深度学习平台(只能有线连接校园网)
账户
yeguifeng
密码
yguifeng
env3 : pytorch1.9+cuda+jupyter+matplotlib
pycuda: pycuda
Timesformer
–data_dir ./trainingVideo --category my_fire --output_dir ./output --image_size 100 --num_chain 10 --batch_size 14 --lr 0.001 --num_frames 30
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LDLIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/cuda-9.0/lib64
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/cuda-9.0/bin
export CUDA_HOME=$CUDA_HOME:/usr/local/cuda-9.0
使用指南
因为这个设备的docker环境无法在线或者本地安装环境。所以,所有的相关的包都应该在自己的电脑上装好,并且一定要装 jupyter,不然用起来不方便。
1.创建镜像
创建基础的镜像,比如我自己来说需要用到pytorch
- 拉取镜像
sudo docker pull pytorch/pytorch:1.9.0-cuda10.2-cudnn7-runtime
sudo docker pull pytorch/pytorch:1.2-cuda10.0-cudnn7-devel
- 查看镜像列表,拉取成功
sudo docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
jupyterv2/pytorch latest 589b7f07ccc4 17 hours ago 3.58GB
jupyter latest 6ebc0b4666fe 1RuntimeError: CUDA error: out of memory CUDA kernel errors might be asynchro7 hours ago 3.58GB
ubuntu latest a8780b506fa4 6 days ago 77.8MB
nvidia/cuda 10.0-cudnn7-devel-ubuntu18.04 ab9007c84133 5 months ago 3.21GB
python 3.6 54260638d07c 10 months ago 902MB
hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 13 months ago 13.3kB
pytorch/pytorch 1.9.0-cuda10.2-cudnn7-runtime 3850639cdf7a 17 months ago 4.42GB
pytorch/pytorch 1.6.0-cuda10.1-cudnn7-runtime 6a2d656bcf94 2 years ago 3.47GB
- 运行镜像
sudo docker run -it pytorch/pytorch:1.9.0-cuda10.2-cudnn7-runtime
打开成功会这样显示
root@92ede4d54808:/workspace#
- 安装相关的库
root@92ede4d54808:/workspace# pip install jupyter
安装成功提示
Attempting uninstall: traitlets
Found existing installation: traitlets 5.0.5
Uninstalling traitlets-5.0.5:
Successfully uninstalled traitlets-5.0.5
Attempting uninstall: ipython
Found existing installation: ipython 7.22.0
Uninstalling ipython-7.22.0:
Successfully uninstalled ipython-7.22.0
Successfully installed Send2Trash-1.8.0 anyio-3.6.2 argon2-cffi-21.3.0 argon2-cffi-bindings-21.2.0 attrs-22.1.0 bleach-5.0.1 debugpy-1.6.3 defusedxml-0.7.1 entrypoints-0.4 fastjsonschema-2.16.2 importlib-metadata-5.0.0 importlib-resources-5.10.0 ipykernel-6.16.2 ipython-7.34.0 ipywidgets-8.0.2 jsonschema-4.17.0 jupyter-1.0.0 jupyter-client-7.4.4 jupyter-console-6.4.4 jupyter-core-4.11.2 jupyter-server-1.23.0 jupyterlab-pygments-0.2.2 jupyterlab-widgets-3.0.3 matplotlib-inline-0.1.6 mistune-2.0.4 nbclassic-0.4.8 nbclient-0.7.0 nbconvert-7.2.3 nbformat-5.7.0 nest-asyncio-1.5.6 notebook-6.5.2 notebook-shim-0.2.2 packaging-21.3 pandocfilters-1.5.0 pkgutil-resolve-name-1.3.10 prometheus-client-0.15.0 pyparsing-3.0.9 pyrsistent-0.19.2 python-dateutil-2.8.2 pyzmq-24.0.1 qtconsole-5.4.0 qtpy-2.3.0 sniffio-1.3.0 terminado-0.17.0 tinycss2-1.2.1 tornado-6.2 traitlets-5.5.0 webencodings-0.5.1 websocket-client-1.4.2 widgetsnbextension-4.0.3 zipp-3.10.0
测试能否打开
root@92ede4d54808:/workspace# jupyter notebook --allow-root
[I 02:05:39.087 NotebookApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: /workspace
[I 02:05:39.087 NotebookApp] Jupyter Notebook 6.5.2 is running at:
[I 02:05:39.087 NotebookApp] http://localhost:8888/?token=88f4ced3086866824ee9755f9aa33338ce8428871a1e92cb
[I 02:05:39.087 NotebookApp] or http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=88f4ced3086866824ee9755f9aa33338ce8428871a1e92cb
[I 02:05:39.087 NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).
[W 02:05:39.093 NotebookApp] No web browser found: could not locate runnable browser.
[C 02:05:39.093 NotebookApp]
To access the notebook, open this file in a browser:
file:///root/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/nbserver-19-open.html
Or copy and paste one of these URLs:
http://localhost:8888/?token=88f4ced3086866824ee9755f9aa33338ce8428871a1e92cb
or http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=88f4ced3086866824ee9755f9aa33338ce8428871a1e92cb
成功打开!
