前言
对 MySQL 数据库,除了使用基本语言处理一些简单的事务外,还可以使用高级SQL语言用于复杂的数据库操作。包括多表联合查询、子查询、触发器、存储过程和视图等功能。
目录
一、数据库函数
1. 数学函数
2. 聚合函数
3. 字符串函数
4. 日期时间函数
二、常用查询
1. 按关键字排序
1.1 语法格式
1.2 示例
2. 区间判断及查询去重
2.1 and/or(且/或)
2.2 查询不重复记录
3. 分组查询
3.1 语法格式
3.2 示例
4. 限制结果条目
4.1 语法格式
4.2 示例
5. 设置别名
5.1 语法格式
5.2 示例
6. 通配符
6.1 一般格式
6.2 示例
7. 子查询
7.1 格式
7.2 查询
7.3 删除
7.4 写入
7.5 更新
7.6 exists 关键字查询
7.7 子查询别名
7.8 返回值取反
三、mysql 视图
1. 概述
2. 视图与表的区别
3. 视图操作
3.1 视图创建
3.2 查看表状态
3.3 视图查询
3.4 视图修改
3.5 视图删除
4. null 值
四、连接查询
1. 概述
2. 内连接
3. 左连接
4. 右连接
一、数据库函数
1. 数学函数
数据库内存储的记录,经常要进行一系列的算术操作,所以 MySQL 支持很多数学函数。
常用的数学函数如下:
| 数学函数 | 描述 |
| abs(x) | 返回 x 的绝对值 |
| rand() | 返回 0 到 1 的随机数 |
| mod(x,y) | 返回 x 除以 y 以后的余数 |
| power(x,y) | 返回 x 的 y 次方 |
| round(x) | 返回离 x 最近的整数 |
| round(x,y) | 保留 x 的 y 位小数四舍五入后的值 |
| sqrt(x) | 返回 x 的平方根 |
| truncate(x,y) | 返回数字 x 截断为 y 位小数的值 |
| ceil(x) | 返回大于或等于 x 的最小整数 |
| floor(x) | 返回小于或等于 x 的最大整数 |
| greatest(x1,x2…) | 返回集合中最大的值 |
| least(x1,x2…) | 返回集合中最小的值 |
示例:
mysql> select abs(-2),rand(),mod(3,2),power(2,2),round(5),round(1.295,2),sqrt(4),truncate(1.295,2),ceil(5),floor(55),greatest(1,3,5),least(1,3,5);
+---------+--------------------+----------+------------+----------+----------------+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+-----------------+--------------+
| abs(-2) | rand() | mod(3,2) | power(2,2) | round(5) | round(1.295,2) | sqrt(4) | truncate(1.295,2) | ceil(5) | floor(5) | greatest(1,3,5) | least(1,3,5) |
+---------+--------------------+----------+------------+----------+----------------+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+-----------------+--------------+
| 2 | 0.5765201352318005 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 1.30 | 2 | 1.29 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 |
+---------+--------------------+----------+------------+----------+----------------+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+-----------------+--------------+
2. 聚合函数
MySQL 中的聚合函数用于对一组值执行计算,并返回单个值作为结果。这些函数可以对数据进行汇总、统计或计算,常见的聚合函数包括 sum、count、avg、max 和 min。
- avg():返回指定列的平均值
- count():返回指定列中非 NULL 值的个数
- min():返回指定列的最小值
- max():返回指定列的最大值
- sum():返回指定列的所有值之和
示例:
mysql> select * from student;
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 65.0 |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
mysql> select sum(score) from student;
+------------+
| sum(score) |
+------------+
| 340.5 |
+------------+
mysql> select min(score) from student;
+------------+
| min(score) |
+------------+
| 50.0 |
+------------+
3. 字符串函数
在 MySQL 中,字符串函数用于处理和操作文本数据。这些函数允许你执行各种操作,如字符串连接、截取、查找、替换等。
常见的字符函数如下:
| 字符串函数 | 描述 |
| length(x) | 返回字符串 x 的长度 |
| trim() | 从字符串的开头和结尾去除空格或其他指定字符 |
| concat(x,y) | 将提供的参数 x 和 y 拼接成一个字符串 |
| upper(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成大写字母 |
| lower(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成小写字母 |
| left(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的前 y 个字符 |
| right(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的后 y 个字符 |
| repeat(x,y) | 将字符串 x 重复 y 次 |
| space(x) | 返回 x 个空格 |
| replace(x,y,z) | 将字符串 z 替代字符串 x 中的字符串 y |
| strcmp(x,y) | 比较 x 和 y,返回的值可以为-1,0,1 |
| substring(x,y,z) | 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始长 度为 z 的字符串 |
| reverse(x) | 将字符串 x 反转 |
示例:
mysql> select length('ab c'),trim(' abc'),concat('a','b'),upper('abc'),lower('ABC'),left('abc',2),right('abc',2),repeat('ab',2),space(2),replace('heaao','aa','ll'),strcmp('1','2'),substring('abcd',2,2),reverse('abc');
+----------------+--------------+-----------------+--------------+--------------+---------------+----------------+----------------+----------+----------------------------+-----------------+-----------------------+----------------+
| length('ab c') | trim(' abc') | concat('a','b') | upper('abc') | lower('ABC') | left('abc',2) | right('abc',2) | repeat('ab',2) | space(2) | replace('heaao','aa','ll') | strcmp('1','2') | substring('abcd',2,2) | reverse('abc') |
+----------------+--------------+-----------------+--------------+--------------+---------------+----------------+----------------+----------+----------------------------+-----------------+-----------------------+----------------+
| 4 | abc | ab | ABC | abc | ab | bc | abab | | hello | -1 | bc | cba |
+----------------+--------------+-----------------+--------------+--------------+---------------+----------------+----------------+----------+----------------------------+-----------------+-----------------------+----------------+
4. 日期时间函数
在 MySQL 中,时间日期函数用于处理日期、时间和时间戳数据,执行各种操作,如日期加减、格式化、提取部分日期等。
常见的日期时间函数如下:
| 日期时间函数 | 描述 |
| curdate() | 返回当前时间的年月日 |
| curtime() | 返回当前时间的时分秒 |
| now() | 返回当前时间的日期和时间 |
| month(x) | 返回日期 x 中的月份值 |
| week(x) | 返回日期 x 是年度第几个星期 |
| hour(x) | 返回 x 中的小时值 |
| minute(x) | 返回 x 中的分钟值 |
| second(x) | 返回 x 中的秒钟值 |
| dayofweek(x) | 返回 x 是星期几,1 星期日,2 星期一 |
| dayofmonth(x) | 计算日期 x 是本月的第几天 |
| dayofyear(x) | 计算日期 x 是本年的第几天 |
示例:
mysql> select curdate(),curtime(),now(),month('2024-03-26'),week(curdate()),hour('18:34:08'),minute(curtime()),second(curtime()),dayofweek(curdate()),dayofmonth(curdate()),dayofyear(curdate());
+------------+-----------+---------------------+---------------------+-----------------+------------------+-------------------+-------------------+----------------------+-----------------------+----------------------+
| curdate() | curtime() | now() | month('2024-03-26') | week(curdate()) | hour('18:34:08') | minute(curtime()) | second(curtime()) | dayofweek(curdate()) | dayofmonth(curdate()) | dayofyear(curdate()) |
+------------+-----------+---------------------+---------------------+-----------------+------------------+-------------------+-------------------+----------------------+-----------------------+----------------------+
| 2024-03-26 | 18:37:45 | 2024-03-26 18:37:45 | 3 | 12 | 18 | 37 | 45 | 3 | 26 | 86 |
+------------+-----------+---------------------+---------------------+-----------------+------------------+-------------------+-------------------+----------------------+-----------------------+----------------------+
二、常用查询
1. 按关键字排序
使用 select 语句可以将需要的数据从 mysql 数据库中查询出来,可以使用 order by 语句来对语句实现排序,可针对多个字段。
1.1 语法格式
select 字段1,字段2,... from 表名 order by 字段a,字段b,... [desc];
# ASC:升序,默认,可以省略
# DESC:降序
# order by 前面也可以使用 where 进一步筛选
注意:
# order by 语句使用多个字段来进行排序,当第一个字段相同的记录存在多条,重复记录再按照第二个字段进行排序
# order by 后面跟多个字段时,字段之间英文逗号隔开,优先级是按先后顺序而定;但 order by 之后的第一个参数只有在出现相同值时,第二个字段才有意义(生效)1.2 示例
准备环境:
mysql> create table student (id int(5) primary key,name char(15),address varchar(20),age char(5),score decimal(3,1));
mysql> insert into student values (1,'zhangsan','nanjin',10,90.5);
mysql> insert into student values (2,'lisi','nanjin',65,80);
