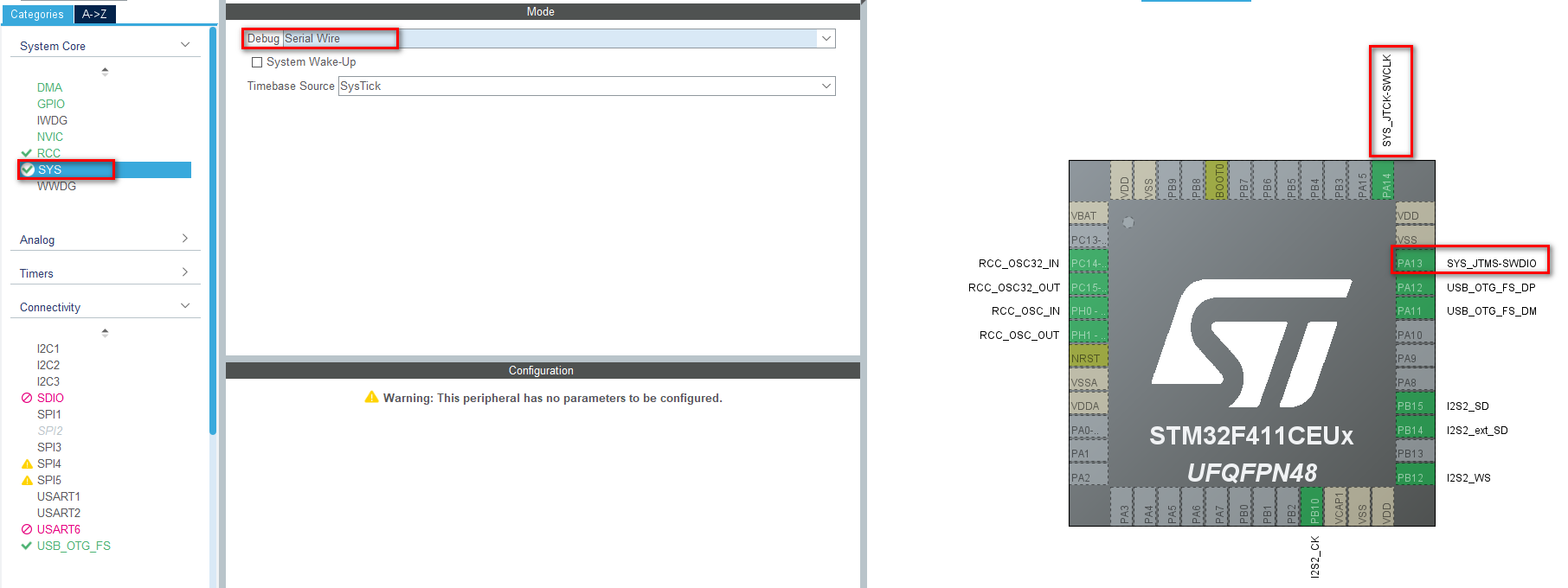
2、配置系统调试接口
我这里的板子为JTAG的SWD下载口
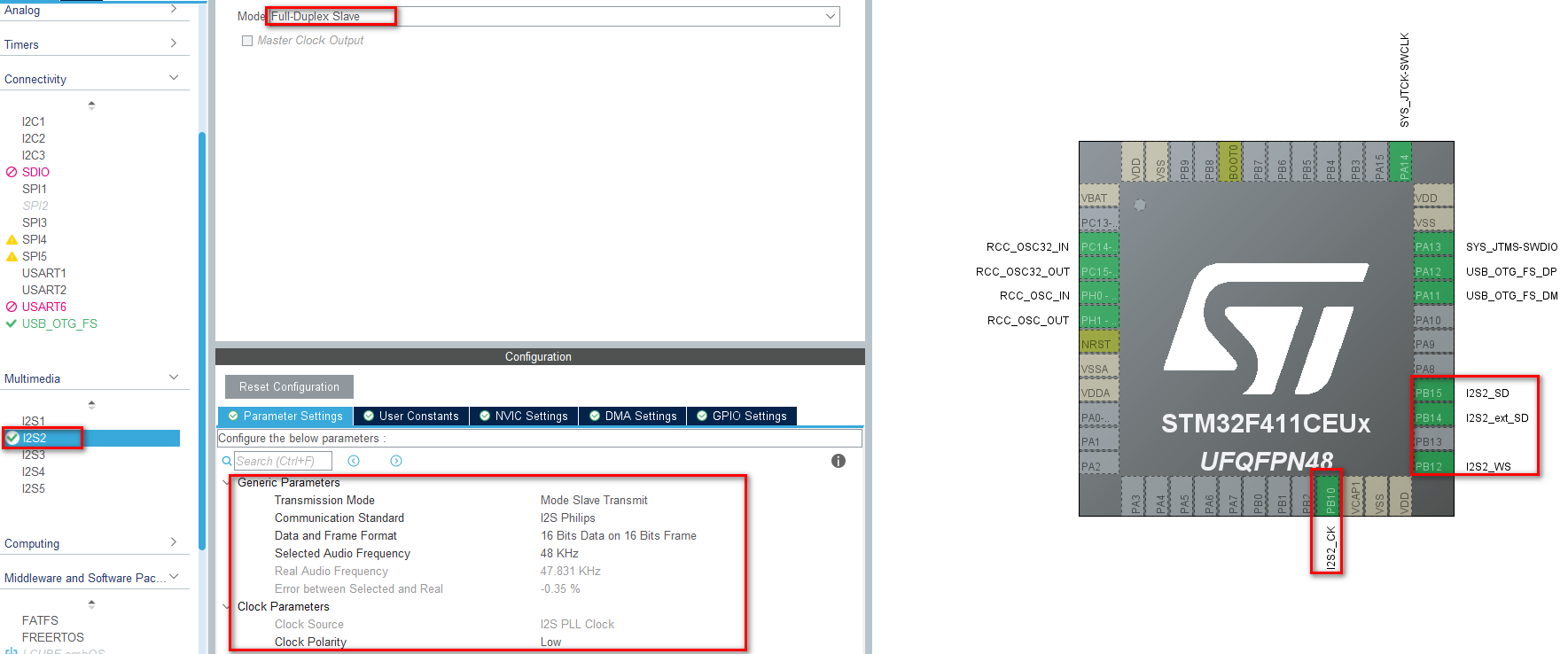
3、配置I2S
根据音频芯片及功能,这里暂时配置为全双工从模式,接收音频数据及发送音频数据,参数和音频芯片测试板配置的一致,不开启主时钟输出看一下是否存在干扰,如果干扰造成噪声等再开启主时钟试一下。
根据官方的说明:Transmission Mode: 传输模式。决定 SD 数据线传输方向(SD_Ext 方向相反)。所以如果设置了Transmit那么SD就是发送,SD_Ext就是接收,反之设置了Receive那么SD就是接收,SD_Ext就是发送。
这个对接线很有帮助,只是软件开发接口不关心,全双工时收发触发及回调都各自只需要一个接口。
Communication Standard: 传输标准。本文中采用 I2S Philips 标准(需要和音频芯片相同标准)。
Data and Frame Format: 数据位宽和帧位宽。如同“传输标准”的配置,保持与编解码器配置一致。
Selected Audio Frequency: 音频频率。可选频率 8KHz、11KHz、16KHz、22KHz、32KHz、44KHz、48KHz、96KHz、192KHz,这里选择 48KHz。如同“传输标准”的配置,保持与编解码器配置一致。
Clock polarity:时钟极性(非激活态时)。
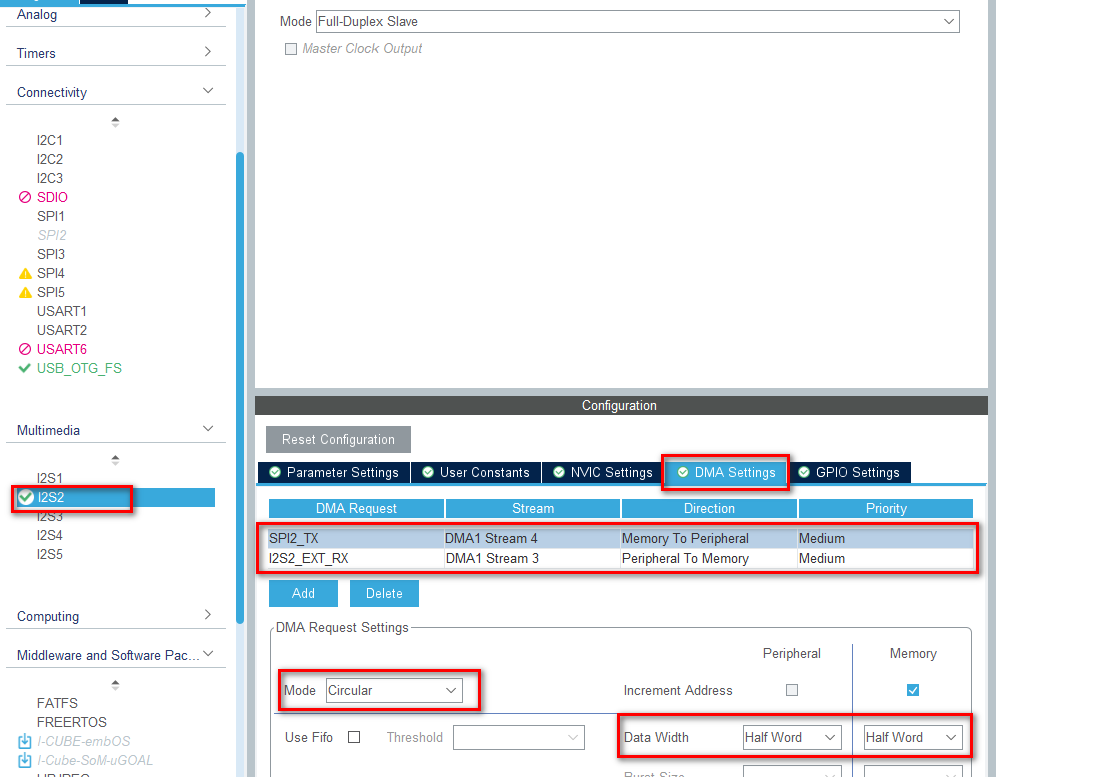
4、配置I2S DMA
根据官网的I2S音频开发介绍,这里配置添加两个DMA,具体如下,推荐Half World,模式推荐循环模式,这样好配合非阻塞回调函数,正常模式更适合阻塞方式处理,但阻塞模式往往速度比较慢,高采样率时丢采样数据的情况比较多:
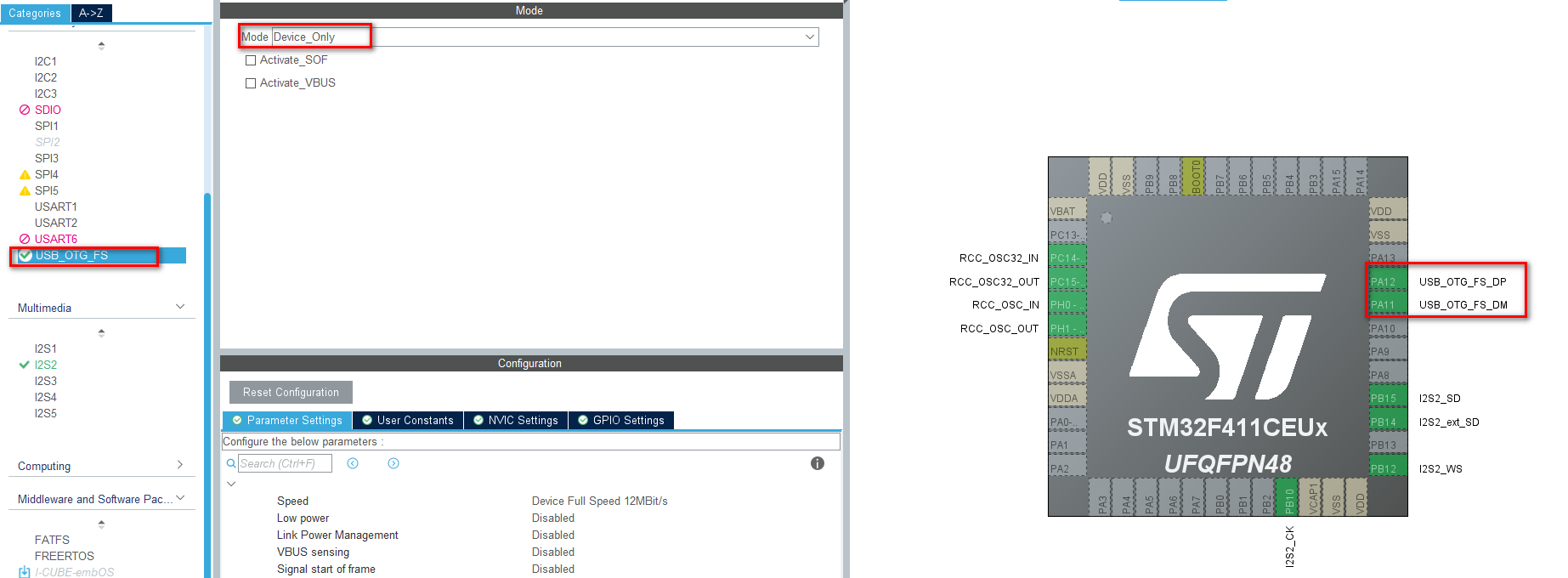
5、配置USB作为虚拟串口
我这里的STM32F411CEUx具备USB口,时钟配置好后USB也是可以配置的,这个usb口目前开发板是type-c的,不太好接U盘和SD卡了,所以用来配置作为一个虚拟串口和上位机通信(后续换了F407ZET6,HS的USB速度 更加快,外围接口较多,外挂U盘、SD卡、flash都可以拿来测试):
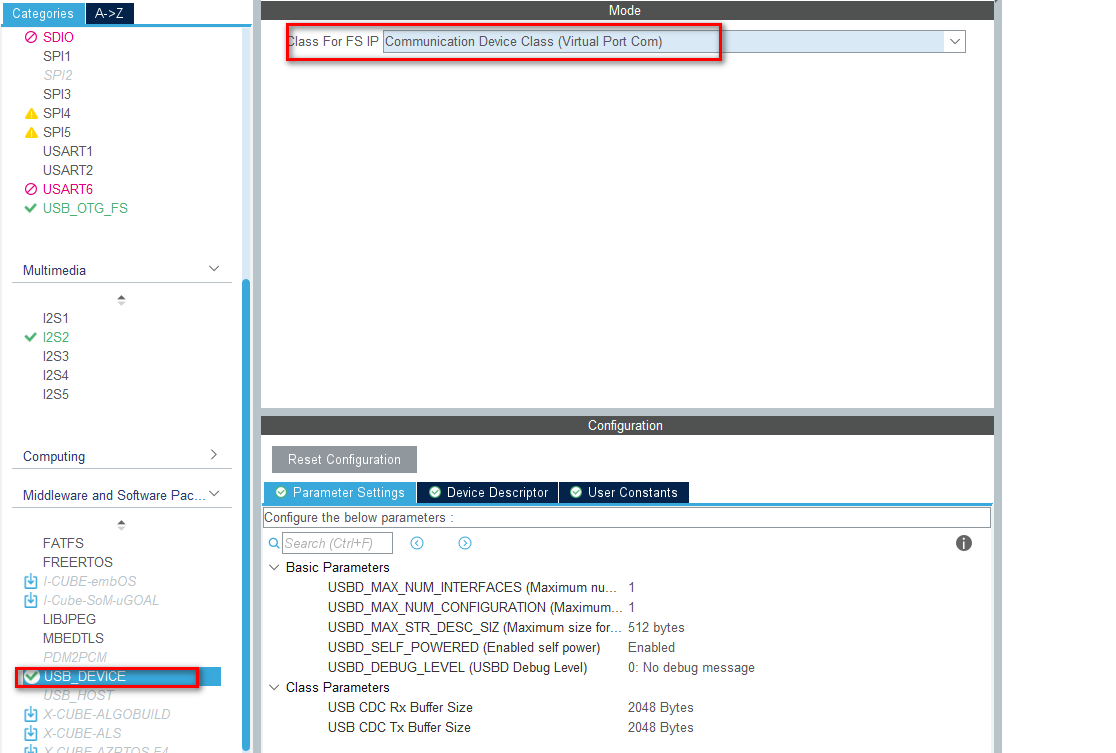
- 配置USB DEVICE为虚拟串口:
6、增加一组串口2作为调试及外部交互用
默认配置即可:
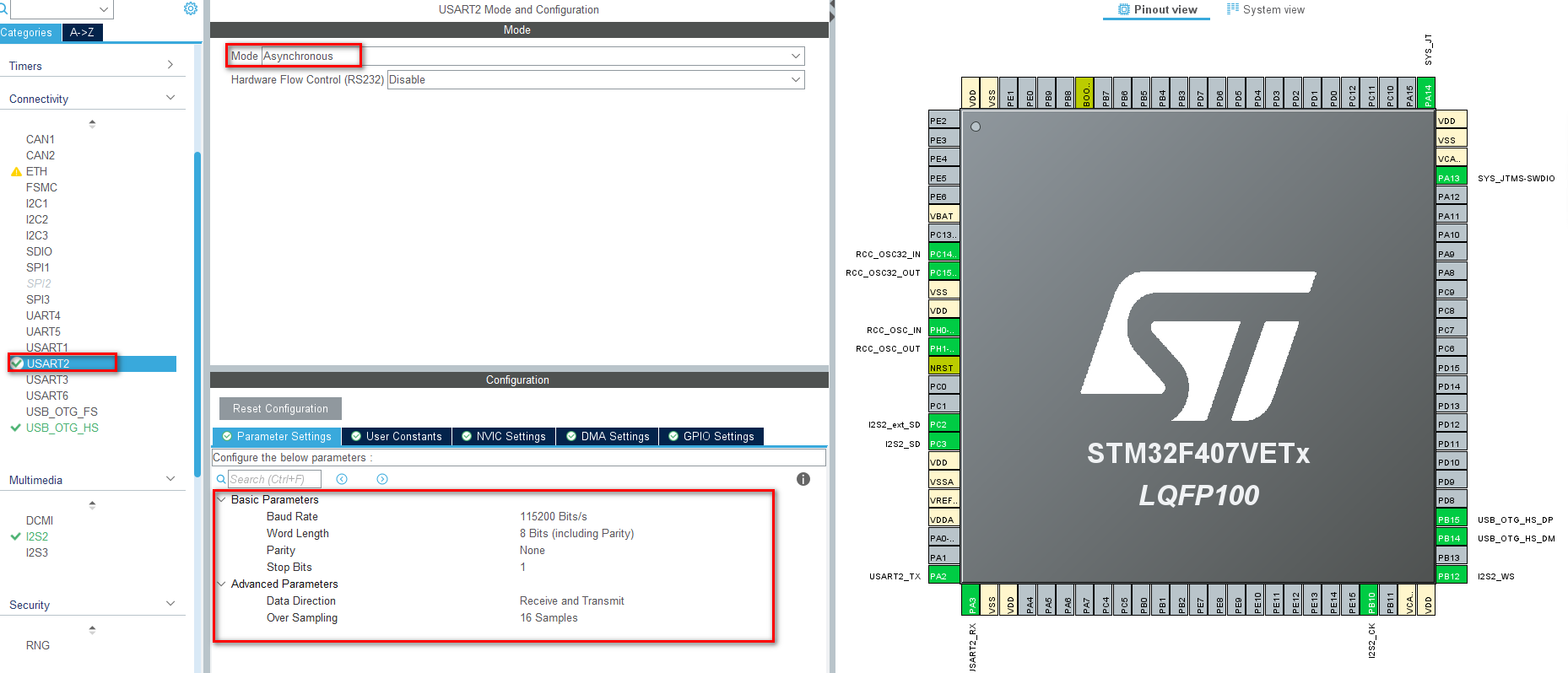
7、时钟配置
时钟配置那里点击解决时钟问题就会自动配置了,不配置外部晶振时钟的话这里USB是没有办法使用的:
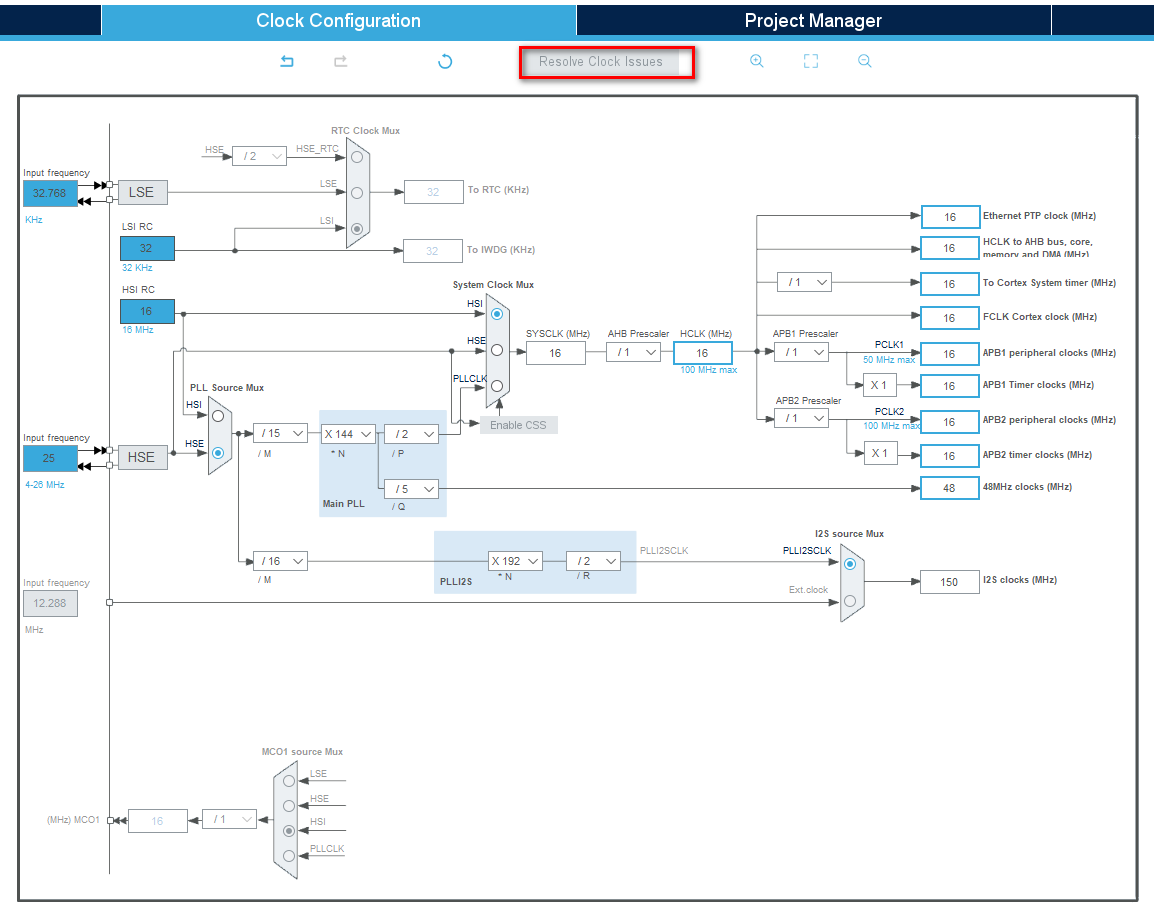
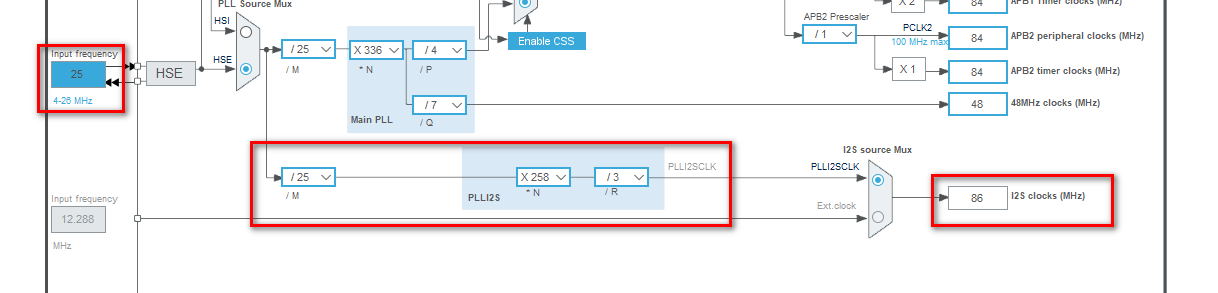
推荐的F4xx的i2s时钟配置(最后的音质调整具体进行了说明):
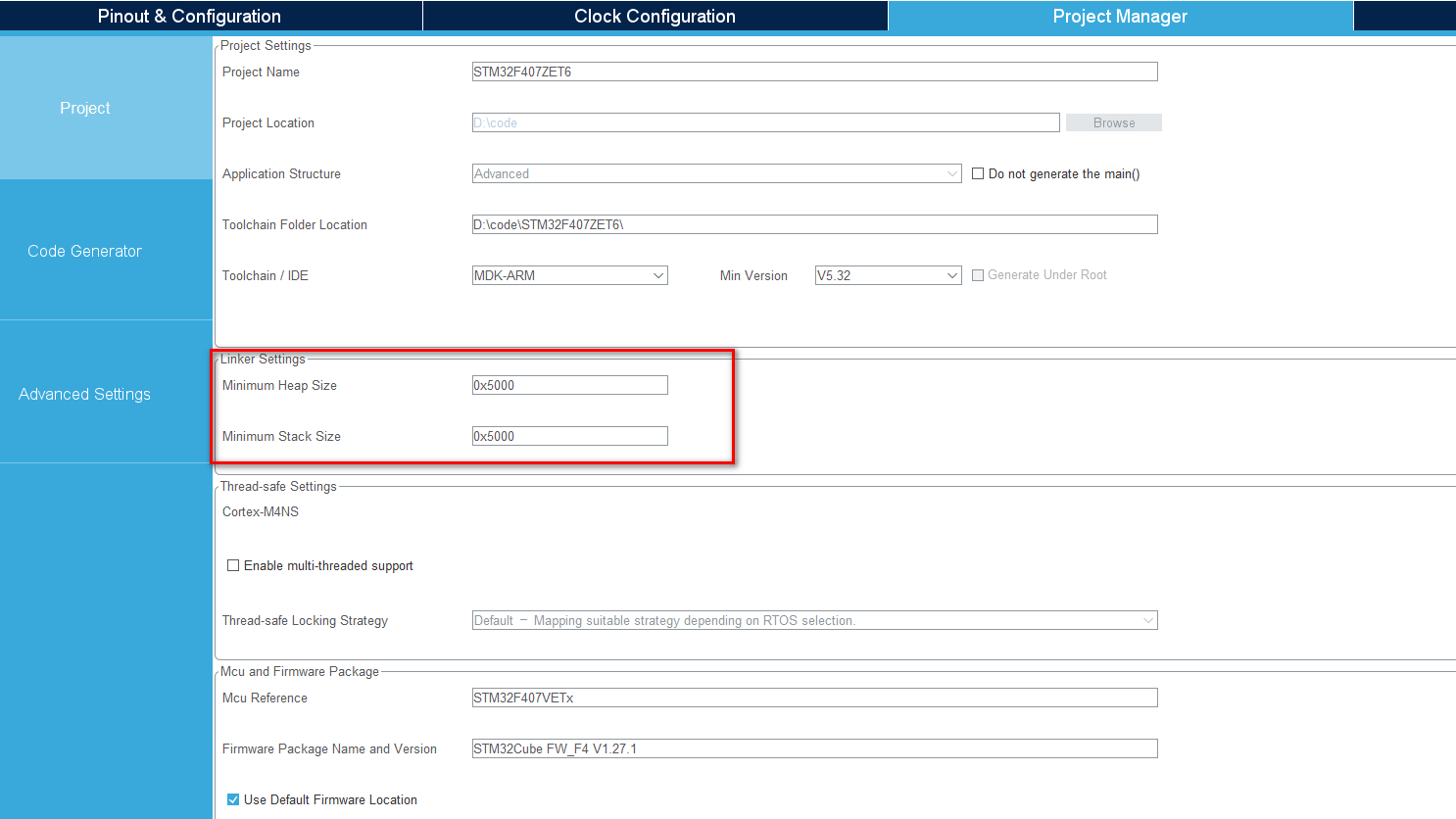
8、配置heap和stack
适当调高heap和stack,我们后面使用的fifo缓存使用malloc需要的heap较大。
之后生成代码即可。
五、MDK配置及程序
1、MDK配置
- 1.用keil打开STM32F411的程序,结果提示下面的问题,就是没有安装固件库,会自动跳转去安装,这个方式往往下载不成功,我们去官网手动下载安装:
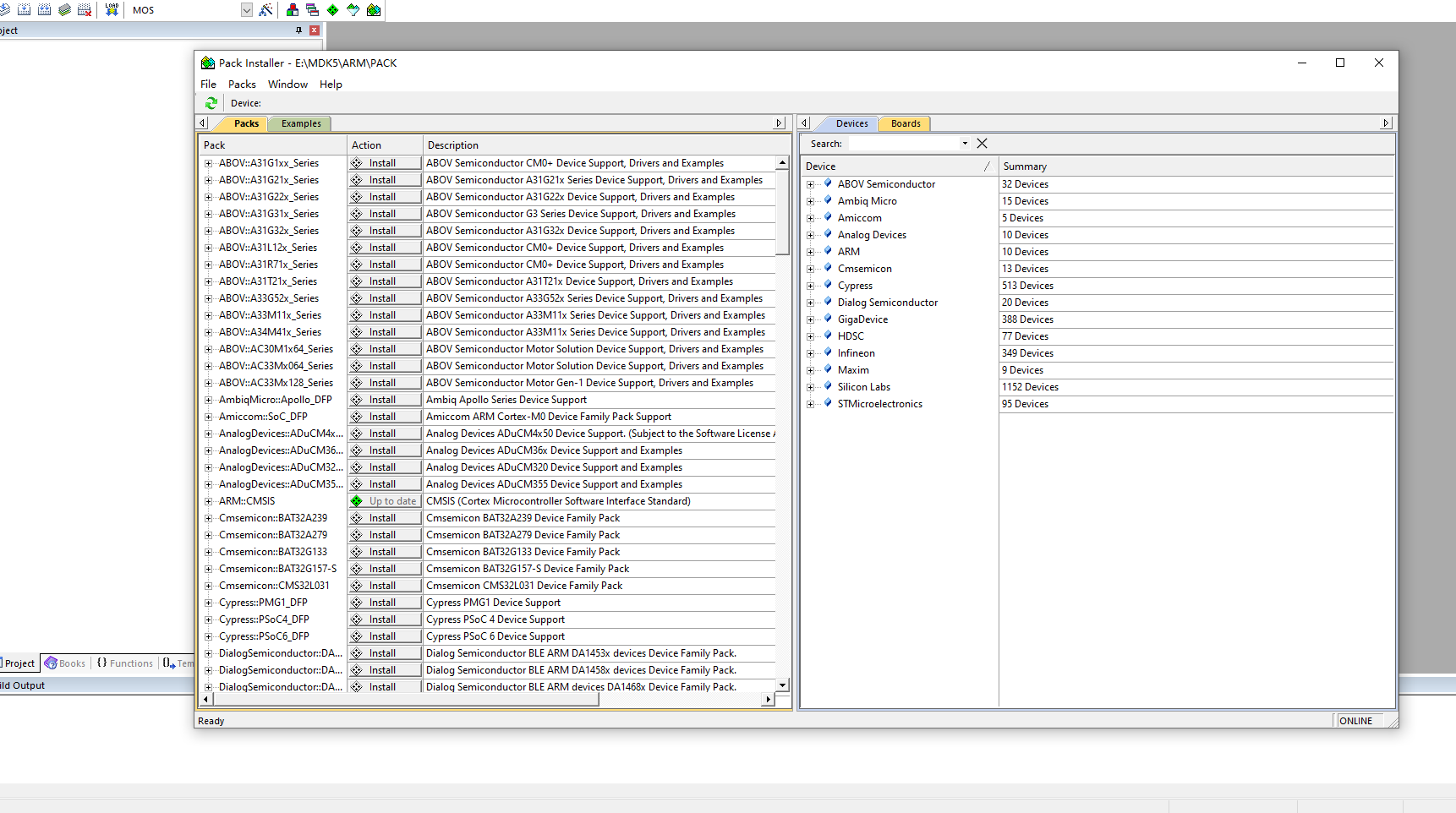
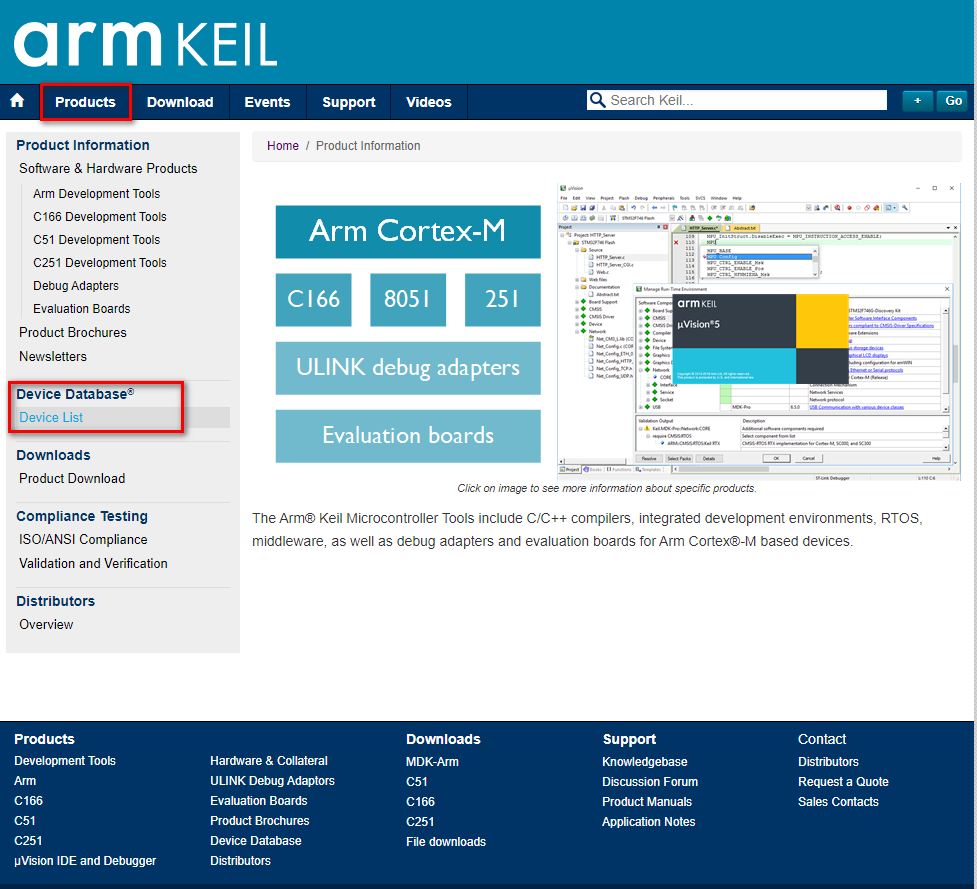
- 2.然后去keil官网下载对应的固件库,官网地址:https://www.keil.com/
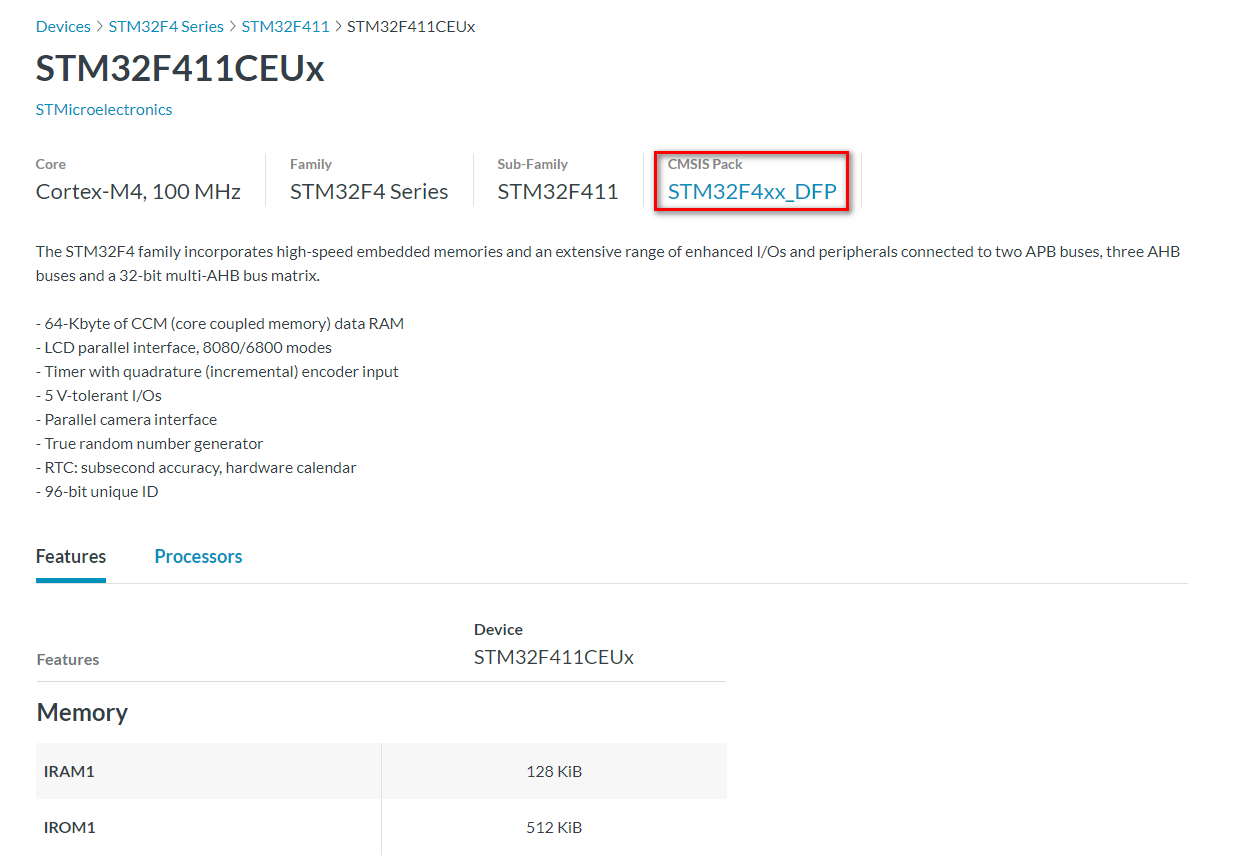
- 3.然后搜索对应的芯片类型,比如我这个就是STM32F411CEUx
下载对应pack即可:
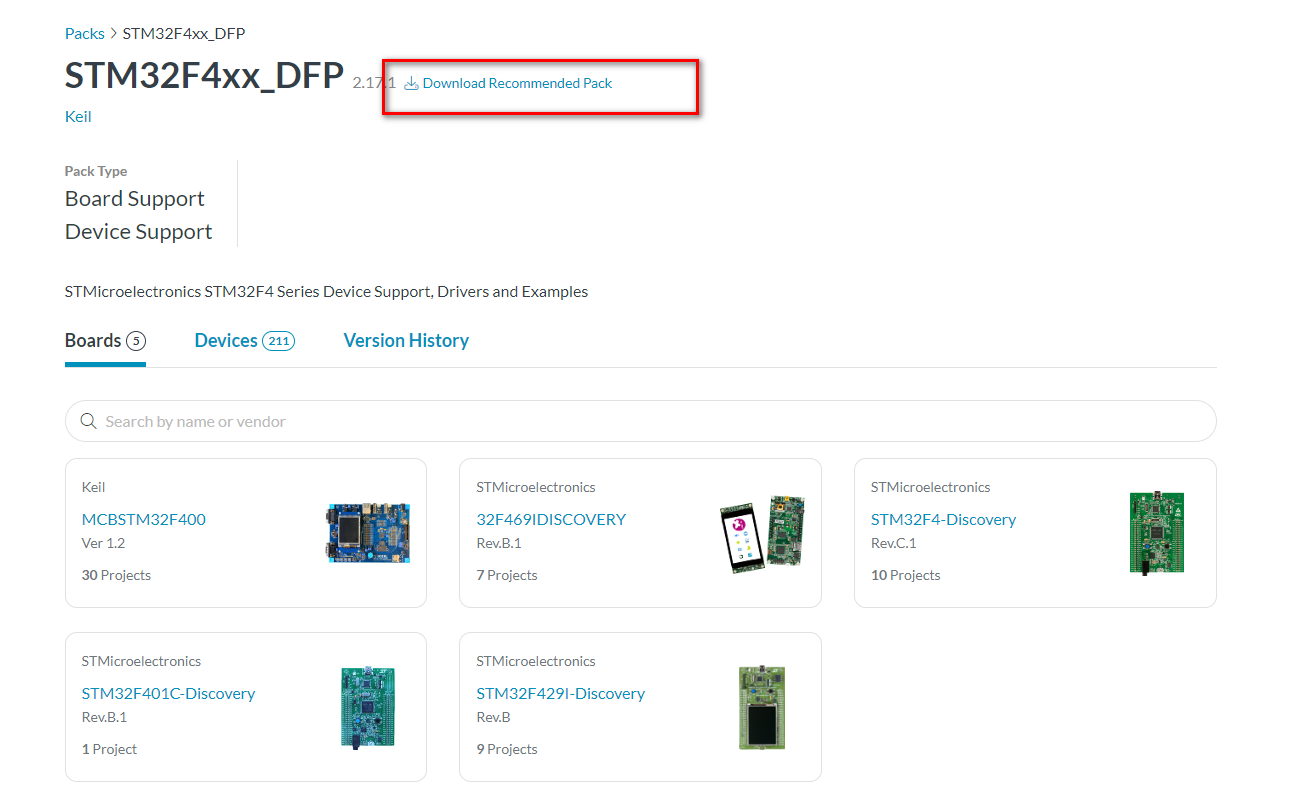
- 4.安装对应下载的xxx.pack,并且目录直接默认是keil安装的目录。
- 5.安装之后再次打开keil就不会报错了,可以看到已经安装的固件库
- 6.JLINK+SW配置(也有可能是ST-LINK等,根据具体板子配置即可)
点击魔法棒,选择Debug,使用J-LINK/J-TRACE Cortex:
之后设置SW端口并scan即可:
然后就可以下载以及debug调试程序了。
2、代码
测试时逻辑比较简单,对于录音:电脑端播放音频通过usb口传给音频测试板,mcu通过I2S接口读取音频内容,再通过usb的模拟串口连接并发送到电脑,在电脑的串口工具中存储接收到的二进制数据存储到文件中,通过工具播放pcm数据。对于放音:将之前的pcm数据获取一部分写死到程序数组中,程序运行时就开始调用I2S接口写入音频芯片,然后在电脑端听声音。(实际使用时会通过外部flash存储音频数据,后续会简单总结spi flash读写)
2.1 转换16进制的hex为pcm并进行播放(可以不需要,直接通过写入原始字节数据到文件后导入播放器播放)
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from scipy import signal
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