root@92ede4d54808:/workspace# python
Python 3.7.10 (default, Feb 26 2021, 18:47:35)
[GCC 7.3.0] :: Anaconda, Inc. on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import torvision
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'torvision'
>>> import torchvision
>>> import torch
>>> from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
>>> from tqdm import tqdm
>>> import copy
>>> import random
runtest:
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torchbnn as bnn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.data.dataset import Dataset
model_o = nn.Sequential(
bnn.BayesLinear(prior_mu=0, prior_sigma=0.1, in_features=28*28, out_features=1024),
nn.ReLU(),
bnn.BayesLinear(prior_mu=0, prior_sigma=0.1, in_features=1024, out_features=10),
)
batch_size = 60000
device = 'cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu' # 0.001
print("device: ", device)
import copy
from tqdm import tqdm
# get data
def get_data():
train = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root="./data", train=True, download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # to tensor
torchvision.transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,)) # standardization
]))
train_loader = DataLoader(train, batch_size=batch_size)
test = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root="./data", train=False, download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # to tensor
torchvision.transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,)) # standardization
]))
test_loader = DataLoader(test, batch_size=batch_size)
return train_loader, test_loader
train_loader, test_loader = get_data()
for _, (X, y) in enumerate(train_loader):
X = X.reshape(batch_size,-1).to(device)
y = y.to(device)
for _, (x_test,y_test) in enumerate(test_loader):
x_test = x_test.reshape(10000,-1).to(device)
y_test = y_test.to(device)
class bnnHmc():
def __init__(self,net,alpha):
super().__init__()
self.net = net
self.alpha = alpha
self.d = sum(p.numel() for p in self.net.parameters())
self.loss = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device)
self.loss_list = []
self.train_acc = []
self.test_acc = []
def step(self, s, path_len=0.001, step_size=0.1):
# Step 1:
proposal_net = copy.deepcopy(self.net) # Copy the sample to put the sample after iteration
p_old = torch.randn(self.d).to(device) * 0.0005 # Randomly choose the original speed
p_new = copy.deepcopy(p_old).to(device) # Randomly choose a new speed
# Calculate potential energy U(x)=-log(p(x))
yhat = self.net(X)
x_0_nlp = - self.loss(yhat, y)
# Calculate kinetic energy
p_0_nlp = (p_old * p_old).sum() / 2
H_0 = p_0_nlp + x_0_nlp
x_0_nlp.backward()
du_dx = torch.tensor([]).to(device)
for i in self.net.parameters():
i = i.grad.reshape(-1)
shape = i.shape[0]
du_dx = torch.cat([du_dx, i.reshape(shape, 1)])
