一. 计算效率
1. 测量代码运行时间 %%time %%timeit
单纯计算 代码块执行的时长
%%time
_sum(np.arange(6))
CPU times: total: 0 ns
Wall time: 1.66 ms
用于多次运行代码块并计算平均执行时间
%%timeit
_sum(np.arange(6))
738 ns ± 10.7 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1,000,000 loops each)2. 装饰器 @nb.jit (import numba as nb) (提高执行的速度)
这个函数接受一个可迭代对象 x,并返回其所有元素的总和。
通过使用 @nb.jit(nopython=True) 装饰器,
函数将在 Numba 中被编译为机器码,以提高执行速度。
@nb.jit(nopython = True)
def _sum(x):
result = 0
for i in x:
result += i
return result
_sum(np.arange(100))3. 闭包
- 在一个函数内部定义了另一个函数,并且这个内部函数引用了外部函数的局部变量
- 简单说就是函数下嵌套一个函数
这里的outer 返回 inner 函数,然后 inner再
当调用 outer("yx") 时,它会返回一个函数 inner,并且这个 inner 函数中的 x 被设定为 "yx"。
但是,inner 函数并不会立即执行,而是被返回给调用者。
我们将返回的函数赋值给变量 func。
此时,func 实际上是一个函数,即 inner 函数。
def outer(x):
def inner(y):
return x + " like "+ y
return inner
func = outer("yx")
func("apple")
结果是 yx like apple3.1 闭包和装饰器的结合
def outer(func):
def inner(y):
x = "吴雨龙"
return func(x + "吃" + y)
return inner
@outer #outer(my_func)
def my_func(text):
return text
result = my_func("苹果")
print(result) # 输出:吴雨龙吃苹果