myfont = matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties(fname='C:\\Windows\\Fonts\\cambria.ttc')
filename = r'data.pcm'
filepath = r'.'
f = open(filepath + '\\' + filename)
if 0: # 这是ascii保存的数据格式
line = f.read()
data = [l.split(' ')[-1] for l in line.split('\n') if l]
data = [int(x) for x in data]
else: # 这是HEX保存的数据格式
line = f.read()[:-1]
print("buffer count", len(line))
data0 = np.array([int(x, base=16) for x in line.split(' ')])
data_1 = data0[0:len(data0):2]
data_2 = data0[1:len(data0):2]
data3 = data_2 * 0x100 + data_1
# data = np.frombuffer(data3, dtype=np.int16)
data = data3.astype(np.int16)
filename2 = filename + "_ascii.pcm"
f=open(filepath + '\\' + filename2, 'w')
np.savetxt(f, data, fmt="%i", newline='\n')
import sounddevice as sd
fs = 16000
src = data
sd.play(1*src/np.max(src), fs, blocking=True)
2.2 python接收串口数据直接写入到文件(i2s接收的音频数据通过串口转发出来)
import serial
def bytes2Hex(argv): # 十六进制显示 方法1
try:
result = ''
hLen = len(argv)
for i in range(hLen):
hvol = argv[i]
hhex = '%02x ' % hvol
result += hhex
except:
pass
return result
def read_com():
portx = "COM23"
bps = 12000000
try:
ser = serial.Serial(portx, bps)
print("串口详情参数:", ser)
with open("data.pcm", "wb") as binary_file:
while ser.isOpen():
data = ser.read(size=2)
if data:
binary_file.write(data)
print(data)
# num = ser.inWaiting() # 查询串口接收字节数据,非阻塞
# if num:
# line = ser.readline().decode()
# line = ser.read(num)
# content = bytes2Hex(line)
# content = str(line)
# content = str(line).strip('b').strip('\'')
# f.write(line)
# f.flush()
# f.write(content)
# print(line)
except:
pass
finally:
ser.close()
binary_filef.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
read_com()
2.3 python读取文件内容通过串口发送给stm32
import serial
def send_com():
portx = "COM28"
bps = 115200
try:
ser = serial.Serial(portx, bps)
print("串口详情参数:", ser)
with open("data.pcm", "rb") as binary_file:
while ser.is_open:
print("serieal open success")
data = binary_file.read(4)
if not data: break
print(data)
ser.write(data)
except:
pass
finally:
ser.close()
binary_file.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
send_com()
2.4 U盘状态判断(外挂U盘存储时使用)
printf("test...\n");
HAL_Delay(1000);
MX_USB_HOST_Process();
HAL_Delay(1000);
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
//判断USB是否进入准备状态APPLICATION_READY
switch(Appli_state)
{
/**
* The generated code from STM32CubeMX has two "confusing" application states
* APPLICATION_START on HOST_USER_CONNECTION and APPLICATION_READY on HOST_USER_CLASS_ACTIVE.