mysql> insert into student values (3,'wangwu','beijin',30,70);
mysql> insert into student values (4,'zhaoliu','shanghai',30,50);
mysql> insert into student values (5,'zhouqi','hangzhou',40,65);
mysql> select * from student;
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 65.0 |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
示例1:按分数分别升序降序排序,只显示 name 和 score 字段
升序:
mysql> select name,score from student order by score asc;
+----------+-------+
| name | score |
+----------+-------+
| zhaoliu | 50.0 |
| lisi | 65.0 |
| zhouqi | 65.0 |
| wangwu | 70.0 |
| zhangsan | 90.5 |
+----------+-------+
降序:
mysql> select name,score from student order by score desc;
+----------+-------+
| name | score |
+----------+-------+
| zhangsan | 90.5 |
| wangwu | 70.0 |
| lisi | 65.0 |
| zhouqi | 65.0 |
| zhaoliu | 50.0 |
+----------+-------+示例2:筛选地址是 nanjin 的学生按分数降序排列,只显示 name、address、score 字段
mysql> select name,address,score from student where address='nanjin' order by score desc;
+----------+---------+-------+
| name | address | score |
+----------+---------+-------+
| zhangsan | nanjin | 90.5 |
| lisi | nanjin | 65.0 |
+----------+---------+-------+示例3:查询信息先按 score 降序排列,相同的按年龄升序排列,只显示 name、score、age 字段
mysql> select name,score,age from student order by score desc,age;
+----------+-------+------+
| name | score | age |
+----------+-------+------+
| zhangsan | 90.5 | 10 |
| wangwu | 70.0 | 30 |
| zhouqi | 65.0 | 40 |
| lisi | 65.0 | 50 |
| zhaoliu | 50.0 | 30 |
+----------+-------+------+2. 区间判断及查询去重
2.1 and/or(且/或)
语法格式:
select *(或者字段) from 表名 where 条件1 and/or 条件2;示例1:查找成绩大于80,或小于60分的信息
mysql> select * from student where score>80 or score<60;
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+示例2:查找成绩大于等于60,且小于80分的信息
mysql> select * from student where score>=60 or score<80;
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 65.0 |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+嵌套多条件:
语法格式:
select *(或者字段) from 表名 where 条件1 and/or (条件2 and/or 条件3);示例3:查找成绩大于90,或满足大于50且小于70分的信息
mysql> select * from student where score>90 or (score>50 and score<70);
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 65.0 |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+2.2 查询不重复记录
语法格式:
select distinct 字段 from 表名;示例:去掉 address 字段重复信息
mysql> select distinct address from student;
+----------+
| address |
+----------+
| nanjin |
| beijin |
| shanghai |
| hangzhou |
+----------+3. 分组查询
通过 SQL 查询出来的结果,还可以对其进行分组,使用 group by 语句来实现 ,group by 通常都是结合聚合函数(对列进行操作)一起使用的。分组的时候可以按一个或多个字段对结果进行分组处理。
常用的聚合函数:
计数:count
求和:sum
平均数:avg
最大值:max
最小值:min3.1 语法格式
select 函数(字段1),字段2 from 表名 where 表达式 group by 字段2 order by 函数(字段1)(或其他字段) [desc];
group by 格式原则:
# 凡是在 group by 后面出现的字段,必须在 select 后面出现;
# 凡是在 select 后面出现的、且未在聚合函数中出现的字段,必须出现在 group by 后面3.2 示例
示例1:按 addres 相同信息的分组,计算相同分数的学生个数(基于 name 个数进行计数)
mysql> select count(name),address from student group by address;
+-------------+----------+
| count(name) | address |
+-------------+----------+
| 1 | beijin |
| 1 | hangzhou |
| 2 | nanjin |
| 1 | shanghai |
+-------------+----------+
示例2:结合 where 语句,筛选分数大于等于60的分组,计算学生个数
mysql> select count(name),address from student where score>=60 group by address;
+-------------+----------+
| count(name) | address |
+-------------+----------+
| 1 | beijin |
| 1 | hangzhou |
| 2 | nanjin |
+-------------+----------+示例3:结合 order by 把计算出的学生个数按降序排列