解释: @outer 装饰器 相当于把 my_func(苹果)整体 传给了 outer,
所以 outer(my_func(苹果)) -- inner(苹果)-- 4. swifter 提高并行处理能力
通过 switer 可以提升 并行处理能力
import swifter
df.swifter.apply(lambda x : x["数量"] * x["单价"],axis=1)5. pandarallel
from pandarallel import pandarallel
pandarallel.initialize(nb_workers=8)
初始化 Pandarallel 库,设置并行处理的工作线程数为 8。
这意味着在后续的 Pandas 操作中,可以同时使用多达 8 个工作线程来并行处理数据,
以提高数据处理速度。
df.parallel_apply(np.sum,axis=1)
parallel_apply 函数会在多个工作线程上并行应用 np.sum 函数到数据框的每一行上,从而加速了计算过程。二. 快速构图
1. np.linspace() 创建等间隔数组
用于创建等间隔的一维数组(向量)
np.linspace(1,10,num=20,endpoint=False)
'''
array([1. , 1.45, 1.9 , 2.35, 2.8 , 3.25, 3.7 , 4.15, 4.6 , 5.05, 5.5 ,
5.95, 6.4 , 6.85, 7.3 , 7.75, 8.2 , 8.65, 9.1 , 9.55])
'''
闭区间 endpoint可以控制区间类型
start end , endpoint = True 区间是闭区间2. 建立 x,y 轴. X大写, y 小写
- import scipy.stats as stats
- 使用
stats来执行各种统计分析,比如计算均值、方差、概率密度函数、累积分布函数
# y = f(x)
X = np.linspace(-5,5,200)
#概率密度函数 均值=中位数=众数=0 标准差=1
y = stats.norm.pdf(X) / np.max(stats.norm.pdf(X))3. 线型图的绘制
3.1 需要的库
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt #画图层