* Any FatFs commands should be executed after APPLICATION_STATE_READY is reached."
*/
case APPLICATION_READY:
printf("ready ok\n");
MSC_Application();
Appli_state = APPLICATION_IDLE;
break;
case APPLICATION_IDLE:
default:
break;
}
2.5 FATFS文件操作(U盘读写文件时使用)
FATFS USBDISKFatFs; /* File system object for USB disk logical drive */
FIL MyFile; /* File object */
extern ApplicationTypeDef Appli_state;
/**
* @brief Main routine for Mass Storage Class
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
//下面函数操作USB 文件读写,可根据需要修改,函数名可自定义
void MSC_Application(void) {
/* FatFs function common result code description: */
/* FR_OK = 0, (0) Succeeded */
/* FR_DISK_ERR, (1) A hard error occurred in the low level disk I/O layer */
/* FR_INT_ERR, (2) Assertion failed */
/* FR_NOT_READY, (3) The physical drive cannot work */
/* FR_NO_FILE, (4) Could not find the file */
/* FR_NO_PATH, (5) Could not find the path */
/* FR_INVALID_NAME, (6) The path name format is invalid */
/* FR_DENIED, (7) Access denied due to prohibited access or directory full */
/* FR_EXIST, (8) Access denied due to prohibited access */
/* FR_INVALID_OBJECT, (9) The file/directory object is invalid */
/* FR_WRITE_PROTECTED, (10) The physical drive is write protected */
/* FR_INVALID_DRIVE, (11) The logical drive number is invalid */
/* FR_NOT_ENABLED, (12) The volume has no work area */
/* FR_NO_FILESYSTEM, (13) There is no valid FAT volume */
/* FR_MKFS_ABORTED, (14) The f_mkfs() aborted due to any parameter error */
/* FR_TIMEOUT, (15) Could not get a grant to access the volume within defined period */
/* FR_LOCKED, (16) The operation is rejected according to thex file sharing policy */
/* FR_NOT_ENOUGH_CORE, (17) LFN working buffer could not be allocated */
/* FR_TOO_MANY_OPEN_FILES, (18) Number of open files > _FS_SHARE */
/* FR_INVALID_PARAMETER (19) Given parameter is invalid */
FRESULT res; /* FatFs function common result code */
uint32_t byteswritten, bytesread; /* File write/read counts */
uint8_t wtext[] = "Hello Test USB!"; /* File write buffer */
uint8_t rtext[100]; /* File read buffer */
/* Register the file system object to the FatFs module */
res = f_mount(&USBDISKFatFs, (TCHAR const *) USBHPath, 0);
if (res != FR_OK) {
/* FatFs Initialization Error */
USBH_UsrLog("f_mount error: %d", res);
Error_Handler();
}
USBH_UsrLog("create the file in: %s", USBHPath);
/* Create and Open a new text file object with write access */
res = f_open(&MyFile, "USBHost.txt", FA_CREATE_ALWAYS | FA_WRITE);