mysql> select count(name),score,address from student where score>=60 group by address order by score desc;
+-------------+-------+----------+
| count(name) | score | address |
+-------------+-------+----------+
| 2 | 90.5 | nanjin |
| 1 | 70.0 | beijin |
| 1 | 65.0 | hangzhou |
+-------------+-------+----------+示例4:查看字段长度
mysql> select count(*) from student;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 5 |
+----------+
4. 限制结果条目
在使用 MySQL select 语句进行查询时,结果集返回的是所有匹配的记录(行)。使用 limit 命令可以限制指定的行,注意第一条信息位置偏移量是0。
4.1 语法格式
select 字段1,字段2,... from 表名 limit [offset,] 行数 # offset:偏移量4.2 示例
示例1:显示前两行
mysql> select * from student limit 1;
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score | # 字段名也算一行
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+示例2:从第二行开始,往后显示两行内容
mysql> select * from student limit 1,2;
+----+--------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+--------+---------+------+-------+
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
+----+--------+---------+------+-------+示例3:结合 order by 语句,按 score 的大小降序排列显示前三名
mysql> select * from student order by score desc limit 3;
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+5. 设置别名
当表的名字比较长或者表内某些字段比较长时,可以设置别名方便书写。
5.1 语法格式
对于列的别名:
select 旧字段名 [as] 新字段名 from 表名;
对于表的别名:
select 字段(s) from 旧表名 as 新表名;5.2 示例
示例1:设置别名
列别名设置:
mysql> select name as 姓名,score as 成绩 from student;
+----------+--------+
| 姓名 | 成绩 |
+----------+--------+
| zhangsan | 90.5 |
| lisi | 65.0 |
| wangwu | 70.0 |
| zhaoliu | 50.0 |
| zhouqi | 65.0 |
+----------+--------+
表别名设置:
mysql> select s.name as 姓名,s.score as 成绩 from student as s;
+----------+--------+
| 姓名 | 成绩 |
+----------+--------+
| zhangsan | 90.5 |
| lisi | 65.0 |
| wangwu | 70.0 |
| zhaoliu | 50.0 |
| zhouqi | 65.0 |
+----------+--------+示例2:以别名方式查询
mysql> select s.name as 姓名,s.age as 年龄 from student as s;
+----------+--------+
| 姓名 | 年龄 |
+----------+--------+
| zhangsan | 10 |
| lisi | 50 |
| wangwu | 30 |
| zhaoliu | 30 |
| zhouqi | 40 |
+----------+--------+示例3:as 作为连接语句操作符——创建新表 student1,将 表查询的记录全部插入 student1 表中
mysql> create table student1 as select * from student;
mysql> select * from student1;
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 65.0 |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
mysql> desc student1;
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(5) | NO | | NULL | |
| name | char(15) | YES | | NULL | |
| address | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| age | char(5) | YES | | NULL | |
| score | decimal(3,1) | YES | | NULL | |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> desc student;
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(5) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | char(15) | YES | | NULL | |
| address | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| age | char(5) | YES | | NULL | |
| score | decimal(3,1) | YES | | NULL | |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
由此可见使用 as 作为连接符创建的表克隆了数据和结构,但是没有“约束”;同时需要留意的是:如果原表有主键,附表 default 字段会默认设置一个0.
示例4:as 也可以接条件语句
mysql> create table student2 as select * from student where score>80;
mysql> select * from student2;
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
6. 通配符
用于替换字符串中的部分字符,通过部分字符的匹配结果;通配符都是跟 like 一起使用的,并协同 where 子句共同来完成查询任务。
常用的通配符有两个:
- %:百分号表示零个、一个或多个字符,类似*
- _:下划线表示单个字符,类似 .