from matplotlib import style
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import scipy.stats as stats
3.2 配置图的大小 颜色 字体等
获取所有的背景主题
print(style.available)
#配置
style.use("fivethirtyeight") #颜色主题
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (10,6.18) # 尺寸大小 单位是英寸
plt.rcParams["figure.dpi"] = 100 #清晰度
plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = ["SimHei"] #微软黑体字
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False #调控负号问题3.3 画图
线形图
plt.plot(X,y,label="PDF") label 是标签
plt.fill(X,y,alpha=0.5) #透明度
y1 = stats.norm.cdf(X) #累积分布函数
plt.plot(X,y1,label="CDF")
plt.legend() # 添加图例,就是说明那条线是哪一个
刻度控制
plt.xticks(np.arange(-5,6)) #np.arange() 是左闭右开的
plt.yticks(np.arange(0,11)/10)
刻度轴标题
plt.xlabel("x的标题",fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel("y的标题",fontsize=15,c="red")
注释部分
plt.text(-3.5,0.7,"我是注释")
去除背景
plt.grid()
保存图形
plt.savefig("./demo.png",dpi=100)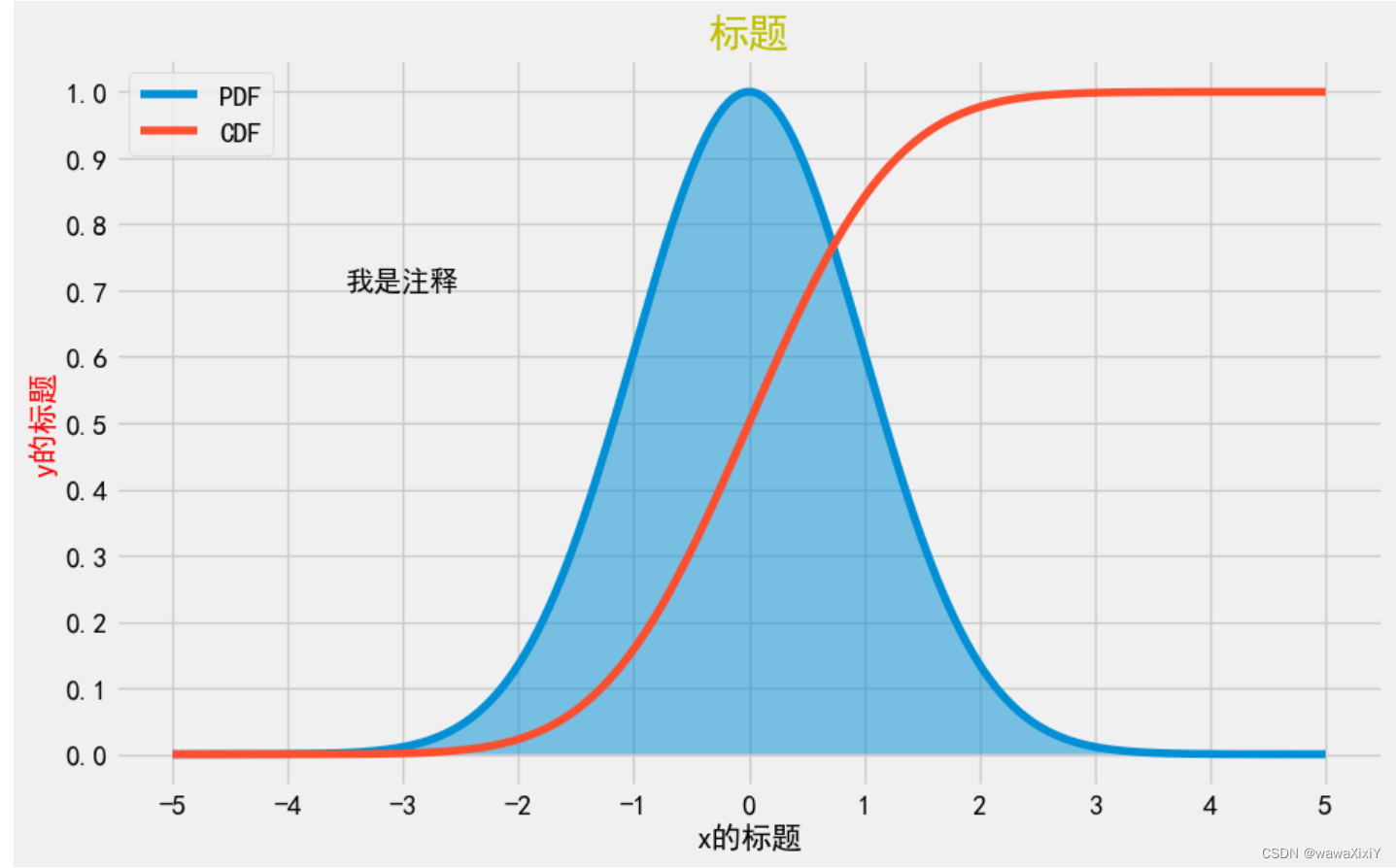
4.点线面控制
%matplotlib inline
X = np.linspace(-5,5,20)
y = np.sin(X)
'''
ls : 线的样式 - 实线 -- 虚线 : 虚线 -.感叹线
