| java数据结构与算法刷题目录(剑指Offer、LeetCode、ACM)-----主目录-----持续更新(进不去说明我没写完):https://blog.csdn.net/grd_java/article/details/123063846 |
|---|
深度优先遍历
| 解题思路:时间复杂度O(
m
∗
n
m*n
m∗n),空间复杂度O($$) |
|---|
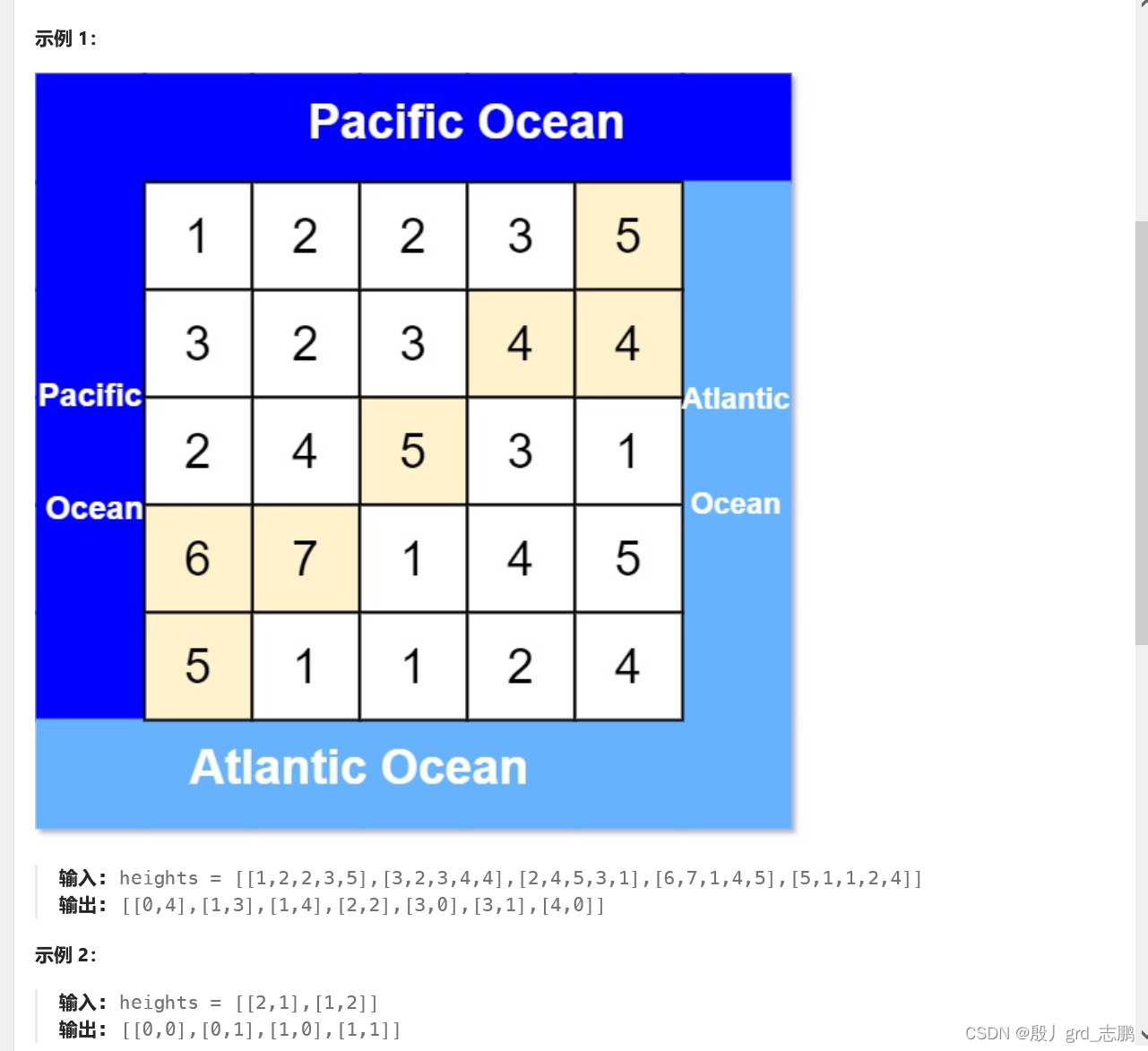
- 从地图中找高点,然后推出是否能流入两个海洋显然不明智
- 我们很清楚,两座海洋的水都是从相邻的岸边流入的。与其找当前地点的水流到哪,不如逆向思维。
- 将题目变为,两座海洋的水从哪来?
- 因此我们遍历陆地的上下左右边界,找到这水从哪流过来的。只要相邻地点比当前位置高,那么水就从高地点流过来的。
- 我们可以创建两个数组,分别记录太平洋的水从哪来(标志为true),大西洋的水从哪里来(标志为true)
- 最后两个数组同时为true的位置,就是既可以流向太平洋又可以流向大西洋的位置。
class Solution {
int[][] heights;
int n,m;
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
this.heights = heights;
this.n = heights.length;this.m = heights[0].length;
ArrayList<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
boolean pacificOcean[][] = new boolean[n][m];
boolean atlanticOcean[][] = new boolean[n][m];
for(int j = 0;j<m;j++) dfs(0,j,pacificOcean);
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) dfs(i,0,pacificOcean);
for(int j = 0;j<m;j++) dfs(n-1,j,atlanticOcean);
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) dfs(i,m-1,atlanticOcean);
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<m;j++){
if(pacificOcean[i][j] && atlanticOcean[i][j]) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(i);list.add(j);
ans.add(list);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int [][] directions = new int[][]{{-1,0},{0,-1},{1,0},{0,1}};
public void dfs(int i,int j,boolean[][] ocean){
ocean[i][j] = true;
for(int[] direction : directions){
int nextI = i+direction[0];
int nextJ = j+direction[1];
if(nextI < 0 || nextJ < 0 || nextI >= n || nextJ >= m || ocean[nextI][nextJ]) continue;
if(heights[i][j]<=heights[nextI][nextJ]) dfs(nextI,nextJ,ocean);
}
}
}