6.1 一般格式
select 字段1,字段2,... from 表名 where 字段 like '通配符表达式';6.2 示例
示例1:筛选 address 以 n 开头的记录,只显示 id 和 address
mysql> select id,address from student where address like 'n%';
+----+---------+
| id | address |
+----+---------+
| 1 | nanjin |
| 2 | nanjin |
+----+---------+示例2:查询名字里是 l 和 i 中间有两个字符的记录
mysql> select * from student where name like 'l__i';
+----+------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+------+---------+------+-------+
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
+----+------+---------+------+-------+
示例3:查询名字中间有 g 的记录
mysql> select * from student where name like '%g%';
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
示例4:组合使用
mysql> select * from student where address like '%zho_';
+----+--------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+--------+----------+------+-------+
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 65.0 |
+----+--------+----------+------+-------+7. 子查询
子查询也被称作内查询或者嵌套查询,是指在一个查询语句里面还嵌套着另一个查询语句。执行顺序由内到外。子语句和主语句查询表可以相同,也可以不同。
7.1 格式
查询:
select 字段1,字段2,... from 表1 where 条件字段 in (select 条件字段 from 表2 where 表达式);
插入:
insert into 表1 select * from 表2 where 条件字段 in (select 条件字段 from 表3);
更新:
update 表1 set 新表达式 where 条件字段 in (select 条件字段 from 表2 where 表达式);
删除:
delete from 表1 where 条件字段 in (select 条件字段 where 表达式);
关键字查询:
select 聚合函数(*) from 表1 where exists (select 字段 from 表2 where 表达式);
子查询别名:(假设定义表别名为a)
select a.字段1,a.字段2,... from (select 字段1,字段2,... from 表) a;环境准备:
mysql> select * from student;
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 65.0 |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
mysql> select * from student1;
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 65.0 |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+7.2 查询
mysql> select name,score from student where id in (select id from student1 where address='nanjin');
# 查询地区是nanjind的信息
mysql> select * from student;
+----------+-------+
| name | score |
+----------+-------+
| zhangsan | 90.5 |
| lisi | 65.0 |
+----------+-------+
7.3 删除
mysql> delete from student where id in (select id where score<70);
# 删除小于70分
mysql> select * from student;
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
7.4 写入
mysql> insert into student select * from student1 where id in (select id from student1 where score<70);
# 插入来自student1表大于70分的数据到student表
mysql> select * from student;
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 65.0 |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
7.5 更新
mysql> update student set score=55 where id in (select id from student1 where id=5);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
# 更新id为5的成绩为55
mysql> select * from student;
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 55.0 |
+----+----------+----------+------+-------+7.6 exists 关键字查询
exists 主要功能是判断子查询结果集是否为空。
mysql> select count(*) from student where exists (select id from student1 where name like 'zhang%');
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 5 |
+----------+
# 判断student1表是否有一个叫zhang开头名字的,存在返回表的行计数7.7 子查询别名
将结果集做为一张表进行查询。
mysql> select a.id,a.name from (select id,name from student) a;
+----+----------+
| id | name |
+----+----------+
| 1 | zhangsan |
| 2 | lisi |
| 3 | wangwu |
| 4 | zhaoliu |
| 5 | zhouqi |
+----+----------+7.8 返回值取反
mysql> select name,score from student where id not in (select id from student1 where score<90);
+----------+-------+
| name | score |
+----------+-------+
| zhangsan | 90.5 |
+----------+-------+
三、mysql 视图
1. 概述
数据库中的虚拟表,不包含真实数据,只是映射;简化SQL语句,简化查询结果集、灵活查询,针对不同的用户呈现不同的结果集;只适合查询,不适合增删改。视图有表之后才能存在,它的内容都来自基本表,一个视图可对应一个或多个基本表。
2. 视图与表的区别
① 视图是已经编译好的sql语句,表不是
② 视图没有实际的物理记录,表有
③ 表占用物理空间,而视图不占用,视图是逻辑概念存在;表可即时修改,但视图只能由创建的语句来修改
④ 视图是查看数据表的一种方法,可以查询数据表中某些字段构成的数据,从安全角度来说,用户接触不到表结构