lw : 线宽
marker : 点样式 o s D d x X
markersize : 点大小
markerfacecolor : 面的颜色
markeredgecolor : 边缘颜色
'''
plt.plot(X,y,ls=":",lw=1,marker="X",markersize=20,markerfacecolor="white",markeredgecolor="orange")
标记数据
for a,b in list(zip(X,y)):
plt.text(a-0.15,b-0.01,s=round(b,2),fontsize=10,color="#ff00005f")
s = : s后面写的是你要标记的数据4.柱状图
#不要使用 数字以外 的数据作为轴
plt.bar(np.arange(data.index.size),data.金额,width=.4)
画图的时候 ,x轴使用的 城市的 下标
xticks 可以执行映射 把数字部分 替换程 文字部分
plt.xticks(np.arange(data.index.size),data.index,rotation=90)
rotation 是把横坐标 字进行转动
for a,b in list(zip(np.arange(data.index.size),data.金额)):
plt.text(a-.1,b,b,rotation=90)
这里的 zip(np.arange(data.index.size) 是因为 直接使用 文字作为横坐标
下面不能 调整 他的位置,因为不能对齐进行加减空画布画法:
针对某一个画布时:要用set_xticks
plt.figure(figsize=(20,6))
#不要使用 数字以外 的数据作为轴
#1.生成一个空画布
axes1 = plt.gca()
#2.把金额的柱状图绘制在 画布1
axes1.bar(np.arange(data.index.size),data.金额,width=.4,color='r',label="销售额") #画图的时候 ,x轴使用的 城市的 下标
#3. 公用一条轴
axes2 = axes1.twinx() #返回画布2
# +.4 偏移图形
axes2.bar(np.arange(data.index.size)+.4,data.数量,width=.4,label="销量")