du_dx = du_dx.reshape(self.d)
# leapfrog dynamic iteration
# 1. P take a half step
p_new += step_size * du_dx / 2 # as potential energy increases, kinetic energy
# 2. Parameters go one step
sum = 0
for i, j in zip(proposal_net.parameters(), range(self.d)):
size = i.numel()
i.data += step_size * p_new[sum:sum + size].reshape(i.data.shape)
sum += size
# 3.Update the parameters required in the second half of the step
yhat = proposal_net(X)
x_1_nlp = - self.loss(yhat, y)
x_1_nlp.backward()
du_dx = torch.tensor([]).to(device)
for i in proposal_net.parameters():
i = i.grad.reshape(-1)
shape = i.shape[0]
du_dx = torch.cat([du_dx, i.reshape(shape, 1)])
# 4. take half a step
du_dx = du_dx.reshape(self.d)
p_new += step_size * du_dx.reshape(self.d) / 2 # second half-step "leapfrog" update to momentum
p_1_nlp = (p_new * p_new).sum() / 2
yhat = proposal_net(X)
x_1_nlp = - self.loss(yhat, y)
H_1 = x_1_nlp + p_1_nlp
acceptance = torch.exp((- H_0 + H_1) * 1000)
rand = torch.rand(1)[0].to(device)
if acceptance > rand:
self.net = proposal_net
self.loss_list.append(-x_1_nlp.data)
else:
self.loss_list.append(- x_0_nlp.data)
if s % 50 == 0:
print("epoch",s,"loss = ",-x_1_nlp)
correct = (yhat.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
self.train_acc.append(correct / 60000 )
print("train_acc:",correct / 60000)
correct = (proposal_net(x_test).argmax(1) == y_test).type(torch.float).sum().item()