⑤ 表属于全局模式中的实表;视图属于局部模式的虚表
⑥ 视图的建立和删除只影响视图本身,不影响对应的基本表。当更新视图数据,会影响到基本表
3. 视图操作
环境增加:
mysql> select * from newstudent;
+------+----------+--------+
| id | name | cardid |
+------+----------+--------+
| 1 | zhangsan | 111 |
| 2 | lisi | 222 |
| 3 | wang | 333 |
+------+----------+--------+
3.1 视图创建
格式:
单表创建视图:
create view v_名称 as select * from 表 where 表达式; # 没有“约束”
多表创建视图:
create view v_名称 (字段1,字段2,字段3,...) as select a.字段1,a.字段2,b.字段3,... from 表1 a,表2 b where a.同名字段=b.同名字段;示例:
单表创建视图:
mysql> create view v_1 as select * from student where score>=60;
多表创建视图:
mysql> create view v_2 (id,name,cardid) as select a.id,a.name,b.cardid from student a,newstudent b where a.name=b.name;
3.2 查看表状态
mysql> show table status\G;
*************************** 5. row ***************************
Name: v_1
Engine: NULL
Version: NULL
Row_format: NULL
Rows: NULL
Avg_row_length: NULL
Data_length: NULL
Max_data_length: NULL
Index_length: NULL
Data_free: NULL
Auto_increment: NULL
Create_time: NULL
Update_time: NULL
Check_time: NULL
Collation: NULL
Checksum: NULL
Create_options: NULL
Comment: VIEW3.3 视图查询
mysql> select * from v_1;
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 70.0 |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
mysql> select * from v_2;
+----+----------+--------+
| id | name | cardid |
+----+----------+--------+
| 1 | zhangsan | 111 |
| 2 | lisi | 222 |
+----+----------+--------+
3.4 视图修改
mysql> update v_1 set score=50 where id=3;
mysql> select * from v_1;
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 50 | 65.0 |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
# 由于创建视图有硬性条件“score>=60”,所以修改后记录会丢失
mysql> update v_1 set age=15 where id=2;
mysql> select * from v_1;
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangsan | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 15 | 65.0 |
+----+----------+---------+------+-------+
mysql> select * from student where id=2;
+----+------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+------+---------+------+-------+
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 15 | 65.0 |
+----+------+---------+------+-------+
# 由此可见,修改视图会影响基础表
mysql> update student set name='zhangs' where id=1;
mysql> select * from v_1;
+----+--------+---------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+--------+---------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangs | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 15 | 65.0 |
+----+--------+---------+------+-------+
# 由此可见,修改基础表会影响视图,注意:这里表不能修改以函数、符合函数方式计算出来的字段3.5 视图删除
格式:
drop view [if exists] 视图名;
示例:
mysql> drop view v_1;
mysql> select * from v_1;
ERROR 1146 (42S02): Table 'school.v_1' doesn't exist
mysql> select * from student;
+----+---------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+---------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangs | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 15 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 50.0 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 55.0 |
+----+---------+----------+------+-------+
# 删除视图,不影响基础表4. null 值
表示缺失的值,即该字段没有值;与“0”或者“空白”的字段不同。null 与空值的区别:空值的长度为0,不占空间,null 值长度为1,占用空间。
mysql> select length(null),length(''),length('abc');
+--------------+------------+---------------+
| length(null) | length('') | length('abc') |
+--------------+------------+---------------+
| NULL | 0 | 3 |
+--------------+------------+---------------+
统计数量:检测null是否会加入统计中
mysql> update newstudent set cardid='' where id=3;
mysql> select * from newstudent;
+------+----------+--------+
| id | name | cardid |
+------+----------+--------+
| 1 | zhangsan | 111 |
| 2 | lisi | 222 |
| 3 | wang | |
+------+----------+--------+
mysql> select count(cardid) from newstudent;