if (res != FR_OK) {
/* 'hello.txt' file Open for write Error */
USBH_UsrLog("f_open with write access error: %d", res);
Error_Handler();
}
/* Write data to the text file */
res = f_write(&MyFile, wtext, sizeof(wtext), (void *) &byteswritten);
if ((byteswritten == 0) || (res != FR_OK)) {
/* 'hello.txt' file Write or EOF Error */
USBH_UsrLog("file write or EOF error: %d", res);
Error_Handler();
}
/* Close the open text file */
f_close(&MyFile);
/* Open the text file object with read access */
res = f_open(&MyFile, "USBHost.txt", FA_READ);
if (res != FR_OK) {
/* 'hello.txt' file Open for read Error */
USBH_UsrLog("f_open with read access error: %d", res);
Error_Handler();
}
/* Read data from the text file */
res = f_read(&MyFile, rtext, sizeof(rtext), (void *) &bytesread);
if ((bytesread == 0) || (res != FR_OK)) {
/* 'hello.txt' file Read or EOF Error */
USBH_UsrLog("f_read error: %d", res);
Error_Handler();
}
/* Close the open text file */
f_close(&MyFile);
/* Compare read data with the expected data */
if ((bytesread != byteswritten)) {
/* Read data is different from the expected data */
USBH_UsrLog("file doesn't match");
Error_Handler();
}
/* Success of the demo: no error occurrence */
USBH_UsrLog("USBHost.txt was created into the disk");
/* Unlink the USB disk I/O driver */
FATFS_UnLinkDriver(USBHPath);
}
uint16_t dma[4] = {0};
uint8_t is_ready = 0;
void HAL_I2S_RxCpltCallback(I2S_HandleTypeDef *hi2s)
{
if(hi2s==&hi2s2){
if (dma[0] || dma[1]) {
if (is_ready) {
FRESULT res; /* FatFs function common result code */
/* Create and Open a new text file object with write access */
res = f_open(&MyFile, "data.pcm", FA_OPEN_EXISTING | FA_WRITE);
if (res != FR_OK) {
/* 'hello.txt' file Open for write Error */
USBH_UsrLog("f_open with write access error: %d", res);
Error_Handler();
}
/* 查找文件的结尾 */
res = f_lseek(&MyFile, f_size(&MyFile));
/* Write data to the text file */
uint32_t byteswritten;
printf("%02x%02x", dma[0], dma[1]);
res = f_write(&MyFile, (uint8_t *) &dma, 2, (void *) &byteswritten);
if ((byteswritten == 0) || (res != FR_OK)) {
USBH_UsrLog("file write or EOF error: %d", res);
Error_Handler();
}
f_close(&MyFile);
}
}
}
}
switch (Appli_state) {
/**
* The generated code from STM32CubeMX has two "confusing" application states
* APPLICATION_START on HOST_USER_CONNECTION and APPLICATION_READY on HOST_USER_CLASS_ACTIVE.
* Any FatFs commands should be executed after APPLICATION_STATE_READY is reached."