self.test_acc.append(correct / 10000 )
print("test_acc:",correct / 10000)
def fit(self, num_steps=1000):
trajectory = []
for s in tqdm(range(num_steps)):
self.step(s)
# 记录每个参数的值
parameters = torch.cat([param.view(-1) for param in self.net.parameters()])[:100]
trajectory.append(parameters.cpu().detach().numpy().tolist())
return np.array(self.loss_list), np.array(self.train_acc), np.array(self.test_acc),np.array(trajectory)
model_hmc = copy.deepcopy(model_o)
model_hmc = model_hmc.to(device)
alpha = 0.001
num_steps = 30000
trainer = bnnHmc(model_hmc, alpha=alpha)
loss,train_acc,test_acc,samples = trainer.fit(num_steps=num_steps)
# save data
np.save('mnist_SPhmc_loss'+'.npy', loss)
np.save('mnist_SPhmc_train_acc'+'.npy', train_acc)
np.save('mnist_SPhmc_test_acc'+'.npy', test_acc)
np.save('mnist_SPhmc_samples'+'.npy', samples)
- 从容器创建一个新的镜像
sudo docker commit 92ede4d54808 ygf_pytorch1.9.0
- 查看镜像列表,有
ygf_pytorch1.9.0表示创建成功
sudo docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
ygf_pytorch1.9.0 latest 9d1753a8697d 8 seconds ago 4.53GB
jupyterv2/pytorch latest 589b7f07ccc4 17 hours ago 3.58GB
jupyter latest 6ebc0b4666fe 17 hours ago 3.58GB
ubuntu latest a8780b506fa4 6 days ago 77.8MB
nvidia/cuda 10.0-cudnn7-devel-ubuntu18.04 ab9007c84133 5 months ago 3.21GB
python 3.6 54260638d07c 10 months ago 902MB
hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 13 months ago 13.3kB