+---------------+
| count(cardid) |
+---------------+
| 3 |
+---------------+
查询空值:
mysql> insert into newstudent (id,name) values(4,'zhou');
# 插入一条数据,cardid输入null
mysql> select * from newstudent;
+------+----------+--------+
| id | name | cardid |
+------+----------+--------+
| 1 | zhangsan | 111 |
| 2 | lisi | 222 |
| 3 | wang | |
| 4 | zhou | NULL |
+------+----------+--------+
mysql> select * from newstudent where cardid is NULL;
+------+------+--------+
| id | name | cardid |
+------+------+--------+
| 4 | zhou | NULL |
+------+------+--------+
# 查询null值
mysql> select count(cardid) from newstudent;
+---------------+
| count(cardid) |
+---------------+
| 3 |
+---------------+
# 再次计数四、连接查询
1. 概述
来自两个或多个表的记录结合起来,基于表之间的共同字段进行拼接。使用较多的连接查询包括:内连接、左连接和右连接。
环境准备:
mysql> select * from student;
+----+---------+----------+------+-------+
| id | name | address | age | score |
+----+---------+----------+------+-------+
| 1 | zhangs | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 |
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 15 | 65.0 |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 50.0 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 55.0 |
+----+---------+----------+------+-------+
mysql> select * from newstudent;
+------+----------+--------+
| id | name | cardid |
+------+----------+--------+
| 1 | zhangsan | 111 |
| 2 | lisi | 222 |
| 3 | wang | |
| 4 | zhou | NULL |
+------+----------+--------+
2. 内连接
在 from 子句中使用关键字 [inner] join 来连接多张表,并使用 on 子句设置连接条件。输出匹配字段共同的数据。
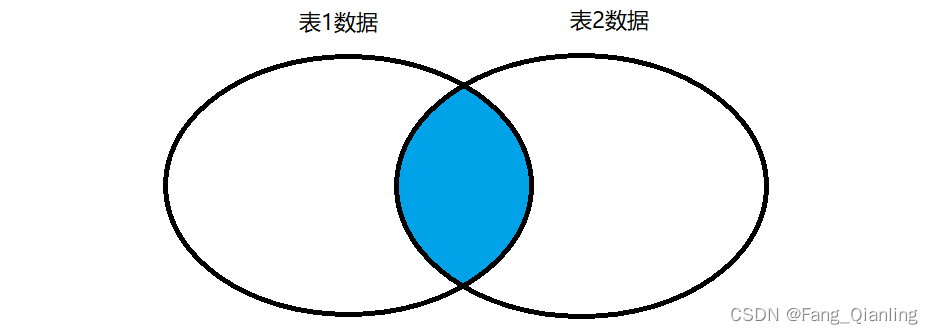
格式:
select 表1[2].字段1,表1[2].字段2,... from 表1 inner join 表2 on 表1.同名字段=表2.同名字段;查询:
mysql> select student.id,student.name from student inner join newstudent on student.name=newstudent.name;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 2 | lisi |
+----+------+
3. 左连接
在 from 子句中使用 left join 或者 left outer join 关键字来表示。左连接中左表的记录将会全部表示出来,而右表只会显示符合搜索条件的记录,这些记录在左表中以 null 补足。
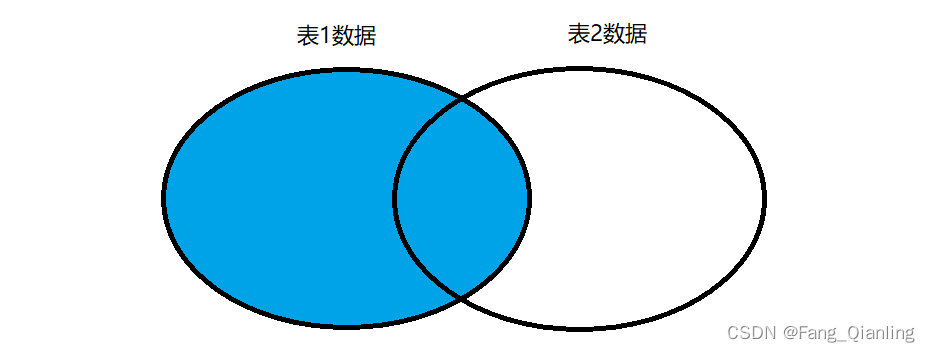
格式:
select * from 表1 left join 表2 on 表1.同名字段=表2.同名字段;查询:
mysql> select * from student left join newstudent on student.name=newstudent.name;
+----+---------+----------+------+-------+------+------+--------+
| id | name | address | age | score | id | name | cardid |
+----+---------+----------+------+-------+------+------+--------+
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 15 | 65.0 | 2 | lisi | 222 |
| 1 | zhangs | nanjin | 10 | 90.5 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 3 | wangwu | beijin | 30 | 50.0 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 4 | zhaoliu | shanghai | 30 | 50.0 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 5 | zhouqi | hangzhou | 40 | 55.0 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+----+---------+----------+------+-------+------+------+--------+
4. 右连接
在 from 子句中使用 right join 或者 right outer join 关键字来表示。右连接跟左连接正好相反,在右连接的查询结果集中,除了符合匹配规则的行外,还包括右表中有但是左表中不匹 配的行,这些记录在左表中以 null 补足。

格式:
select * from 表1 right join 表2 on 表1.同名字段=表2.同名字段;查询:
mysql> select * from student right join newstudent on student.name=newstudent.name;
+------+------+---------+------+-------+------+----------+--------+
| id | name | address | age | score | id | name | cardid |
+------+------+---------+------+-------+------+----------+--------+
| 2 | lisi | nanjin | 15 | 65.0 | 2 | lisi | 222 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | zhangsan | 111 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | wang | |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 4 | zhou | NULL |
+------+------+---------+------+-------+------+----------+--------+



![[AIGC] 对比MySQL全文索引,RedisSearch,和Elasticsearch的详细区别](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/99c7f2b5f3de4de39beef3b3acdf136c.png)