*/
case APPLICATION_READY:
printf("ready ok\n");
// MSC_Application();
FRESULT res; /* FatFs function common result code */
/* Register the file system object to the FatFs module */
res = f_mount(&USBDISKFatFs, (TCHAR const *) USBHPath, 0);
if (res != FR_OK) {
/* FatFs Initialization Error */
USBH_UsrLog("f_mount error: %d", res);
Error_Handler();
}
USBH_UsrLog("create the file in: %s", USBHPath);
/* Create and Open a new text file object with write access */
res = f_open(&MyFile, "data.pcm", FA_CREATE_ALWAYS | FA_WRITE);
if (res != FR_OK) {
/* 'hello.txt' file Open for write Error */
USBH_UsrLog("f_open with write access error: %d", res);
Error_Handler();
}
f_close(&MyFile);
HAL_I2S_Receive_DMA(&hi2s2, dma, sizeof(dma));
Appli_state = APPLICATION_IDLE;
is_ready = 1;
break;
case APPLICATION_IDLE:
break;
case APPLICATION_DISCONNECT:
FATFS_UnLinkDriver(USBHPath);
is_ready = 0;
Appli_state = APPLICATION_IDLE;
break;
default:
break;
}
2.6 fifo缓存实现(解决i2s dma读写和存储读写时速度不对等问题)
//******************************************************************************************
//!
//! \file FIFO.h
//! \brief Genernal FIFO Model Interface.
//! You can use uniform FIFO Model to manager Any type of data element.
//! \author cedar
//! \changed damom.li
//! \changed sky.huang
//! \date 2016-11-03
//! \email xuesong5825718@gmail.com
//!
//! \version: 1.1 add fifo_s_gets_noprotect function
//!
//! Copyright (c) 2013 Cedar MIT License
//!
//! Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
//! of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
//! in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to
//! use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of
//! the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so,
//! subject to the following conditions:
//!
//! The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
//! copies or substantial portions of the Software.
//!
//! THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
//! IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
//! FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
//! AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
//! LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
//! OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS
//! IN THE SOFTWARE.
///
//******************************************************************************************
#ifndef __FIFO_H__
#define __FIFO_H__
#ifdef __cplusplus
"C"
{
#endif
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MUTEX_DECLARE(mutex) unsigned long mutex
#define MUTEX_INIT(mutex) do{mutex = 0;}while(0)
#define MUTEX_LOCK(mutex) do{__disable_irq();}while(0)
#define MUTEX_UNLOCK(mutex) do{__enable_irq();}while(0)
//******************************************************************************************
//! CONFIGURE MACRO
//******************************************************************************************
#define FIFO_NDEBUG
#define USE_DYNAMIC_MEMORY //!< Use system malloc/free function
//******************************************************************************************
//! Macro Function
//******************************************************************************************
//******************************************************************************************
//! PUBLIC TYPE
//******************************************************************************************
//! FIFO Memory Model (Single Byte Mode)
typedef struct
{
char *p_start_addr; //!< FIFO Memory Pool Start Address
char *p_end_addr; //!< FIFO Memory Pool End Address
int free_num; //!< The remain capacity of FIFO
int used_num; //!< The number of elements in FIFO
char *p_read_addr; //!< FIFO Data Read Index Pointer
char *p_write_addr; //!< FIFO Data Write Index Pointer
MUTEX_DECLARE(mutex);
} fifo_s_t;
//! FIFO Memory Model
typedef struct
{
char *p_start_addr; //!< FIFO Memory Pool Start Address
char *p_end_addr; //!< FIFO Memory Pool End Address
int free_num; //!< The remain capacity of FIFO
int used_num; //!< The number of elements in FIFO
int unit_size; //!< FIFO Element Size(Unit: Byte)
char *p_read_addr; //!< FIFO Data Read Index Pointer
char *p_write_addr; //!< FIFO Data Write Index Pointer
MUTEX_DECLARE(mutex);
} fifo_t;
//******************************************************************************************
//! PUBLIC API
//******************************************************************************************
#ifdef USE_DYNAMIC_MEMORY
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Create An New FIFO Instance(in Single Mode).
//! This function allocate enought room for N blocks fifo elements, then return the pointer
//! of FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] uint_cnt is count of fifo elements.
//! \retval The Pointer of FIFO instance, return NULL is failure to allocate memory.
//!
//! \note -# You must enable USE_MEMORY_ALLOC macro and ensure your system have <stdlib.h>
//! Header file before use this function.
//! \note -# Functions FIFO_Create and FIFO_Destory must be used in pairs.
//!
//******************************************************************************************
fifo_s_t *fifo_s_create(int uint_cnt);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Destory FIFO Instance(in Single Mode).
//! This function release memory, then reinit the FIFO struct.
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of FIFO instance
//! \retval None.
//!
//! \note -# You must enable USE_MEMORY_ALLOC macro and ensure your system have <stdlib.h>
//! Header file before use this function.
//
//******************************************************************************************
void fifo_s_destroy(fifo_s_t *p_fifo);
#endif // USE_DYNAMIC_MEMORY
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Initialize an static FIFO struct(in single mode).
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO instance.
//! \param [in] p_base_addr is the base address of pre-allocate memory, such as array.
//! \param [in] uint_cnt is count of fifo elements.
//! \retval 0 if initialize successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_init(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, void *p_base_addr, int uint_cnt);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Put an element into FIFO(in single mode).
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [in] element is the data element you want to put
//!
//! \retval 0 if operate successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_put(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char element);
int fifo_s_puts(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char *p_source, int len);
int fifo_s_puts_noprotect(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char *p_source, int len);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get an element from FIFO(in single mode).
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval the data element of FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
char fifo_s_get(fifo_s_t *p_fifo);
int fifo_s_gets(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char *p_dest, int len);
int fifo_s_gets_noprotect(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char *p_dest, int len);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Pre-Read an element from FIFO(in single mode).
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [in] Offset is the offset from current pointer.
//!
//! \retval the data element of FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
char fifo_s_preread(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, int offset);
int fifo_s_prereads(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char *p_dest, int offset, int len);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief FIFO is empty (in single mode)?
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval - None-zero(true) if empty.
//! - Zero(false) if not empty.
//
//******************************************************************************************
char fifo_s_isempty(fifo_s_t *p_fifo);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief FIFO is full (in single mode)?
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval - None-zero(true) if full.
//! - Zero(false) if not full.
//
//******************************************************************************************
char fifo_s_isfull(fifo_s_t *p_fifo);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get FIFO the number of elements(in single mode)?
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval The number of elements in FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_used(fifo_s_t *p_fifo);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get FIFO the number of elements(in single mode)?
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval The number of elements in FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_free(fifo_s_t *p_fifo);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Flush the content of FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval 0 if success, -1 if failure.
//
//******************************************************************************************
void fifo_s_flush(fifo_s_t *p_fifo);
int fifo_s_discard(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, int len);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Create An New FIFO Instance.
//! This function allocate enought room for N blocks fifo elements, then return the pointer
//! of FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] UnitSize is fifo element size.
//! \param [in] UnitCnt is count of fifo elements.
//! \retval The Pointer of FIFO instance, return NULL is failure to allocate memory.
//!
//! \note -# You must enable USE_MEMORY_ALLOC macro and ensure your system have <stdlib.h>
//! Header file before use this function.
//! \note -# Functions FIFO_Create and FIFO_Destory must be used in pairs.
//!
//******************************************************************************************
fifo_t *fifo_create(char unit_size, int unit_cnt);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Destory FIFO Instance.
//! This function release memory, then reinit the FIFO struct.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of FIFO instance
//! \retval None.
//!
//! \note -# You must enable USE_MEMORY_ALLOC macro and ensure your system have <stdlib.h>
//! Header file before use this function.
//
//******************************************************************************************
void fifo_destory(fifo_t *p_fifo);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Initialize an static FIFO struct.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO instance.
//! \param [in] pBaseAddr is the base address of pre-allocate memory, such as array.
//! \param [in] UnitSize is fifo element size.
//! \param [in] UnitCnt is count of fifo elements.
//! \retval 0 if initialize successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_init(fifo_t *p_fifo, void *p_base_addr, char unit_size, int unit_cnt);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Put an element into FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [in] pElement is the address of element you want to put
//!
//! \retval 0 if operate successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_put(fifo_t *p_fifo, void *p_element);
int fifo_put_noprotect(fifo_t *p_fifo, void *p_element);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get an element from FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [out] pElement is the address of element you want to get
//!
//! \retval 0 if operate successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_get(fifo_t *p_fifo, void *p_element);
int fifo_get_noprotect(fifo_t *p_fifo, void *p_element);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Pre-Read an element from FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [in] Offset is the offset from current pointer.
//! \param [out] pElement is the address of element you want to get
//!
//! \retval 0 if operate successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_pre_read(fifo_t *p_fifo, char offset, void *p_element);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief FIFO is empty ?
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval - None-zero(true) if empty.
//! - Zero(false) if not empty.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_is_empty(fifo_t *p_fifo);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief FIFO is full ?
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval - None-zero(true) if full.
//! - Zero(false) if not full.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_is_full(fifo_t *p_fifo);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get FIFO the number of elements?
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval The number of elements in FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_used(fifo_t *p_fifo);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get FIFO the number of elements?
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval The number of elements in FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_free(fifo_t *p_fifo);
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Flush the content of FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval 0 if success, -1 if failure.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_flush(fifo_t *p_fifo);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif // __FIFO_H__
//******************************************************************************************
//!
//! \file FIFO.c
//! \brief Genernal FIFO Model Interface.
//! You can use uniform FIFO Model to manager Any type of data element.
//! \author cedar
//! \changed damom.li
//! \changed sky.huang
//! \date 2016-11-03//! \date 2013-12-16
//! \email xuesong5825718@gmail.com
//!
//! \version: 1.1 add fifo_s_gets_noprotect function
//!
//! Copyright (c) 2013 Cedar MIT License
//!
//! Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
//! of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
//! in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to
//! use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of
//! the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so,
//! subject to the following conditions:
//!
//! The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
//! copies or substantial portions of the Software.
//!
//! THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
//! IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
//! FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
//! AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
//! LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
//! OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS
//! IN THE SOFTWARE.
///
//******************************************************************************************
#include "fifo.h"
//******************************************************************************************
//! ASSERT MACRO
//******************************************************************************************
#ifndef ASSERT
#ifdef FIFO_NDEBUG
#define ASSERT(x)
#else
#define ASSERT(x) \
do \
{ \
if (!(x)) \
printf("[assert]: %s, %d", __FILE__, __LINE__); \
while (!(x)) \
; \
} while (0)
#endif
#endif // ASSERT
#ifdef USE_DYNAMIC_MEMORY
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Create An New FIFO Instance(in Single Mode).
//! This function allocate enought room for N blocks fifo elements, then return the pointer
//! of FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] uint_cnt is count of fifo elements.
//! \retval The Pointer of FIFO instance, return NULL is failure to allocate memory.
//!
//! \note -# You must enable USE_MEMORY_ALLOC macro and ensure your system have <stdlib.h>
//! Header file before use this function.
//! \note -# Functions FIFO_Create and FIFO_Destory must be used in pairs.
//!
//******************************************************************************************
fifo_s_t *fifo_s_create(int uint_cnt)
{
fifo_s_t *p_fifo = NULL; //!< FIFO Pointer
char *p_base_addr = NULL; //!< Memory Base Address
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(uint_cnt);
//! Allocate Memory for pointer of new FIFO Control Block
p_fifo = (fifo_s_t *)malloc(sizeof(fifo_s_t));
if (NULL == p_fifo)
{
//! Allocate Failure, exit now
return (NULL);
}
//! Allocate Memory for pointer of new FIFO
p_base_addr = malloc(uint_cnt);
if (NULL == p_base_addr)
{
//! Allocate Failure, exit now
free(p_fifo);
return (NULL);
}
//! Initialize General FIFO Module
fifo_s_init(p_fifo, p_base_addr, uint_cnt);
return (p_fifo);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Destory FIFO Instance(in Single Mode).
//! This function release memory, then reinit the FIFO struct.
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of FIFO instance
//! \retval None.
//!
//! \note -# You must enable USE_MEMORY_ALLOC macro and ensure your system have <stdlib.h>
//! Header file before use this function.
//
//******************************************************************************************
void fifo_s_destroy(fifo_s_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
ASSERT(p_fifo->p_start_addr);
//! Free FIFO memory
free(p_fifo->p_start_addr);
//! Free FIFO Control Block memory
free(p_fifo);
return; //!< Success
}
#endif // USE_DYNAMIC_MEMORY
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Initialize an static FIFO struct(in single mode).
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO instance.
//! \param [in] p_base_addr is the base address of pre-allocate memory, such as array.
//! \param [in] uint_cnt is count of fifo elements.