#xticks 可以执行映射 把数字部分 替换程 文字部分
axes1.set_xticks(np.arange(data.index.size),data.index,rotation=90)
for a,b in list(zip(np.arange(data.index.size),data.金额)):
axes1.text(a-.1,b,b,rotation=90)
for a,b in list(zip(np.arange(data.index.size),data.数量)):
axes2.text(a+.25,b,b,rotation=90)
axes1.grid(False)
axes2.grid(False)
#调节legend的位置
axes1.legend(loc=[0,1]) # 当前的 1 比例是整个画布的长度或宽度比例
axes2.legend(loc=[0.1,1])5.多图组合
#1.先设置空画布
axes1 = plt.gca()
#2.在空画布当中绘制图形 ,x轴 最好使用 索引
inds = np.arange(data.index.size)
axes1.bar(inds,data.金额,color="purple",label="销售额")
#3.将x轴进行映射
axes1.set_xticks(inds,data.index,rotation=90,fontsize=10)
#4.设置共轴
axes2 = axes1.twinx()
axes2.plot(inds,data.数量,color="orange",alpha=0.8,ls="--",lw=1.5,marker="o",markerfacecolor="b",label="销量")
#5.设置y轴的标签
axes1.set_ylabel("销售额(元)")
axes2.set_ylabel("销量(件)")
#6.设置图例
axes1.legend(loc=[0,1.1])
axes2.legend(loc=[0,1.04])
axes1.grid(False)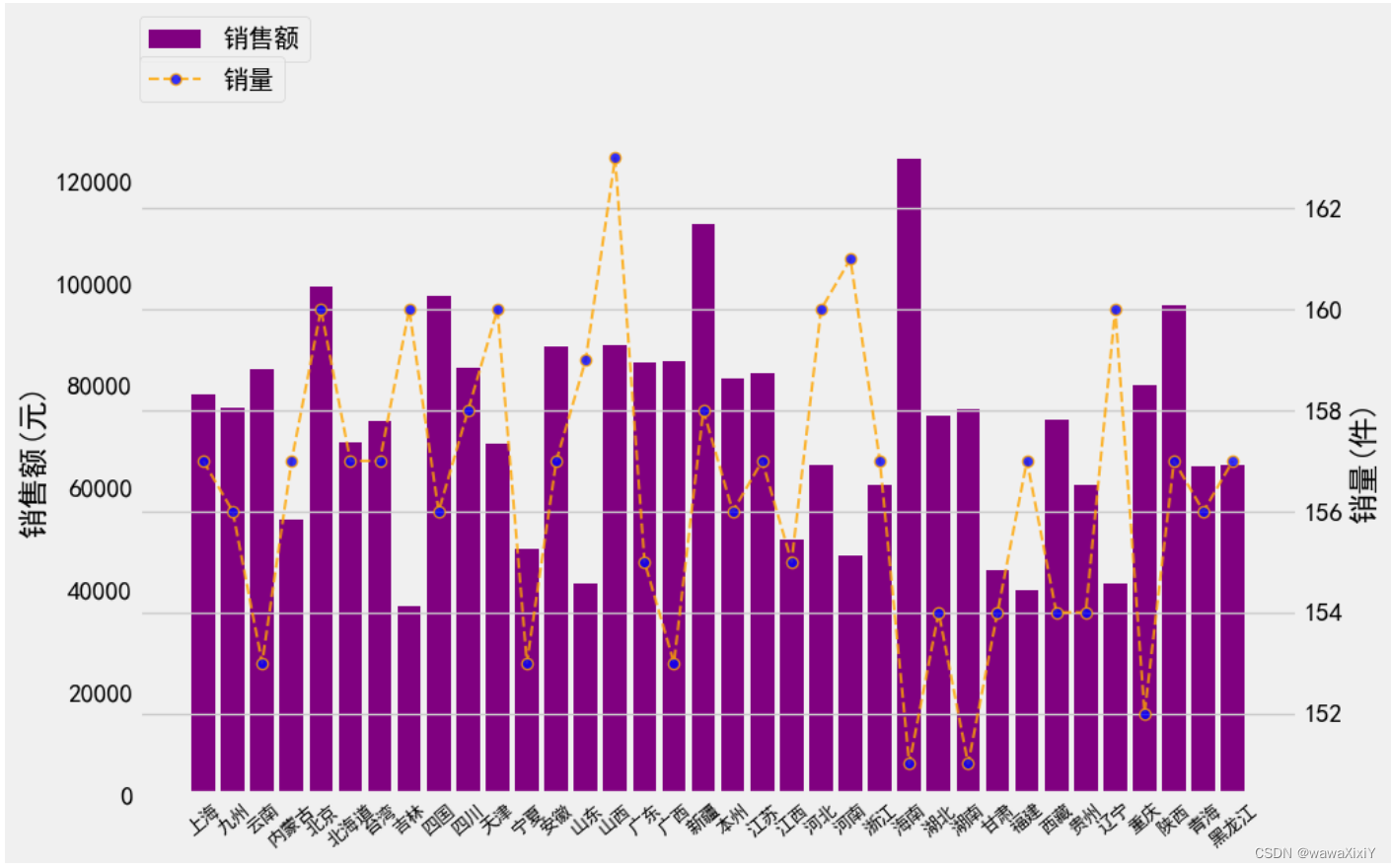
6. 直方图
pd.cut(d,bins=10) 分箱
plt.hist(d,bins=10)7. 饼图
import seaborn as sns 颜色调色板