pytorch/pytorch 1.9.0-cuda10.2-cudnn7-runtime 3850639cdf7a 17 months ago 4.42GB
pytorch/pytorch 1.6.0-cuda10.1-cudnn7-runtime 6a2d656bcf94 2 years ago 3.47GB
- 保存镜像为
.tar格式,并修改权限,不然不能打开也无法上传到服务器
ygf@ygf:~$ sudo docker save -o ygf_pytorch1_9_0.tar ygf_pytorch1.9.0:latest
ygf@ygf:~$ sudo chmod 777 ygf_pytorch1_9_0.tar
2. 上传到服务器
Images ->import
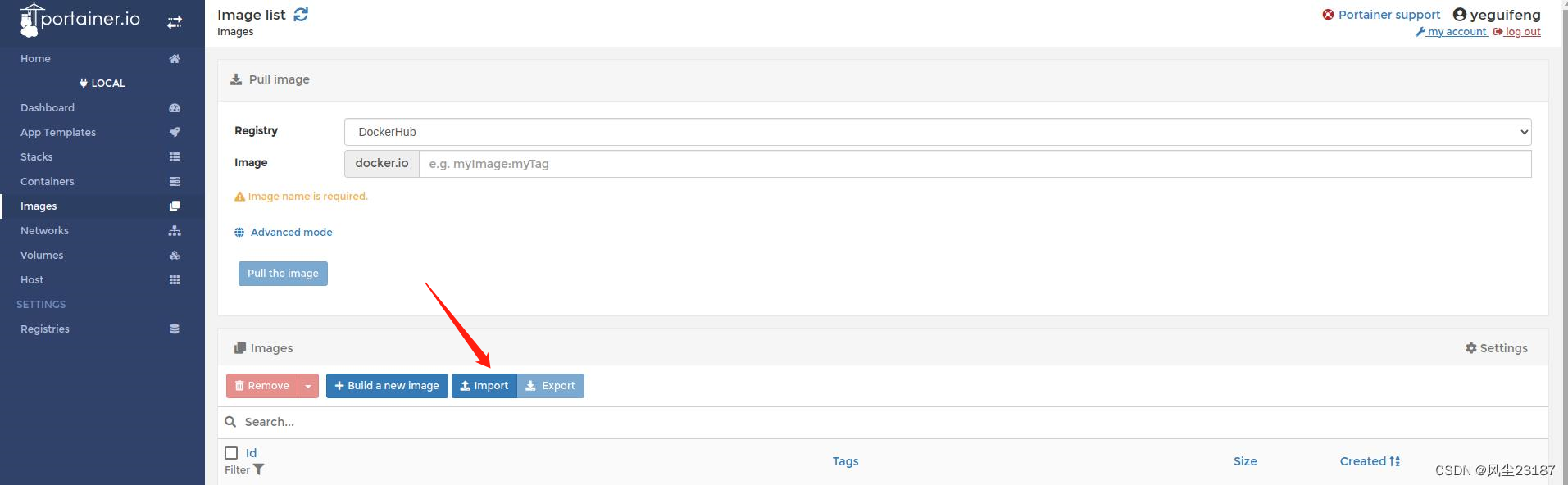
2. 选择之前的文件,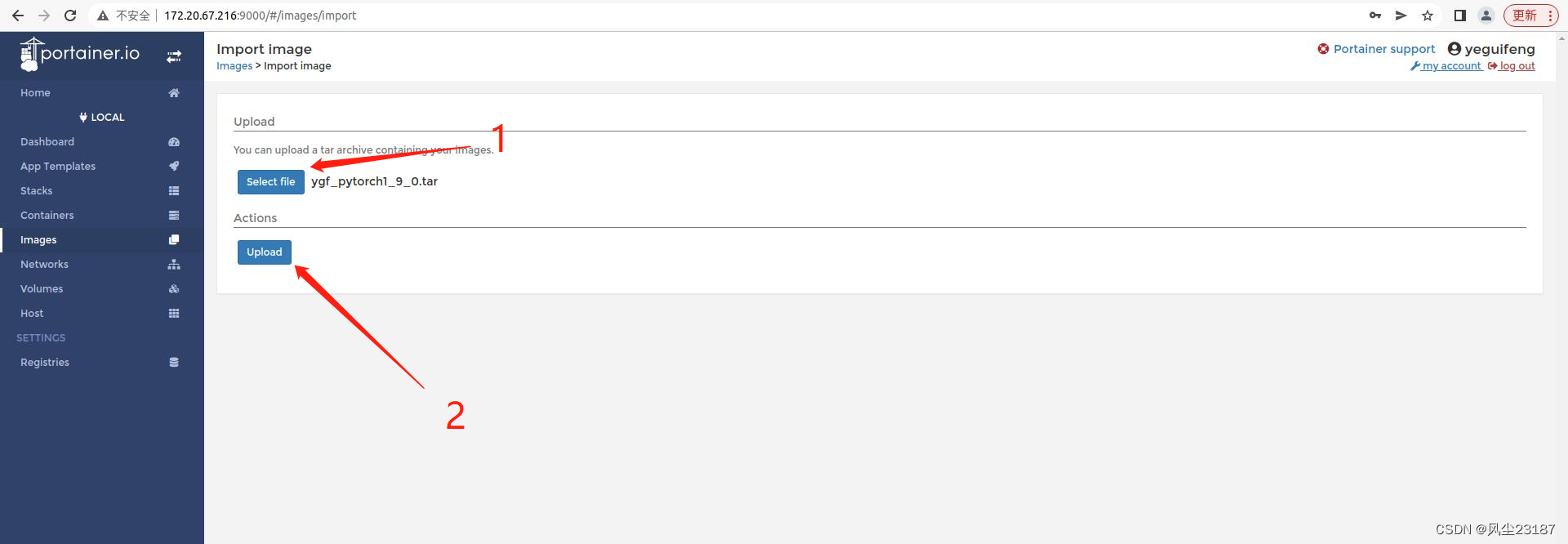
3. 查看镜像库
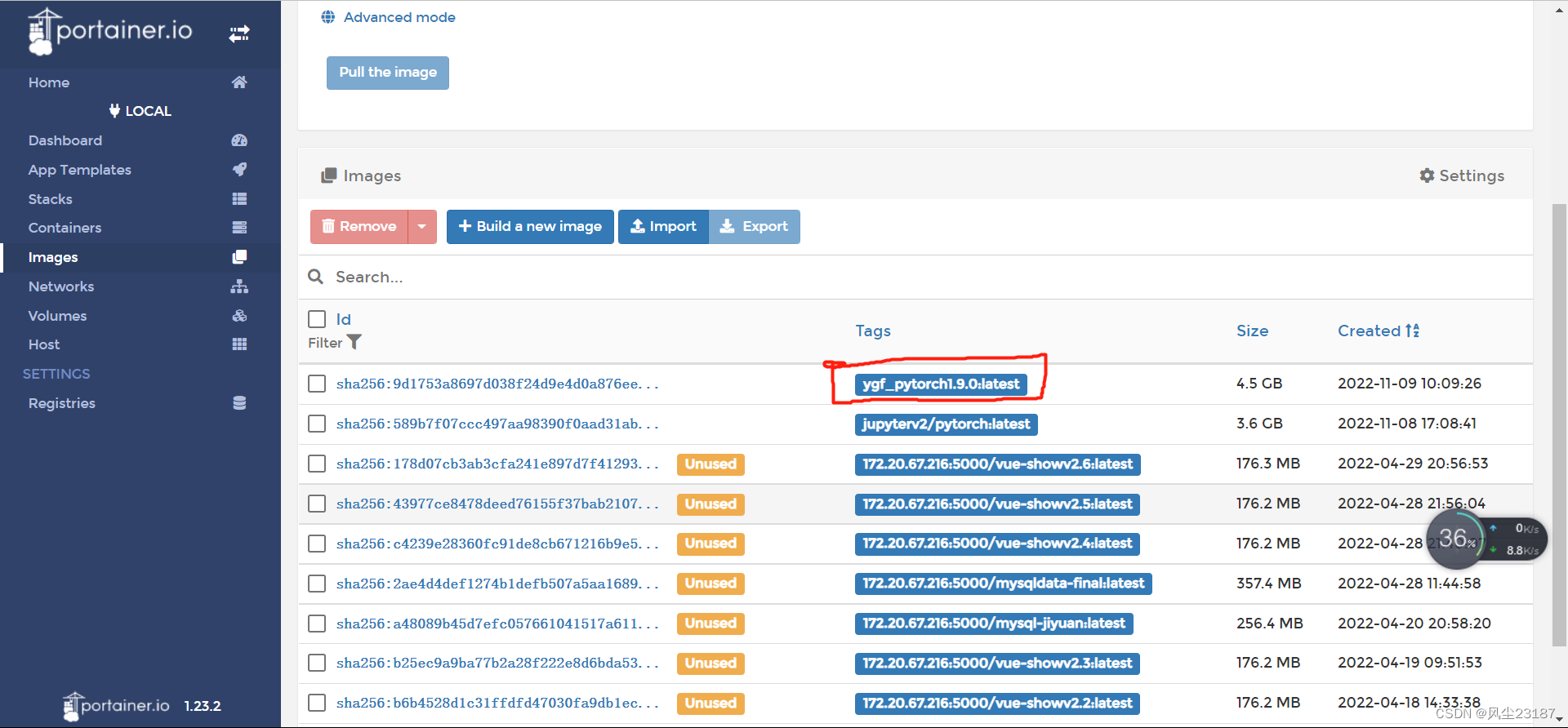
说明导入成功。
3. 创建新的Container
-
Containers->Add container
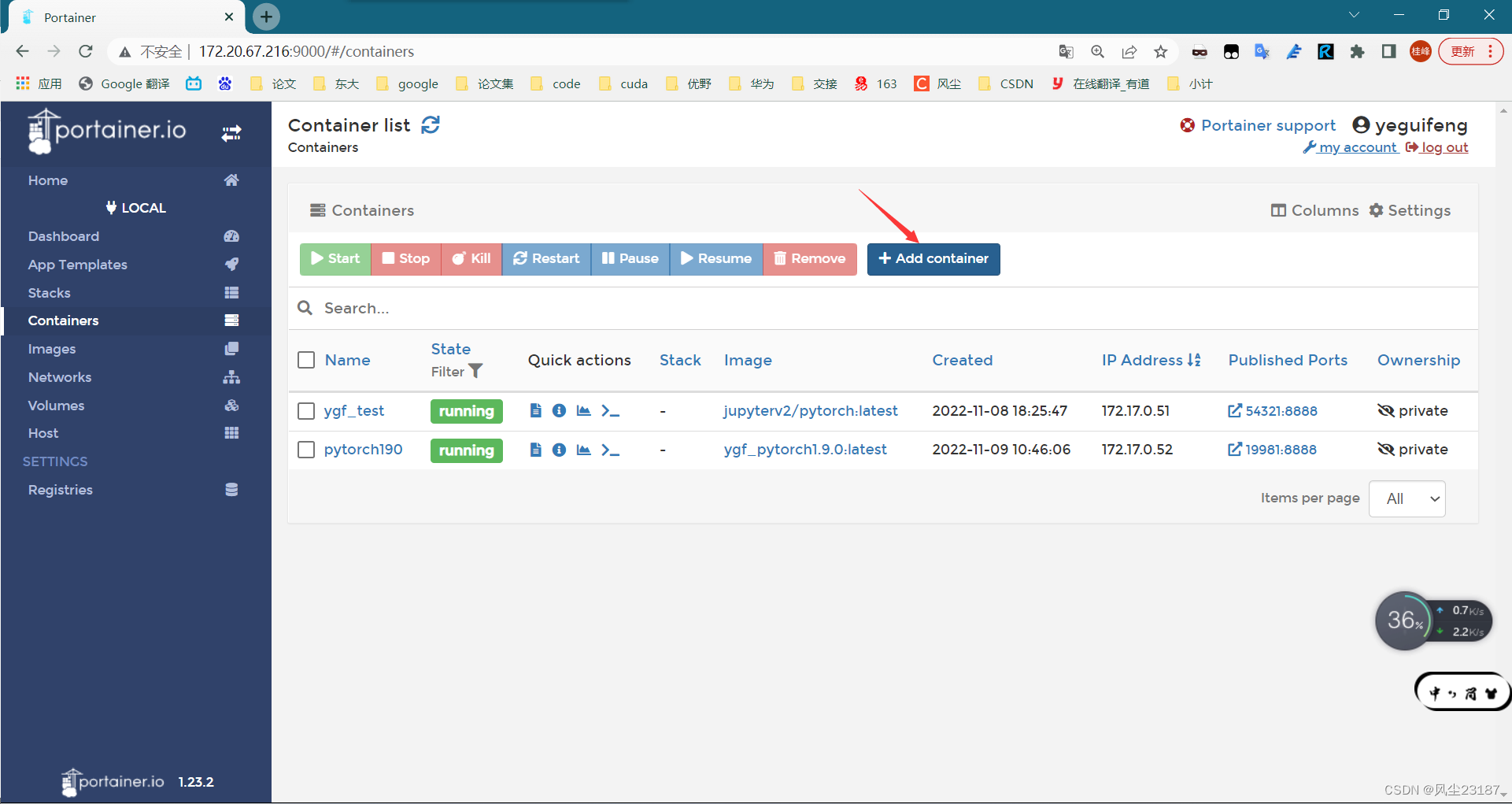
-
Container初始化
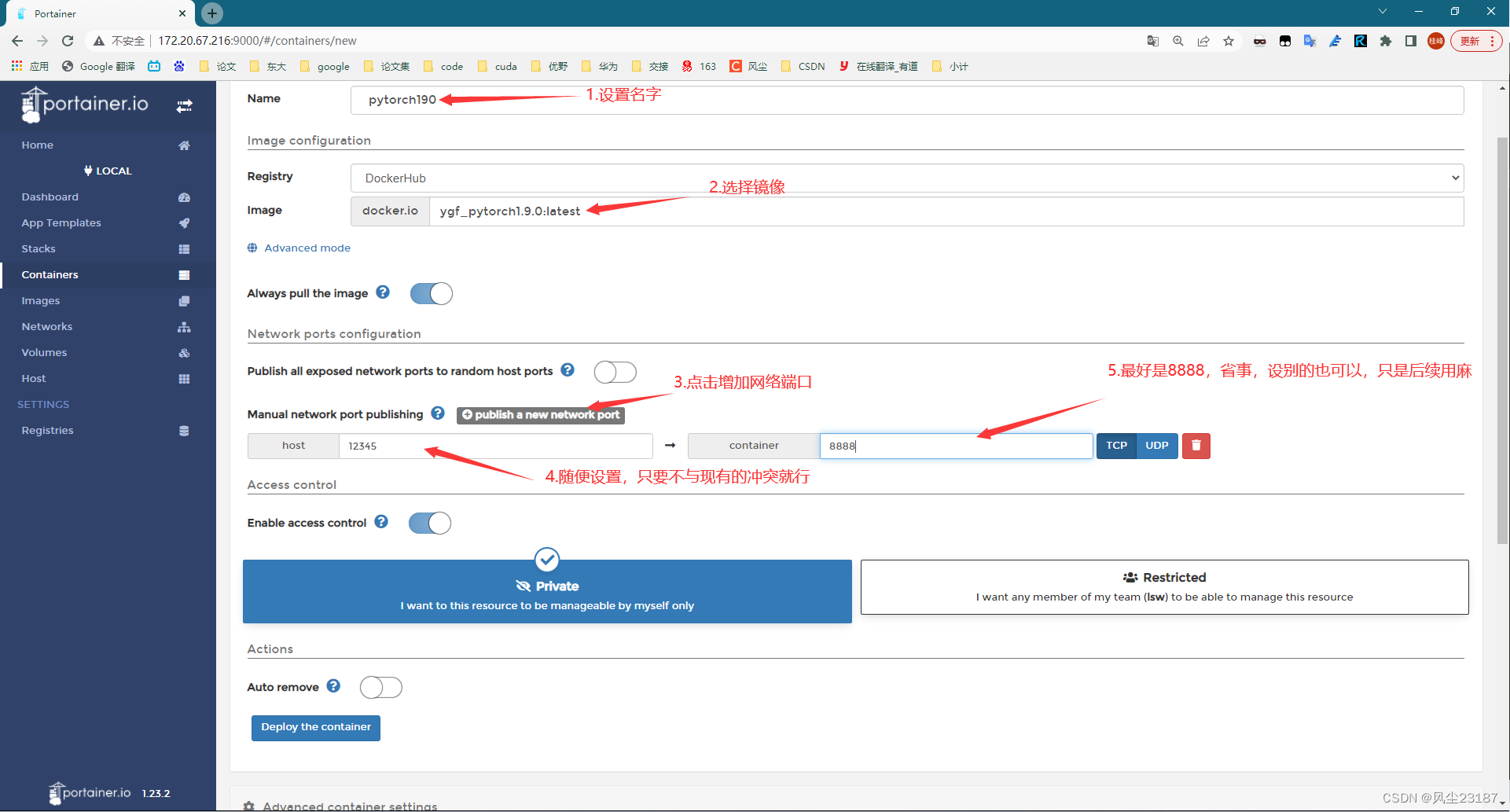
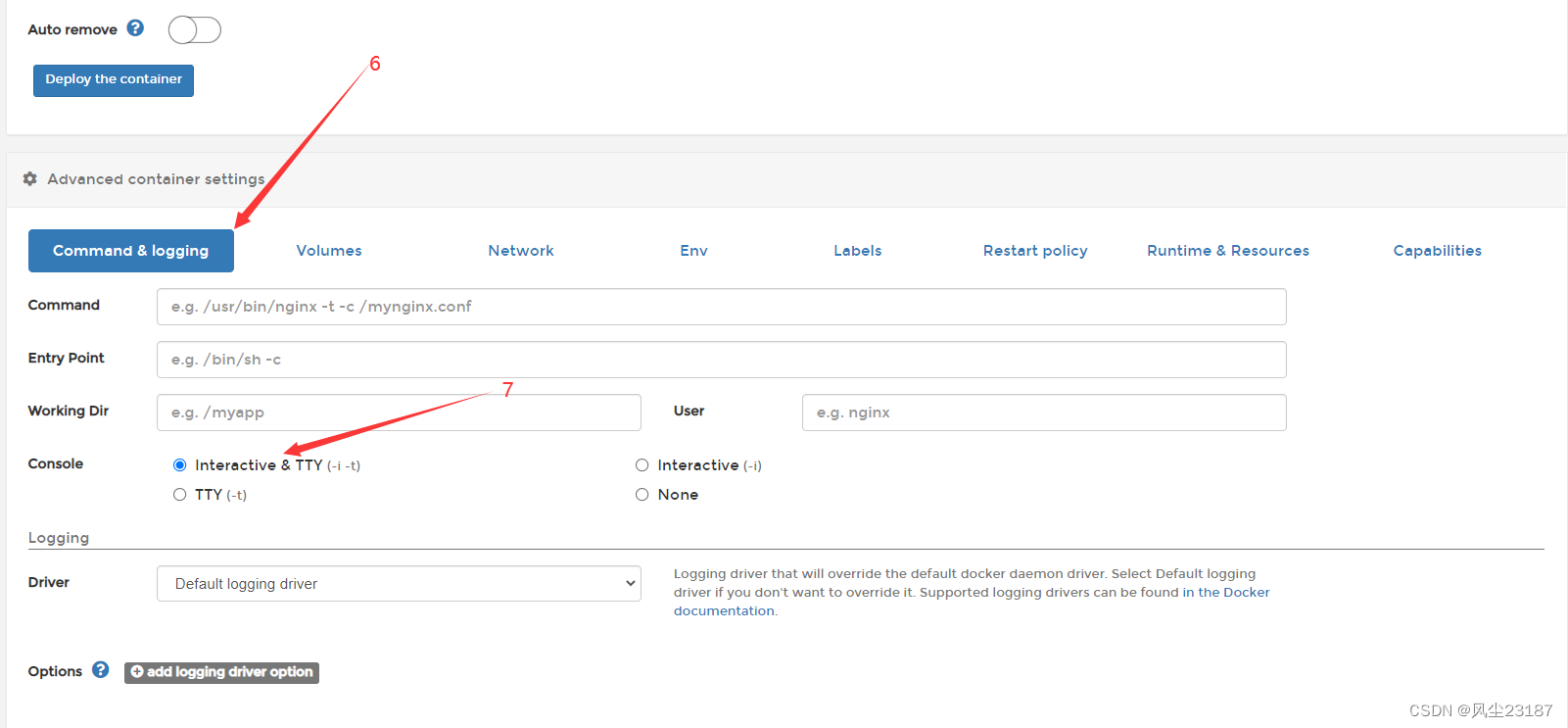
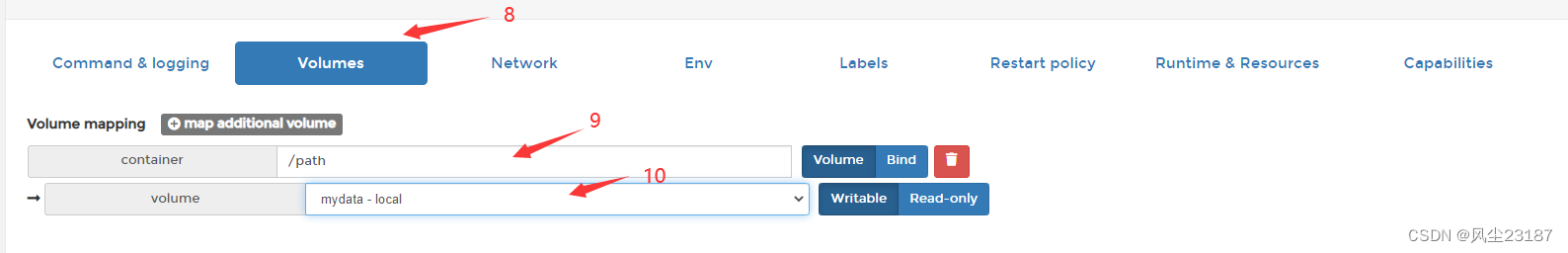
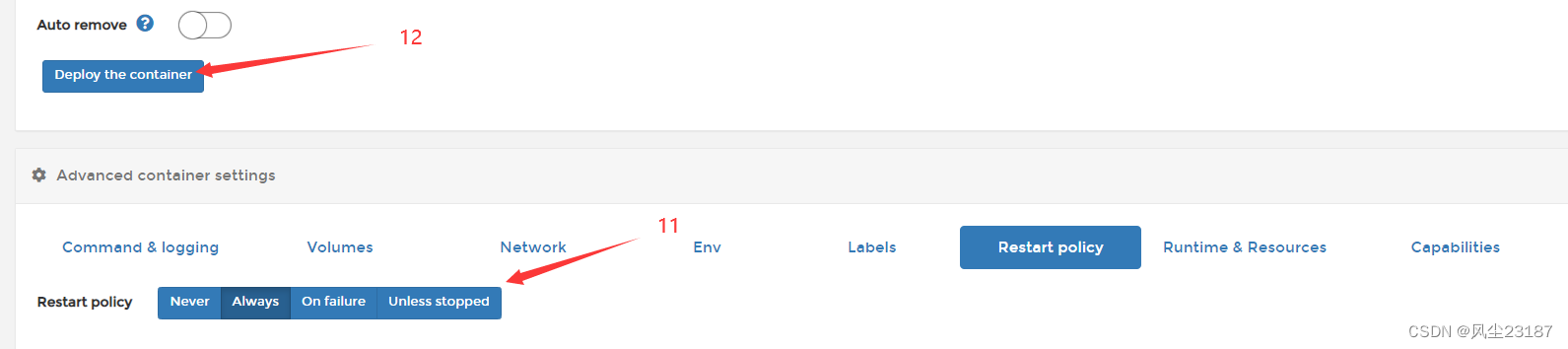
-
查看container
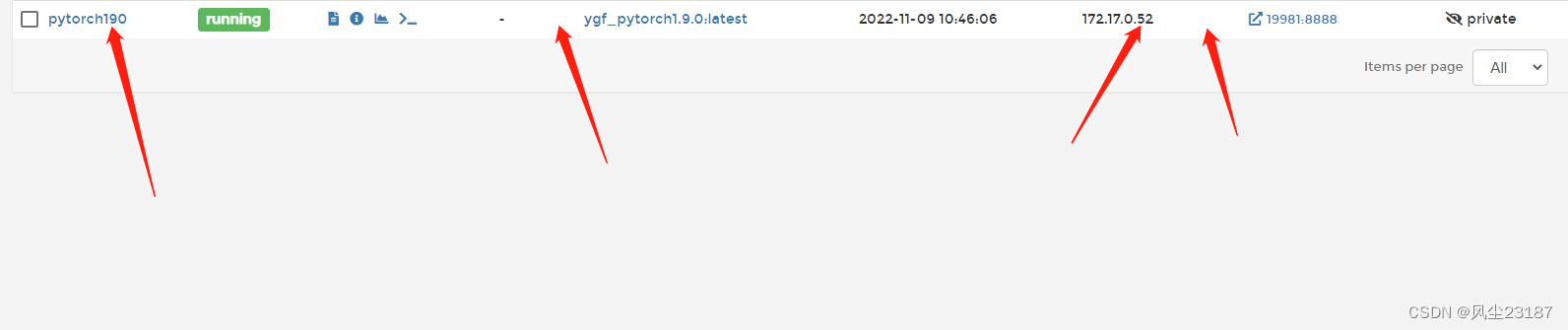
都没错。
4. 运行
-
打开终端
-
打开
jupyter
jupyter notebook --ip 0.0.0.0 --no-browser --allow-root
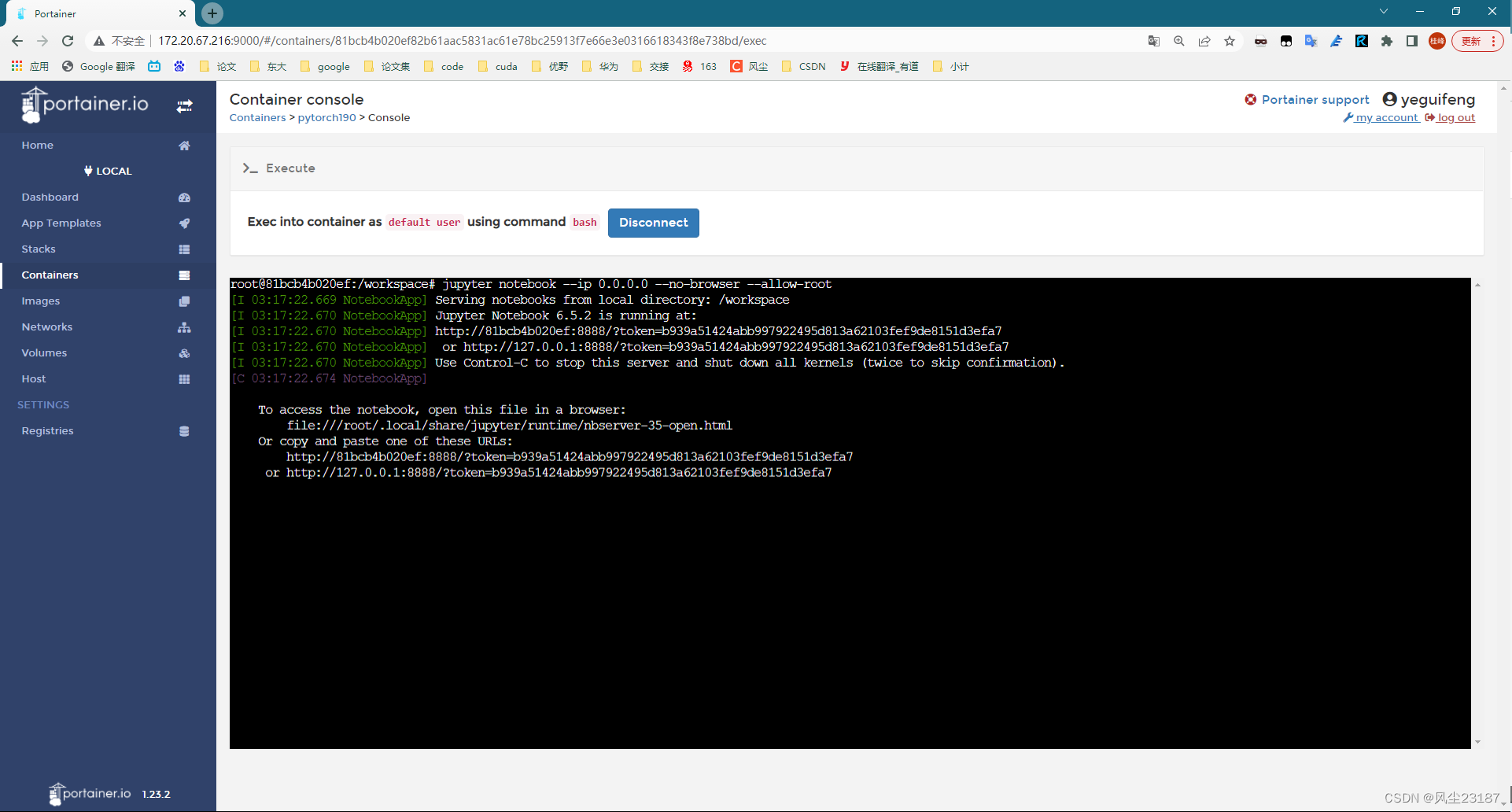
3. 远程访问jupyter
http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=b939a51424abb997922495d813a62103fef9de8151d3efa7
改为
http://172.20.67.216:19981/?token=b939a51424abb997922495d813a62103fef9de8151d3efa7
# http://172.20.67.216:35545/?token=23ed775cc21a3caf096a0f470f3ce797e4dc5a9e7bd79b5d
# http://172.20.67.216:23187/?token=?e6ccc855e0c78a9846daf89ccb6c851315e2d53d511fe0e2
# http://172.20.67.216:36544/?token=eb8d2584c37d52b6dd06cb28884ac59b137aef306d13aeb2
修改方式如下:

访问成功!