//! \retval 0 if initialize successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_init(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, void *p_base_addr, int uint_cnt)
{
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
ASSERT(p_base_addr);
ASSERT(uint_cnt);
//! Initialize FIFO Control Block.
p_fifo->p_start_addr = (char *)p_base_addr;
p_fifo->p_end_addr = (char *)p_base_addr + uint_cnt - 1;
p_fifo->free_num = uint_cnt;
p_fifo->used_num = 0;
p_fifo->p_read_addr = (char *)p_base_addr;
p_fifo->p_write_addr = (char *)p_base_addr;
//! Inint mutex for new FIFO
MUTEX_INIT(p_fifo->mutex);
return (0);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Put an element into FIFO(in single mode).
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [in] element is the data element you want to put
//!
//! \retval 0 if operate successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_put(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char element)
{
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
if (0 == p_fifo->free_num)
{
//! Error, FIFO is full!
return (-1);
}
MUTEX_LOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
if (0 == p_fifo->free_num)
{
//! Error, FIFO is full!
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return (-1);
}
if (p_fifo->p_write_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
p_fifo->p_write_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
}
*(p_fifo->p_write_addr) = element;
p_fifo->p_write_addr++;
p_fifo->free_num--;
p_fifo->used_num++;
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return (0);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Put some elements into FIFO(in single mode).
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [in] p_source is the data element you want to put
//! \param [in] the number of elements
//! \retval the number of really write data, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_puts(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char *p_source, int len)
{
int retval;
int len_to_end;
int len_from_start;
ASSERT(p_fifo);
if (NULL == p_source)
{
return -1;
}
if (0 == p_fifo->free_num)
{
return 0;
}
MUTEX_LOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
if (0 == p_fifo->free_num)
{
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return 0;
}
if (p_fifo->p_write_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
p_fifo->p_write_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
}
len = (len < p_fifo->free_num) ? len : p_fifo->free_num;
len_to_end = p_fifo->p_end_addr - p_fifo->p_write_addr + 1;
if (len_to_end >= len) //no rollback
{
len_to_end = len;
memcpy(p_fifo->p_write_addr, p_source, len_to_end);
p_fifo->p_write_addr += len_to_end;
}
else //rollback
{
len_from_start = len - len_to_end;
memcpy(p_fifo->p_write_addr, p_source, len_to_end);
memcpy(p_fifo->p_start_addr, p_source + len_to_end, len_from_start);
p_fifo->p_write_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr + len_from_start;
}
p_fifo->free_num -= len;
p_fifo->used_num += len;
retval = len;
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return retval;
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Put some elements into FIFO, ingnore the interrupt
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [in] p_source is the data element you want to put
//! \param [in] the number of elements
//! \retval the number of really write data, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_puts_noprotect(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char *p_source, int len)
{
int retval;
int len_to_end;
int len_from_start;
ASSERT(p_fifo);
if (NULL == p_source)
{
return -1;
}
if (0 == p_fifo->free_num)
{
return 0;
}
if (p_fifo->p_write_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
p_fifo->p_write_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
}
len = (len < p_fifo->free_num) ? len : p_fifo->free_num;
len_to_end = p_fifo->p_end_addr - p_fifo->p_write_addr + 1;
if (len_to_end >= len) //no rollback
{
len_to_end = len;
memcpy(p_fifo->p_write_addr, p_source, len_to_end);
p_fifo->p_write_addr += len_to_end;
}
else //rollback
{
len_from_start = len - len_to_end;
memcpy(p_fifo->p_write_addr, p_source, len_to_end);
memcpy(p_fifo->p_start_addr, p_source + len_to_end, len_from_start);
p_fifo->p_write_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr + len_from_start;
}
p_fifo->free_num -= len;
p_fifo->used_num += len;
retval = len;
return retval;
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get an element from FIFO(in single mode).
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval the data element of FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
char fifo_s_get(fifo_s_t *p_fifo)
{
char retval = 0;
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
//TODO:
if (0 == p_fifo->used_num)
{
return 0;
}
MUTEX_LOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
if (0 == p_fifo->used_num)
{
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return 0;
}
if (p_fifo->p_read_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
p_fifo->p_read_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
}
retval = *p_fifo->p_read_addr;
// Update information
p_fifo->p_read_addr++;
p_fifo->free_num++;
p_fifo->used_num--;
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return (retval);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get some element from FIFO(in single mode).
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval the number of really read data.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_gets(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char *p_dest, int len)
{
int retval;
int len_to_end;
int len_from_start;
ASSERT(p_fifo);
if (NULL == p_dest)
{
return -1;
}
if (0 == p_fifo->used_num)
{
return 0;
}
MUTEX_LOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
if (0 == p_fifo->used_num)
{
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return 0;
}
if (p_fifo->p_read_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
p_fifo->p_read_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
}
len = (len < p_fifo->used_num) ? len : p_fifo->used_num;
len_to_end = p_fifo->p_end_addr - p_fifo->p_read_addr + 1;
if (len_to_end >= len) //no rollback
{
len_to_end = len;
memcpy(p_dest, p_fifo->p_read_addr, len_to_end);
p_fifo->p_read_addr += len_to_end;
}
else //rollback
{
len_from_start = len - len_to_end;
memcpy(p_dest, p_fifo->p_read_addr, len_to_end);
memcpy(p_dest + len_to_end, p_fifo->p_start_addr, len_from_start);
p_fifo->p_read_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr + len_from_start;
}
p_fifo->free_num += len;
p_fifo->used_num -= len;
retval = len;
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return retval;
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get some element from FIFO(in single mode).
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval the number of really read data.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_gets_noprotect(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char *p_dest, int len)
{
int retval;
int len_to_end;
int len_from_start;
ASSERT(p_fifo);
if (NULL == p_dest)
{
return -1;
}
if (0 == p_fifo->used_num)
{
return 0;
}
if (p_fifo->p_read_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
p_fifo->p_read_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
}
len = (len < p_fifo->used_num) ? len : p_fifo->used_num;
len_to_end = p_fifo->p_end_addr - p_fifo->p_read_addr + 1;
if (len_to_end >= len) //no rollback
{
len_to_end = len;
memcpy(p_dest, p_fifo->p_read_addr, len_to_end);
p_fifo->p_read_addr += len_to_end;
}
else //rollback
{
len_from_start = len - len_to_end;
memcpy(p_dest, p_fifo->p_read_addr, len_to_end);
memcpy(p_dest + len_to_end, p_fifo->p_start_addr, len_from_start);
p_fifo->p_read_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr + len_from_start;
}
p_fifo->free_num += len;
p_fifo->used_num -= len;
retval = len;
return retval;
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Pre-Read an element from FIFO(in single mode).
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [in] Offset is the offset from current pointer.
//!
//! \retval the data element of FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
char fifo_s_preread(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, int offset)
{
char *tmp_read_addr;
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
if (offset > p_fifo->used_num)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
// Move Read Pointer to right position
tmp_read_addr = p_fifo->p_read_addr + offset;
if (tmp_read_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
tmp_read_addr = tmp_read_addr - p_fifo->p_end_addr + p_fifo->p_start_addr - 1;
}
return *tmp_read_addr;
}
}
/*
*
*
*
*
*/
int fifo_s_prereads(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, char *p_dest, int offset, int len)
{
int retval;
char *tmp_read_addr;
int len_to_end;
int len_from_start;
ASSERT(p_fifo);
if (NULL == p_dest)
{
return -1;
}
if (0 == p_fifo->used_num)
{
return -1;
}
if (offset >= p_fifo->used_num)
{
return -1;
}
MUTEX_LOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
if (0 == p_fifo->used_num)
{
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return -1;
}
if (offset >= p_fifo->used_num)
{
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return -1;
}
tmp_read_addr = p_fifo->p_read_addr + offset;
if (tmp_read_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
tmp_read_addr = tmp_read_addr - p_fifo->p_end_addr + p_fifo->p_start_addr - 1;
}
len = (len < (p_fifo->used_num - offset)) ? len : (p_fifo->used_num - offset);
len_to_end = p_fifo->p_end_addr - tmp_read_addr + 1;
if (len_to_end >= len) //no rollback
{
len_to_end = len;
memcpy(p_dest, tmp_read_addr, len_to_end);
}
else //rollback
{
len_from_start = len - len_to_end;
memcpy(p_dest, tmp_read_addr, len_to_end);
memcpy(p_dest + len_to_end, p_fifo->p_start_addr, len_from_start);
}
retval = len;
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return retval;
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief FIFO is empty (in single mode)?
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval - None-zero(true) if empty.
//! - Zero(false) if not empty.
//
//******************************************************************************************
char fifo_s_isempty(fifo_s_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameter.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
return (p_fifo->used_num ? 0 : 1);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief FIFO is full (in single mode)?
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval - None-zero(true) if full.
//! - Zero(false) if not full.
//
//******************************************************************************************
char fifo_s_isfull(fifo_s_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameter.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
return (p_fifo->free_num ? 0 : 1);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get FIFO the number of elements(in single mode)?
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval The number of elements in FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_used(fifo_s_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameter.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
return p_fifo->used_num;
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get FIFO the number of elements(in single mode)?
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval The number of elements in FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_s_free(fifo_s_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameter.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
return p_fifo->free_num;
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Flush the content of FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] p_fifo is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval 0 if success, -1 if failure.
//
//******************************************************************************************
void fifo_s_flush(fifo_s_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
//! Initialize FIFO Control Block.
MUTEX_LOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
p_fifo->free_num = p_fifo->p_end_addr - p_fifo->p_start_addr + 1;
p_fifo->used_num = 0;
p_fifo->p_read_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
p_fifo->p_write_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
}
int fifo_s_discard(fifo_s_t *p_fifo, int len)
{
//! Check input parameters.
char *tmp_index;
ASSERT(p_fifo);
MUTEX_LOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
if (len > p_fifo->used_num)
{
len = p_fifo->used_num;
}
tmp_index = len + p_fifo->p_read_addr;
if (tmp_index > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
tmp_index = tmp_index - p_fifo->p_end_addr + p_fifo->p_start_addr - 1;
}
p_fifo->p_read_addr = tmp_index;
p_fifo->free_num += len;
p_fifo->used_num -= len;
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return len;
}
#ifdef USE_DYNAMIC_MEMORY
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Create An New FIFO Instance.
//! This function allocate enought room for N blocks fifo elements, then return the pointer
//! of FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] UnitSize is fifo element size.
//! \param [in] UnitCnt is count of fifo elements.
//! \retval The Pointer of FIFO instance, return NULL is failure to allocate memory.
//!
//! \note -# You must enable USE_MEMORY_ALLOC macro and ensure your system have <stdlib.h>
//! Header file before use this function.
//! \note -# Functions FIFO_Create and FIFO_Destory must be used in pairs.
//!
//******************************************************************************************
fifo_t *fifo_create(char unit_size, int unit_cnt)
{
fifo_t *p_fifo = NULL; //!< FIFO Pointer
char *p_base_addr = NULL; //!< Memory Base Address
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(unit_size);
ASSERT(unit_cnt);
//! Allocate Memory for pointer of new FIFO Control Block.
p_fifo = (fifo_t *)malloc(sizeof(fifo_t));
if (NULL == p_fifo)
{
//! Allocate Failure, exit now.
return (NULL);
}
//! Allocate memory for FIFO.
p_base_addr = malloc(unit_size * unit_cnt);
if (NULL == p_base_addr)
{
//! Allocate Failure, exit now.
free(p_fifo);
return (NULL);
}
//! Initialize General FIFO Module.
fifo_init(p_fifo, p_base_addr, unit_size, unit_cnt);
return (p_fifo);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Destory FIFO Instance.
//! This function release memory, then reinit the FIFO struct.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of FIFO instance
//! \retval None.
//!
//! \note -# You must enable USE_MEMORY_ALLOC macro and ensure your system have <stdlib.h>
//! Header file before use this function.
//
//******************************************************************************************
void fifo_destory(fifo_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
ASSERT(p_fifo->p_start_addr);
//! Free FIFO memory
free(p_fifo->p_start_addr);
//! Free FIFO Control Block memory.
free(p_fifo);
return; //!< Success
}
#endif // USE_DYNAMIC_MEMORY
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Initialize an static FIFO struct.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO instance.
//! \param [in] pBaseAddr is the base address of pre-allocate memory, such as array.
//! \param [in] UnitSize is fifo element size.
//! \param [in] UnitCnt is count of fifo elements.
//! \retval 0 if initialize successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_init(fifo_t *p_fifo, void *p_base_addr, char unit_size, int unit_cnt)
{
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
ASSERT(p_base_addr);
ASSERT(unit_size);
ASSERT(unit_cnt);
//! Initialize FIFO Control Block.
p_fifo->p_start_addr = (char *)p_base_addr;
p_fifo->p_end_addr = (char *)p_base_addr + unit_size * unit_cnt - 1;
p_fifo->free_num = unit_cnt;
p_fifo->used_num = 0;
p_fifo->unit_size = unit_size;
p_fifo->p_read_addr = (char *)p_base_addr;
p_fifo->p_write_addr = (char *)p_base_addr;
MUTEX_INIT(p_fifo->mutex);
return (0);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Put an element into FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [in] pElement is the address of element you want to put
//!
//! \retval 0 if operate successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_put(fifo_t *p_fifo, void *p_element)
{
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
ASSERT(p_element);
// Full ?
if (0 == p_fifo->free_num)
{
//! Error, FIFO is full!
return (-1);
}
//! Copy Data
MUTEX_LOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
if (0 == p_fifo->free_num)
{
//! Error, FIFO is full!