sns.palplot(sns.color_palette("hls",10)) 设置的颜色
#获取最大值索引
mi = da.金额.reset_index(drop=True).idxmax()
#飞离效果 数组生成
ex = np.zeros(da.shape[0])
ex[mi]=0.1
a = plt.pie(
da.金额,
labels=da.index,
colors = sns.color_palette("hls",da.shape[0]),
autopct="%.2f%%", # 计算每块的比例
explode = ex, # 分离效果
wedgeprops={"width":.4}, # 宽带边缘属性
pctdistance=0.75, # 就是调整比例数值位置
textprops={"fontsize":10,"color":"k"} #比例数字属性
)
plt.legend(labels=[f"{a}={b}元" for a,b in zip(da.index,da.金额)],loc=[0,-.4],ncol=2)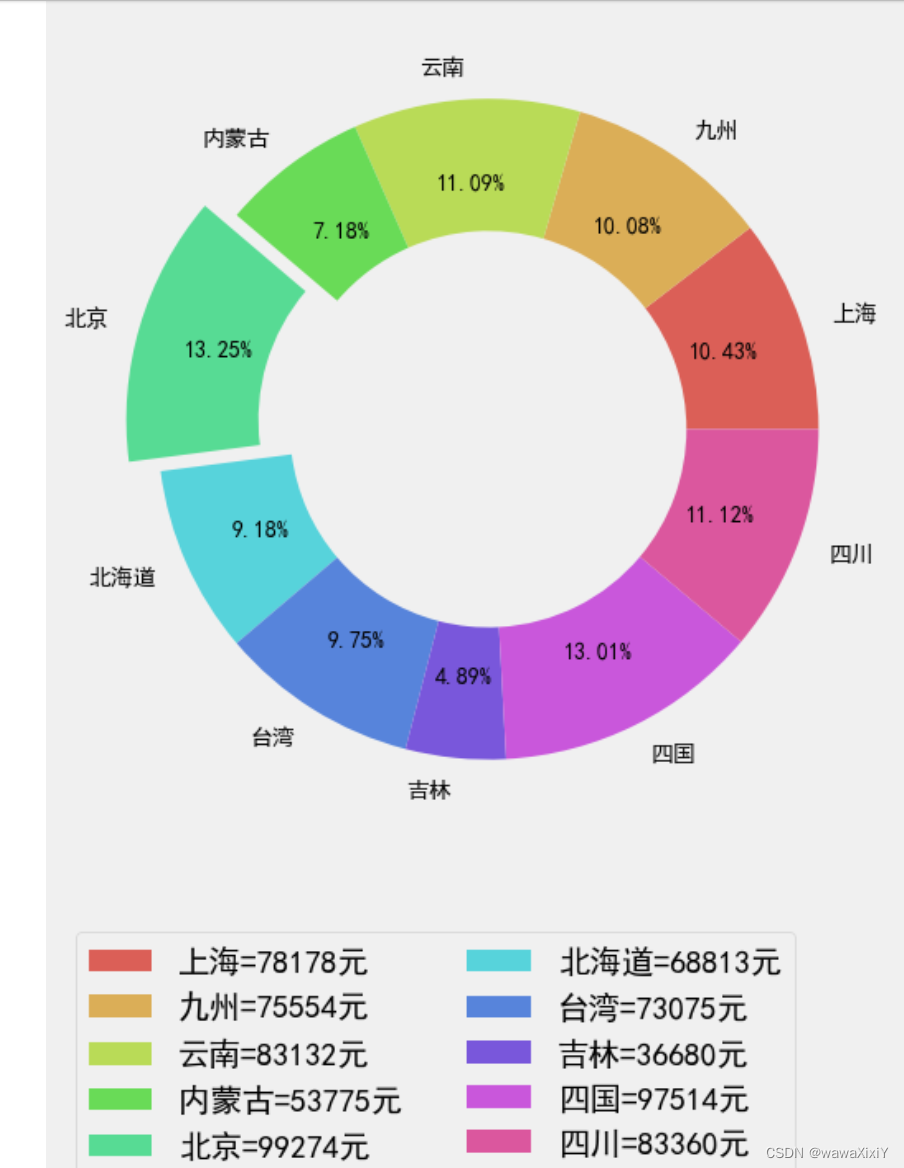
8. 旭日图
plt.pie(
total.金额,
colors = sns.color_palette("summer",total.shape[0]),
autopct="%.2f%%",
radius=0.5, #半径
)
a = plt.pie(
tmp.金额,
labels=tmp.省份,
colors = sns.color_palette("summer",tmp.shape[0]),
explode=np.full(tmp.shape[0],0.01),
wedgeprops={"width":.4},
pctdistance=0.75,
textprops={"fontsize":10,"color":"k"}
)
plt.text(0.1,0.1,"中国")
# plt.text(0.1,-0.1,"日本")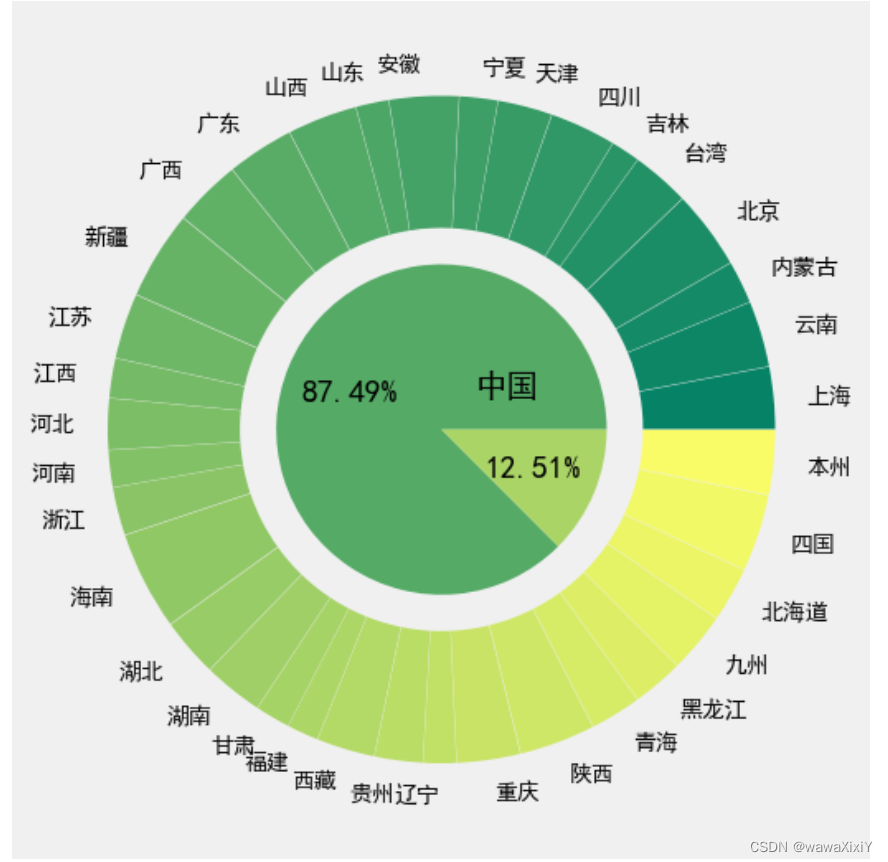







![[dvwa] Command Injection](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/6a3b0c1fe9464b2698dfdaba0c1b33ac.png)