import copy
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import altair as alt
import pandas as pd
import scipy.stats
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import norm
from scipy import stats
from tqdm import tqdm
import math
import time
import numpy as np
from pycuda import autoinit
import pycuda.gpuarray as gpuarray
import numpy as np
from pycuda.compiler import SourceModule
import pycuda.driver as drv
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_probability as tfp
N = 500
beta0 = -1.0
beta_true = 2.0
sigma_true = 0.5
X = np.random.uniform(-1,1,N).astype(numpy.float32)
Y = beta0 + X *beta_true + sigma_true*np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=1, size=N)
Y = Y.astype(numpy.float32)
data = {'x' : X,'y' : Y}
# Define the CUDA kernel for log likelihood computation
# 似然计算函数 GPU版本
mhmod = SourceModule(
"""
#include <cmath>
__global__ void log_likelihood_kernel(float *x, float *y, float *net, float *result,int data_num) {
const int idx = threadIdx.x;
const float MPI = 3.14159265359;
for(int i=0;i<data_num;i++){
float y_hat = net[0] + net[1] * x[i];
double temp = (y[i] - y_hat) / net[2];
result[i] = -0.5 * log(2 * MPI * net[2] * net[2]) - 0.5 * temp * temp;
}
}
"""
)
pmod = SourceModule(
"""
#include <cmath>
__global__ void log_likelihood_kernel(float *x, float *y, float *nets, float *result,int num_nets,int data_num, int nets_num, float *trans_data) {
const int idx = threadIdx.x;
const float MPI = 3.14159265359;
for(int i=0;i<data_num;i++){
float y_hat = nets[idx * num_nets] + nets[idx * num_nets + 1] * x[i];
double temp = (y[i] - y_hat) / nets[idx * num_nets+2];
result[idx *data_num +i] = -0.5 * log(2 * MPI * nets[idx * num_nets+2] * nets[idx * num_nets+2]) - 0.5 * temp * temp;
}
for(int i=0;i<nets_num;i++){
if(idx != i){
for(int j=0;j<num_nets;j++){
double temp = nets[idx*num_nets + j] - nets[i*num_nets+j];
trans_data[idx] += -0.5 * log(2 * MPI) - 0.5 * temp * temp;
}
}
}
}
"""
)
# Get the CUDA kernel function
muti_loglik_cuda = pmod.get_function("log_likelihood_kernel")
def muti_loglik_pycuda(data, nets):
# Allocate memory for the result on the GPU
result = np.zeros(nets.shape[0]*data['x'].shape[0]).astype(numpy.float32)
nets_num = nets.shape[0]
nets_size = nets.shape[1]
nets = nets.reshape(-1)
data_num = data['x'].shape[0]
trans_data = np.zeros(nets_num).astype(numpy.float32)
# Run the CUDA kernel
muti_loglik_cuda(drv.In(data['x']), drv.In(data['y']), drv.In(nets), drv.Out(result),np.int32(nets_size),np.int32(data_num),np.int32(nets_num),drv.Out(trans_data),block=(nets_num,1, 1), grid=(1, 1))
return np.sum(result.reshape([nets_num,-1]),axis=1)/ data["y"].shape[0] * 50+trans_data
# Get the CUDA kernel function
log_likelihood_cuda = mhmod.get_function("log_likelihood_kernel")
def loglik_pycuda(data, net):
# Allocate memory for the result on the GPU
result = np.zeros_like(data['x'])
# Set up grid and block dimensions
data_num = data['x'].shape[0]
# Run the CUDA kernel
log_likelihood_cuda(drv.In(data['x']), drv.In(data['y']), drv.In(net), drv.Out(result),np.int32(data_num),block=(1,1, 1), grid=(1, 1))
# Return the mean log likelihood
return np.sum(result) / data["y"].shape[0] * 50
# Define the CUDA kernel for log likelihood computation
# 似然计算函数 GPU版本
#result[idx] = -0.5 * log(2 * MPI * net[2] * net[2]) - 0.5 * temp * temp;
# Compile the CUDA kernel
pmpmod = SourceModule(
"""
#include <cmath>
__global__ void log_likelihood_kernel(float *x, float *y, float *nets, float *result,int num_nets,int data_num,float *tran_table,float *trans_values, int deep) {
const int idx = threadIdx.x;
const float MPI = 3.14159265359;
trans_values[idx] = 0;
for(int i=0;i<data_num;i++){
float y_hat = nets[idx * num_nets] + nets[idx * num_nets + 1] * x[i];
double temp = (y[i] - y_hat) / nets[idx * num_nets+2];
result[idx *data_num +i] = -0.5 * log(2 * MPI * nets[idx * num_nets+2] * nets[idx * num_nets+2]) - 0.5 * temp * temp;
}
for(int d=0; d<deep; d++){
int net_from_index = tran_table[idx*deep*2+d*2];
int net_to_index = tran_table[idx*deep*2+d*2+1];
for(int j=0;j<num_nets;j++){
double temp = nets[net_from_index*num_nets+j] - nets[net_to_index*num_nets+j];
trans_values[idx] += -0.5 * log(2 * MPI) - 0.5 * temp * temp;
}
}
}
"""
)
# Get the CUDA kernel function
muti_loglik_cuda_pmp = pmpmod.get_function("log_likelihood_kernel")
def muti_loglik_pycuda_pmp(data, nets, tran_table):
# Allocate memory for the result on the GPU
result = np.zeros(nets.shape[0]*data['x'].shape[0]).astype(numpy.float32)
nets_num = nets.shape[0]
nets_size = nets.shape[1]
nets = nets.reshape(-1)
tran_table = tran_table.reshape(-1).astype(numpy.float32)
data_num = data['x'].shape[0]
trans_values = np.zeros(nets_num).astype(numpy.float32)
deep = np.log2(nets_num)
# Run the CUDA kernel
muti_loglik_cuda_pmp(drv.In(data['x']), drv.In(data['y']), drv.In(nets), drv.Out(result),np.int32(nets_size),np.int32(data_num),drv.In(tran_table),drv.Out(trans_values),np.int32(deep),block=(nets_num,1, 1), grid=(1, 1))
return np.sum(result.reshape([nets_num,-1]),axis=1)/ data["y"].shape[0] * 50+trans_values
class MHtrain():
def __init__(self, net, alpha):
super().__init__()
self.net = net.astype(numpy.float32)
self.alpha = alpha
self.d = self.net.shape[0]
def updata(self,net):
rand_step = np.random.normal(0, self.alpha, net.shape).astype(numpy.float32)
return rand_step + net
def step(self, data, function):
new_net = self.updata(self.net)
ratio = math.exp(function(data, new_net) - function(data, self.net))
random_number = np.random.rand()
if(random_number<ratio):
self.net = new_net
def fit(self, data=None, num_steps=1000, function = loglik_pycuda):
parameter_trace = np.empty([num_steps, self.d])
t = time.time()
dalte_time = 1
time_trace = []
index_begin = 0
ess_list = []
for s in tqdm(range(num_steps)):
self.step(data, function)
if time.time()-t>dalte_time:
t = time.time()
index_end = s
parameters = parameter_trace[index_begin:index_end,0]
ess = tfp.mcmc.effective_sample_size(tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters))
ess_list.append(ess)
time_trace.append(self.net)
index_begin = s
parameter_trace[s:(s + 1),:] = self.net
return parameter_trace,np.array(ess_list)
net_init = np.array([1,1,1]).astype(numpy.float32)
class MPtrain():
def __init__(self, net, alpha, N):
super().__init__()
self.net = net.astype(numpy.float32)
self.alpha = alpha
self.N = N
self.d = self.net.shape[0]
def updata(self,net):
rand_step = np.random.normal(0, self.alpha, net.shape).astype(numpy.float32)
return rand_step + net
def log_trans_prob(self, net, net_star):
log_trans_prob = np.array([0.0])
len = net.shape[0]
for i in range(len):
log_trans_prob += np.log(stats.norm.pdf(net[i],net_star[i]))
return log_trans_prob
def step(self, data, nets, function):
# Step 1:
# 计算接受率(可并行)
A = np.empty([self.N+1 , 1])
K = np.empty([self.N+1 , 1])
A[:, 0] = function(data,nets)
# 根据接受率采样
A = (A - np.mean(A)) / np.std(A)
B = pd.DataFrame(np.exp(A).reshape(-1))
index = pd.DataFrame(np.linspace(0, self.N, self.N + 1).astype(np.int32))
index_weight = index.sample(self.N+1,replace=True, weights=B[0]).values.reshape(-1)
new_proposal_nets = copy.deepcopy(nets)
for i,j in zip(index_weight,index.values.reshape(-1)):
new_proposal_nets[j] = nets[i]
I = np.random.choice(np.linspace(0, self.N, self.N + 1).astype(np.int32), 1)
self.net = new_proposal_nets[I[0]]
return new_proposal_nets
def fit(self, data=None, num_steps=1000, function = muti_loglik_pycuda):
parameter_trace = np.empty([num_steps*(self.N+1), self.d])
nets = np.empty([self.N+1, self.d]).astype(numpy.float32)
t = time.time()
dalte_time = 1
time_trace = []
ess_list = []
index_begin = 0
for s in tqdm(range(num_steps)):
# 1.产生建议参数
nets[0] = self.net
for i in range(1,self.N+1):
nets[i] = self.updata(nets[0])
# 2.优化采样
new_proposal_nets = self.step(data,nets,function)
if (time.time()-t>dalte_time):
t = time.time()
index_end = s
parameters = parameter_trace[index_begin*(self.N+1):index_end*(self.N+1),0]
ess = tfp.mcmc.effective_sample_size(tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters))
ess_list.append(ess)
time_trace.append(self.net)
index_begin = s
parameter_trace[s*(self.N+1):(s + 1)*(self.N+1),:] = new_proposal_nets
return parameter_trace,np.array(ess_list)
# GPU
# ess_data = []
# Ns = [3,7,15,31,63,127]
# for N in Ns:
# print(N)
# train = MPtrain(net_init,alpha = 0.02, N=N)
# parameter_trace,ess_list = train.fit(ess_data,10000,function=muti_loglik_pycuda)
# ess_data.append(ess_list[-10:])
# np.save("MP_3_7_15_31_63_127",np.array(ess_data))
# sample_num = parameter_trace.shape[0]
# line = np.linspace(0,sample_num,sample_num)
# for i in range(train.d):
# plt.plot(line,parameter_trace[:,i],label="par"+str(i))
# plt.show()
# plt.boxplot(np.array(data))
class PMPtrain():
def __init__(self, net, alpha, N):
super().__init__()
self.net = net.astype(numpy.float32)
self.alpha = alpha
self.N = N
self.d = self.net.shape[0]
def updata(self,net):
rand_step = np.random.normal(0, self.alpha, net.shape).astype(numpy.float32)
return rand_step + net
def log_trans_prob(self, net, net_star):
log_trans_prob = np.array([0.0])
len = net.shape[0]
for i in range(len):
log_trans_prob += np.log(stats.norm.pdf(net[i],net_star[i]))
return log_trans_prob
def step(self, data, nets,tran_table, function):
# Step 1:
# 计算接受率(可并行)
tree_deep = math.log2(self.N+1)
A = np.empty([self.N+1 , 1])
K = np.empty([self.N+1 , 1])
A[:, 0] = function(data,nets,tran_table)
# 根据接受率采样
A = (A - np.mean(A)) / np.std(A)
B = pd.DataFrame(np.exp(A).reshape(-1))
index = pd.DataFrame(np.linspace(0, self.N, self.N + 1).astype(np.int32))
index_weight = index.sample(self.N+1,replace=True, weights=B[0]).values.reshape(-1)
new_proposal_nets = copy.deepcopy(nets)
for i,j in zip(index_weight,index.values.reshape(-1)):
new_proposal_nets[j] = nets[i]
I = np.random.choice(np.linspace(0, self.N, self.N + 1).astype(np.int32), 1)
self.net = new_proposal_nets[I[0]]
return new_proposal_nets
def fit(self, data=None, num_steps=1000, function = muti_loglik_pycuda_pmp):
parameter_trace = np.empty([num_steps *(self.N+1), self.d])
nets = np.empty([self.N+1, self.d]).astype(numpy.float32)
tree_deep = math.log2(self.N+1)
tran_table = np.ones([self.N+1,int(tree_deep),2]).astype(np.int32())*-1
t = time.time()
dalte_time = 1
time_trace = []
index_begin = 0
ess_list = []
for s in tqdm(range(num_steps)):
# 1.产生建议参数
nets[0] = self.net
for i in range(int(tree_deep)):
j = int(math.pow(2,i))
for k in range(int(j)):
nets[k+j] = copy.deepcopy(self.updata(nets[k]))
tran_table[k][i] = np.array([k,k+j])
tran_table[k+j][i] = np.array([k+j,k])
if i-1>-1 & tran_table[k+j][i-1][0]==-1:
tran_table[k+j][:i] = tran_table[k][:i]
# 2.优化采样
new_proposal_nets = self.step(data, nets, tran_table, function)
if (time.time()-t>dalte_time):
t = time.time()
index_end = s
parameters = parameter_trace[index_begin*(self.N+1):index_end*(self.N+1),0]
ess = tfp.mcmc.effective_sample_size(tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters))
ess_list.append(ess)
time_trace.append(self.net)
index_begin = s
parameter_trace[s*(self.N+1):(s + 1)*(self.N+1),:] = new_proposal_nets
return parameter_trace,np.array(ess_list)
# GPU
# train = PMPtrain(net_init,alpha = 0.02, N=7)
# parameter_trace,ess_list = train.fit(data,10000,function= muti_loglik_pycuda_pmp)
# plt.boxplot(ess_list[-10:])


![[蓝桥杯练习]通电](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f58214a38e02480b848dd66f4ab6038e.png)



![[计算机效率] 磁盘空间分析工具:FolderSize](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/015ecd1d564947faa6dadeb70494cb00.png)

![CTF下加载CTFtraining题库以管理员身份导入 [HCTF 2018]WarmUp,之后以参赛者身份完成解题全过程](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/16f5aad85bd64fc3b1f1ca9c27766b57.png)