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return (-1);
}
if (p_fifo->p_write_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
p_fifo->p_write_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
}
memcpy(p_fifo->p_write_addr, p_element, p_fifo->unit_size);
p_fifo->p_write_addr += p_fifo->unit_size;
p_fifo->free_num--;
p_fifo->used_num++;
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return (0);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Put an element into FIFO without protect.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [in] pElement is the address of element you want to put
//!
//! \retval 0 if operate successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_put_noprotect(fifo_t *p_fifo, void *p_element)
{
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
ASSERT(p_element);
// Full ?
if (0 == p_fifo->free_num)
{
//! Error, FIFO is full!
return (-1);
}
if (p_fifo->p_write_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
p_fifo->p_write_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
}
memcpy(p_fifo->p_write_addr, p_element, p_fifo->unit_size);
p_fifo->p_write_addr += p_fifo->unit_size;
p_fifo->free_num--;
p_fifo->used_num++;
return (0);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get an element from FIFO without protect.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [out] pElement is the address of element you want to get
//!
//! \retval 0 if operate successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_get(fifo_t *p_fifo, void *p_element)
{
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
ASSERT(p_element);
// Empty ?
if (0 == p_fifo->used_num)
{
//! Error, FIFO is Empty!
return (-1);
}
//! Copy Data
MUTEX_LOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
if (0 == p_fifo->used_num)
{
//! Error, FIFO is Empty!
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return (-1);
}
if (p_fifo->p_read_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
p_fifo->p_read_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
}
memcpy(p_element, p_fifo->p_read_addr, p_fifo->unit_size);
p_fifo->p_read_addr += p_fifo->unit_size;
p_fifo->free_num++;
p_fifo->used_num--;
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return (0);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get an element from FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [out] pElement is the address of element you want to get
//!
//! \retval 0 if operate successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_get_noprotect(fifo_t *p_fifo, void *p_element)
{
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
ASSERT(p_element);
// Empty ?
if (0 == p_fifo->used_num)
{
//! Error, FIFO is Empty!
return (-1);
}
if (p_fifo->p_read_addr > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
p_fifo->p_read_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
}
memcpy(p_element, p_fifo->p_read_addr, p_fifo->unit_size);
p_fifo->p_read_addr += p_fifo->unit_size;
p_fifo->free_num++;
p_fifo->used_num--;
return (0);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Pre-Read an element from FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//! \param [in] Offset is the offset from current pointer.
//! \param [out] pElement is the address of element you want to get
//!
//! \retval 0 if operate successfully, otherwise return -1.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_pre_read(fifo_t *p_fifo, char offset, void *p_element)
{
char *_pre_red_index = (void *)0;
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
ASSERT(p_element);
// OverFlow ?
if (offset >= p_fifo->used_num)
{
return (-1);
}
// Move Read Pointer to right position
_pre_red_index = p_fifo->p_read_addr + p_fifo->unit_size * offset;
while (_pre_red_index > p_fifo->p_end_addr)
{
_pre_red_index = _pre_red_index - p_fifo->p_end_addr + p_fifo->p_start_addr - 1;
}
//! Copy Data
memcpy(p_element, _pre_red_index, p_fifo->unit_size);
return (0);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief FIFO is empty ?
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval - None-zero(true) if empty.
//! - Zero(false) if not empty.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_is_empty(fifo_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameter.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
return (0 == p_fifo->used_num);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief FIFO is full ?
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval - None-zero(true) if full.
//! - Zero(false) if not full.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_is_full(fifo_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameter.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
return (0 == p_fifo->free_num);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get FIFO the number of elements?
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval The number of elements in FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_used(fifo_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameter.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
return (p_fifo->used_num);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Get FIFO the number of elements?
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval The number of elements in FIFO.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_free(fifo_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameter.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
return (p_fifo->free_num);
}
//******************************************************************************************
//
//! \brief Flush the content of FIFO.
//!
//! \param [in] pFIFO is the pointer of valid FIFO.
//!
//! \retval 0 if success, -1 if failure.
//
//******************************************************************************************
int fifo_flush(fifo_t *p_fifo)
{
//! Check input parameters.
ASSERT(p_fifo);
//! Initialize FIFO Control Block.
MUTEX_LOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
p_fifo->free_num = (p_fifo->p_end_addr - p_fifo->p_start_addr) / (p_fifo->unit_size);
p_fifo->used_num = 0;
p_fifo->p_read_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
p_fifo->p_write_addr = p_fifo->p_start_addr;
MUTEX_UNLOCK(p_fifo->mutex);
return (0);
}
2.7 重定向printf到串口打印
#ifdef __GNUC__
/* With GCC, small printf (option LD Linker->Libraries->Small printf
set to 'Yes') calls __io_putchar() */
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#else
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE
{
/* Place your implementation of fputc here */
/* e.g. write a character to the EVAL_COM1 and Loop until the end of transmission */
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, (uint8_t *)&ch, 1, 0xFFFF);
return ch;
}
2.8 结合fifo和i2s dma读取i2s音频数据并通过usb虚拟串口转发上位机
HAL_Delay(1000);
printf("dma size:%lu\n", sizeof(dma));
g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo = fifo_s_create(480);
if (!g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo) {
printf("fifo cre failed.\n");
return -1;
}
HAL_I2S_Receive_DMA(&hi2s2, (uint16_t *)dma, 2);
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
if (!fifo_s_isempty(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo)) {
char res[4] = {'\0'};
if (fifo_s_gets(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo, res, sizeof(res)) > 0) {
CDC_Transmit_HS((uint8_t*)res, sizeof(res));
}
}
}
fifo_s_destroy(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo);
uint16_t dma[2] = {'\0'};
fifo_s_t *g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo = NULL;
void HAL_I2S_RxCpltCallback(I2S_HandleTypeDef *hi2s)
{
if(hi2s==&hi2s2) {
if (dma[0] || dma[1]) {
if (!fifo_s_isfull(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo)) {
fifo_s_puts(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo, (char*)dma, sizeof(dma)/2);
}
}
}
}
2.9 usb虚拟串口接收上位机的pcm数据并通过i2s dma写入音频卡播放
static int8_t CDC_Receive_HS(uint8_t* Buf, uint32_t *Len)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 11 */
uint16_t len = *Len;
// printf("recv len:%d\n", len);
// printf("recv:%s\n", Buf);
if (!fifo_s_isfull(g_i2s_dma_send_fifo)) {
fifo_s_puts(g_i2s_dma_send_fifo, (char*)Buf, *Len);
} else {
printf("fifo is full!\n");
}
USBD_CDC_SetRxBuffer(&hUsbDeviceHS, &Buf[0]);
USBD_CDC_ReceivePacket(&hUsbDeviceHS);
return (USBD_OK);
/* USER CODE END 11 */
}
2.10 融合收发DMA(只有一个方向可以生效,收发需要配置不通模式,无法实现全双工收发,而且需要配置SPI全局中断)
fifo_s_t *g_i2s_dma_send_fifo = NULL;
uint16_t dma[2] = {'\0'};
fifo_s_t *g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo = NULL;
void HAL_I2S_RxCpltCallback(I2S_HandleTypeDef *hi2s)
{
if(hi2s==&hi2s2) {
if (dma[0] || dma[1]) {
if (!fifo_s_isfull(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo)) {
fifo_s_puts(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo, (char*)dma, sizeof(dma)/2);
}
}
}
}
HAL_Delay(1000);
printf("dma size:%lu\n", sizeof(dma));
g_i2s_dma_send_fifo = fifo_s_create(4 * 4800);
