多线程
线程是操作系统能够进入运算调度的最小单位。它被包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位。
进程:是程序的基本执行实体。
并发:在同一个时刻,有多个指令在单个CPU上交替执行。
并行:在同一时刻,有多个指令在多个CPU上同时执行。
多线程的实现方式
1.继承Thread类的方式进行实现
package MyThread;
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"helloworld");
}
}
}
package MyThread;
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread t1=new MyThread();
MyThread t2=new MyThread();
t1.setName("线程1");
t2.setName("线程2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
2.实现Runnable接口的方式进行实现
package MyThread.a02ThreadDemo02;
public class MyRun implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(t.getName()+"Helloworld");
}
}
}
package MyThread.a02ThreadDemo02;
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRun mr=new MyRun();
Thread t1=new Thread(mr);
Thread t2=new Thread(mr);
t1.setName("线程1");
t2.setName("线程2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
3.利用Callable接口和Future接口方式实现
package MyThread.a03ThreadDemo03;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int sum=0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum=sum+i;
}
return sum;
}
}
package MyThread.a03ThreadDemo03;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
MyCallable mc=new MyCallable();
FutureTask<Integer> ft=new FutureTask<>(mc);
Thread t1=new Thread();
t1.start();
Integer result = ft.get();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
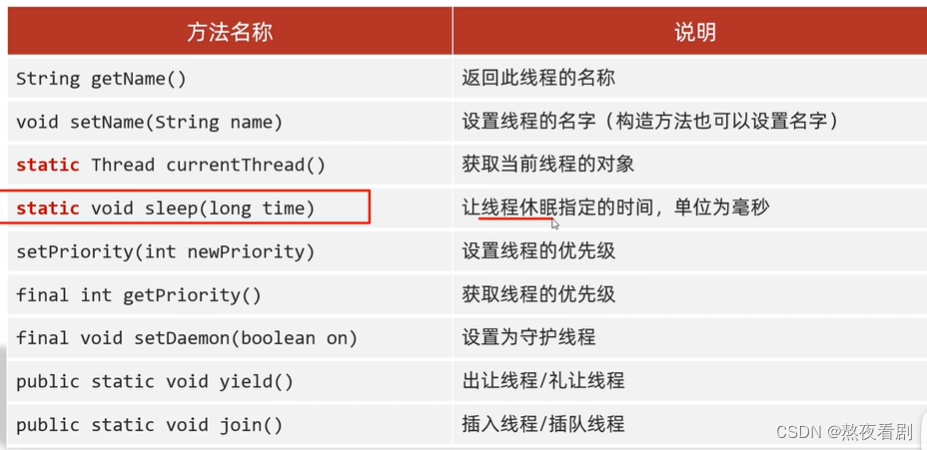
常见的成员方法
package MyThread.a04ThreadDemo;
public class MyThread extends Thread{
public MyThread() {
}
public MyThread(String name){
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"@"+i);
}
}
}
package MyThread.a04ThreadDemo;
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//getName
//1.如果我们没有给线程设置名字,线程也是有默认的名字的
//格式:Thread-x(x序号,从0开始的)
//2.如果我们要给线程设置名字,可以用set方法进行设置,也可以用构造方法
//当jvm虚拟机启动之后,会自动的启动多条线程,其中有一条线程就叫main线程
//它的作用就是调用main方法,并执行里面的代码
/* MyThread t1=new MyThread();
MyThread t2=new MyThread();
MyThread t3=new MyThread("karry");
MyThread t4=new MyThread("roy");
t1.start();
t2.start();*/
//哪条线程执行到这个方法,此时获取的就是哪条线程的对象
Thread t=new Thread();
String name = t.getName();
System.out.println(name);
}
}
线程的优先级
package MyThread.a05threadDEMO;
public class MyRun implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+i);
}
}
}
package MyThread.a05threadDEMO;
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRun mr=new MyRun();
Thread t1=new Thread(mr,"karry");
Thread t2=new Thread(mr,"roy");
System.out.println(t1.getPriority());
System.out.println(t2.getPriority());
t1.setPriority(1);
t2.setPriority(10);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
守护线程
package MyThread.a06threaddemo;
public class MyThread1 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"@"+i);
}
}
}
package MyThread.a06threaddemo;
public class MyThread2 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"@"+i);
}
}
}package MyThread.a06threaddemo;
import MyThread.a04ThreadDemo.MyThread;
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread1 t1=new MyThread1();
MyThread2 t2=new MyThread2();
t1.setName("karry");
t2.setName("roy");
t2.setDaemon(true);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}