if (!g_i2s_dma_send_fifo) {
printf("fifo cre failed.\n");
return -1;
}
g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo = fifo_s_create(480);
if (!g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo) {
printf("fifo cre failed.\n");
return -1;
}
HAL_I2S_Receive_DMA(&hi2s2, (uint16_t *)dma, 2);
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
if (!fifo_s_isempty(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo)) {
char res[4] = {'\0'};
if (fifo_s_gets(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo, res, sizeof(res)) > 0) {
CDC_Transmit_HS((uint8_t*)res, sizeof(res));
}
}
if (!fifo_s_isempty(g_i2s_dma_send_fifo)) {
char res[4 * 48] = {'\0'};
if (fifo_s_gets(g_i2s_dma_send_fifo, res, sizeof(res)) > 0) {
printf("res:%02x%02x\n", res[0], res[1]);
while (HAL_I2S_GetState(&hi2s2) != HAL_I2S_STATE_READY) {
}
int ret = HAL_I2S_Transmit_DMA(&hi2s2,(uint16_t*)res, sizeof(res));
// int ret = HAL_I2SEx_TransmitReceive_DMA(&hi2s2,(uint16_t*)res, dma, 48);
// int ret = HAL_I2S_Transmit(&hi2s2,(uint16_t*)res, 48, 0xFFFF);
if (ret != HAL_OK) {
printf("ret:%d\n", ret);
while (HAL_I2S_GetState(&hi2s2) != HAL_I2S_STATE_READY) {
}
}
}
}
}
fifo_s_destroy(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo);
fifo_s_destroy(g_i2s_dma_send_fifo);
2.11 全双工收发进行录音和放音(最终版本结合DMA收和发)
官方给到的例子也是全双工方式进行读写的,注意回调接口别搞错了(https://community.st.com/t5/stm32-mcus-products/stm32f411-hal-driver-i2s-full-duplex-ext-sd-issue/td-p/442735 社区这里提问的人就是搞错了回调接口):
fifo_s_t *g_i2s_dma_send_fifo = NULL;
uint8_t dma[2 * 2] = {'\0'};
uint8_t send_dma[2 * 2] = {'\0'};
fifo_s_t *g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo = NULL;
uint8_t is_record = 1;
uint8_t is_player = 0;
typedef enum {
RECORD_START,
RECORD_STOP,
PLAYER_START,
PLAYER_STOP,
} I2S_STATE;
void HAL_I2SEx_TxRxCpltCallback(I2S_HandleTypeDef *hi2s)
{
if(hi2s==&hi2s2) {
if (is_record) {
if (dma[0]) {
if (!fifo_s_isfull(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo)) {
fifo_s_puts(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo, (char *) dma, sizeof(dma));
}
}
}
if (is_player) {
if (!fifo_s_isempty(g_i2s_dma_send_fifo) && is_player) {
char res[4] = {'\0'};
if (fifo_s_gets(g_i2s_dma_send_fifo, res, sizeof(res)) > 0) {
// printf("i am here.\n");
memcpy(send_dma, res, sizeof(res));
}
}
}
}
}
HAL_Delay(1000);
printf("dma size:%lu\n", sizeof(dma));
g_i2s_dma_send_fifo = fifo_s_create(4 * 4800);
if (!g_i2s_dma_send_fifo) {
printf("fifo cre failed.\n");
return -1;
}
g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo = fifo_s_create(480);
if (!g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo) {
printf("fifo cre failed.\n");
return -1;
}
// HAL_I2SEx_TransmitReceive(&hi2s2, send_dma, dma, 2, 1000);
HAL_I2SEx_TransmitReceive_DMA(&hi2s2, (uint16_t*)send_dma, (uint16_t*)dma, (sizeof(dma)/2));
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
if (!fifo_s_isempty(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo)) {
char res[4] = {'\0'};
if (fifo_s_gets(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo, res, sizeof(res)) > 0) {
CDC_Transmit_HS((uint8_t*)res, sizeof(res));
}
}
}
fifo_s_destroy(g_i2s_dma_recv_fifo);
fifo_s_destroy(g_i2s_dma_send_fifo);
2.12 其它方式
还有一种方式创建较大的缓存区,增加HAL_I2SEx_TxRxHalfCpltCallback回调在接收到一半时处理缓存的前半部分,HAL_I2SEx_TxRxCpltCallback回调处理后半部分缓存。以上都是基于HAL库,还有不基于HAL库的方式,但是不建议使用,HAL库更容易移植一些。
3、难点
3.1 录音
主要是调整i2s dma对应的配置以及将读取到的数据转发给上位机保证不丢采样内容,这个调整尝试过程属于摸着石头过河,很不好调试。比如我这里接收时i2s每次接收两个字节,但是通过usb虚拟串口转发上位机时每次需要发送4个字节,如果每次只发送2个字节则采样数据会丢失一半左右,中间还需要增加fifo缓存解决接收和发送速度不对等的问题。
3.2 放音
测试方式比较麻烦,最好有外接的放音设备,部分音频控制板可以配置自身扬声器显示自身麦克风声音,这样I2S的收发都可以通过一个音频控制卡听到了(但测试录音时记得关闭麦克风):
3.3 缓存问题
i2s dma收发和存储读写时的速度不对等问题,比如录音时需要从i2s dma读取然后存储到外挂U盘或者flash或者直接串口转发,这时dma读取和存储就有不对等的问题,可能导致采样数据丢失,因此需要中间缓存保证采样数据不丢失,也可以降低采样率;放音时一般一次读取的内容太多导致一次性发送dma时超过缓存大小,因此也最好增加缓存一次性发送一部分内容到dma。
此外,对应i2s的spi全局中断要开启,否则可能出现状态busy的问题:
3.4 底噪问题
发送时进行简单数据过滤,单声道的过滤另一声道的杂音,即不发送部分采样值,以及清空缓存时注意结合半缓存接收回调处理。
如果声音有了,但是有杂音可以录制一下空音看是否有杂音,如果空音有杂音,可以量一下声卡和单片机的主频,可能作为从模式的一方主频并未禁用,导致连接主频mclk后有干扰导致的杂音。
除了硬件问题外,软件读写文件也需要注意,这也容易引起底噪,比如录音时flash的擦除影响写文件,放音时读取文件往dma填充时读取文件的大小和填充0不正常导致放音底噪,这里一定记得参考一下官网的audio示例(回调中获取过半和完全传输完成的标志后再填充,之后还原标志):
void WavePlayBack(uint32_t AudioFreq)
{
UINT bytesread = 0;
/* Start playing */
AudioPlayStart = 1;
RepeatState = REPEAT_ON;
/* Initialize Wave player (Codec, DMA, I2C) */
if(WavePlayerInit(AudioFreq) != 0)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* Get Data from USB Flash Disk */
f_lseek(&FileRead, 0);
f_read (&FileRead, &Audio_Buffer[0], AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE, &bytesread);
AudioRemSize = WaveDataLength - bytesread;
/* Start playing Wave */
BSP_AUDIO_OUT_Play((uint16_t*)&Audio_Buffer[0], AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE);
LEDsState = LED6_TOGGLE;
PauseResumeStatus = RESUME_STATUS;
PressCount = 0;
/* Check if the device is connected.*/
while((AudioRemSize != 0) && (AppliState != APPLICATION_IDLE))
{
/* Test on the command: Playing */
if(CmdIndex == CMD_PLAY)
{
if(PauseResumeStatus == PAUSE_STATUS)
{
/* Stop Toggling LED2 to signal Pause */
LEDsState = STOP_TOGGLE;
/* Pause playing Wave */
WavePlayerPauseResume(PauseResumeStatus);
PauseResumeStatus = IDLE_STATUS;
}
else if(PauseResumeStatus == RESUME_STATUS)
{
/* Toggling LED6 to signal Play */
LEDsState = LED6_TOGGLE;
/* Resume playing Wave */
WavePlayerPauseResume(PauseResumeStatus);
PauseResumeStatus = IDLE_STATUS;
}
bytesread = 0;
if(BufferOffset == BUFFER_OFFSET_HALF)
{
f_read(&FileRead,
&Audio_Buffer[0],
AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE/2,
(void *)&bytesread);
BufferOffset = BUFFER_OFFSET_NONE;
}
if(BufferOffset == BUFFER_OFFSET_FULL)
{
f_read(&FileRead,
&Audio_Buffer[AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE/2],
AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE/2,
(void *)&bytesread);
BufferOffset = BUFFER_OFFSET_NONE;
}
if(AudioRemSize > (AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE / 2))
{
AudioRemSize -= bytesread;
}
else
{
AudioRemSize = 0;
}
}
else
{
/* Stop playing Wave */
WavePlayerStop();
f_close(&FileRead);
AudioRemSize = 0;
RepeatState = REPEAT_ON;
break;
}
}
#ifdef PLAY_REPEAT_DISABLED
RepeatState = REPEAT_OFF;
/* Stop playing Wave */
WavePlayerStop();
f_close(&FileRead);
/* Test on the command: Playing */
if(CmdIndex == CMD_PLAY)
{
LEDsState = LED4_TOGGLE;
}
#else
LEDsState = LEDS_OFF;
RepeatState = REPEAT_ON;
AudioPlayStart = 0;
/* Stop playing Wave */
WavePlayerStop();
f_close(&FileRead);
#endif /* PLAY_REPEAT_DISABLED */
}
3.5 音质问题
目前音频播放有丢低音的情况,播放的音频比较尖锐,缺少低沉浑厚的声音,感觉感觉是单片机的问题。
主要还是配置参数的问题,保证晶振频率设置正确,以及PLLI2SN和PLLI2SR设置好,这个可以通过stm32CubeMX配置后设置。
//采样率计算公式:Fs=I2SxCLK/[256*(2*I2SDIV+ODD)]
//I2SxCLK=(HSE/pllm)*PLLI2SN/PLLI2SR
//一般HSE=8Mhz
//pllm:在Sys_Clock_Set设置的时候确定,一般是8
//PLLI2SN:一般是192~432
//PLLI2SR:2~7
//I2SDIV:2~255
//ODD:0/1
//I2S分频系数表@pllm=8,HSE=8Mhz,即vco输入频率为1Mhz
//表格式:采样率/10,PLLI2SN,PLLI2SR,I2SDIV,ODD
const u16 I2S_PSC_TBL[][5]=
{
{800 ,100,2,24,0}, //8Khz采样率
{1102,429,4,19,0}, //11.025Khz采样率
{1600,213,2,13,0}, //16Khz采样率
{2205,429,4, 9,1}, //22.05Khz采样率
{3200,213,2, 6,1}, //32Khz采样率
{4410,271,2, 6,0}, //44.1Khz采样率
{4800,100,2, 4,0}, //48Khz采样率
{8820,316,2, 3,1}, //88.2Khz采样率
{9600,344,2, 3,1}, //96Khz采样率
{17640,361,2,2,0}, //176.4Khz采样率
{19200,393,2,2,0}, //192Khz采样率
};
//设置IIS的采样率(@MCKEN)
//samplerate:采样率,单位:Hz
//返回值:0,设置成功;1,无法设置.
u8 I2S2_SampleRate_Set(u32 samplerate)
{
u8 i=0;
u32 tempreg=0;
samplerate/=10;//缩小10倍
for(i=0;i<(sizeof(I2S_PSC_TBL)/10);i++)//看看改采样率是否可以支持
{
if(samplerate==I2S_PSC_TBL[i][0])break;
}
RCC_PLLI2SCmd(DISABLE);//先关闭PLLI2S
if(i==(sizeof(I2S_PSC_TBL)/10))return 1;//搜遍了也找不到
RCC_PLLI2SConfig((u32)I2S_PSC_TBL[i][1],(u32)I2S_PSC_TBL[i][2]);//设置I2SxCLK的频率(x=2) 设置PLLI2SN PLLI2SR
RCC->CR|=1<<26; //开启I2S时钟
while((RCC->CR&1<<27)==0); //等待I2S时钟开启成功.
tempreg=I2S_PSC_TBL[i][3]<<0; //设置I2SDIV
tempreg|=I2S_PSC_TBL[i][4]<<8; //设置ODD位
tempreg|=1<<9; //使能MCKOE位,输出MCK
SPI2->I2SPR=tempreg; //设置I2SPR寄存器
return 0;
}
后续发现音质问题解决了,可能原因(包括杂音):
- 1、是采样率匹配问题,采样率设置不对一定会导致杂音、快进慢放等问题;
- 2、一个是单双声道问题,生成wav文件时如果声卡设备转换为双声道但是按照单声道处理就会有问题,数据量是双声道的,但是存储时处理了一半;
- 3、还有一个可能就是声卡设备的干扰问题,比如声卡i2s或者某些引脚接线不对导致影响数字信号采集;
- 4、还有发现一个问题,声卡i2s的收和发的数据长度设置不一致,比如发设置了标准的16位长度,而接收设置了16位扩展32位长度,导致i2s初始化后接收可能正常,但是发送时声卡收不到数据从而导致录音没有声音;
- 5、如果使用spi flash+fatfs进行音频文件写入的,那么音频波形快进样式也可能是spi flash的驱动问题导致的,正片擦除后写入时写入速度快就不会有这个问题,需要在写入前先擦除,如果写入时再擦除会影响写入速度从而影响录音;(调试时可以用示波器先确认硬件对应引脚输出的频率是否符合预期)
采样率的时钟频率F4按照下图配置即可(比如48khz的固定为258的PLLI2SN和3的PLLi2SR,不同外部输入时钟可以设置对应分频后为1MHZ,比如8MHZ的则设置8分频,25MHZ的设置为25):
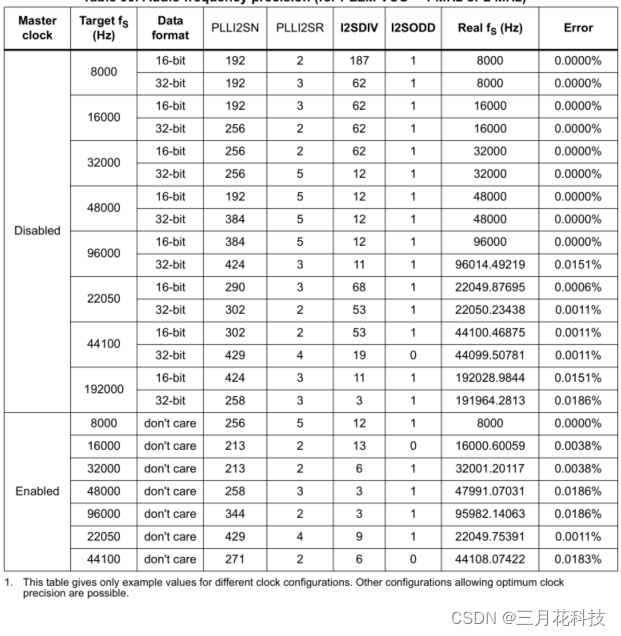
比如我这里是25MHZ的:(如果是8MHZ的则M设置为8,后面N和R固定为258和3)

4、结果
由于是音频内容不太好展示,主要是通过Audacity或者cool edit pro软件来导入原始的pcm数据进行测试,主要配置导入时的参数即可(实时测试时可以通过串口查看波形)。
结果(波形的高度和声音的大小也有关系,此外,对于48khz的音频stm32也有1%左右的采样丢失问题,会有一定的失真的问题,因此,对于人声采集一般建议还是低采样,比如8khz):
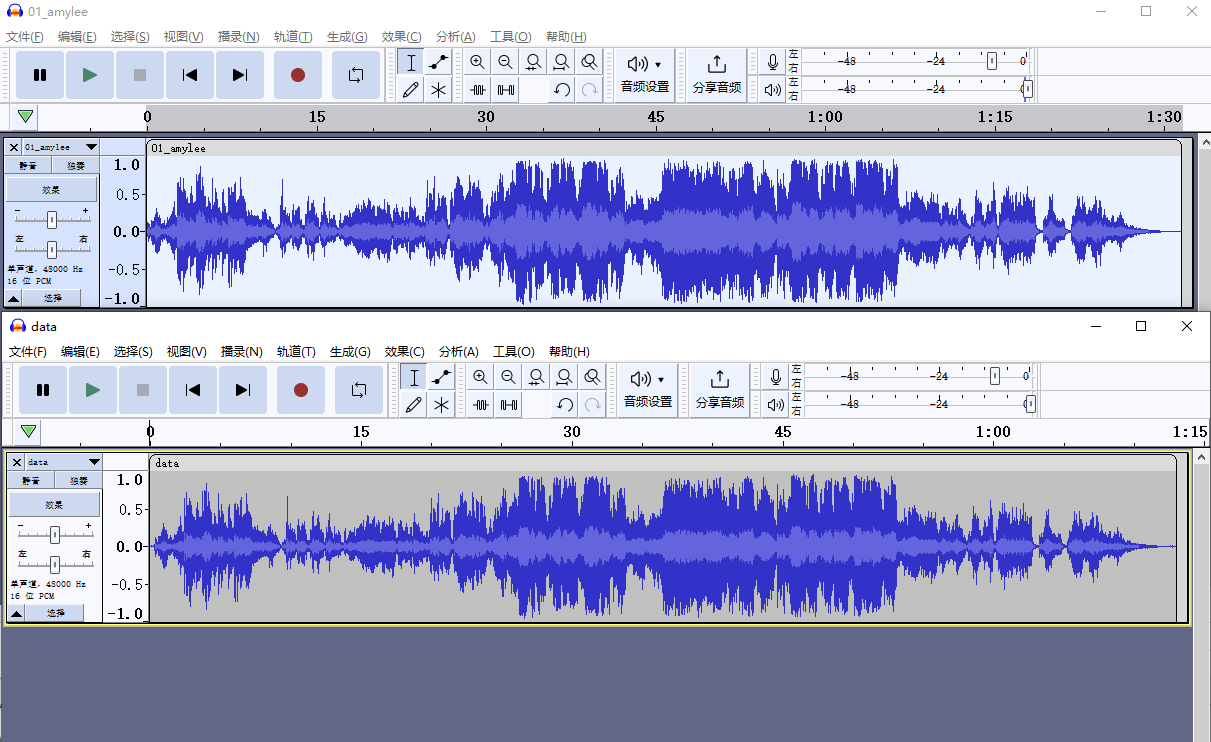
六、最后
使用单片机进行音频的研究确实本人还是第一次,而且资料较少,相对于带系统的Linux、Windows等开发音频软件较复杂,因此这次花费时间较长,所幸最终是研究出来了,官方社区加持以及一些前人总结帮了不少忙,即使这样也还是走了不少弯路,因此希望本总结也能帮助更多的人。